To make expanded polystyrene (foam), suspension polystyrene is needed. Granules of this material can be of different sizes - from 0.4 to 3.2 mm (depending on the brand of raw material). The granules contain a low-boiling component, pentane, which helps them increase several times under certain conditions. It is on this property of the material that the production technology of expanded polystyrene is based.
Scheme of external insulation using polystyrene foam.
Stages of polystyrene foam production
The technology for manufacturing polystyrene foam consists of foaming suspension polystyrene. To obtain the desired result, use steam. Next, the granules are sintered. Then a large block is formed, which is subsequently cut into sheets. But, before loading the raw materials into the bunker, the granules are mechanically mixed with various modifier additives.
To make the finished material more fire resistant, fire retardant additives are added to its composition. To protect polystyrene foam from the effects of heat and oxygen, antioxidants and heat stabilizers are used, and abiotic components are used to prevent molding. In the production of extruded polystyrene foam, nucleate stabilizers are introduced, which help to obtain a more uniform and fine pore structure.
Return to contents
Foaming polystyrene granules
Technological diagram for the production of expanded polystyrene sheets.
Foaming of suspension polystyrene occurs in two stages. Moreover, for each batch of raw materials the optimal time for passing this stage is determined. It depends on the quality of the raw materials. This period must be strictly observed, since if the time intervals increase, the granules may be destroyed.
The first stage of material processing takes place in the pre-expander. This unit is a container with holes in the bottom through which steam is supplied. It is also equipped with an activator for stirring the granules. During foaming (about 5 minutes), the temperature in the container is maintained at about 100-110° C.
The foaming process occurs as follows. Thanks to the action of water vapor, pentane, which is part of the suspension polystyrene granules, is activated. They soften and grow in volume, and the amount of material can increase 30-50 times. The integrity and tightness of the cells are maintained.
To accelerate the foaming process, the granules are mixed using a mechanical activator. At the end of this cycle, the material rises under pressure. Through the unloading window it is pushed into an intermediate container, and then, using pneumatic transport, it is moved to a bunker for storage.
Return to contents
Drying and curing foam granules
Scheme of polystyrene foam as insulation.
Polystyrene granules that have been foamed contain about 10-15% moisture. There is a vacuum inside them, as condensation of pentane and steam residues has occurred. As a result, under the influence of these factors, compression of the granules may occur, which will lead to a decrease in the volume of the material and an increase in bulk density. It is for this reason that the foam production technology involves a drying stage.
The purpose of this stage:
- strengthening the outer walls of the granules;
- restoration of internal pressure.
Due to the fact that warm air (about 35° C) penetrates into the cells of the material, polystyrene acquires the necessary parameters of compression resistance. Moreover, the lower the bulk density of the material, the faster air will be absorbed.
The drying process takes about 5 minutes. In some cases, it is combined with the transportation stage. During material transfer, humidity can be reduced to 6-3%. In addition to the loss of moisture, drying contributes to a significant increase in the fluidity of the material.
Scheme of the main types of polystyrene foam.
This, in turn, allows the aging bins to be filled more efficiently. These special devices consist of a metal base with a fixed bag made of breathable fabric. Granules are stored in them at a temperature not exceeding 22-28° C. The duration can range from 6 hours to a day. This time depends on the volumetric bulk weight of the granules: as the weight decreases, the period increases, but it should not exceed 14 days, since during this period isopentane evaporates and the granules lose their ability to foam.
Meanwhile, there are several methods of aging. To reduce the holding time, the method of pumping granules using an air flow from hopper to hopper is used. With this approach, 2-3 hours are enough for the material to acquire the necessary indicators of water absorption and strength.
Return to contents
Block production and cutting
The production or baking of blocks is carried out in a special block mold. This rectangular steel device has double walls, and the inside is perforated (this is necessary for steam supply).
Diagram of an expanded polystyrene panel.
After the mold has warmed up, granules are poured into it and it is hermetically sealed. Re-foaming is also carried out under the influence of water steam under pressure.
The quality of expanded polystyrene is affected by the timely termination of the formation process. If it is interrupted before the required time, then the insufficiently foamed granules will not fuse well. If the material is overexposed, the cells are destroyed and shrinkage phenomena appear. In both cases, the quality of the product deteriorates significantly.
This is followed by a cooling process. The resulting blocks are placed in the workshop, where they can remain from 12 to 720 hours. During this time, the material loses excess moisture. It is its excess that does not allow cutting immediately after cooling. To obtain slabs of the required thickness, an automatic machine is used. And heated nichrome strings are used as the cutting element. At the final stage, the sheets are placed on a vertical cutting machine and trimmed.
Preparing for work
To make polystyrene foam with your own hands, you will have to do a number of preparatory work in order to then do everything quickly and efficiently. Products can be made in the form of slabs or blocks. It all depends on which material is more convenient to use for the job. For example, slabs are used for insulation; they are glued to the surface. To construct any structural forms or for formwork, the use of blocks is required; they are additionally reinforced.
After forming, the blocks have the following dimensions:
- width 25 cm;
- height 25 cm;
- length 95 cm.
Expanded polystyrene is 98% air, it is lightweight and inexpensive.
The process itself, how to make polystyrene foam at home, can be classified as simple, but demanding. The chemical reaction is accompanied by the release of formaldehyde volatiles. If you are not careful, cases of poisoning are likely not only for the manufacturer himself, but also for those around him.
Production scheme:
- availability of raw materials (you need to purchase special granules, which are the basis for creating the material);
- pre-foaming agent, with the help of which the mass is created;
- a bunker for working and storing material;
- block molds for polystyrene foam;
- storage of finished products, cutting and sorting;
- pneumatic transport;
- steam generator;
- compressor;
- steam receiver;
- crusher for waste.
During manufacture, it is necessary to ensure that there is good ventilation to remove all vapors generated during operation. It is recommended that work be carried out in a separate room.
Return to contents
Extruded polystyrene foam
The production process of extruded polystyrene foam is somewhat different from the production of polystyrene foam, although the chemical composition of these materials is quite similar. Extrusion is a unique technological process that involves extruding a material that has high viscosity. Such raw materials are passed through an extrusion head - a special forming device that allows you to obtain a product with a cross-section of the desired shape.
The starting material for extruded polystyrene foam is general-purpose polystyrene.
Table of characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam.
The granules are foamed, but not with the help of water vapor, but with the use of a special agent.
Previously, various freons (hard, soft and mixtures thereof) were used as foaming materials for the production of extruded polystyrene foam. Nowadays, freon-free components based on CO2 are used.
To produce extruded polystyrene foam, certain conditions are created that trigger the polystyrene conversion process. As in the production of foam plastic, the granules are foamed, and a viscous mass is obtained. According to the technology, not individual granules are processed, but a liquid-like substance.
The finished material consists of a mass of closed cells that are filled with air and has a solid microstructure. The cell sizes are 0.1-0.2 mm.
At the end of production, the remaining foaming agent is usually replaced by ambient air within 24 hours. There are no micropores in the finished material between the cells.
With strict adherence to the production technology of both conventional polystyrene foam and extruded polystyrene foam, the result is a lightweight and durable material that has low thermal conductivity and vapor permeability, and is also resistant to water absorption.
How to make the right choice?
When choosing, you should pay attention to the appearance of the insulation. A high-quality thermal insulation board is a smooth, bright white color; any other shades indicate that the production technology has been violated. The same is evidenced by foreign or pungent chemical odors emanating from the material. The edges of the slab should not crumble or crumble. There should be no dents, damage or chips on the surface.
The granules forming the slab should be approximately the same size and distributed evenly over the surface of the insulating sheet, without gaps or voids between them. When breaking, the break line must pass not only between intact granules, but also directly inside them, otherwise this will mean that the granules are poorly sintered with each other during the production process.
Expanded polystyrene slabs cannot be stored outdoors, as they quickly lose their thermal insulation properties.
You only need to buy material that has been stored in a closed warehouse.
Products must be labeled, and the labeling must contain complete information about the manufacturer, physical, mechanical and thermal characteristics of the product.
The quality of expanded polystyrene is regulated by GOST 155-8868 “Polystyrene foam boards. Technical conditions".
Preparatory activities
Before you start purchasing equipment, you need to prepare the appropriate premises.
For this reason, the room where polystyrene foam will be produced must have a high-quality ventilation system. Consequently, it is unlikely that you will be able to set up your own production workshop in a city apartment. You will need a separate room, ideally a whole barn or even a hangar on a suburban area, located as far as possible from residential premises. With this cleared up, now let’s look at what exactly you might need in your work.
Equipment for the production of foam plastic
Necessary equipment
The minimum set of specialized equipment for the manufacture of the described material consists of:
- steam generators, as well as batteries for them;
- compensators;
- pre-expanders;
- coolers;
- receiving bins;
- slicing units;
- block forms;
- crushers.
The manufacturing and sales process itself should begin with getting to know suppliers, who, by the way, can help with finding distributors of raw materials and additional equipment. Most of the domestic market is filled with Chinese devices. It is possible to deliver products to their destination, prepare appropriate documentation for customs, etc. A separately paid specialist can come to you to set up and launch the system. As for European equipment, it will cost about two to three times more, although the quality will certainly be much better.
Adhesive for penoplex
Previously, we reviewed brands of glue suitable for penoplex; in addition to this article, we advise you to read this information and read about it here
Purchases required for the production process
So, you have drawn up a business plan, you know what the future volume of work and the required capital investments will be, now the main thing remains for you - to purchase equipment for the production of foam plastic. The settings below will be used in the process.
- Batteries or steam generators necessary for the normal functioning of pre-foamers. This category also includes pneumatic conveying pipes, scales, transformers, condensation outlets, and so on.
- Actually, pre-foamers. They are necessary for preliminary beating of polystyrene granules (in this case they will be exposed to steam) until the material reaches the required density (it varies between 10-50 kilograms per cubic meter). There are many varieties of prefoamers, but they are all conditionally divided into several categories depending on the following parameters:
- presence/absence of a built-in steam generator, feed dispenser, hopper;
- material used in manufacturing (“stainless steel” or carbon steel);
- principle of operation (in cycles or continuously);
- performance;
- capacity of the granule receiver and chamber.
- A crusher with a built-in fan, necessary for grinding waste left after cutting. By the way, in the future this waste will also be used in production.
- A container equipped with a special bag-like liner in which secondary foaming will be carried out. Such equipment for the production of foam plastic is required in order to obtain raw materials with a density of 7-8 kilograms per cubic meter. Determining the dimensions of the frame should be done by a qualified technologist.
- 5. A packaging machine that will wrap finished sheets of material with shrink or polyethylene film.
- 8. Block form, where polystyrene granules are sintered into a monolithic material under the action of hot steam. Subsequent cooling can be either natural or vacuum. The procedure is controlled via a remote control.
- 9. Compressor with a vacuum pump - they are necessary in order to speed up the work process. They are installed separately depending on the required density of the final product and power.
6. Receiving hopper. This mechanism can be equipped with a fan with air heating mode, or it (the fan) can be connected to it separately. In this bunker, the raw materials are aged and dried. Devices can differ not only in terms of power, but also in useful volume.
7. Table for cutting expanded polystyrene into sheets of the required thickness and dimensions. First of all, such tables differ in configuration; many modern models are additionally equipped with rangefinders, special saws designed for tongue and groove, transformers that heat the strings, and much more. For long profile-type elements (such as insulation for slate, baseboards, columns or platbands), the table can be replaced with a machine for three-dimensional format. In this case, control is carried out using a special computer program.
Making polystyrene foam at home
First you need to purchase raw materials - foaming polystyrene. Expandable polystyrene is a product of the chemical industry. When purchasing it, you should pay attention to the warranty storage lines. The rule here is that the “older” the foaming polystyrene granules are, the longer the foaming process takes and the more difficult it is to obtain the required density.
It is important to immediately draw the attention of readers of this article to the fact that making small quantities of polystyrene foam at home is, to put it mildly, unprofitable. If the conditions require insulating boards or baguettes, which fill the building materials market, it is much easier and cheaper to buy them and not fool yourself.
But for enthusiasts who specialize in the production of exclusive designer products (like handmade craftsmanship), the technology will be useful - making polystyrene foam at home , which will be described below. Since this material adheres well, it is possible to invent and come up with complex products from segments of different shapes and cross-sections.
What can foam molds be made from?
Various materials can be used to make foam molds, from ceramics to wood. Molds made of steel or tin-casting molds last a long time.
You can also use heat-resistant plastic. If you decide to use silicone culinary molds as forms for polystyrene foam, they must be strengthened with alabaster or plaster - simply fill a suitable container with alabaster or gypsum solution and dip the mold into it to the very edges. It is quite difficult to weld the finished product to the mold, as is gluing foam plastic to other surfaces.
Manufacturing technology and processing of polystyrene foam at home
The technology for producing polystyrene foam at home involves two-stage steaming of the raw materials. In this case, all kinds of household appliances can be used as a source of steam: a steam mop or a Karcher-type washing unit with a steam generation function.
The amount of steam generated by these devices will be quite sufficient for the production of small products that fit on the palms of the hands. As a rule, these products are used to decorate the interior of premises.
The first steaming of polystyrene foam can be organized in a regular metal bucket. Fill it 20% (1/5) of the volume with foaming polystyrene granules, immerse the hose from the steam generator into the thickness of the granules and, running the device in a circular motion, treat the granules with steam.
After a certain period of time, the granules will increase in size and fill the bucket to the very top. Now you should distribute the primary processed raw material into molds and process it with steam until the granules stick together.
Expanded polystyrene production technology
This technology consists of several stages; let’s get acquainted with each of them.
Stage one. Procurement of raw materials
The raw material in this case is expanded polystyrene foam, that is, products of the chemical industry. The parameters of the material produced depend on how high quality it is and what its service life is. After all, the older the raw material is, the longer it has been stored, the more difficult it will be to foam its granules. As for density, this indicator directly depends on the dimensions of the final granules: the larger they (granules), the higher the indicator will be. Conversely, low-density products can be made using small granules.
Note! If the foam plastic that you plan to sell will be used in construction work, then a fire retardant (this is a substance that prevents ignition) must be added during production.
The manufacturing process itself must begin with the formation of water vapor, the temperature of which will be 115-170 degrees, and the pressure - from 0.8 to 6 atmospheres. For this purpose, foam production equipment such as a steam generator is used. By the way, the steam generator itself, depending on the type of energy resources used, can be:
And in order for the maximum volume of generated steam to be used, it is necessary to use a steam accumulator.
Stage two. Foaming the granules
The raw material is supplied to the foamer in the quantity necessary to create a material of a particular brand, after which steam is supplied. The granules, being exposed to this steam, begin to foam, which is accompanied by their increase in volume by approximately 25-50 times. As a rule, to obtain 1 cubic meter of raw materials that have already undergone foaming, about 15 kilograms of raw materials are required.
The foaming procedure itself lasts no more than seven minutes. At the end of this procedure, the granules are fed into a special drying unit, which removes excess moisture formed when exposed to steam.
Stage three. Drying
Next, the granules, as we just noted, are fed into a drying apparatus, in which they are treated with heated air and are deprived of excess moisture, but the original volume remains the same. Typically, air enters from below, permanently mixing the particles.
The drying procedure itself takes no more than five to ten minutes.
Stage four. aging
In such bunkers the granules are finally stabilized. The duration of this process depends mainly on environmental conditions. The number of bins themselves depends on the level of system performance, and their dimensions and volume are determined by the height of the ceiling in the workshop.
It is worth noting that different brands of polystyrene foam are often stored in separate bins. The material can be aged for 5 to 12 hours, after which the already stabilized granules are sintered.
Stage five. Foam sintering
Through a special loading hole, the block mold is filled with prepared granules, and they are supplied here under the influence of air, which is pumped by a compressor. Next, the granules are sintered under the action of the same steam coming from the steam accumulator. Note that the quality of baking granules depends on three factors, such as:
After this, the polystyrene foam is cooled (for this purpose, foam production equipment such as a vacuum unit is used) and takes on the required shape. The duration of the procedure depends on the brand, although on average it takes no more than 10-12 minutes.
Stage six. cutting
The final stage of production is cutting. At the end of baking, the unit door opens and the polystyrene foam block is pushed onto a special table under the action of a pneumatic pusher. The slabs are laid out vertically, after which they need to be left for several days. This is necessary so that they finally get rid of excess moisture and undergo stabilization.
After this, the blocks are cut by a special machine into sheets of the required dimensions and thickness. If necessary, protrusions and grooves are made (the waste, as noted above, will be subject to further processing).
The slabs are packaged and sold. As you can see, in reality there is nothing complicated here, as you can see when watching the thematic video material.
Where to start?
Production planning:
- Organization of the workplace, preparation of the necessary equipment.
- Purchase of granulated polystyrene, which will be used as the main raw material. The granules are poured into a container to create the material.
- Saturation of the mass with steam at a certain temperature, aging, baking blocks or slabs.
Before starting work, you should ensure that you have the following tools and equipment:
- mass container;
- steam generator;
- steam accumulator (it is necessary to control the volume of steam);
- compressor;
- bins for granules, special molds for obtaining material of the required parameters;
- machine for cutting material;
- pneumatic transport;
- measuring utensils, scales to determine the finished volume.
An important step is the purchase of raw materials, i.e. polystyrene granules. Today this is not so difficult to do; manufacturers offer bags of granules of 25 kg each. It is important to choose the right size, quality of mass, and country of manufacture. It is best to take raw materials from a trusted company whose product quality has the necessary properties.
The choice of granule sizes depends on what kind of polystyrene foam needs to be made. The smaller the granules, the harder the material can be obtained
. You should take into account how much time the pellets have already spent in the warehouse. The longer the raw material has lain in the warehouse, the more time is needed for foaming and steam treatment. Failure to comply with the rules can lead to deterioration in quality, the material will ultimately not be entirely suitable for use, and this is a waste of time and money. It is necessary to correctly purchase raw materials, take into account the processing time, and fulfill all the conditions for baking. An important step is cutting, since the thickness of the slabs must be the same, discrepancies are not allowed.
Return to contents
How polystyrene foam is made
Earlier we told you what polystyrene foam is. We remember that this material consists of numerous cells filled with air. This means that the manufacturing process must include foaming the material.
That’s right: the foaming process is one of the most important in the production of expanded polystyrene .
However, that's not all.
Stages of foam manufacturing technology
Typically the process includes:
1. Foaming. During this process, the raw materials are placed in a special container (foaming agent), where, under pressure (a steam generator is used), the granules increase approximately 20-50 times. The operation is completed within 5 minutes. When the granules reach the required size, the operator turns off the steam generator and unloads the foam material from the container.
2. Drying the resulting granules. At this stage, the main goal is to remove excess moisture remaining on the granules. This is done using hot air - it is directed from bottom to top. At the same time, for better drying, the granules are shaken. This process also does not last long - about 5 minutes.
3. Stabilization (tracking). The granules are placed in bunkers, where the aging process takes place. The duration of the process is 4.12 hours (depending on the ambient temperature and the size of the granules).
Important note: the polystyrene foam manufacturing technology may exclude the 2nd stage (drying). In this case, stabilization (tracking) will last longer - up to 24 hours.
4. Baking. This stage of foam production is often called molding. The idea is to connect the previously obtained granules together. To do this, they are placed in a special mold, after which the granules are sintered under pressure and under the influence of high temperature water vapor. Lasts approximately 10 minutes.
5. Maturation (aging). The goal is to rid the resulting polystyrene foam sheets of excess moisture, as well as remaining internal stresses. To do this, the sheets are placed in a free space in the production workshop for several days. In some cases, ripening can take up to 30 days.
6. Cutting. The manufactured foam blocks are placed on a special machine, on which the blocks are cut into sheets of appropriate thickness, length, width. This manufacturing process is performed using nichrome strings heated to a specific temperature. Accordingly, both horizontal and vertical cutting of blocks is carried out.
This is how foam is made.
Of course, after the listed 6 stages, the 7th stage can be performed - processing the remaining scraps . As a result, they are mixed with other granules, which will then undergo the same processes - sintering, curing.
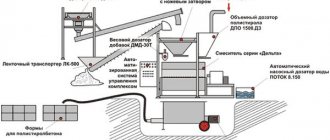
The equipment that is used in the production of polystyrene foam is shown in table form:
Health safety comes first
There is a common belief that polystyrene foam is a favorite treat for mice, but this is far from the case. Since it does not contain nutrients, it does not attract rodents as food at all. Mice are capable of chewing through polystyrene foam, as well as other materials, seeking sources of water or food, or looking for shelter for offspring. To protect against pests, thermal insulation boards are covered with metal mesh, bricks or plastered. If there is an abundance of rodents on the site, it is necessary to carry out deratization measures.
Since polystyrene foam is a biologically neutral material, it is not susceptible to rotting. Fungus, mold, and pathogenic bacteria cannot multiply on its surface. Proof of this is the fact that foam plastic is used not only for insulating buildings. Food containers are made from it, that is, this material is suitable for long-term contact even with food.
As for fire safety, modern thermal insulation boards are enriched with fire retardants - special substances that prevent smoldering and burning. Buildings insulated with polystyrene foam can withstand from 15 to 60 minutes of burning without collapsing. This time is enough for emergency evacuation in case of fire. Since polystyrene foam does not contain chlorine, when it burns, it does not release hydrocyanic acid or phosgene, and also produces less carbon monoxide than when burning wood or wool.
However, this does not mean that when using polystyrene foam you do not need to pay attention to basic fire safety measures. During construction, care should be taken to ensure that polystyrene foam does not come into contact with air and, especially, with open fire. This material should not be used for thermal insulation of baths or saunas, since the upper temperature limit for its operation is limited to 80°C. When purchasing, be sure to check the sanitary, hygienic and fire safety certificates.
Foam manufacturing technology directly affects quality
As we said above, the market is now filled with a considerable amount of low-quality material. It can be produced in garages or some warehouses.
But the main problem is not where the material is made (although the environment also affects quality), the main problem is not following all the rules for making polystyrene foam.
What deviations may there be from the correct production of expanded polystyrene?
The most varied - from poor-quality granulation to poor, inaccurate cutting of foam blocks into sheets.
Some smart guys don’t carry out stabilization or aging at all. For them, the speed of production of polystyrene foam is exclusively important.
“The more, the better—we’ll earn more money!”
Because of this, the characteristics of the foam are greatly deteriorated:
- it may turn out to be fragile, fragile,
- granules may be poorly connected to each other,
- density may be uneven.
This can also occur due to low-quality, faulty equipment that was used in production - foamers, dryers, compressors, steam generators, etc.
And another important point : with poor manufacturing technology, foam plastic can have a sharp, unpleasant odor. The following picture is possible: they brought brand new sheets of expanded polystyrene home, put them in a garage or other room, and. Soon they heard that the room was filled with some kind of pungent, unpleasant smell.
This is very bad. This means that the foam is still “floating”, releasing harmful substances. It is especially dangerous when such low-grade material is stored in residential areas.
Where and for what is polystyrene foam used?
Structure of a wall panel filled with expanded polystyrene: 1. Filler - expanded polystyrene. 2-3. Galvanized painted sheet metal (profiled steel sheet, coating - galvanized, powder coated). 4-5. Protective film.
Polystyrene foam is widely used for external and internal thermal insulation of premises. External insulation includes insulation of walls, facades, and foundation bases. Walls made of aerated concrete, foam concrete, brick, and expanded clay are well suited for insulation with this material. It is not advisable to insulate wooden walls with polystyrene foam.
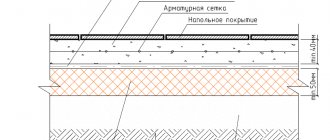
The thickness of thermal insulation boards for external thermal insulation varies between 50-80 mm. They are attached with special glue and additionally secured with dowels for strength. Before choosing a material for thermal insulation, you should take into account that it is easier to plaster polystyrene foam boards than mineral wool. Before plastering, reinforcement must be done.
The use of expanded polystyrene for internal insulation of premises also guarantees good sound insulation. To protect the insulation from fire, you need to cover the walls with plasterboard. The thickness of the slabs for internal thermal insulation is 20-30 mm.
Insulation with expanded polystyrene is an integral part of the installation of “warm floors”. Floors heat up much faster, and the heat is evenly distributed over their entire surface. The use of a substrate made of thermal insulation material for a “warm floor” system hardly halves the energy consumption that is spent on maintaining the desired temperature. On balconies and loggias, it is also preferable to insulate floors with polystyrene foam, since working with it in confined spaces is much more convenient than with mineral wool or roll insulation. If laminate or parquet is going to be laid on insulated floors, lathing must be done first.
Expanded polystyrene is also widely used for thermal insulation of pipelines, protection of telephone and electrical cables.
Conclusions on the production of polystyrene foam
- The technology is quite simple, but requires mandatory compliance with all prescribed norms and rules.
- Material (which will look like high-quality material) can be obtained even with significant deviations from the production rules. And “handicraft” companies (bad people) take advantage of this.
Therefore: buy only products from reliable, trusted manufacturers (who monitor quality) . Check that sellers have the appropriate quality certificates.
Now you know how polystyrene foam is made, you know the main features of manufacturing technology and which material should be preferred. Good luck!