To build wall panels made of cellular concrete with your own hands, you must strictly follow the technologies, taking into account all the features of this working material. The construction of walls is a critical stage of construction, so it is important to first learn about the possible difficulties that may arise when working with porous concrete. In addition, it is important to choose the right adhesive composition and determine the required thickness of the walls being built.
Advantages and disadvantages
In construction, cellular concrete is classified as a lightweight building material and is usually used for the construction of one- or two-story buildings. It consists of sand-lime cement, water, sand and blowing agents. Such components, when proportionate, make artificial stone a high-quality building material. The advantages of cellular concrete include:
- Light weight. Thanks to this quality, the blocks are easy to transport and carry out loading and unloading operations.
- Environmentally friendly. Cellular concrete does not contain chemical elements that are hazardous to human health or harmful to the environment, therefore it is considered a harmless building material, second only to wood in terms of environmental friendliness.
- It can be processed and can take on any shape.
- Has precise geometric dimensions.
- Fire safety. Constructions made from cellular concrete blocks belong to the first degree of fire resistance.
- Excellent noise and sound insulation.
- Economic benefit.
Aerated concrete structures require additional finishing, as they have an increased tendency to crack.
But, despite the impressive list of advantages, walls made of cellular concrete also have disadvantages, namely:
- Fragility. The building material does not withstand mechanical stress well and requires protective measures to be taken when transporting and working with it.
- Prone to cracks. Due to soil movements and shrinkage, numerous cracks may appear on the surface of the walls.
- High ability to absorb water vapor from the air. As a result, blocks made of cellular concrete do not tolerate winter well and require additional insulation.
- Requires reinforcement.
Knowing the disadvantages of cellular concrete, you can mitigate them and, as a result, build a reliable and durable building.
What is the difference between a gas block and a foam block and which is better?
Aerated concrete and foam concrete are produced on the basis of cellular concrete. Both materials are environmentally friendly and completely safe for humans. However, there is a certain difference between them that should be taken into account when choosing building materials:
Production technology
Foam blocks are made from lime, cement, water, foaming agent and various industrial wastes. The resulting solution is poured into containers and hardens naturally.
The production of aerated concrete is carried out as follows: cement, quartz sand, water, lime and aluminum powder are mixed and pressed in an autoclave oven or hardened under high temperatures.
Block geometry
When figuring out whether an aerated concrete block or a foam concrete block is better, consider the following: the first has ideal shapes, while the second may have quite noticeable irregularities on its surface. The error in the geometry of gas blocks is no more than 1 mm. For foam blocks this figure often reaches 2-3 mm.
Thermal and sound insulation properties
Both materials are characterized by high frost resistance and excellent heat and sound insulation properties. However, gas blocks have a more precise geometry, which allows the construction of walls without “cold bridges”. In addition, foam concrete often has a heterogeneous structure: a large number of cavities accumulate in one place, while in another there are practically none. Because of this, the heat and sound insulation properties of the material can vary greatly.
Strength characteristics
The most durable and reliable option is autoclaved gas blocks. They are used in the construction of load-bearing walls in low-rise construction (up to three floors). Foam concrete - with a similar density - is less durable. Walls made of foam blocks require high-quality reinforcement.
Moisture absorption
This is the only parameter in which gas blocks are slightly inferior to foam blocks. Foamed concrete blocks do not absorb moisture well, while aerated concrete is characterized by pronounced absorbent properties. This parameter, however, also has a “downside”: walls made of aerated blocks can “breathe”, due to which a comfortable microclimate is formed in the house; foam blocks, in turn, practically do not allow steam to pass through, so the air in a building built from this material will be quite dry.
Now you know the difference between a gas block and a foam block, and you can accurately determine which is better. Foamed concrete is inferior to aerated concrete in a number of parameters, so aerated concrete is preferable in construction.
In the Keramik Group online store you can buy high-quality foam blocks from trusted manufacturers. Affordable prices for foam blocks. Delivery of orders is carried out in Moscow and other cities of the Russian Federation.
What are they putting it on?
Ready store glue
Experienced developers recommend erecting wall panels from cellular concrete using a ready-made adhesive mixture, which can be easily purchased at any construction store. This type of block fastening is relatively new on the construction market, but has already established itself as a durable and easy-to-use material. In addition, industrial glue, unlike cement, is better suited for the construction of high-rise buildings. And by laying a 0.2-0.3 cm layer of adhesive mortar between the concrete, it will be possible to build a building with excellent thermal conductivity, which does not require an additional layer of thermal insulation. But a significant disadvantage of store-bought glue for many builders is its high price, which not everyone can afford.
Homemade mixture
A solution of cement, sand and water has the ability to fill and hide unevenness in cellular concrete.
It is most financially profitable to fasten cellular blocks with a solution prepared on the basis of sand, cement and water. This mixture can easily be made with your own hands, without any experience or the use of heavy equipment. The main thing is to comply with the proportions recommended by GOST. The advantage of such a solution is the possibility of using an imperfect form of cellular concrete, since a layer of solution can cover all the irregularities. A significant disadvantage of the cement-sand mass is the need for additional thermal insulation of the structure being constructed.
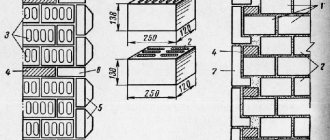
Wall thickness
Typically, the process of laying walls made of cellular concrete does not cause any particular difficulties for the developer. But, nevertheless, it is important to adhere to the basic recommendations that will help you quickly build a high-quality building. First of all, you should decide on the wall thickness. This criterion is influenced by various factors: climate characteristics, region of residence. So, according to building codes and regulations, for warm areas where precipitation is minimal, it is necessary to build a wall with a thickness of within 38 cm. But for regions where sub-zero air temperatures prevail, it is advisable to make the wall size from 60 cm.
Production stages
For quick and complete work, it is recommended to first prepare all the necessary tools.
Initially, you need to prepare the equipment and building mixture for fastening the cellular blocks together. During the construction process you will need the following:
- level;
- concrete mixer;
- drill;
- empty containers;
- grinding;
- trowel;
- putty knife.
If the blocks are laid in the cold season, then you will additionally need special anti-frost additives, which are added to the cement-sand mixture or you buy an adhesive solution that already contains them.
Next, they begin laying the first row on a foundation that has been cleared of dust and dirt. It is important to lay the cellular blocks evenly using a building level. The second and subsequent strips are laid out only on the adhesive solution, which should cover the entire side surface of the masonry and the width of the previously laid blocks. Aerated concrete lintels must be additionally strengthened with reinforcement and filling.
If necessary, install internal partitions, you can also use cellular blocks. Such walls are quite durable and have good thermal insulation. The walls inside the building are erected according to the same rules as the outside ones. First of all, markings are made and only then the blocks are laid.
Characteristics of cellular concrete blocks
If lower results of re-testing in terms of strength and frost resistance are received, a batch of blocks is accepted according to the indicators obtained during control. If values for the average density of concrete are underestimated or overestimated by one grade, a batch of blocks is accepted according to the indicators obtained during control.
The possibility of using accepted blocks that do not meet the specified strength, average density, release humidity and frost resistance indicators is established by the design organization. The blocks in the package must not be stuck together and can be easily disassembled by hand.
Properties of block products
Each batch of blocks is accompanied by a quality document, which indicates: - name and address of the manufacturer; — symbol of blocks; — designation of this standard; — number and date of issue of the quality document; — batch number, volume or number of units shipped.
Dimensions, difference in lengths of diagonals, curvature of edges and edges are checked according to GOST. All measuring instruments used must be at least class 2 accuracy. It is allowed to use special non-standardized measuring instruments that have passed metrological certification in accordance with the requirements of GOST 8. The Regulations on the implementation of state metrological supervision are in force; decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated April 6, 2010 N. Control of the depth of damage to ribs and corners is carried out by measuring a perpendicular lowered from the vertex of a corner or from an edge to the conditional plane of the defect, in accordance with the scheme for measuring the depth of damage to the corners and edges of the blocks with a depth gauge according to GOST. Technical characteristics of the blocks are controlled in accordance with the requirements of the following standards: - compressive strength - according to GOST; - medium density - according to GOST Blocks are transported in containers according to GOST or on pallets according to GOST with rigid fixation with shrink film or bandaging them with steel tape according to GOST or other fastening that ensures the immobility and safety of the blocks.
Transportation of blocks is carried out by any type of transport in accordance with the requirements of GOST and “Technical conditions for loading and securing cargo.” It is prohibited to load blocks in bulk and unload them by dropping them. Blocks must be stored sorted by type, category, strength class, grade by average density and stacked in stacks no more than 2.5 m high. Blocks must be protected from moisture. D, D, D The “-” sign means that concrete of this medium density is not recommended.
The electronic text of the document was prepared by Codex JSC and verified against: official publication M. Personal data confidentiality policy. Document text Status Scanned copy.
Types of porous compositions
Search in the text. GOST Small blocks made of cellular concrete for walls. Technical conditions. This document is presented in djvu format.
Advantages and disadvantages
Specifications MKS Main parameters and dimensions 1. An example of a symbol for a block of type I, compressive strength class B2.5, average density grade D, frost resistance grade F35, category 2: I-B2.5DF The same for block type V, compressive strength class B5, medium density grade D, frost resistance grade F75, category 1: V-B5DF 1.
Characteristics 1. Requirements for materials and concrete 1. The grades of concrete for frost resistance must be, depending on their mode of operation and the estimated winter temperatures of the outside air in the construction areas, not less than: F25 - for external wall blocks; F15 - » » internal » 1. Marking 1.