Disadvantages of foundations made of FBS blocks
Prefabricated foundations made from FBS foundation blocks do not require installation or dismantling of formwork.
Quickly installed. Immediately after installation, the foundation is ready for the construction of the walls of the house, since, unlike a monolithic foundation, there is no need to wait for the concrete to harden. However, the large size of FBS blocks makes constructing a foundation from them for a private home not the most convenient and cheap:
- To install foundation blocks, it is necessary to use expensive lifting equipment.
- The height of the foundation has to be adjusted to the size of the block. For this reason, the foundation is almost always higher than necessary.
- Horizontal reinforcement in masonry joints has to be performed at the wrong level, which requires an increase in the cross-section of the reinforcement.
- To fit long blocks under a relatively short foundation of a private house, you have to cut a lot of blocks, or make non-standard inserts in the foundation wall, for example, made of brick, which weaken the foundation.
- The standard width of the blocks also does not fit well with the thickness of the walls of the house. The foundation wall turns out to be thicker than necessary.
A foundation made from FBS blocks turns out to be excessively material-intensive, heavy and expensive.
What are concrete wall blocks?
Walling is a durable material, but it has low thermal efficiency. Therefore, during the construction of a residential building, they are placed together with insulation. The latter can be facing bricks, decorative stone, plaster and the like.
As a rule, the standard size of blocks is 20 x 20 x 40. These parameters are optimal for ease of laying this material, and also allow you to complete the project in a short construction time.
Due to its hollowness, the wall block allows you to implement any structural solution. Using them, it is easy to build walls, as well as quickly, evenly and efficiently lay corners.
Design features and types of blocks
Blocks for prefabricated foundations are made from heavy and medium concrete. In the standard version, these are rectangular-shaped products, but for laying the bottom row of a strip foundation (mainly on wet soils), cushion-type panels can be used - trapezoidal, with an increased support area.
Mortgage lugs protrude from the top edge of the block for movement using a crane. The metal hinges are cut off after installing the panel in place.
Products are classified by configuration, presence of reinforcement, and type of concrete. Manufacturers produce:
- FBS – solid panels without reinforcement, suitable for arranging the foundations of high-rise buildings and building basements;
- FBP - hollow concrete blocks for the foundation, they serve as permanent formwork during the construction of walls of exploited basements, for the construction of industrial facilities (during the installation of structures, the voids are filled with mortar, having previously installed reinforcement);
- F – reinforced concrete (with reinforcement) solid concrete blocks for the foundation;
- FL – foundation pads intended for installation of strip-type foundations;
- BF – high-strength blocks made of heavy concrete, designed for increased loads;
- FBV are solid blocks that have a longitudinal recess for laying communications and installing jumpers.
When choosing elements for assembling the foundation, you should pay attention to the markings of the material. It contains the following information: block type, dimensions, type of concrete.
The density of concrete depends on the brand of cement, type of filler, etc. This characteristic directly affects the weight of the product and its compressive strength. Foundation blocks are made of three types of concrete:
- T – heavy. The product is characterized by maximum density and the ability to withstand high loads and frost resistance.
- C – silicate. It has medium density and appropriate performance characteristics.
- P – porous. The use of expanded clay filler makes it possible to obtain blocks with relatively low weight. They are less durable, but cheaper and require less investment in transportation.
Types of concrete wall blocks
On the modern construction market you can find a large amount of material for the construction of private houses, cottages, garages and other structures. The best option, as we have already mentioned, is considered to be a wall block. Let's now try to understand the concept of “concrete wall blocks”.
This material is divided into two categories:
- hollow blocks (those that have through or non-through voids);
- solid blocks (those that do not have any voids).
If we compare these two types, then solid blocks are used during construction. This is explained by their greatest strength. For the construction of a one-story house, you can use and But if a large load is planned for a particular wall in the future, then in this case the voids of the block are filled with mortar or concrete.
Dimensions and weight of concrete blocks for the foundation
When choosing a material for arranging an underground foundation using prefabricated technology, the dimensions of the blocks are taken into account. Please note: the markings indicate dimensions (length*width*height) in decimeters, rounded up.
The most common sizes:
- width 300, 400, 500, 600 mm (3, 4, 5, 6 dm);
- length 780, 880 mm (8, 9 dm) for additional blocks, 1180, 2380 mm (12, 24 dm) for standard panels;
- height 280.580 mm (3.6 dm).
Less common are panels whose length is 280, 380, 480, 580, 1780 mm (3, 4, 5, 6, 18 dm) and height 380, 480 mm (4.5 dm). The size grid of concrete blocks for a strip foundation (FL) differs from the standard one, since the products have a trapezoidal cross-section due to the expanded base.
In addition to the panels of the listed dimensions, concrete blocks of 200x200x400 mm are produced. These are products of a separate FSB-4 standard, the weight of the blocks is 310 kg. They are actively used in private housing construction.
The table below shows the main characteristics of FSB panels of the most common dimensions, made of heavy concrete (this is indicated by the letter T in the marking).
| Product brand | Dimensions (mm) | Concrete class | Product weight (kg) | ||
| length | width | height | |||
| FBS 9.3.6-T | 880 | 300 | 580 | 87,5 | 350 |
| FBS 9.4.6-T | 880 | 400 | 580 | 87,5 | 470 |
| FBS 9.5.6-T | 880 | 500 | 580 | 87,5 | 590 |
| FBS 9.6.6-T | 880 | 600 | 580 | 87,5 | 700 |
| FBS 12.4.3-T | 1180 | 400 | 280 | 87,5 | 310 |
| FBS 12.5.3-T | 1180 | 500 | 280 | 87,5 | 380 |
| FBS 12.6.3-T | 1180 | 600 | 280 | 87,5 | 460 |
| FBS 12.4.6-T | 1180 | 400 | 580 | 87,5 | 640 |
| FBS 12.5.6-T | 1180 | 500 | 580 | 87,5 | 790 |
| FBS 12.6.6-T | 1180 | 600 | 580 | 87,5 | 960 |
| FBS 24.3.6-T | 2380 | 300 | 580 | 87,5 | 970 |
| FBS 24.3.6-T | 2380 | 400 | 580 | 87,5 | 1300 |
| FBS 24.3.6-T | 2380 | 500 | 580 | 87,5 | 1630 |
| FBS 24.3.6-T | 2380 | 600 | 580 | 87,5 | 1960 |
The weight of concrete blocks for the foundation depends on the density of the material: for example, if heavy concrete of class 75 or 100 is used for the manufacture of panels, the weight of the product with the same dimensions will differ less or more from that given in the table above.
More detailed tables that are used when calculating foundations include the density of the material, the cross-section of the reinforcement (for reinforced blocks), the volume of products and other characteristics.
When choosing between a monolithic and prefabricated foundation, you need to consider the pros and cons of a structure made from prefabricated elements. The use of concrete blocks for the foundation of a house instead of a monolith allows:
- spend a minimum of time on construction - there is no need to wait until the mortar hardens and gains strength, you can immediately begin building walls;
- reduce the amount of manual labor, since installation of formwork, assembly of reinforcement cage and preparation of large volumes of cement mortar are not required;
- carry out work in adverse weather conditions.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the Foundation for a bathhouse made of bricks.
Concrete blocks are suitable for installing the underground foundation of buildings of any type and size on different types of soil. Products with high density are resistant to significant temperature changes and have high frost resistance. A well-installed foundation will last at least 100 years.
Using ready-made blocks also has a number of disadvantages:
- To carry out the work, special equipment is required, since the products are heavy;
- it is impossible to equip a prefabricated foundation on soils prone to heaving;
- the finished underground structure needs reliable waterproofing to protect it from groundwater and flood waters;
- the final cost of a prefabricated foundation is usually higher compared to a monolithic one.
The choice of foundation technology depends on the characteristics of the building, loads on the underground part, soil characteristics and other factors. A universal option is a strip foundation made of ready-made panels; it is used in the construction of private houses, multi-storey buildings, and buildings for various purposes. In private housing construction, blocks of the FBS-4 standard (200x200x400 mm) are also used to create column-type foundations.
A strip foundation made of concrete blocks is arranged in the form of a closed loop. The height and width of the tape depends on the designed loads on the underground foundation. The tape should be located under external walls and internal capital partitions to evenly distribute loads.
Work progress:
- On the prepared site, markings are made and a trench with gentle walls is dug for the strip foundation. The depth of the foundation depends on the characteristics of the soil and the depth of freezing.
- A cushion of washed sand is installed at the bottom of the pit. The height of the carefully compacted layer of sand is about 10 cm, the surface of the pillow should be leveled horizontally.
- When constructing massive buildings or on soil with high humidity, trapezoidal FL blocks are laid on top of the cushion, centering them along the axes of the trench;
- Laying FBS begins from the corners. The blocks are aligned along their axes, fastened together with mortar, which is placed on the top edge and ends. Installation is carried out according to the principle of brickwork. Before laying the upper tier, the loops are cut off from the blocks of the lower layer.
- The finished structure is waterproofed, after which the construction of walls can begin.
The construction of a columnar foundation from concrete blocks is carried out as follows:
- pits are prepared in such a way that support pillars are located at all angles, intersections of walls and partitions, at the base of doorways, at several points under long walls;
- a sand cushion is compacted at the bottom of the pits;
- the pillars are mounted from solid blocks with ligation of each row, the minimum cross-section of the columns is 400x400 mm;
- To provide rigidity to the base, a monolithic grillage is installed or the pillars are connected into a spatial structure using a steel channel, I-beam or beam attached to the heads of the pillars, welded from a 4x4 cm angle.
A prefabricated foundation for a private house, cottage, bathhouse, or outbuilding can be done with your own hands.
Other types of wall blocks
Thanks to technological progress, today all kinds of materials for building materials have appeared in construction stores. This is not limited to concrete wall blocks alone. Over the past decade, their varieties have become much more numerous. All of them differ in their characteristics, as well as in their price category.
So, in addition to concrete, today it is worth noting the following wall blocks:
- aerated concrete;
- gas silicate;
- expanded clay concrete;
- polystyrene concrete;
- foam blocks.
All these materials are also in great demand in the modern construction market, as are concrete blocks. But still, they have more positive aspects. First of all, this concerns greater thermal conductivity and sound insulation. Secondly, they are all laid on a very thin layer of mortar or special glue, which makes the process of laying them less labor-intensive. In addition, it is worth considering that all this material has ideal angles. Therefore, in order to create a perfectly flat wall, you need to make plumb lines and adjust everything to them.
It is also worth adding that after building a house, internal walls made of aerated concrete or silicate, for example, do not need to be plastered. To make them smooth, simply apply several layers of putty.
The only disadvantage of these types of blocks is the cost. The price for this material is high. Therefore, not everyone can afford to buy them.
Shallow block foundation for a house with stone walls
It is recommended to use a prefabricated foundation for a house on a site without a large slope and with homogeneous soil.
During seasonal fluctuations, the groundwater level should not rise above the base of the foundation. If the groundwater level is high, it is better to use a strip foundation made of monolithic concrete.
A foundation made of small-format masonry materials is suitable for constructing a house foundation on non-heaving, slightly and moderately heaving soils.
If the soil on the site is very heaving, then the foundation can be made provided that the soil is protected from freezing. Find out here the degree of soil heaving in your area.
Solid concrete or expanded clay concrete blocks are used for laying foundation walls. These blocks have fairly low water absorption, high frost resistance and the necessary compressive strength. For concrete blocks, these indicators are slightly better than for blocks made of expanded clay concrete. The latter are lighter than concrete blocks.
It is possible to lay a foundation of solid ceramic bricks. But this material is now rarely used for foundation laying. The small size of the brick increases the complexity of masonry. In general, a brick foundation is more expensive than a concrete block foundation.
To protect the house from deformations caused by the forces of frost heaving of the soil, the base of the foundation is usually laid at the depth of soil freezing. But there are other options for constructing foundations on heaving soils.
Shallow, thermally insulated foundation for a house on heaving soil
A modern solution for houses without a basement on heaving soils is the installation of a shallow, thermally insulated strip foundation.
The idea behind constructing this foundation is that the heaving soil near the foundation is protected from freezing and it stops heaving in winter.
To do this, the foundation and the surrounding soil are insulated with a layer of polystyrene foam or extruded polystyrene foam.
The design of the load-bearing part of a thermally insulated foundation made of masonry blocks can be done as described below for the foundation of a house on slightly heaving soils.
Read: “Thermally insulated shallow strip foundation for heaving soils”
On non-heaving, slightly heaving and even moderately heaving soils, a shallow foundation for a private house can be made from masonry materials and without soil insulation.
On non-heaving or slightly heaving soils, for a private house or bathhouse, a shallow foundation is installed. For these conditions, it is sufficient to perform horizontal reinforcement of the masonry rows.
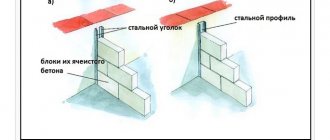
Construction of a foundation made of masonry materials on slightly heaving and frost-protected soils: 1 - foundation laying; 2 - masonry of the base; 3 - blind area; 4 - horizontal waterproofing; 5 - backfilling the floor on the ground; 6 - masonry reinforcement mesh every 20 cm of masonry;
The foundation masonry is reinforced with a masonry mesh with a wire diameter of 4-5 mm. and cell size 100x100 mm. The width of the foundation base (dimension in the figure) is calculated based on the load-bearing properties of the soil and the weight of the building - find out here.
The width of the base of the foundation for a house with light walls made of wood, or frame walls, for most slightly heaving soils is usually sufficient in the range of 20 - 40 cm (larger sizes apply to three-story buildings). For these houses, the width of the base is made equal to the thickness of the foundation wall.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the passage of a chimney through a concrete ceiling
For stone houses with heavy walls made of bricks or blocks, the width of the foundation base on slightly heaving soils is increased to 0.6 - 0.8 m (the larger size applies to three-story houses with reinforced concrete floors). Here the foundation walls are thinner than the width of the base.
If the width of the base exceeds the thickness of the foundation walls, then the walls of the prefabricated foundation made of blocks are installed on a strip of monolithic reinforced concrete base of the required width. A reinforcement cage is placed in the lower part of the sole before pouring concrete.
The bottom of the foundation trench is leveled by pouring a layer of sand and gravel mixture. On non-heaving and slightly heaving soils, the total thickness of the leveling sand cushion is no more than 200 mm. It is necessary to thoroughly compact the layer of bulk soil. The thinner the layer of soil, the easier it is to compact it.
A polymer profiled membrane is laid on the sand bed. The first row of blocks is laid on a membrane, on a masonry mortar.
If the walls of the house are made of aerated concrete blocks, then a monolithic reinforced belt must be made on top of the base.
On soils with a medium degree of heaving, two monolithic reinforced concrete belts are added to the foundation structure made of masonry materials. One belt is a monolithic reinforced foundation base. The second belt is placed along the top of the foundation or plinth.
In addition, an anti-heaving sand cushion is made under the base of the foundation.
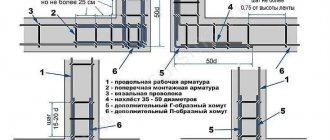
Not buried foundation for a wooden or frame house or bathhouse on medium heaving soils: 1 - sand and gravel anti-heaving cushion; 8 - laying the foundation and plinth; 10 - soil backfill of the floor along the ground; 11 - monolithic reinforced concrete belt along the top of the base; 13 - monolithic reinforced concrete base of the foundation.
The thickness of the monolithic reinforced concrete belt along the top of the plinth (11) and the base (13) of the foundation is 10 cm. A reinforcing mesh with 2 or 3 bars of working reinforcement of class A-III, with a diameter of 10 mm, is placed in the monolithic belt.
It is convenient to place a monolithic sole (13) on top of a profiled membrane laid on a compacted sand bed (1).
For light wooden and frame houses, it is dangerous to bury the foundation into the ground. The lateral surface of buried foundations is affected by the tangential forces of frost heaving of the soil. These forces may be sufficient to lift a light building out of the ground.
For light wooden and frame buildings, a non-buried foundation (in the figure above) will be more economical and safer. Due to the absence of a side surface buried in the ground, such a foundation is not affected by the tangential forces of frost heaving of the soil.
Shallow strip foundation for a house with stone walls on medium-heaving soils. 1 - monolithic reinforced concrete base of the foundation; 2 - backfilling of the sinuses; 3 - sand and gravel anti-heaving cushion; 4 - reinforcement frame; 5 - blind area; 6 - backfilling the floor on the ground; 7 - horizontal waterproofing; 8 - wall of the house
The width of the base of the foundation of a house with stone walls, as a rule, is greater than the thickness of the walls. For these conditions, it is advantageous to make a monolithic reinforced strip of the base of a precast foundation of increased height. On top, on the base, lay the underground and above-ground (basement) parts of the foundation from small-format concrete blocks or bricks.
On weak and medium heaving soils, it is advantageous to make the width of the trench equal to the width of the base of the foundation. Concrete is poured into the trench at random, without formwork. A reinforcement cage is first installed in the trench. This method is suitable for fairly dense soils in which the vertical walls of the trenches do not crumble.
On medium-heaving soils, sheets of insulation, extruded polystyrene foam 40 mm thick, are fixed to the trench walls. A layer of insulation separates the concrete from the soil, which reduces the impact of the tangential forces of frost heaving on the foundation walls. This solution allows you to avoid backfilling the sinuses of the foundation trenches.
For a house with stone walls, in areas without a strong slope, it is enough to deepen the base of the foundation 0.3-0.4 m from the surface of the earth.
What should you pay attention to when choosing concrete wall blocks?
As a rule, when a consumer chooses wall blocks, prices are the main criterion for his final choice. Unfortunately, buyers neglect technical indicators, trying to save on housing construction.
In addition to the hollowness that we talked about above, it is necessary to pay attention to the frost resistance of the material. This characteristic is denoted by the letter F. When purchasing concrete blocks, you need to inquire about this indicator. It can vary from F15 to F200.
Frost resistance of blocks implies the ability to maintain their primary characteristics (in this case, strength) during significant changes in temperature and moisture. Many of you have probably seen that a wall or corner of a newly built house began to crumble or crumble after a few years in the spring. This suggests that the frost resistance index is very low. Thus, experts recommend not saving and choosing the material with the largest F number.
Foundation waterproofing and water protection for a house with a basement
A cheap prefabricated strip foundation for a house with a basement can be made from hollow concrete blocks with vertical reinforcement of the basement walls.
For the foundation walls of a house with a basement, it is convenient to use vibro-pressed hollow concrete blocks - Besser blocks.
The presence of voids in the blocks makes it easy to perform vertical reinforcement of the foundation. The reinforced foundation can withstand lateral loads well. The option with vertical reinforcement is recommended for foundations with a basement. Vertical reinforcement rods are placed in coaxial voids in the masonry blocks. Voids with reinforcement are filled with concrete of class B15.
To support the reinforced concrete slabs of the basement along the top of the foundation walls made of expanded clay concrete and hollow concrete blocks, it is necessary to make a monolithic reinforced concrete belt.
A monolithic reinforced belt along the top of a prefabricated foundation from any blocks should also be made for laying walls on them from blocks of aerated concrete (gas silicate) or porous ceramics.
Vertical reinforcement is made of hollow concrete blocks in the basement walls. To construct a monolithic reinforced concrete belt (banding beam), tray concrete blocks are used.
The monolithic foundation pad is connected to the lower row of hollow blocks using reinforcement outlets. All voids in the bottom row of blocks are filled with concrete.
For basement walls, it is recommended to fill all the voids in the blocks with concrete to the full height of the wall.
If the foundation does not have a basement, then it is enough to fill the voids of the lower row of blocks with concrete, as well as reinforce and fill the vertical sections in the corners of the walls with concrete.
The sinuses of the foundation pit with the basement are filled with soil from the outside only after the installation of the floor slabs. Otherwise, under the influence of lateral soil pressure, the foundation walls may collapse.
A prefabricated foundation for a house with single-layer or double-layer walls is laid in one layer. The foundation for a three-layer house wall is also made of three layers - a load-bearing layer, an insulation layer and a cladding. The facing layer is made of narrow (12 cm) concrete blocks or solid ceramic bricks. The best material for cladding is clinker brick.
The thickness of the foundation walls is usually chosen to be the same as the thickness of the stone walls of the house. For a house with wooden or frame walls, the thickness of the foundation walls is made in the range of 250 - 300 mm.
Foundation walls in a house with a basement require enhanced protection from moisture. For conditions when the groundwater level is below the base of the foundation, coating waterproofing in the form of a layer of polymer-bitumen mastic is applied to the surface of the walls.
The outer walls of the basement are additionally covered with two layers of waterproofing roll material.
The profiled membrane is convenient and profitable to use for waterproofing the floor in the basement. There is no need to make a concrete base for adhesive waterproofing.
Only wall drainage can provide reliable protection of the basement from water. Be sure to do it.
Wall drainage around the foundation will reliably protect the basement of the house from water
Read: “Wall drainage around the foundation.”
Reviews of concrete wall block
Today, the greatest demand among builders is concrete wall blocks. The prices for this material are the lowest (from 38 rubles for 1 block), in addition, concrete blocks have a number of positive characteristics that are heard in customer reviews.
Firstly, concrete is a non-flammable material. It perfectly resists even open fire.
Secondly, concrete blocks have high sound insulation, as noted in reviews. Thus, any structures can be built from them.
Thirdly, modules and parts made of any other materials can be attached to a wall made of concrete blocks.
Fourthly, this material is considered environmentally friendly. It is believed that a concrete wall block “breathes”, so you will feel comfortable in your future “living” house.
And the last important point is good thermal insulation. Although expert reviews recommend covering walls made from such a block with brick or other material.
According to this, we can conclude that concrete wall blocks are an excellent option for building an inexpensive, high-quality country house.
Expanded clay concrete blocks
Expanded clay concrete building stones combine the positive qualities of red brick and cellular concrete products. They are made from cement, sand, water and expanded clay. The last component gives the material lightness and high thermal insulation abilities. At the same time, the strength characteristics of the product do not deteriorate at all.
Expanded clay concrete hollow blocks come in two types:
- wall;
- septal
The length of products of the first type varies from 90 to 390 mm. The width of one block starts from 138 mm and reaches 288 mm. The height of the wall stone is 138 mm (there are options with a value of 188 mm). The weight of one block is 12 kg.
The dimensions of the partition varieties are 390 x 90 x 188 mm. The weight of such products is 6.5 kg. The cost of a standard block is about 40 rubles, while partition products have a price tag of 20 rubles per piece.
Concrete block façade painting
After sealing the seams and plastering the window slopes, they begin to paint the outer walls with facade paint. To paint the walls, you can use any façade paint from well-known manufacturers. The color is chosen according to the taste of the home owner. Light, rich traditional tones from yellow to white look especially advantageous. Corner parts should be painted in a different color, contrasting with the color of the wall.
Watch the video and admire how the master masterfully lays besser blocks.
Prompt delivery of expanded clay concrete blocks is carried out the next day after ordering, with all documents.
Features and application of expanded clay concrete blocks in Moscow
Expanded clay blocks were originally developed as an insulating layer for a wall made of durable concrete. However, over time it became clear that this design was ineffective and did not meet sanitary standards. That is why today, thanks to the use of vibropresses, a material made on the basis of expanded clay and a cement mixture, which is an expanded clay block, has acquired the necessary strength and can act as a full-fledged building material when constructing the load-bearing structure of a building.
The advantage of blocks made of expanded clay and concrete:
- the specific gravity of the material is 2.5 times less compared to brick and concrete, so there is no load on the foundation;
- the low thermal conductivity of expanded clay blocks allows significant savings on coolant, while a pleasant microclimate is created in the room, since the building material “breathes”;
- if a hollow material is chosen for construction, this makes it possible to install a hidden frame in the body of the wall, which will significantly increase its load-bearing capacity;
- Moscow expanded clay concrete blocks are distinguished not only by their strength, but also by their frost resistance, so the masonry made from them will retain its integrity, regardless of the weather conditions outside;
- one block of this material replaces seven bricks in volume, so its installation will require much less time and binding mortar;
- A block made of expanded clay concrete is distinguished by a variety of shapes and textures. The façade of a building made from this material does not require additional finishing.
Today, expanded clay concrete blocks in Moscow are also called bioblocks, since they are made from environmentally friendly materials and do not emit harmful substances into the environment. The positive characteristics of expanded clay concrete blocks have long been appreciated in Germany, Holland, Poland, and Scandinavian countries. There, 40% of houses are built from this material.
Cladding the walls of a house made of concrete blocks
Cladding the walls of a house in order to create a protective and decorative covering of the facade can be done, like other walls made of stone materials, in various ways:
- laying a facing layer of vibro-pressed concrete brick BO 1.5 on a cement-sand mortar.
- laying a facing layer of vibro-pressed hollow concrete blocks BO 1.1 - 1.4 or BP.
- laying a facing layer of ceramic facing bricks.
- using plastering systems from different manufacturers.
- fiber cement boards such as Eternit and their analogues.
- facade systems as well as other materials.
The facing masonry is connected to the load-bearing layer of the wall with metal or fiberglass ties. The total cross-sectional area of the bonds must be taken to be at least 0.4 cm2
per 1
m 2
wall area.
It is better to use galvanized masonry mesh as connections.
The mesh increases the load-bearing capacity and crack resistance of the masonry of the load-bearing and facing layers of the wall, forms mounting niches into which insulation boards are inserted, and ensures fixation of the insulation layer on the vertical plane of the load-bearing wall.
How to properly insulate and brick walls
Cladding walls with vibropressed concrete facing bricks BO 1.5 or hollow BO blocks has certain advantages over facing with facing ceramic bricks.
Facing vibropressed bricks and blocks can have different color shades and texture of the front surface. The palette of colors in which blocks can be painted is wide: red, terracotta, cherry, purple, yellow, milk chocolate, pine bark, etc.
Color blocks by adding
into the concrete mass of special high-quality iron oxide coloring pigments that can retain their color for decades. By alternating cladding blocks of different colors and textures, you can give the facade of a house any look.
The use of Besser blocks makes it possible to obtain an almost finished facade
, not requiring any additional finishing. True, colored blocks are noticeably more expensive. However, ordinary gray blocks can be painted with facade paints.
Vibro-pressed concrete products have very good frost resistance.
In this indicator, they are significantly superior to traditional brick.
A very low (2-6%) water absorption coefficient allows the blocks to easily withstand any rainfall and frost. Thanks to these properties, finishing from Besser blocks does not require additional maintenance for decades.
Insulation of walls made of concrete Besser blocks
Exterior walls made of concrete blocks must be insulated.
1 – facing layer, masonry made of BO blocks on cement-sand mortar. 2 – layer of insulation up to 150 mm
. 3 – load-bearing layer, masonry made of BS blocks on cement-sand mortar.
W/m°C are used as wall insulation.
.
When performing thermal engineering calculations of three-layer wall structures, the following masonry characteristics are taken into account:
- the masonry of the load-bearing layer of vibro-pressed BS wall blocks, with the voids filled with concrete, on a cement-sand mortar has a thermal conductivity coefficient = 1.40 W/m°C
. - laying a facing layer of vibro-pressed concrete brick BO 1.5 on a cement-sand mortar with a masonry density of 2100-2200 kg /m 3
- thermal conductivity coefficient = 1.20
W/m°C
; - laying a facing layer from vibro-pressed hollow concrete blocks BO or BP based on concrete with an average density of 2100 * 2200 kg/m 3
with a masonry density (taking into account the hollowness of the blocks) of about 1500
kg/m 3
- thermal conductivity coefficient = 0.60
W/m° WITH
; - laying a facing layer of ceramic facing bricks, facing bricks and an average density of masonry of 1800 kg/m 3
- thermal conductivity coefficient = 0.70
W/m°C
.
The following can serve as insulation:
- Polystyrene foam boards PSB-S (with fire retardant);
- Plates made of extruded polystyrene foam;
- Semi-rigid mineral wool slabs on a synthetic binder with a density of 75–125 kg/m 3
;
When choosing insulation, you should take into account that polystyrene foam insulation is flammable and fire hazardous.
Mineral wool insulation boards must have a hydrophobizing (water-repellent) impregnation. A wall with such insulation must have a ventilated gap between the insulation and the cladding. Why is a ventilated gap necessary?
Concrete building blocks - what is it and where is it used?
Concrete blocks are a piece material that is made from heavy concrete and various fillers, but it should be remembered that the higher the grade of cement and the finer the fraction of crushed stone used in the manufacture of this building material, the better its technical characteristics.
Concrete blocks Moscow are characterized by high strength and density, therefore they will be an excellent structural material for the construction of strip-type foundations. They are characterized not only by high load-bearing capacity, but also by water resistance and low thermal conductivity, which is why they are used to organize the ground and basement floors of a building. Using modern technologies in the production of concrete blocks, they are given different shapes, which simplifies the construction process.
Types of concrete blocks:
- foundation wall blocks are a traditional material made from concrete and filler. Used to build a foundation. Dimensions range from length 880 to 2380 mm, width 300, 400, 500, 600 mm, height 280 and 580 mm. Their weight is up to 2000 kg. They are placed on pallets only by crane, for which they have special fastenings. The second option is concrete blocks 20x20x40 and similar sizes. Used for the construction of basement floors and basement walls. They have a monolithic structure and are durable;
- foundation hollow concrete blocks Moscow - are also used to organize basement floors, but, thanks to the cavities inside the material, the masonry made from them can be additionally reinforced with iron reinforcement.
Both concrete and expanded clay blocks Moscow can be ordered from our company. Many years of experience guarantees high quality products. We can provide wholesale supplies with delivery of material using our own transport directly to the work site.