Why does the humidity in the house increase?
One of the most valuable properties of aerated concrete, along with low heat transfer, is its good vapor permeability. This is the ability of a material to pass moisture from the air through itself. We are talking not only about atmospheric phenomena, but also about the moisture inside the house, which saturates the air during the life of its inhabitants. Washing, cleaning, cooking and even just breathing a person suspends billions of tiny droplets of water in the air. If you do not drain it in time, moisture will fall on the walls, worsening the microclimate in the house, leading to damage to the material of the walls, floors, and ceilings. That is why there are building standards that require the mandatory organization of ventilation in houses, norms and rules for calculating maximum permissible values. This is why aerated concrete is so valuable as a building material that effectively removes moisture from the air in the house to the outside.
The process of insulating external walls with foam plastic
Scheme for applying glue to foam boards.
In regions with a predominant humid climate, it is not recommended to use polystyrene foam as insulation. Moisture accumulating between aerated concrete blocks and foam plastic will inevitably lead to rotting of the aerated concrete blocks.
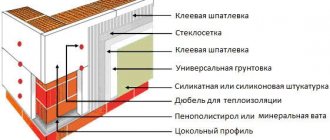
Work on insulating walls made of aerated concrete is carried out in several successive stages:
- wall preparation,
- insulation of indoor walls,
- external insulation,
- finishing of surfaces.
The preparatory stage consists of cleaning the surface of the walls from dirt, sealing possible cracks and crevices with cement-based plaster, various mastics and putties.
Installation diagram of the base profile.
Foam plastic slabs begin to be laid on the wall surface from the bottom row and from the corner of the building. The adhesive mixture is applied with a notched trowel to the entire surface of the slab. If the wall is not very smooth, then this method is not suitable. In this case, apply glue to a strip about 5-8 cm wide along the edge of the slab and place several dots with a diameter of about 10 cm in the center. The thickness of the adhesive layer should be 15-20 mm. After this, the plate is applied to the wall and pressed against it. The remaining slabs in the row are tightly attached to the previously installed ones.
Subsequent rows are laid offset relative to the bottom row to create a semblance of brickwork. For a more durable connection of the insulation to the wall, you need to additionally install plastic umbrella dowels. To do this, holes are drilled in the corners and in the center of each slab so that they penetrate 5 cm or more deep into the aerated concrete. The dowels are hammered into these holes. The hats are recessed into the foam by about a millimeter. A plastic core is driven into the center of the dowel until it stops. The remaining part is cut off with a knife.
The remaining gaps between the foam plates create cold bridges. They must be eliminated using polyurethane foam or a special sealant. After this, the walls can be primed and finished with plaster, then painted.
If you plan to finish with other materials such as siding and lining, then even before installing the insulation boards on the wall, you need to mount a frame of wooden beams or metal guides to which the cladding material will be attached.
Return to contents
Which aerated concrete conducts water vapor better?
The vapor permeability coefficient shows how much water vapor a wall material 1 m thick passes through in 1 hour over an area of 1 m2 in mg. This figure will be different for different walls. For example, if for a D400 gas block it is 0.23 mg/m*h*Pa, then for reinforced concrete it is only 0.03, and for ceramic brick it is from 0.11 to 0.15. Even for aerated concrete blocks of different densities it is different: the lower the density of the material, the better it removes moisture. In this regard, it is worth noting that aerated concrete D400 has higher vapor permeability than D500 and D600. These will be both warmer and drier walls, which allows you to save on the number of ventilation ducts installed. The porous structure of aerated blocks is designed in such a way that moisture is not retained inside even when freezing, but is forced to the surface through open cells.
Suitable plaster
Types of aerated concrete blocks.
Strong temperature changes are extremely dangerous for aerated concrete walls. The fact is that aerated concrete that has absorbed water can be destroyed by frost or other precipitation. During the process of cyclic freezing (thawing), moisture is retained, which leads to catastrophic consequences. Cracks appear in the outer layer, and moisture is retained in the inner layer, which leads to the appearance of mold and a decrease in the service life of aerated concrete walls. The question arises: how to plaster aerated concrete so that it lasts as long as possible?
Suitable plaster should perform several functions:
- Water repellent. Protection of sensitive aerated concrete from precipitation and pressure.
- Vapor permeable. This is a very important point that should influence the choice of plaster. Aerated concrete blocks have high vapor permeability, which means that plaster mixtures should have the same effect.
- High frost resistance (at least 35 units). Temperature changes, periods of winter frosts and melting should not damage the protective layer of aerated concrete.
- Non-flammability. Class A1 plaster is suitable for such purposes.
- Compression resistance. The CS1 class is ideal for these tasks.
- Resistant to cracks and physical impact.
- Good adhesion to aerated concrete (about 0.6 MPa).
Aerated concrete is a porous material, which is why the plaster used for it must not allow moisture to pass through.
At the moment, acrylic plaster is very popular; it is inexpensive, but short-lived. But it is worth remembering that such plaster is not suitable for aerated concrete. Due to its low vapor permeability, moisture will be retained inside, and when it freezes and turns into ice, it will increase.
As a result, the top layer will be destroyed, and mold will inevitably appear.
To cover aerated concrete use:
- Silicate plaster. It is resistant to mold and has self-cleaning properties. When precipitation occurs, it may change color. When it dries, the color returns.
- Silicone plaster. It has good adhesion to the base, high vapor permeability, and is self-cleaning. The disadvantage of this option is the high price.
- Mineral plaster. This type of plaster is durable, has good resistance to cracking, and does not attract dust. It is important that mineral plaster is subject to subsequent repairs. However, due to the need for mandatory additional painting of this type of material, the construction process may be delayed.
Features of finishing walls made of aerated concrete.
This property also requires a special approach to finishing work. It is important that finishing materials do not impair the vapor permeability of aerated concrete. Plasters, paints, primers, insulation must have the same or higher vapor permeability, and facing materials must be installed with a ventilation gap for free air circulation. The best thermal insulation for a house made of aerated concrete is mineral wool with a vapor permeability of 0.30, and the least suitable is polystyrene foam (with a coefficient of 0.03 mg/m*h*Pa). In addition, internal finishing work with the presence of “wet” processes in a house made of aerated concrete should be carried out before external finishing, so that the water entering the air is freely discharged onto the facade and dries quickly.
Features of the material
Many of the nuances of using polystyrene foam as an insulation material for aerated concrete can be understood from its positive and negative properties. The list of the former is several times larger than the latter, so it is important to know about the pluses:
- ease of transportation;
- ease of giving the required shape to the material;
- elasticity of the material;
- environmental friendliness;
- ease of self-installation;
- minimal thermal conductivity of the material;
- reducing heating costs;
- absence of sudden temperature changes inside the house.
The ease of transporting polystyrene foam is due to its low weight. The latter can be achieved by a special method of material production, in which polystyrene granules are filled with gas, which subsequently makes up 98% of the total volume of insulation. The weight of one sheet of material is practically not felt, which means that during the installation process you can do without assistants, and lifting the foam to floors above the first will not require significant effort. In the process of laying insulation, it is necessary to trim the material; in some situations, the shape of the insulation can hardly be called standard, but this is not a problem with foam plastic, since it can be formed with almost any sharp object. In addition, the insulation has sufficient plasticity to give it curved shapes of acceptable radii.
During the sanitary research process, no harmful releases of material were identified that could cause various diseases during operation. This makes it possible to classify polystyrene foam as an environmentally friendly material. The thermal conductivity of polystyrene foam remains one of the lowest among insulation materials. It is only 0.038 watts divided by a meter multiplied by Kelvin. Thanks to this indicator, it is possible to reduce costs during the heating season, as well as on air conditioning in the summer. In most situations, it is possible to avoid the use of cooling equipment, since the coolness accumulated at night or in the early morning is well retained inside the room.
Among the disadvantages of using polystyrene foam, you should know about:
- fragility;
- fire hazards;
- instability to UV rays;
- high material density;
- used by rodents as a place of residence.
The strength of the foam leaves much to be desired. It is not difficult to damage the material with a small blow, which requires additional processing. Facade insulation options contain special substances that reduce the flammability of the material, but this does not exclude the possibility that foam plastic can melt in a fire, releasing harmful substances. The material also does not tolerate proximity to all types of paints that are based on organic solvents. The insulation requires additional finishing to protect it from the sun's rays. If this is not done in time, the surface of the material will lose its strength and it will begin to crumble. Pests can settle inside sheets of foam plastic, which over time will negate its insulating properties.
Build a house from foam concrete or aerated concrete?
Building a house from foam concrete or aerated concrete will cost much less than building from traditional brick. Cellular concrete is a lightweight material, so creating a massive foundation is not necessary; a lightweight structure is sufficient.
| Foam concrete | Aerated concrete |
The use of such materials makes it possible to reduce the thickness of the walls, which means that less building materials will be required. Large block sizes will allow you to spend less mortar on masonry and speed up the work process. The reliability of foam concrete and aerated concrete lies in their non-flammability, which cannot be said about buildings made of wood and timber. However, due to the worse thermal insulation properties of foam concrete at equal densities, it will be required 2-3 times more than aerated concrete to ensure thermal comfort at home.
Having examined the differences between aerated concrete and foam concrete, we can say with confidence that the first material wins in terms of its quality characteristics.
Comparison of foam concrete and aerated concrete
| Characteristic | Aerated concrete | Foam concrete |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | 0,084-0,147 | 0,22-0,37 |
| Brands by density | 300, 400, 500, | 600, 700, 800, 900 |
| Strength | Class B2.5 at D400 | Class B2.5 at D700-800 |
| Vapor permeability | Aerated concrete is higher than foam concrete at the same density | |
| Deviations of geometric dimensions | +/- 1 mm | Up to 30 mm |
| Masonry, seam thickness | Laying with glue. Seam 1-3 mm | For sand-cement mortar. Seam up to 16mm |
| Foundation | Foam concrete has a higher specific gravity, therefore, with the same strength, the load on the foundation of foam concrete is higher | |
| Installation | Because foam concrete blocks are heavier, making it more difficult to carry out work on the construction of walls and their further finishing | |
| Working with material | Foam concrete blocks are more dense and uneven in structure, so they are more difficult to saw | |
| Durability | More than 100 years | About 50 years |