Why is it important
If you pour more liquid into a batch than required, the quality of the concrete deteriorates sharply. After laying it, the monolith delaminates, and the strength of the layer decreases many times over. But without water, cement hydration cannot occur, so there is no escape from it.
Excess moisture that has not entered into the hydration reaction is not bound; it forms pores in the monolith, which reduce the strength of concrete. The pores expand as they approach the surface of the monolith, and the concrete begins to crumble.
When moisture does not leave the concrete layer until winter, it will certainly freeze, after which it will begin to tear the monolith from the inside, further reducing its strength. At the time of mixing, excess water increases the mobility of the solution, and this is not always justified. Only the correct ratio of water to cement guarantees that the concrete meets the required parameters.
Test batch
Scheme for preparing concrete: 1 – Mixing the dry mixture with water, 2 – Mixing on plywood, 3 – Concrete mixer, 4 – Hose for adding water, 5 – Cement, 6 – Sand.
It is assumed that all work is done manually using a shovel or trowel (in this case, the portion is minimal, but if the attempt fails, you don’t mind throwing it away). When the ratio is more accurately determined, it is wiser to use a concrete mixer, the use of which significantly affects the quality and speed of mixing while reducing physical activity.
A shovel of cement and 3 shovels of sand are poured onto the prepared site or into a container with low sides. A little water is added to moisten the mixture, which is thoroughly mixed with a shovel. After this, a large fraction (5 shovels) is added. During the mixing process, water is added gradually until a viscous, homogeneous mixture is obtained. For a test batch, as well as for subsequent batches, it is advisable to pour water from a bucket, and not from a hose, in order to see what quantity to stop at.
To a first approximation, you can control the quality of the resulting concrete mixture as follows. A small amount of concrete mixture is collected by hand, a ball-shaped lump is formed from it and placed on any surface. During the sculpting process, no traces of cement should remain on your hands. If this lump hardens, maintaining its shape, the kneading was a success. The indicators of ready-made concrete, manufactured while maintaining the obtained water-cement ratio for concrete, allow us to assert that it corresponds to grade 75. You can start kneading large volumes while maintaining the resulting proportions. If the lump “swims”, it means there is an excess of water; if there are signs of separation, there is not enough water.
You can also check the finished hardened concrete for compliance with its characteristics of grade 75, when time allows you to wait for complete hardening. You can try to split the concrete with a few blows of the hammer on the chisel. If the chisel penetrates the concrete no more than 5 mm, the concrete corresponds to grade 75. If you can’t break off a piece of concrete, its quality is excellent!
You need to remember the basic rule of kneading. Only water can be added to the finished mixture; the remaining components, especially cement, are poured only in the sequence indicated above. If, as a result of the test batch, the required concrete quality indicators are not achieved, the batch will have to be repeated, slightly changing the proportions. Most likely, the proportion of cement will have to be increased.
Water-cement ratio
When the water-cement ratio used for concrete is low, the monolith quickly becomes strong and difficult to process. But it will gain final hardness more slowly. Although it will increase frost resistance. With a high water value, slow hardening occurs, but it will become easier to fill the form with concrete, and additional strength will occur before 28 days.
According to theory, cement needs a quarter of its own volume of water to react. But this is only when the cement is fresh, without dust, and has optimal humidity. In fact, almost no one washes the ingredients that are added to the cement mixture. Therefore, some water is necessary to moisten and absorb them.
Mistakes when mixing concrete mixture with water
Figure 1. The influence of the water-cement ratio
A common mistake made by home craftsmen who mix concrete themselves is excessive use of water. From a human point of view, this is understandable, since the material then becomes mobile, making it easier to lay and level. However, you should find a middle ground.
Incorrect actions to care for the monolith also become a serious mistake. Concrete, if poured with water and then covered with polyethylene on top, will receive many times better strength indicators.
All processes occurring within the monolith are influenced by chemistry. Therefore, professional builders always use aggregates with normal moisture content for mixing and always follow the recommended recipe for preparing the composition, selecting the optimal ratio of cement to water for a particular situation.
Optimal w/c ratio for different grades of concrete
Since the chemical reaction that causes cement to harden becomes completely impossible without water, the water-cement ratio is extremely important for the concrete formation process. For the event to take place, only a quarter of the water is enough, if you take it from the mass of cement. However, in practice, such a mixture is almost impossible to knead, which is why more water is added to increase the plasticity of the material. However, excessive addition of liquid is dangerous, since its excess causes the mixture to fill the form by gravity, seep through the formwork, and evaporate from the solution for too long. As a result, the monolith will receive pores, which then develop into cracks.
Concrete is not guaranteed to become stronger from excess liquid. To facilitate the placement of cement mortar inside the mold and ensure its filling, in practice it is customary to use a ratio of 0.6 water to cement. It should be noted that the indicated water-cement ratio is relevant for concrete grade M75. To prepare it correctly, 150 liters of clean water are required per cube of solution.
Figure 2. Allowable water-cement ratio
Let's take a closer look at what water does in a cement mixture and what its operating principle is. The liquid is necessary for the correct passage of the cement setting reaction and its subsequent hardening. About a third of the total volume is spent on this. The rest gives the solution fluidity, making it convenient to work with. Therefore, more water is used only to improve the comfort of handling the mixture. It is this volume that can be reduced by introducing plasticizers, mixing hard concrete, and then compacting it with special vibrators.
Advance paynemt
It is quite possible for a person who knows how to count to make a list and deliver all the materials in full and sufficient quantities to the construction site in advance. Most often in individual construction, rigid concrete is used in the manufacture of strip foundations or interfloor ceilings. Before starting construction, it is necessary to ensure that enough consumables are delivered to the site of the upcoming work so that it is sufficient for the intended stage. How to calculate the required amount of cement, sand and gravel? What are the requirements for these components of the concrete mixture?
When calculating, you can take the most common ratio between the amount of cement, sand and gravel used. This is 1:3:5 respectively. In this case, we obtain the weight of the required fraction (except for cement) with an error of about 10%.
Technological scheme for preparing concrete mixture.
For example, it is planned to cast a concrete strip foundation for a house. In this case, the design value of the perimeter of the house is multiplied by the width and height of the planned foundation (all in meters). The number of cubic meters obtained as a result of calculations is multiplied by 250 kg (approximately the amount of cement required to produce a cube of rigid concrete mixture). The remaining components are calculated from the ratio taken as a basis: sand is 3 times more than cement, gravel or crushed stone (large fraction) is 5 times. The mass of a cubic meter of hardened concrete is about 2.5 tons.
Additives for concrete
To improve the comfort of laying the mortar, the batch is saturated with water, although this action causes a deterioration in the frost resistance of the monolith and a drop in the strength of the concrete. In order to maintain the required water-cement ratio without disturbing the plasticity of the mixed mass, instead of an additional volume of liquid, plasticizers are added to the composition along with other complex additives, which make it possible to obtain good plasticity of the mixture even with low moisture content.
Such a composition will retain a high degree of brand strength, will remain frost-resistant, remaining mobile, well filling the entire volume of the mold without the formation of voids in space. Thanks to this, even the need for additional vibration is eliminated. Using additives, excellent water-cement ratio parameters are obtained without wasting excess cement and without losing the strength of the monolith.
Material requirements
Properly selected components in terms of quality and fractions to obtain durable hard concrete grade 75 is half the success. What characteristics of cement and fillers should I pay attention to?
Cement, the quality of which is directly related to the strength of hardened concrete, for reasons of saving on its cost, M200 or M300 is taken. The use of higher quality cements will be much more expensive; this difference cannot be covered by slightly reducing the percentage of cement to fillers. The strength characteristics of the specified grades of cement, subject to the water-cement ratio for concrete, make it possible to obtain high-quality concrete of at least 75 grade at your own construction site.
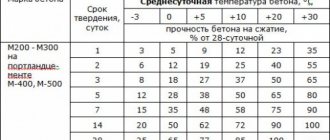
Table of concrete grades and their main characteristics.
It should be noted that the brand of concrete and the brand of cement that is included in the mixture are not the same thing. The ratio looks something like this: to produce concrete, for example, grade 75, you will need M200 or M300 cement, that is, the grade of cement taken should be 2.5-3 times higher. When buying cement, you should pay attention to the date of its release, since as the shelf life increases, the quality decreases, and after 1.5 years of storage, even under ideal conditions, cement can only be used for arranging garden paths. At the household level, you can check the relative quality of cement. To do this, cement is poured onto an open dry palm and the hand is clenched into a fist. High-quality material “flows” through your fingers with virtually no residue.
There are also requirements for sand. It is preferable to use fine-grained (the size of an individual grain of sand is up to 1.25 mm). It allows you to obtain a mixture in which the air gaps, which reduce the rigidity of concrete, are minimized. The sand must be free of dust and foreign inclusions of organic origin.
The size of gravel or crushed stone should not exceed 1/3 of the width of the formwork.
Under no circumstances should crushed limestone be used for rigid concrete.
If reinforcement is being used, the particle size cannot exceed 1/4 of the smallest size of the structure being cast and 3/4 of the clearance between the reinforcement bars. Failure to comply with the specified proportions can lead to the formation of voids in the finished concrete product, which will inevitably reduce the strength indicators.