Requirements of state standards for concrete strength
The state establishes methods for assessing and monitoring the strength of concrete and the procedure for marking the material based on the results of tests. GOST 10180-2012 defines methods for testing the strength of concrete, as an assessment of the behavior of control samples when exposed to force in the following way:
- compression;
- axial tension;
- bending stretching;
- splitting tension.
GOST 18105-2010 provides definitions of the actual, standardized and required strength of concrete. These and other State Standards, SNiPs and technical regulations of manufacturing plants constitute the regulatory framework governing production procedures, test methods and requirements for the strength of concrete structures.
Stages
Setting stage
The setting of the solution occurs in the first 24 hours from the moment of its cultivation. This time directly depends on the ambient temperature.
At room temperature (20 degrees), this process takes less than one hour: setting begins after 2 hours from the time of preparation of the mixture, and the completion of this process ends after 3 hours.
At a lower temperature, the start time of the setting stage is slightly delayed, and the duration of the process increases disproportionately.
So, for example, at an outside temperature of 0 degrees, setting begins only after 6-10 hours have passed after preparing the solution, and will end only after 15 or 20 hours. At high temperatures, the duration of this process reaches a minimum and can be only 15-20 minutes.
During its setting, the cement mixture remains viscous and is subject to external influence. Due to thixotropy, in which the viscosity decreases when exposed to a solution, concrete that has not completely set during mixing does not enter the hardening stage.
This property is used when transporting concrete mixture using concrete mixers. They are constantly mixed using a mixer, which allows you to preserve the properties of the concrete mixture. With this impact, the concrete truck is able to keep the cement mixture in an unhardened state for a long time.
But, with prolonged external exposure, the mixture “cooks” and loses some of its qualities. The “welding” process occurs especially quickly in the warm season.
Hardening stage
This process begins immediately after the concrete has completely set. Hardening and strength gain will continue for several more years, but at the same time, the grade of concrete can be determined after 4 weeks .
How does concrete gain strength?
After a certain time, the concrete solution turns into a monolithic structure with the properties of artificial stone. This occurs due to the hydration reaction of building mixtures. The kinetics of strength gain determines how long concrete hardens and is a process of interaction between minerals in the composition of cement and depends on many factors. First of all, it is necessary to note the effect of temperature and air humidity on the physical and chemical processes in the mortar. The higher the ambient temperature, the faster the concrete gains its strength, and vice versa - as the temperature decreases, the process slows down until the concrete completely stops hardening at zero degrees. When the air temperature is expected to be low, electrical heating of the concrete is used in concreting structures. When electrically heated concrete, freezing of freshly laid concrete mortar is not allowed if the air temperature drops to 5 degrees C or lower.
Construction mixtures with antifreeze additives directly improve the properties of concrete mortar to accelerate the process of strength gain at low air temperatures.
Strength, brand, class of concrete. Determination methods. Control samples.
The choice and purchase of a specific type and brand (class) of concrete mixture is determined by your project. If there is no project, then you can trust the recommendations of your builders. If you have some doubts about the competence of your builders, you can try to figure it out yourself.
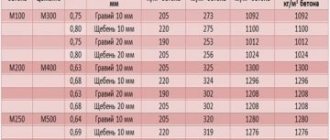
The numbers of the concrete grade (m-100, m-200, etc.) indicate (on average) the compressive strength in kgf/sq.cm. Compliance with the required parameters is checked by compression (with a special press) of cubes or cylinders cast from a sample of the mixture and kept for 28 days of normal hardening.
In modern construction, such a parameter as concrete class is more often used. In general, this parameter is similar to a brand, but with minor nuances: brands use the average strength value, while classes use guaranteed strength. However, this does not matter to you. I won’t fool you with strength variation coefficients and other technical nuances. The design documentation, if you have one, of course, should indicate what class of concrete should be used. In accordance with ST SEV 1406, all modern design requirements for concrete are specified in classes. I don’t know to what extent this is observed, because 90% of construction organizations order concrete in stamps...
The main thing for you is that the brand of concrete that was brought to you matches what you actually ordered. Of course you can check, but not right away. What's worth doing.
When unloading concrete, take a sample and cast a couple of cubes measuring 15x15x15 cm. To do this, you can put together special shapes of the required size from planks. Before pouring concrete into molds, it is advisable to moisten the boxes so that dry wood does not take a lot of moisture from the concrete, thereby negatively affecting the process of cement hydration. The poured mixture must be pierced with a piece of reinforcement or something similar: poke it into the mixture, like pounding mashed potatoes, so that unfilled spaces (shells) do not form in the poured sample, excess air comes out, and the mixture becomes denser. You can also compact the mixture by hitting the sides of the boxes with a hammer. Store the cast cubes at medium temperature (about 20 degrees) and high humidity (about 90%).
After 28 days, you can bring all this magnificence to any independent laboratory with a clear conscience; They will suppress all this for you and give you a verdict - whether the concrete corresponds to the declared brand or does not correspond. However, it is not necessary to wait 28 days; for this, there are intermediate stages of hardening at the age of 3, 7, 14 days. During the first 7 days, concrete gains about 70% of its design strength.
What nuances may arise when collecting and storing sample cubes:
- Do not dilute the mixture with water in the concrete mixer truck.
- Take samples directly from the concrete mixer tray.
- Thoroughly compact the concrete mixture in the molds by bayoneting (mashed potatoes)
- Store samples in proper conditions: not in the sun or on the stove :-)) It is better in a cool basement, or just in the shade.
That's all about the cubes. If you suddenly forgot to take samples, but would like to know that everything is in order, contact an independent laboratory that can measure the strength on site. For this purpose, there are so-called non-destructive methods for studying strength: testing using shock pulse methods using a sclerometer. People call it tapping concrete. Ultrasonic and other methods for determining strength are also used.
The relationship between the class and grades of concrete in terms of strength with a standard coefficient of variation v = 13.5%
| Concrete class | Average strength of this class, kgf/sq.cm | Nearest brand of concrete |
| В3.5 В5 В7.5 В10 В12.5 В15 В20 В25 В30 В35 В40 В45 В50 В55 В60 | 46 65 98 131 164 196 262 327 393 458 524 589 655 720 786 | M50 M75 M100 M150 M150 M200 M250 M350 M400 M450 M550 M600 M600 M700 M800 |
By clicking on the links below, you can see the main areas of application of a particular brand of concrete.
- m 100 in 7.5
- m 150 in 12.5
- m 200 at 15
- m 250 in 20
- m 300 at 22.5
- m 350 in 25
- m 400 at 30
- m 450 in 35
- m 500 at 40
Strengthening schedule
A visual representation of how long concrete takes to dry is given by graphs of concrete strength gain. Depending on the air temperature and the grade of concrete, the time it takes for the concrete to harden and achieve the safe and required strength is determined. The hardening graphs constructed allow us to conclude that the drying process of the concrete mixture is uneven. So, in the first five days of the solution’s life, the fastest increase in strength occurs; this period is called “curing” of concrete. The strength of concrete on the 7th day is 60-70% of its brand strength, and this figure approaches 100% on the 28th day after preparing the solution.
The time it takes for concrete to gain strength directly depends on its class; the higher the quality of the cement in the composition, the higher the grade of concrete. For low-quality concrete, the percentage of critical strength is more important. This pattern is reflected in the following table:
| Concrete grade by compressive strength | Critical strength threshold in % of brand |
| M15-150 | 50 |
| M200-300 | 40 |
| M400-500 | 30 |
Other factors affecting strength gain
In addition to humidity and temperature, this process is influenced by:
- type of cement;
- water-cement ratio;
- the degree of compaction of the mass during the pouring process.
This is how concrete prepared with Type B cement (fast-hardening Portland cement) gains strength during the first 24 hours:
- 45% - at t = 30 degrees;
- 16% - at 5 degrees.
How long does it take for concrete to gain strength when it contains excess water? There is a direct relationship here: the more water, the longer the pouring takes to mature.
Moreover, a mass compacted manually, and not too carefully, will not achieve brand strength under any circumstances.
Based on the above, we can conclude: when building a foundation for a house or other serious building, it is best to use concrete prepared in a factory, and when pouring, compact the concrete with vibrators.
Stages of concrete strength development
The entire process of hardening concrete stone can be divided into the following stages:
Setting - the duration of this stage depends on the temperature of the medium:
- at zero air temperature, setting begins 8 hours after preparing the concrete solution and lasts 15-20 hours;
- at 20 degrees C, setting begins in the second hour of the solution’s life and lasts on average another hour.
The higher the air temperature, the faster the setting stage of the building mixture will begin and end. In addition, the brand of concrete also plays a role here. Below are some examples of such influence:
- concrete grade M200 - setting lasts 2-2.5 hours;
- concrete grade M300 - 1.5-2 hours;
- concrete grade M400 - on average 1-1.5 hours.
Already during transportation of the solution, the setting stage begins, but due to the constant mechanical action during its mixing and thixotropy, its duration is significantly accelerated.
Hardening is the second stage of concrete strength gain. Hardening of concrete occurs due to the mechanism of cement hydration; in other words, concrete is dried due to the evaporation of moisture.
Minerals in cement have varying degrees of hydration. The early strength of cement is ensured by allite, which is the most reactive mineral. Another mineral, bellite, does not lose its ability to hydrate for several decades. That is, theoretically, the concrete hardening stage can continue for many years after construction is completed. In practical work, builders allow about a month for the curing stage.
The transformation of concrete mortar into a durable monolithic structure depends on a set of environmental factors and the quality of the source materials. The strength of concrete is monitored at all stages: from the selection of building mixtures to the assessment of the strength of already erected structures using mechanical and ultrasonic methods.
Return to list
Find out the cost of delivering concrete to your site
from our manager by phone or through the request form
Technological features of the process
The strength gain of concrete, depending on temperature, can occur quickly or slowly. According to GOST and SNiP standards, normal conditions for proper hardening of concrete are 15-25° heat and 90-95% humidity. If the concrete pouring temperature is more than 25°, it is necessary to enter a multiplying factor.
To measure the curing temperature of concrete, special technical thermometers are used. They come in different types: infrared, bimetallic, wireless.
The concrete maturation process can be divided into two stages:
- Setting - internal chemical processes in the solution have already begun, but the mixture itself still remains mobile. Constantly stirring the solution at this stage prevents the hardening process from starting. The setting time directly depends on the ambient temperature: at +20° - setting begins after 1.5 - 2 hours and lasts about an hour, and at 0 - +1° the process will start only after 6 - 10 hours and will last about 15-18 hours.
- Hardening of concrete begins immediately after setting. In order for the solution to gain strength corresponding to the product labeling, it is necessary to wait from two weeks to several months. There is a direct relationship between the strength of concrete and the ambient temperature - the colder it is outside, the longer it will take to build strength.
A month after pouring, the strength gain does not end, but continues for several more years. 28 days are only necessary to obtain the stated characteristics.
Table of characteristics of concrete mixtures
| Class | Brand | Euro class | Mobility | Strength | Waterproof | Frost resistance | Rigidity |
| AT 10 | M150 | c8/10 | P2 - P4 | 163 kg/cm2 | W2 - W4 | F 50 | Zh1 – Zh4 |
| B15 | M200 | s12/15 | P2 - P4 | 196 kg/cm2 | W2 - W4 | F 100 | Zh1 – Zh4 |
| IN 20 | M250 | s16/20 | P2 - P4 | 275 kg/cm2 | W4 - W6 | F 150 | Zh1 – Zh4 |
| B22.5 | M300 | s18/22 | P2 - P4 | 296 kg/cm2 | W6 | F 200 | Zh2 - Zh4 |
| B25 | M350 | s20/25 | P2 - P4 | 337 kg/cm2 | W6 - W8 | F 200 | Zh2 - Zh4 |
| B30 | M400 | s25/30 | P3 - P5 | 392 kg/cm2 | W10 | F 300 | Zh3 - Zh4 |
| B35 | M450 | s30/37 | P3 - P5 | 458 kg/cm2 | W10 - W12 | F 200 - F300 | Zh3 - Zh4 |
| B40 | M550 | s32/40 | P3 - P5 | 524 kg/cm2 | W10 - W16 | F200 - F300 | Zh3 - Zh4 |
| B45 | M600 | s35/45 | P4 - P5 | 591 kg/cm2 | W12 - W18 | F200 - F400 | Zh3 - Zh4 |