Problems with bricklaying in winter
When laying bricks in cold weather, it is most difficult to provide the building with the required strength. When the air temperature is below zero, the water contained in the fastening solution freezes, thereby stopping the necessary process of cement hydration. If the water does not have time to turn into ice, but at the same time gets from cold areas to warm ones, this will lead to the fact that the surface of the bricks will be covered with ice. After some time, the ice located both inside the masonry and on the surface of the bricks will melt, but the adhesion of the mortar will decrease significantly. After complete thawing, the strength of the masonry will decrease by about a quarter of the required standards. In addition, when the water in the solution turns into ice and then thaws, free spaces are formed in the masonry, which can cause the structure to collapse over time.
Features and Issues
If it is not possible to transfer stone work to warm weather in winter, the following factors should be taken into account:
- Laying bricks in frost is technologically more difficult than at above-zero temperatures.
- The duration of hardening of the cement mortar increases 3-4 times if the air temperature is 15 degrees.
- Cement mortar will not harden at zero temperature.
- Cold reduces the structure, elasticity and strength of the mixture.
- Ingress of moisture can damage the integrity of the brick.
- Gives uneven precipitation during thawing.
- At -20, masonry is not recommended, while at -30 it is strictly prohibited.
- Winter construction costs are 30% higher than summer construction costs.
In winter, you can lay bricks, but you need to monitor the quality of the cement mixture. Winter bricklaying is not complete without an additive that increases strength.
If work began in the warm season and did not end with the onset of winter, it is not advisable to postpone construction by six months. In addition, it is difficult to predict how long the subzero temperature will last. With the onset of frost, the composition of the cement-water solution changes, which significantly increases the cost of the process. An important factor is uncomfortable working conditions in winter.
How to prepare mortar for bricklaying
Despite the existing disadvantages, bricklaying in cold weather can be no less durable than in the warm season. However, this requires a special solution.
The mortar for bricklaying under conditions must include anti-frost additives that will ensure a decrease in temperature. It is recommended to use a brand of at least 50, where the necessary additives are already included. The most important thing is to monitor the solidification process of the solution. To do this, small nests with plugs are made in the masonry so that the temperature can be measured both inside and outside with a thermometer.
Bricklaying in winter conditions
Optimal masonry for winter can be done by artificial heating or freezing. In some cases, at very low temperatures, additional greenhouses need to be installed above the masonry itself.
Winter mortar for bricklaying
When getting to work, you need to take into account that all antifreeze additives are poisonous to humans. You can work with them only in special clothing, safety glasses and thick gloves.
For the same reason, any mixtures that contain chemical additives are allowed to be used only for the construction of retaining walls and foundations. Laying bricks in winter conditions using chemical mixtures is strictly prohibited for the construction of residential premises.
Methods for laying bricks in winter
Masonry in sub-zero weather is most often carried out in the following ways:
- Electric heating
Since this method is quite labor-intensive and energy-consuming, it is recommended to use it only when constructing small sections of walls. During the laying of walls, electrodes are placed horizontally into the finished mortar, through which electricity will later be conducted. When heated, the electrodes will also heat the masonry seams, which, accordingly, will prevent the formation of ice. However, for effective electric heating it is extremely important that the joints are completely filled.
Bricklaying in sub-zero weather
- Construction of a greenhouse
This method is very effective, but quite labor-intensive. Its essence lies in the fact that a frame of slats is installed around the future wall or part of the wall. The frame is covered with plastic film or materials with similar properties. To provide heat to the future structure and the masonry mortar, any heat source must be installed inside the frame, for example, a stove, generator, electric heater, etc.
In order for winter bricklaying to be erected in accordance with all required standards, it is necessary to heat the greenhouse for several days. Since it is almost impossible to build a frame greenhouse over an entire house or even over one wall, this method is suitable exclusively for the construction of individual elements.
Laying facing bricks in winter
- Freezing method
Laying facing bricks in winter is most effective if the work is done using the freezing method. The essence of the freezing method is based on the fact that a special cement mortar for winter bricklaying can set again some time after thawing.
For masonry using the freezing method, you can only use heated mortar and bricks that are completely free of frost. If ice has already formed on the bricks, it is more convenient to remove it using an injection burner. In addition, for this method it is recommended to use the highest grade of solution.
Is it possible to lay brick in winter?
The solution tends to cool quickly, which causes ice to form in it. Therefore, when heated, it must be used up in a maximum of half an hour. To avoid freezing, the solution must be diluted in small portions.
Also, the answer to the question whether it is possible to lay bricks in winter also depends on the quality of the work. During winter masonry, it is necessary to pay special attention to the filling of joints, especially vertical ones.
What is added to the mortar in winter for laying bricks?
Sometimes the process of building a building is very delayed; it continues after the arrival of cold weather. But summer cement mixtures for construction consist of 3-4 main components, one of which is water, which becomes ice at negative temperatures. Therefore, special options for mortars for laying bricks in winter were invented. They contain additives that reduce the freezing point of water in the mixture.
The hardening of the solution occurs due to the reaction between water and cement. As a result, a gel-like mass is created, which over time becomes a stone. And the lower the temperature around, the slower the solidification process will occur. So, at a level of 5°C, this process will last 4 times slower than it would at 20°C. But when the mark reaches 0 °C, hardening stops altogether.
Negative temperatures negatively affect the structure, as well as the strength of future hardened cement. In addition, the interaction between the two binder components stops completely, due to the fact that the water becomes ice. In addition, in solid form it increases in volume. This causes the solution to lose the strength it had before freezing.
Also, due to freezing, cement loses its elasticity significantly, due to which the compaction of horizontal joints in the masonry is insufficient. In addition, after thawing, uneven settlement occurs, and this already threatens the strength of the structure being built. That is why it is recommended to use mortar for winter bricklaying. It is created by adding the required amount of special additives to the usual mixture, which impart frost-resistant properties.
In the summer, when the outside temperatures are above zero, classic cement mortar is used to build walls or other types of brickwork. It is easy to prepare with your own hands from the following ingredients:
- Cement;
- Sand;
- Lime (in simpler mixtures it may not be used at all).
First, a limestone dough is created. It is made by mixing water with lime. Next, the resulting slurry is filtered using a fine sieve. Separately, but in parallel, a mixture consisting of sand and cement is mixed. Next, the resulting limestone dough is poured into it, as well as the required volume of water and mixed until a homogeneous mass is created. It is with this mortar that bricks are held together in the summer. In cold times, things happen a little differently.
The winter solution differs from its summer counterpart only in certain additives. They allow you to reduce the level of freezing of the cement mixture, due to which it does not lose its state of aggregation and continues to harden. When the “summer” solution is ready, certain chemicals are added to it to impart the desired properties:
- Calcium chloride;
- Potash, also known as potassium carbonate;
- You can also use sodium nitrite.
The use of each of these substances has a specific effect on the mixture. But the goal is the same - to reduce the temperature when the water turns into a solid state. The choice of substance for a particular case depends on the air temperature. Such additives are added to the solution during the mixing process immediately after pouring water. Due to this, it is possible to evenly distribute inclusions throughout the entire composition of the cement mixture and achieve the desired result.
However, after reading a recipe, you should not rush to implement it. Modifications of the solution do not always show the desired effect. So, if you add salt to the mortar for laying bricks, this will lead to its subsidence. This situation has a very specific justification. When the brick mortar used for construction in winter contains a significant amount of salt, after the onset of positive temperatures, the wall will shrink and tilt.
The point here is not even the amount of salt added, but the very fact of its presence. When industrial additives, such as sodium chloride, are used, they are one of the components of the entire antifreeze mixture. Together they lead to a chemical reaction, due to which a new substance is formed, so they should not be perceived separately.
Application
There are not many rules when using mortar for laying bricks in winter, but you need to know them. Otherwise, a building erected at sub-zero temperatures will sag or even collapse after the onset of cold weather. First of all, the temperature of the solution during installation should not be lower than 5 °C. Once it has frozen, defrosting it again will no longer allow the creation of staples. This is due to the loss of its properties.
The next rule for using a frost-resistant solution in winter is to add calcium carbonate. It is prohibited to use this inclusion when laying silicate products. And in the case of using ceramic bricks, approach with increased attention to the quality of the masonry itself.
Folk remedies
Some people add regular automotive antifreeze to the mortar to give it the desired properties. But after introducing it into the composition, it is necessary to constantly monitor the quality of hardening. Otherwise, the cement mortar will not harden correctly. To do this, do-it-yourself winter brickwork must have a small number of nests in which plugs will be inserted.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Gas stove for a bath: advantages and disadvantages, how to choose, do-it-yourself installation
It is necessary to build walls when the masonry mixture for bricks is supplemented with antifreeze, carefully and taking the necessary precautions. This is due to the fact that such inclusions belong to inorganic solvents, as well as mineral salts. Therefore, during the masonry process, workers must use protective clothing, gloves, and face and eye protection. Failure to comply with these measures results in chemical burns.
When, after winter hardening, the mortar in the erected wall begins to thaw, a sharp loss of stability occurs. And in the case of uneven thawing, it even leads to deformation of the wall. Due to this, it is important to control the process and take timely measures to maintain the stability of the erected structure.
When the masonry is laid using the freezing method, during its thawing, they carefully observe how it occurs. More attention is paid to the power elements on which the stability of the entire erected structure depends. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the constructed masonry until the thawing ends and constant above-zero temperatures occur.
Due to the fact that the walls of the building, located on different sides, are exposed to natural heating unevenly, it is recommended to cover the northern side with parchment. This will create equal conditions and a uniform thawing process
The following PMDs are most often used in our country:
- Potassium carbonate (potash) with thorough preliminary cleaning of the surface and short-term wetting with suspensions of potash and clay.
- Technical sodium nitrite.
- A mixture of sodium nitrite and potash
- Finished NCM product (urea is added to the mixture of potash and sodium nitrite).
- .Calcium and sodium chloride. They can only be used in the absence of reinforcement, as they cause metal corrosion.
In building codes and regulations there are special tables depending on the required amount of PMD on external temperatures, and one should focus on the ten-day forecast.
Finishing work
After erecting a brick wall to a level no higher than one floor, it is necessary to install prefabricated floors. If the masonry is carried out using the freezing method, the height of the erected structure in winter should not exceed 15 m.
In addition, it is extremely important to monitor the masonry once the thaw arrives. In order to provide additional stability and strength to the brickwork in the spring, it is necessary that the distance between it and the transverse walls does not exceed 20 m. In addition to all of the above, the walls on the south side must be covered with glassine or moistened.
It is considered an unacceptable construction mistake to lay bricks in cold weather. This is explained by the fact that the water in the solution cools at low temperatures, which slows down the hardening process of the cement. If temperatures drop below zero, the water freezes and the evaporation process stops.
If someone thinks that laying bricks in cold weather will not harm the construction in any way, and that the frozen mortar can dry perfectly after the thermometer rises, he is very mistaken.
When the temperature rises above zero, the following metamorphoses occur with fresh masonry:
- uneven shrinkage of masonry;
- significant loss of structural strength.
So is it possible to lay bricks in the cold? The answer to this question is a couple of small secrets, taking into account which it will be possible to complete construction in the winter.
Other methods of protection
If antifreeze additives are not used, and the air temperature drops lower and lower, you can protect the cement in other ways:
- Using warm water when mixing concrete. This is a method of quickly freezing masonry, which avoids disruption of the hydration process.
- Warming up the construction site using electric heaters. A very expensive method.
- Protection with slabs or shields wrapped in any heat-insulating material, for example, polyethylene film. You just need to remember that they can stick to the surface of the poured solution, so it’s worth considering the option of supports for thermal insulation.
Using the same slabs, you can try to warm up unhardened concrete that has already been damaged by frost.
Finishing work with cement, for example, plastering the surface, even if the order of sand, clay, gypsum and other materials has already been carried out, is best left until spring, when a stable above-zero temperature has established. Otherwise, no matter how careful the plasterers’ work, the finish will fall off the wall within a few days.
Of course, I apologize wildly, but under no circumstances, under any circumstances, add salt to your solution! This will only reduce its quality and strength. There are other additives for these purposes.
Why do you need an antifreeze additive (AMD) in the solution? It prevents the water in the solution from freezing, thereby ensuring the hardening (crystallization) process and strengthening of your solution through the interaction of water with cement! As a rule, it is supplied in liquid form, but it also comes in dry, powder form.
Features of masonry work in winter
In order to ensure the design strength of a stone or brick wall in winter, the following methods are used:
- freezing the solution;
- performing work with the addition of chemical antifreeze additives and heating the solution.
Let's look at each of these methods in more detail.
Freezing the solution
Guided by the provisions of SNiP 3.03.01-87
, it is possible to freeze mixtures when constructing a structure no more than 15 m high.
This could not be more relevant for country and country construction done with your own hands.
- It is prohibited to carry out construction at low temperatures for objects that will withstand significant dynamic and vibration loads (it is impossible to build in seismic zones in freezing temperatures!);
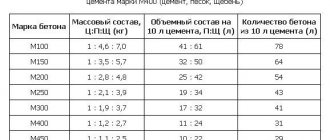
- you need to take a brand no smaller than M10;
- It is also necessary to take into account that construction must begin at positive temperatures and the walls must stand until the seam reaches the required thickness due to its compression with brick or stone to the calculated values. Start laying bricks during the day when the temperatures are above zero, and if your construction site freezes at night, nothing will happen to it.
If you decide to cool the mixture in advance so as not to waste the warm part of the day cooling it, then know:
- the cold solution will form a thick layer (the correct distribution of the solution can be seen in the photo);
- it will take a lot of time to evenly apply it to a building brick or stone;
- The seams may turn out to be uneven, which can lead to distortion of the masonry or subsequent spalling of the mortar from a wide seam.
Advice! Start laying as soon as the thermometer shows a value above zero; the solution should be of medium heat, and steam should not be released from it. Don't put too much. A fresh wall should stand until frost. Work if the temperature is expected to drop below -20ºС is prohibited.
If you order a solution, make sure that its temperature at the time of delivery is from +5 to +15ºС
. At the time of construction, stones or building bricks must be thoroughly cleared of snow, ice and frozen dirt.
When carrying out construction work, it should be taken into account that the lower the temperature, the higher the grade of the solution should be.
Using solutions with antifreeze components
When explaining the question of how to lay bricks in frost, you should remember the use of anti-frost additives to the mortar. The following additional components are used:
- urea with calcium nitrite;
- calcium chloride;
- sodium nitrite;
- sodium chloride;
- potash.
Each drug must be accompanied by instructions describing the exact proportions and technical parameters. The use of sodium and calcium chlorides contributes to an increase in the hygroscopicity of the masonry and the occurrence of efflorescence (the appearance of salt stains on the walls).
Therefore, they are usually used on the masonry of the underground part of the house. Their content in the solution should not exceed 1,5-7%
from the entire mass of the mixture.
The use of these additives is permitted at temperatures not lower than minus 15ºС.
Sodium nitrite is used in the construction of the above-ground part of the house. The sodium nitrite content should be 2-10% of the total mass of the solution. It is used at temperatures 0-14ºС
.
Potash is included in construction mixtures in quantities 5-15%
.
used at thermometer values of -5-30ºС.
Advice! Do not exceed the concentration of these substances. The solution will lose its plasticity. It will be difficult to apply.
To increase the plasticity and mobility of the solution, it is prepared with the addition of sulfite-yeast mash - up to 2% of the total mass of the solution used. The addition of antifreeze components cannot but affect such an indicator as the price of the solution.
However, if construction cannot be stopped in any way, a slight increase in the cost of masonry will not be able to stop anyone. The use of anti-frost components is prohibited when constructing a room in which high humidity will be maintained.
To warm up the masonry (backfill brick) or other stone, cinder block, etc., then use this method as heating the masonry.
Warm-up options:
- air heating;
- steam heating;
- electric heating
These methods must be used until the masonry has matured and the mortars have acquired the necessary strength.
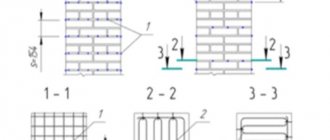
- Electric heating is carried out by placing plate or rod electrodes into the seams and connecting them to the network;
- Steam heating is carried out by erecting formwork around a new area and supplying steam until the solution settles;
- Air heating is carried out using a heater and a sectional greenhouse built around the structure. Most often used when constructing a foundation.
Conclusion
After the onset of the autumn-winter period, it is not at all necessary to stop construction work. The use of these methods will allow construction to continue without slowing down. In the video provided in this article you can find additional useful information on the topic.
They try to carry out construction work in the summer. Winter is not the optimal period for this. At what temperature can bricks be laid so that the laid walls are durable and beautiful? This is worth talking about in more detail.
What is an antifreeze additive to the solution?
Cement is used for the construction of various structures, such as foundations, walls, floors. For any type of work, it is necessary to make a special solution that will be ideally suited and create a high-quality structure.
When a house is being built, of course, you want the process to go faster, without stopping even in winter. In order to justify working at sub-zero temperatures and understand how brickwork reacts to frost, we will consider the physical and technical nuances of masonry and ways to “bypass” the climate.
In the construction of brick walls, in the classic version it is supposed to use mortar. In order not to discover America, you can use ordinary cement mortar:
- Sand (quarry; river - expensive option).
- Cement (grade 400 - for any work).
- Water.
Among the three components of cement, only water prevents winter construction. This happens because the bricks in the masonry are not bonded with mortar at subzero temperatures.
When the temperature drops below freezing, water turns to ice. As a result, the desired physical reaction does not occur between the ingredients of the solution.
Theoretically, it is possible to lay the mortar, but in this case it will freeze to its natural state of hardness, and therefore there will be neither the strength of the masonry nor the binding of the mortar.
Thus, when the temperature drops, it is impossible to lay bricks according to standard work patterns. However, there are other options for the composition of solutions and winter work.
Properties of the solution
In addition to various methods, chemical additives are also required. Basically these are special anti-cold products.
During construction, special nests are created in the seams, plugged with plugs, and temperature measurements are constantly taken. It should be taken into account that a brick, for example, is solid, conducts cold quite slowly, so there is time for the mortar to set.
While the exothermic reaction is taking place, adding heat, the solution is “pressed” by the brick from below and above.
As a result, we obtain a table in which the temperature of the solution corresponds to the air measurement indicators.
- 5 degrees - minus 10 degrees;
- 10 degrees – minus 10-20 degrees;
- 15 degrees – minus 20 degrees.
Freezing method
In this case, even despite the negative temperature, brick laying is carried out in the open air, while the mortar has a fairly high temperature.
This method is based on the fact that the mortar in the seams is frozen and gradually hardens in the spring (partly directly during the laying process). Thus, thermal energy is constantly released during the chemical interaction of cement and water.
Important! This method allows you to build walls with a height of no more than 15 m. Given the technical safety standard, the strength can be calculated in accordance with the spring period of hardening of the cement mortar.
Chemical additives
Another way is chemical additives. They perform several functions:
- The freezing rate of water decreases several times at sub-zero temperatures.
- The solution sets and hardens faster, but does not lose its qualities.
Basic additives that can be used if given instructions:
- Potash (reduces the hardening time of the solution at temperatures below minus 25 degrees). When the solution sets quickly, it loses some of its properties, so you can add yeast mash - 1%.
- Sodium nitrate (not less than 15 degrees).
Important! Most modern additives are poisonous, and therefore you need to follow safety rules and work exclusively in protective clothing.
Thermos method
Using this method, it is possible to carry out work at sub-zero temperatures. If using the standard method it is possible to carry out work at temperatures down to minus 5 degrees, then when it is further reduced, either chemical additives or other working methods are required.
The thermos method is that the cement mortar releases heat during laying, sufficient to maintain the process of good hardening. In addition, two conditions must be taken into account:
- Before installation, the brick is heated. For this you need an ordinary blowtorch. Both solid brick and double silicate M 150 are subject to heating.
- The masonry is covered with a layer of thermal insulation every few square meters or rows.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what type of wood is best to build a bathhouse from?
This method is quite simple, so if you need to continue construction when cold weather sets in, then even a beginner will not have any difficulty using it. The main thing is that you can do everything yourself, conveniently and quickly.
Electric heating
The essence of the electric heating method is to attach sewn-on electrodes on the side of the outer wall. An electric current is passed through the cement mortar, thereby heating it.
When the building mixture warms up, the brick receives heat, resulting in a warm island being formed on the wall. Thus, without changing the physical properties of the solution, the masonry gradually hardens.
Advice! When it is necessary to use electric current during construction, it is important not only to provide insulation, but also to have a heated base.
The question of what temperature is optimal for laying bricks becomes relevant in cases where it is impossible to conduct electricity or when there are no chemical additives. But at the same time, construction often stops altogether in winter.
This is especially important in the private sector, since engineering networks and communications need to be installed there. The optimal temperature for work is up to minus 5-7 degrees; if it is further reduced, the above methods should be used.
However, the question of temperature for masonry will cease to be acute when there is ordinary salt. If you use it, work continues at any negative temperature. Moreover, this effective method is cost-effective because it is inexpensive.
On the other hand, in the future, excess salt may protrude from the wall. In this case, the facade will need to be repainted several times.
All these methods help in construction virtually all year round. Supporting information can be found in the video posted for this article (also on how to prepare a solution during construction in winter).
When conducting construction in winter, it becomes most problematic to provide structures with the necessary strength. When the temperature drops below zero, the liquid in the solution crystallizes. Thus, the process of cement hydration stops.
As the air temperature rises, the ice formed inside the masonry and on the surface of the building material begins to melt, which necessarily causes a decrease in the adhesion of the mortar. Another negative effect is the formation of small cavities in the concrete structure, which can subsequently lead to fairly rapid destruction of walls and ceilings.
To ensure that the cement joint has time to acquire a sufficient level of strength before the liquid freezes, experts traditionally use the following antifreeze additives in the masonry mortar:
- Potash (potassium carbonate).
- Sodium formate.
- Sodium chloride.
- Sodium nitrite (sodium nitrogen).
- Potassium chloride.
To carry out work in conditions where the ambient temperature drops to -15 °C, the optimal solution would be to use antifreeze additives in the form of nitrite and sodium formate.
In case of more serious cooling down to -30 °C, it is advisable to use potash. The advantage of this solution is protection against corrosion in the case of the construction of reinforced floors. The use of potash also helps prevent the appearance of efflorescence on the hardened solution. As for chlorine-containing additives, the latter do not slow down the destruction of reinforcing parts of building structures.
When making compositions for brickwork, it is important to maintain the required proportions. They depend, first of all, on the ambient temperature.
Let's look at the average standards typical for the use of the most popular “antifreeze” in the table. It reflects the consumption of antifreeze additives as a percentage of the mass of cement.
| Air temperature | Sodium formate | Potash | Sodium nitrite |
| -5 оС | 2-3 % | 5-6 % | 4-6 % |
| -10 оС | 3-4 % | 6-8 % | 6-8 % |
| -15 оС | 4-5 % | 8-10 % | 8-10 % |
Additives to bricklaying in winter are added to masonry mortars to slow down their freezing, reduce setting time and increase the adhesion strength of bricks while ensuring the preservation of the basic characteristics of the mortar, including the mobility of the mixture.
The preparation of solutions with PMD does not differ from conventional technologies; mixing with chemical additives is carried out in the form of aqueous solutions. When performing work, the solution should have a positive temperature of about 5 degrees. and must be used completely before setting begins.
When preparing, it is necessary to strictly adhere to the attached instructions, which, depending on the type of PMD, set out:
- proportions of additives depending on weather conditions;
- Possibility of use in buildings for various purposes.
The minimum grade of solutions used is M50. Most additives, according to experts, are not recommended for use in the construction of residential buildings.
How is brickwork made?
First you need to remember a little school physics course. Any brickwork is done using a special mortar. It is made on the basis of cement with the addition of sand and water. As for water, its presence in the solution slows down the process of building a house. According to the laws of physics, at sub-zero temperatures of bricklaying, the water in the solution turns into ice. Even if it does not freeze completely, the bricks can be partially covered with ice. As the ambient temperature rises, the ice will melt and the strength of the masonry will be halved. The ice will turn to water throughout the entire structure and it will quickly collapse.
So at what temperature should bricklaying be done? It is recommended to carry out all masonry work at positive temperatures. Work at sub-zero temperatures is also allowed, but it should not fall below -5°C. Otherwise, after winter the entire building will collapse. For masonry in winter conditions, you need a special solution with anti-frost additives. Currently, such additives make it possible to build brick structures even at -50°C. This is very important in areas where it is cold most of the year.
After finishing the masonry process, you need to monitor the solution. To control the masonry, holes are made in several places and closed with plugs. The temperature of the solution is measured inside these holes. If it is impossible to comply with the thermal regime, it is recommended to turn on the equipment that heats the masonry. In severe frosts, you can install greenhouses above the masonry. When working in the cold, you should remember that antifreeze additives are harmful to humans. Therefore, you need to work in a special suit and follow certain technologies.
Methods for conducting masonry work in winter
The main problem when asking whether brickwork can be done in winter arises with the mortar. Since it contains water, it is clear that at subzero temperatures it begins to freeze. At the same time, the solution begins to “tear”, it loses its ability to bear loads.
Below are options for carrying out this work during the cold season:
- Standard technology.
Builders claim that masonry work can be carried out without changing technology down to -5 0 C. But in this case it is necessary to use a solution with anti-frost additives that “help harden” at negative air temperatures. So be sure to check with the manufacturer which solution you need. And the instructions for using such a mixture will remove all questions; ask the supplier to give it to you; - Construction of greenhouses.
A kind of greenhouse is being built around the construction being carried out. It is usually made from a wooden frame covered with film. Autonomous air heaters (“guns”) are installed inside and heat the structure until the solution gains its strength. This method of doing work turns out to be lengthy, labor-intensive and expensive, because the heater consumes a lot of fuel, and it must work for days. This technique is rarely used by builders; it is more popular in private construction, since everything can be done with your own hands;
- Warming up the masonry.
It involves passing current through the structure. Special electrodes are connected to the wall, and the masonry is heated using electricity. It is allowed to install the next row of masonry only on a heated surface.
This method is more popular for monolithic work. Electrical wires are connected to fittings, which heat the concrete. When reinforcing brickwork, you can do the same and attach the electrodes to the outlets of the mesh. You can also use special eclectic mats that simply cover the wall;
Advice! Don't forget that the air temperature drops at night. And since the solution needs at least 24 hours to enter a solid state, protect the structure overnight.
- Thermos method.
Here it is necessary to warm up the brick before it is laid in the structure. It is based on the fact that when the solution hardens, it releases a certain heat, and in combination with a heated brick, the heat should be enough to prevent the water in the cement-sand mixture from freezing. After completing the work, the wall should be “wrapped” with insulation, plywood and other means.
Technologies for using the solution
Technologies include:
- electric heating;
- heating plant device;
- freezing
Electric heating is a rather expensive and labor-intensive method. It can be produced during the construction of small sections of walls. The process is carried out as follows: electrodes are placed into the mortar during brick laying at subzero temperatures. A current is passed through them, and the seams gradually dry out without the formation of ice.
Making a greenhouse is a highly effective and economical method, but quite labor-intensive. At the site where the wall is being built, you need to make a frame and cover it with polyethylene curtains. A heater is installed inside the resulting tent and further construction can be carried out.
The freezing process is applied by using a frost-resistant solution that can set when warm weather arrives. The disadvantages of this method include the fact that you constantly need to monitor the absence of frost on the brickwork. When they appear, you must immediately use an injection burner and get rid of frost.
After a cold winter, when the first thaw occurs, you need to carefully examine the condition of the masonry and its strength. The overall strength is affected by the transverse walls inside the building. They are usually located at a distance of up to 20 m from each other. The more often they are located, the stronger the building. But it is still better to build it at positive air temperatures.
Brick laying problems in winter
Many people ask the question: “Why can’t you lay bricks in the cold?” Let's remember the composition of the solution and physics. So, a mixture consisting of water, sand and cement is used. It is water that plays the key role here. This is what slows down the whole process. At sub-zero temperatures, water becomes solid and turns into ice. Therefore, no hydration process occurs between the masonry and the mortar. Even if the water in the masonry does not have time to freeze, some of the bricks will be covered with ice. When the air temperature rises and the ice begins to melt, the strength of the masonry will drop by half. The water that was inside the entire structure will also melt, and the entire structure will collapse quickly. And yet at what temperature can bricks be laid? In order for a regular one to set and dry, it must be at least -5°C outside. Otherwise, in the spring the building will collapse.
Technological solution: antifreeze additives
Modern cement mixtures are protected from the negative effects of frost by special antifreeze additives included in the composition: sodium chloride, calcium chloride, sodium formate, etc. For ground work in the open air, sodium nitrite (up to −15 ° C) or potash (up to −30 °С). Under the influence of salts, the water does not have time to freeze, giving the solution the opportunity to harden correctly and in a timely manner. The main thing is to strictly adhere to the rules for using such mixes:
- the solution temperature is not lower than plus five degrees Celsius;
- do not freeze the prepared astringent product;
- apply immediately after preparation.
How to prepare mortar for winter masonry?
But, despite all these subtleties, a way was found to increase the temperature to which bricks can be laid. To do this, you need to use a special solution that contains With their help, it was possible to reduce the temperature limit to -50°C. This method of constructing buildings is especially popular in places where the air temperature is below zero for most of the year.
After the masonry is laid, it remains to monitor the hardening of the solution. To do this, peculiar holes with plugs are made in the masonry, inside of which the temperature is measured using a thermometer.
If it is impossible to maintain the thermal regime during hardening, special equipment is connected to heat and dry the masonry. If this happens, it may be necessary to install additional greenhouses. They are mounted above the masonry. Now for builders the question of at what temperature bricks can be laid is not so pressing.
It must be borne in mind that additives that prevent the solution from freezing are harmful to humans. Therefore, you need to lay bricks only in a special protective suit.
Several ways to lay bricks in the cold season
For high-quality work in sub-zero weather, the following technologies are used.
Electric heating This is the most labor-intensive and energy-consuming method. It is used in the construction of small sections of walls. During the laying process, electrodes are placed in the solution, through which they are passed. With its help, the seams dry out, and the formation of ice is excluded.
Arrangement of a hothouse. This method is highly efficient and economical, but at the same time quite labor-intensive. At the place where the wall will be driven out, a frame is installed on which plastic curtains will be stretched. A heat source is installed inside the resulting tent and construction begins. Such a greenhouse must be heated for a long time until the masonry dries.
Freezing. Here they use a frost-resistant solution, which can set again after the onset of warm weather. During the work process, it is important to ensure that there is no frost on the consumable material. If there are any, get rid of them using an injection burner.
Construction in the cold season
It is often simply necessary to complete the construction that has begun in order to meet the required deadlines. In this regard, we are forced to use complex technologies. And since many people make walls and load-bearing structures from brick, the question arises: is it possible to build a brick house in winter?
Experts answer that it is possible, but difficult. To understand the essence of the issue, let's look at the masonry itself and its components:
- brick is the base of the wall, it is the one that performs the load-bearing function and its strength depends on its brand;
- the mortar is a binder and “holds” the bricks together;
- worker doing bricklaying. Yes, we also include it in the main component, since without a qualified worker, as they say, you cannot build a house. Let it be a person without special education, but he must be familiar with the principles of masonry work.
Brick
Decide in what design the material will be used:
- in a load-bearing wall;
- in the interior partition.
Building bricks are divided into grades, which indicate its load-bearing capacity. Markings range from 75 to 300. For example, material marked M75 carries a load of 75 kg per 1 cm square. Also, so is empty.
Brick is distinguished by the material from which it is made:
- silicate. It is made from sand and lime, it is white in color, and its price is low. heavy, but at the same time fragile, this complicates its transportation; if transported incorrectly, it results in a lot of damage;
- ceramic, made from a special mixture of clay, red in color. It is more expensive, but more resistant to damage;
- facing. The name speaks for itself, but in addition to its decorative properties, it is also harder. Therefore, it can even be used in foundations;
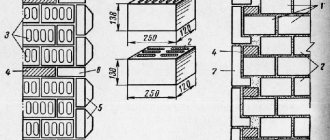
- double. Typically the brick is 250mm long, 120mm wide and 65mm thick. Depending on the type, these indicators may differ. The double brick has an increased width, which speeds up the work process and reduces mortar consumption. The most commonly used double sand-lime brick is M 150;
- clinker. It is characterized by increased strength;
- refractory. It is also called fireclay. It is made using special technology and can withstand temperatures up to 800 degrees. Used in masonry structures where resistance to fire and high temperatures is required.
Solution
Mortar mixtures are also divided by brand. When laying walls, a mortar with a grade of at least M50 is used; it is prepared from a mixture of sand and cement. Next, the composition is diluted with water in the amount that is produced during the work.
Important! The hardened mortar must not be diluted with water and used in masonry. Such a mixture will lose its physical properties, and its use will lead to rapid destruction of the structure.
Typically, the solution supplied by the manufacturer is delivered in dry form. The mason dilutes it with water as it is produced. There is no point in diluting everything at once, since it will simply harden before it is laid in the structure.
Advice! Don't make the mixture too thin. Firstly, it will lose its physical properties and will not bear the proper load. Secondly, such a solution will fill the voids of the brick and will be consumed in larger quantities.
Final stage
Once the answer to the question of at what temperature bricks can be laid has been found, and the foundation for future walls has already been laid, we move on to the final work. After the height of the wall becomes equal to the height of the first floor, prefabricated floors are installed.
When a thaw occurs, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the masonry. Additional strength is provided by internal transverse walls; the distance between them should not exceed 20 meters. The more often the transverse walls are located, the stronger the structure.
Brick laying is a complex process, and frost only makes this procedure more difficult. Strict adherence to and implementation of all stages of work will allow you to build a strong and reliable building even in winter.
So you found out at what temperature you can lay and got acquainted with the methods of laying bricks in winter.
- Masonry by freezing
- Antifreeze additives
- Masonry in thermoses
- Electrically heated masonry
If the construction of a house has begun, then you really want it to be completed as quickly as possible. So much so that they are ready to work even in cold weather, processing walls or installing roofs. The question is how well these desires correspond to the possibilities.
Brickwork in winter requires not only the skill of a mason, but also the presence of certain tools.
Behavior of masonry mortar at sub-zero temperatures
In the classic version, cement mortar is required for masonry. Its main components are cement, sand and water. And if the first two components make absolutely no difference when they are mixed - in winter or summer, then with water the situation is different.
Water freezes at subzero temperatures. It will also freeze in the prepared mortar, turning into ice and significantly reducing its astringent properties, since there will be practically no exchange of moisture between the mortar and the brick.
But this is not all the trouble: when freezing, the water will expand in volume, and the solution will expand with it. The volume of such a solution increases by approximately 9%, but the strength will decrease by approximately the same amount, since the solution will become more friable. The lower the sub-zero temperature, the faster the water in the solution will freeze, the more strength the brickwork will lose.
Moreover, until it freezes completely, it will move from warmer to colder zones, forming an ice crust around the laid brick, thereby preventing the seam from completely sealing. The strength of such masonry in severe frosts can be almost zero.
When heat sets in, the water thaws and returns to its normal state, softening the hardened solution. But the original structure of the solution is not completely restored after thawing, so there is practically no hope of restoring its astringent properties after thawing the water. Depending on the brand of cement and the temperature at which the work was carried out, brickwork laid in winter can lose up to half of its design strength.
To avoid negative consequences in the cold, several methods have been developed to allow the solution to retain its astringent properties for a period sufficient for the masonry to set:
- freezing masonry;
- antifreeze additives;
- masonry in thermoses;
- electric heating
Each of these methods has its own characteristics and its own temperature limit, below which masonry cannot be carried out.
Return to contents
Undoubtedly, it is advisable to carry out any construction in the warm season. But situations in life are different and sometimes you have to take up the trowel even in the cold winter period. Before laying bricks in winter, you need to keep in mind some important features of doing brickwork at low temperatures.
How does bricklaying in winter differ from bricklaying in summer?
Hardening of the cement-sand mortar occurs as a result of contact of the cement binder with moisture. As a result of chemical reactions, the initially liquid mixture acquires the properties of stone. This process largely depends on temperature: if the solution is cooled to zero degrees and below, the cement hydration process stops; at 20 degrees it proceeds normally, while at 5 degrees the hardening rate is reduced by three.
Low temperatures in winter make masonry work difficult. Because of
bricklaying in winter
When the chemical process in the solution stops, all the water is converted to ice. At the same time, it expands in volume, which leads to a loss of strength of that part of the solution that has already partially hardened.
During freezing, the cement mortar rapidly loses its elasticity, as a result of which the masonry joints do not have time to compact. Because of this, when the masonry thaws in the spring, uneven settlement is observed, which can lead to the collapse of the structure. To avoid such problems, brickwork must be built in winter using additional additives to the mortar, as well as special methods for heating the structures being built.
Options for solving the problem
When deciding to lay brick in winter, you can choose one of the laying methods that seems most convenient to you. There are three main ways to maintain brickwork in winter: freezing, using anti-frost components and heating. Let's consider the listed methods in more detail.
- Freezing is a method of allowing the mortar to freeze in the joints immediately after the brick is installed. When the thaw arrives, the cement will begin to thaw and gain strength. It should be noted that this method is suitable for the construction of small structures, otherwise overloads occurring during thawing can cause destruction of the masonry. The lowest temperature at which it remains possible to build brick walls in
Table of additives depending on temperature
areas of northern Russia is -30 degrees. The choice of brand of solution depends on weather and temperature conditions. The ratio of components in the masonry mixture is selected so that during thawing the structure does not warp and the hardening process of the solution proceeds normally.
- Masonry with heated mortar. In this case, when laying, a solution heated to a certain temperature is used. The heated masonry mixture brought from the mortar plant must be consumed within half an hour, until its temperature drops to zero. You cannot add heated water to a freezing solution, since freezing causes ice lumps to appear inside the seams, causing the solution to become loose and unable to gain strength during the thawing process.
- Chemical antifreeze additives. To speed up the cement hydration reaction, antifreeze components are added to the solution, thanks to which the water remains liquid at subzero temperatures. In this case, the solution has time to harden and gain hardness even before freezing. For this, sodium and calcium chloride, potassium carbonate, and sodium nitrate are used. These substances are used in cases where the buildings being constructed do not require thorough finishing. When building brick structures, walls made of blocks or stone, potassium carbonate can be used without resorting to subsequent heating.
The temperature of the cement mortar modified with antifreeze additives should be above +5 degrees. Do not use a solution that has been frozen and then thawed when heated water is added.
Folk mortar for bricklaying in winter with salt: pros and cons
Chemical additives for bricklaying in winter are quite expensive. In order to somehow save money, folk craftsmen came up with the idea of adding salt and detergent to the solution instead. Everything ingenious is simple, because table salt is sodium chloride, which, among other things, is used in additives.
Approximate proportions for mixing folk mortar, which allows you to lay bricks in winter, are as follows: for one batch of mortar, 200 liters, add one pack of salt and half a liter of detergent. Salt will prevent the water in the solution from freezing, and the detergent will make cement and sand more elastic. The resulting solution will be better applied to the brick, and the second brick, thanks to this solution, will be better connected.
Is it worth using a solution with salt for laying bricks in winter?
But after reading the recipe for the solution, do not rush to use it. The attitude of specialists towards such modification of the solution is far from positive. There is an opinion that when salt is used in a solution, the brickwork may sag. This statement has some basis. If you add too much salt to the mortar, and the frost is very strong, the mortar will shrink when the temperature rises above zero and the brickwork will tilt.
And the point here is not even in the amount of salt, but in its addition itself. Of course, sodium chloride is used in industrial additives, but it is only one of the components of the antifreeze mixture. In chemistry, mixing components gives rise to a new substance, that is, it is irrational to perceive the components of additives separately.
In preparing this article, we conducted a small study of reviews from home craftsmen who decided to use salt when laying bricks. Believe me, there were practically no positive ones! People complained that after using such a solution in the spring, the masonry collapsed, salt appeared on the brick, wallpaper fell off the walls, and everything in the same spirit. So is it worth the risk? Isn't it wiser to spend some money on purchasing an anti-frost additive than to redo the entire masonry later?
In any case, it’s up to you to decide how to lay bricks in winter. Choose any method convenient and accessible to you. For our part, we hope that this short article will help you make the best decision. Good luck with your construction!
We recommend watching the video: Mixing mortar for masonry in cold weather
Masonry by freezing
In fact, this is ordinary bricklaying, only done with heated mortar. For such masonry, you need to use only bricks cleared of snow and ice.
To prepare the solution in winter, use warm water.
The process of performing this masonry has its own specifics. The main thing with such masonry is to have time to lay the brick before the mortar freezes. It is best to prepare the solution in a heated room and deliver it to the construction site already heated.
If this is not possible due to large distances, then the solution can be prepared on site using water heated to 80ºC or sand heated to 60ºC. Preparing such a solution in large quantities is pointless, since it will harden unused, and it will not be possible to heat it back up by adding hot water. Water will only add ice-filled pores to the solution, thereby reducing the already low strength. When preparing the solution indoors, it can still be saved by returning it back to the heat, but if this is not possible, then the solution will have to be thrown away.
The solution is applied to only one brick, laying is carried out pressed all the time. When forcing out the last row, simultaneously with laying the bricks, the vertical seams are also filled with mortar. Such masonry may initially be even stronger than summer masonry, since it gains strength due to the freezing of the masonry mortar, and not due to its hardening.
However, as it thaws, such masonry loses up to 20-30% of its design strength. Subsequently, over the course of a month, this figure will decrease, since the usual process of strength gain will occur in the thawed solution. The final strength of such masonry will be 80-95% of normal, which can be considered a completely satisfactory result.
But such masonry, in addition to the lack of strength, has another negative point. When the solution thaws, such masonry inevitably shrinks. With the correct masonry technique, the shrinkage will be no more than 2 mm per 1 m of height, which will not cause serious harm to the building. But when doing masonry, shrinkage must be taken into account initially, making openings 5 mm larger than with conventional masonry. During shrinkage, this gap will disappear, and the integrity of the structure will remain intact.
But there is one important nuance in this process. The building settles as the masonry thaws, i.e. First, the southern side of the task thaws and sinks, then the eastern and western, and last, the northern. If the building is heated from the inside, then settlement will proceed from the inside of the walls to the outside, and in places where there are large loads on the wall it will occur faster. For the brick walls themselves this is a minor problem, but the door and window frames installed in them, as well as the construction of the roof, are at risk of serious deformation.
To protect such masonry from possible movements during the thawing period, its corners and wall joints are reinforced with anchored reinforcing bars. If the walls or partitions are thin, they are supported on both sides with temporary spacers. Door and window frames are additionally reinforced with wooden or iron posts. After thawing, temporary fastenings are removed, but not earlier than 12 days after its completion.
Return to contents
Freezing method
The method is applicable for the construction of buildings up to 4 floors and a height of ≤ 15 m. The essence is to use conventional mortars to ensure their initial setting, which is ensured by heating water to 80 degrees and sand ≤ 60°C, further strengthening occurs upon the onset of thaws.
The following requirements must be strictly observed:
- at the time of installation, the temperature of the solution should be: with an average daily temperature of up to - 10° - plus 5°; to minus 20° - 10° and 15° at temperatures below -20°C. In the first 2 cases, a grade of mortar is used higher than the design one by one; in the third, the excess should be two grades;
- Bricklaying in winter is carried out throughout the entire area at the same time;
- per mile, the mortar is laid immediately on a maximum of two adjacent bricks, on a backfill ≤ 8;
- the finished solution should be applied for ≤ 30 minutes;
- the mason's mortar container must have a lid, be heated or insulated;
- a frozen solution cannot be used; heating it by adding hot water is unacceptable;
- It is prohibited to remove frozen ice crust on the walls with hot water; you can use a blowtorch or hot steam, which will additionally heat the bricks;
- after completing the daily laying, the grip is covered with heat insulators;
- Before the thaw, everything unnecessary (equipment, tools, building materials and debris) is removed from the floors.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Primer for gvl under tiles
Antifreeze additives
When using this method, chemical additives are added to the prepared solution. At sub-zero temperatures in a solution with such additives, the freezing rate of water slows down several times, and the solution itself sets faster. The solution itself does not lose its qualities at all.
But the vast majority of such additives are poisonous, so you cannot work with them without reliable protective equipment. Yes, and with protective equipment you need to be extremely careful. Most often, sodium nitrite or potash is added to the solution.
In order to lower the freezing point in the solution, antifreeze additives must be used.
If the air temperature has not dropped below minus 15ºС, then it is better to use a solution with the addition of sodium nitrite, adding it in an amount of 5% of the weight of the cement used to prepare the cement solution. You can work with this solution for 1.5 to 3 hours, depending on the air temperature.
At frosts below 15ºС, but not more than 30°С, potash is added to the solution. It is added from 5 to 10% by weight of the cement used. To make the solution set more slowly, sulfite-yeast mash is added to it. But even with its use, the serviceability time of such a solution does not exceed 1 hour. However, solutions with the addition of potash cause corrosion of silicates, so this solution cannot be used when laying silicate bricks.
The addition of cheap table salt (NaCl) can also lower the freezing point of the solution, since it contains sodium. But its use will inevitably lead to the appearance of a white coating on the walls, the so-called efflorescence, which is sometimes more difficult to get rid of than to properly remove brickwork. Therefore, such an additive can only be used in the masonry of outbuildings, the appearance of which is not given much importance.
Return to contents
How to do it yourself?
If the work will be carried out when it is cold, then the water for the mixture must be heated.
Before starting work, be sure to study some instructions, the implementation of which leads to an effective result:
- If work is carried out in snowfall, the construction of a protective shelter will be required.
- To prepare the mixture, use warm water and heat the ingredients before cooking.
- The temperature of the mixture after the mixer should be in the range of 15-25 degrees Celsius.
- The amount of salt added depends on the air temperature: from 0 to -5 degrees. - you need 2% of the total mass, and from 6-15 degrees below zero - 4%.
- The characteristics of the concrete mixer and the duration of mixing determine the homogeneity of the solution.
Compliance with the strength requirements for concrete in frosty weather is set out in SNiP 3.03.1-87. According to these requirements, it is not recommended to increase the strength of the structure by more than 20% than stated in the project.
View “SNiP 3.03.01-87” or
Since chloride salts promote corrosion damage, calcium nitrite nitrate is added. To improve plasticity, urea is added in an amount of 7-10% of the total volume. When preparing frost-resistant additives with your own hands, you also use ammonia water, the amount of which in the solution depends on temperature indicators. When antifreeze is used, they are guided by special calculation tables for various jobs and thermometer readings. But experts recommend buying only this type of impurity.
The solution will become more plastic if it contains urea.
Ammonia water is added to the mixture, taking into account the ambient temperature.
Rules for adding to the solution
Antifreeze additives are added together with water to sand, cement and plasticizer. Such impurities can only be used at sub-zero temperatures from 15 to 25 degrees. The mass of additives in the mixture takes up 0.02% of the amount of cement. At temperatures lower than expected, add 0.05% more additives with each degree. And we must also not forget about insulating the structure for two days. It is important to remember the safety precautions during work: use gloves, prevent the solution from getting into your eyes and skin, and do not pour it into the sewer, pond or soil.
Masonry in thermoses
The thermos as a masonry method is based on changing the working method. It relies on the well-known fact that cement mortar always releases a certain amount of heat. Under normal conditions, this heat is enough to carry out brickwork at a temperature of 3-5ºC without any problems.
To prevent the masonry mortar from cooling too quickly, it is recommended to use a thermal insulating coating.
To push down the specified temperature threshold, the brick is heated immediately before installation. Moreover, this method is suitable for almost any type of brick - from ordinary solid to double silicate and clinker facing. In domestic conditions, an ordinary blowtorch is most often used for heating. You can also use a gas burner, but at low temperatures liquefied gas in cylinders may burn poorly.
Every 3-5 rows, the masonry laid in this way is covered with a heat-insulating layer. The heated brick masonry wrapped in this way will continue to heat itself for a long time. This method is simple to implement and does not require special techniques or protective equipment, so every DIYer can easily handle it if for some reason he has to do the laying in the cold. The only thing is that without an assistant warming up the bricks, the work will move very slowly.
Return to contents