According to the cement data, GOST 31108 2003 establishes the requirements and technical conditions that should be taken as a basis during the production of cement . This standard does not apply to special purpose materials and materials that must be produced on the basis of other documentation.
General construction cement GOST 31108 2003 has been in effect for 13 years. Standards that help establish technical requirements for cement and methods for testing it, which are harmonized with global rules and recommendations, make it possible to rationally and correctly assess the quality of the material produced, which is produced in the CIS countries and the EU.
General construction technical conditions for cement GOST 31108 2003
The action in question did not cancel the previous variation 10178, which is still used when it is technically and economically beneficial to the manufacturer.
It operates in parallel with 31108-2003 and manufacturers take it as a basis only when signed documents or other agreements provide for the use of cement, which has certain characteristics. The latter must be fully harmonized with the requirements of EN 197-1.
GOST 31108-2003 will become the basis for the development of a number of new documents in the field of construction, which is based on the characteristics of cement, which are harmonized with the requirements of EN 197-1.
Cements GOST 31108 2003, GOST 30515 2013, their technical characteristics must not contradict standard requirements, and be produced in accordance with technological documentation, which is approved in advance by manufacturers.
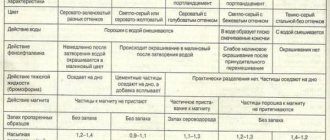
There are several types of cement according to GOST 31108 2003:
- Portland cement;
Portland cement
- Portland cement with additives of mineral origin: slag, pozzolana, material formed as a result of burning solid fuel at thermal power plants, clay burned as a result of underground combustion, silica fume, sedimentary rock containing lime, composite Portland;
- slag Portland cement;
Slag Portland cement
- pozzolanic cement;
Pozzolanic
- composite cement.
What is cement made from? Portland cement clinker is the basis for cement production. In addition to the main component, manufacturers often use mineral additives such as gypsum or other materials that contain CaSO4.
Gypsum
The latter material plays one of the main roles in adjusting the setting time of cement. Individual components can be introduced into it to regulate construction and technical properties, and chemical additives that improve the grinding process and (or) facilitate the transportation of cement through pipelines.
The main differences between GOST 31108-2003 and the current GOST 10178-85: - compressive strength classes similar to those established by EN 197-1 have been introduced instead of grades; - for cements of all strength classes, in addition to the requirements for strength at the age of 28 days, additional standards for strength at the age of two days are established, with the exception of classes 22.5N and 32.5N, and for cements of classes 22.5N and 32.5N - in age 7 days; — for all strength classes, except for class 22.5, a division of cements according to hardening speed has been introduced into normal-hardening and fast-hardening, which will minimize cement consumption in construction due to its optimal selection according to hardening speed. According to GOST 31108-2003, the designations of cements will change. The symbol of cement will consist of: - the name of the cement (CEM I - Portland cement, CEM II - Portland cement with mineral additives) - Portland cement with mineral additives is divided into subtypes A and B - for subtype A the amount of mineral additives is limited from 6% to 20%, for type B - from 21% to 35%; - abbreviated designation of cement, including the designation of the type and subtype of cement and the type of additive (granulated slag is designated by the letter Ш; pozzolana - P; composition of slag and pozzolana (tripoli, opoka) - K (Ш-П)); — strength class (22.5; 32.5; 42.5 and 52.5, which means the minimum compressive strength at 28 days, MPa); - subclass designations (compressive strength at the age of 2 (7) days - N (normally hardening) and B (fast-hardening), except for class 22.5); - designation of the standard to which the cement complies. Examples of symbols: 1. Portland cement class 42.5, normal hardening: Portland cement TsEM I 42.5N GOST 31108-2003; 2. Portland cement with slag from 6% to 20%, strength class 32.5, quick-hardening: Portland cement with slag TsEM II/A-Sh 32.5B GOST 31108-2003; 3. Portland cement with slag from 21% to 35%, strength class 32.5, normal hardening: Portland cement with slag TsEM II/V-Sh 32.5N GOST 31108-2003; 4. Composite Portland cement with a total content of granulated blast furnace slag and pozzolana from 6% to 20%, strength class 32.5, normal hardening: Composite Portland cement with slag TsEM II/A-K (Sh-P) 32.5N GOST 31108-2003. When producing cement according to GOST 31108-2003, auxiliary components can be added in an amount of 5% to all types of cements (including CEM I). Any mineral or inert additives regulated by GOST 31108-2003 can be used as auxiliary components of cement. Auxiliary components should not significantly increase the water demand of cement, nor reduce the durability of concrete or the protection of reinforcement from corrosion. The correspondence of cement designations (by plant) according to GOST 10178-85 and GOST 31108-2003 is relative due to differences in material compositions and differences in test methods, however, the construction and technical properties of cement produced according to GOST 31108-2003 are comparable to cement produced according to GOST 10178-85.
Properties of cement, definitions
Construction and technical properties of cement. The set of properties of cement that characterize its ability to form a strong and durable cement stone as a result of hardening. Cement activity. The actual compressive strength of samples made from standard cement mortar, manufactured and tested under standard conditions established by the regulatory document. Uniformity of changes in cement volume. The property of cement during the hardening process is to form cement stone, the deformation of which does not exceed the values established by the regulatory document. Heat dissipation. Indicates the amount of heat released by cement during its reaction with water. As a result of this reaction, cement and water form the so-called “cement mixture”, which is then used to create concrete, plaster, cement products, etc. The heat release of cement is calculated for one cubic meter of the finished material or product. Water separation. Indicates how much water is separated during the process of stratification of cement paste due to the precipitation of cement particles. As a rule, cement used in construction has low water retention. If the water separation of cement exceeds permissible standards, this can lead to large financial costs associated with excess moisture. Self-stressing of cement. The ability of cement stone to stress the reinforcement embedded in it. Shrinkage of cement. Reduction in the linear dimensions of cement stone during hardening. Backfilling and technical properties of cement. The set of properties of cement that characterize its suitability for plugging wells. Corrosion resistance of cement. The ability of cement stone to withstand the chemical and physical effects of an aggressive environment. Sulfate resistance of cement. The ability of cement stone to withstand the destructive effects of aqueous media containing sulfate ions. Frost resistance. A property of cement stone that characterizes its ability to undergo repeated and alternate freezing and subsequent thawing. Due to the fact that cement in its pure form is not used in construction, it does not have frost resistance as such. The main thing is the brand of cement and the presence of a certain amount of modifying additives. Percentage of additives. Shows what percentage of modifying additives the cement contains. This indicator is indicated by a capital letter D, next to which the percentage of additives in cement is indicated. For example, the designation D10 indicates that the cement contains ten percent additives that improve certain qualities of the material. Maximum strength qualities. The ability of cement to cope with certain loads. Denoted by the capital letter M or the abbreviation PC. Next to the letter M or the abbreviation PC, the load that the cement can handle must be indicated. For example, the designation PC700 indicates that cement is able to withstand a load of 700 kg/cm. Grinding fineness. Determines the dispersion of cement. In this case, the dispersion of cement can be expressed either as the specific surface area or as the remainder of the material on the control sieve. The fineness of cement grinding largely depends on the equipment used for its production. In addition, it is during the grinding process that various additives are introduced into the cement.
M400 technical specifications
Few owners of future houses realize that the durability of the structure will depend on the quality and density of cement. When choosing a material, builders take good adhesion as a basis, and also study and analyze in detail the components that make up the composition; physical features also play an important role here.
Today, one of the most purchased cements is the M400 brand, which is a type of Portland cement. It is often used in various construction fields, the reason is hidden in high quality and affordable pricing.
The GOST discussed in the article underlies the creation of this material; its quality is controlled not only at the production stage. The reason is hidden in the high importance of reliability and stability of future structures.
As for production, cement is obtained through grinding the intermediate product clinker with the further addition of minerals from the class of sulfates CaSO4•2H2O and other chemical elements.
The decoding of the abbreviation 400 indicates that after complete hardening the material will withstand a load without any problems, which will fluctuate around four hundred kilograms .
M400
The content of CaSO4•2H2O in the cement composition, according to the GOST under consideration, cannot be more than 5%; active mineral components, as a rule, range from 0 to 20% of the total components. It was the additives that played one of the main roles in the water resistance and anti-corrosion properties of the material.
This may explain the possibility of using cement 400 when creating reinforced concrete structures; they will also be resistant to changes in moisture.
The material in question is considered durable. Manufacturers determine this characteristic through multiple freezing and thawing during the testing phase. For cement 400, this technical characteristic is equal to one hundred cycles.
It is often used during the construction of facilities that will be used in the Far North. Few people know that in these parts temperatures often reach -50. High water resistance of cement 400 was achieved thanks to special additives.
Cement can be used to construct structures that will be devoid of external protective finishing. This is because the M400 can withstand rain and moisture fluctuations for a long time.
The production of the cement in question is carried out in accordance with technical standards. Finished products are subject to mandatory quality control.
Today, companies produce three types of brands:
- BEFORE.
- D2OB
- D2O
Each type is distinguished by its individual properties, composition, and area of use. If you want to achieve instant hardening of the solution, choose the first type.
It is also characterized by high water resistance, thanks to which “DO” is often used for the construction of structures with high environmental humidity (underwater and underground structures). “DO” also showed excellent performance at the stage of collecting concrete and reinforced concrete structures.
The second type of four hundredth cement is famous for the active mineral additives that are included in its composition, thanks to which it can be used during the construction of residential areas. “D2O” also finds its application in industrial and agricultural construction.
This cement is actively used in the CIS countries and Europe. It hardens significantly longer than the previous option, the average time is 10 hours.
The main advantage of “D2O” is its resistance to moisture and frost.
M400 D20
The last type M400 can be classified as a fast-hardening material. It is actively used during the construction of industrial facilities. The main feature of this brand is its high strength, which can be noticed within a few minutes after complete hardening.
Appendix I (mandatory). Assessment of cement quality level based on variables
The general test conditions and the accuracy of weighing materials must comply with the requirements of GOST 310.1.
After extraction, the raw materials (chalk/limestone, clay/loam) are crushed into pieces no larger than 10 cm and mixed - the output is coarse sludge.
Therefore, humidity is one of the most important indicators that you need to pay attention to. The strength, stability of the material, its ability to withstand a wide variety of loads, drying speed and much more will depend on it.
In 1856, the first cement plant opened in Russia. A real construction breakthrough was achieved with the introduction of cement-derived materials - concrete and reinforced concrete; we didn’t have to wait long, it happened in the middle of the 19th century.
Therefore, humidity is one of the most important indicators that you need to pay attention to. The strength, stability of the material, its ability to withstand a wide variety of loads, drying speed and much more will depend on it.
Under such conditions, cement loses its most important indicator – activity (15%/month). After six months of “such” storage, the cement can be safely thrown away.
Professionals use special devices - moisture meters - to measure the moisture content of concrete screeds. With the help of these high-precision electronic assistants, it is possible to determine the moisture level of the concrete layer within a few seconds. These compact instruments also measure wood moisture. Moisture meters are expensive devices, so it is not advisable to buy them for one-time use.
A sample is taken in the amount of 1 kg from one bag of every 300 bags in a batch when cement is supplied in bags and 1 kg from every 15 tons of cement when cement is supplied by road.
The setting time of cement is the beginning and end of this process. The beginning of the loss of mobility (or plasticity) of the cement paste is taken as the starting point, and some hardening is taken as the end point. It is necessary to know the setting time, since freshly prepared solutions can only be used before setting begins.
Regulatory documents for specific types of cement may establish additional strength classes or restrictions on the classes used.
M500
Cement M 500 is a white binder powder, which, when interacting with water, begins to harden and form a stable and durable base for the future material.
In other words, this is the same cement as the one discussed above, but it is only produced according to special technologies with the addition of individual components, thanks to which it is possible to achieve a crystal white material and certain characteristics (for example, high weather resistance can be distinguished).
Type 500 is produced by processing and reducing to powder form a low-iron intermediate industrial product, clinker, a mineral from the class of sulfates CaSO4•2H2O and active mineral additives.
If clinker needs to be bleached, manufacturers use gas technology, which is based on reducing the percentage of oxidation of the coloring oxide.
M 500
According to the pricing policy, cement 500 is several times more expensive than another gray analogue, all due to the more expensive production technology. White cement of the highest grade is characterized by 80% whiteness and above, grade 2 - three percent less than whiteness, grade 3 - ten percent less.
The minimum compressive strength of type 500 is 50 MPa. When purchasing a product, you must carefully study the labeling; it must have the initials “Before” on it. This means that the product does not contain any unnecessary additives. In addition, manufacturers often indicate the following characteristics:
- color characteristics of the material – from 80%;
- sediments that do not dissolve – 0.11%;
- when it starts to set – 1.6 hours;
- when it finishes setting – 2.08 hours;
- strength during compression: after 48 hours – 37 MPa, after 672 hours – 58 MPa.
A distinctive feature of cement 500: resistance to frost and moisture, thanks to this the material can be safely used at high humidity.
Structures made from cement 500 can withstand a minimum of one hundred freezing and thawing cycles (this is an average figure, in practice it is significantly higher).
Sand is a universal material; not a single construction project or renovation can do without it. It's all about the density of quarry sand.
Decorative bark beetle plaster is often used to decorate the walls of houses and other structures. Here is the technology for its application.
The screed is a mandatory component of any floor, which is placed under the floor covering. Follow the link to learn how to make a floor screed.
The species in question is also characterized by excellent sulfate resistance. All thanks to the special composition, which contains a small amount of alkali.
Builders and manufacturers note the high rate of hardening of this material, which speeds up repair and finishing work several times. Cement M 500 is often used for decorative purposes.
For more information about the M500 cement brand, watch the video:
Pros and cons of M500
Cement 500 has many advantages :
- Thanks to the ideal white color, various decorative ideas can be realized;
- At the construction stage, it is rational to use color additives. As a result, you can get the ideal mixture, grout, and you can safely vary the color of the concrete;
- The material will withstand harsh Russian winters without any problems ; it is highly frost-resistant;
- At the production stage, cement is crushed as much as possible, thanks to this it is possible to achieve uniformity in future products or structures, they turn out as if polished.
Not surprisingly, cement also has a number of disadvantages. The first thing that builders need to pay attention to is that the material is quite intricate and requires increased concentration of attention during its use.
So, at the construction or work stage, you should strictly follow the clear recommendations that the manufacturer pays attention to. The first point concerns the tools and materials that will be used when working with the concrete mixture.
They must be as clean as possible, and cleanliness concerns not only the forms and forms, but also the concrete mixer.
All materials and equipment must be cleaned of corrosion, grease, sediment accumulation and other contaminants.
When working with elements (this also applies to the iron base of structures), they should be covered with a three-centimeter ball of concrete, while the protruding parts are insulated in order to prevent the appearance of rust.
Aggregate moisture
When considering apparent specific gravity, it was mentioned that in a concrete mixture, the volume occupied by the aggregate includes the total volume of all the grains along with all their pores. If it is necessary to exclude the suction of water into the filler, then it is necessary that the pores be filled with water, that is, the filler is in a water-saturated state. On the other hand, any moisture on the surface of the aggregate will be an additive to the mixing water. When it rains, the aggregate becomes moist and, with the exception of material located on the surface of the stacks, retains this moisture for a long time. This especially applies to fine aggregate. Surface (film) or free moisture, i.e. moisture in excess of that contained in the aggregate in a water-saturated and surface-dry state, must be taken into account when calculating the composition of concrete. The percentage of surface moisture in aggregate relative to its weight in a saturated surface-dry state is called moisture content. Since the amount of water absorption corresponds to the amount of water contained in the aggregate, saturated with water, but in a surface-dry state, and the humidity corresponds to the amount of surface moisture, the total water content in the wet aggregate is equal to the sum of its water absorption and humidity. Since the moisture content of aggregate varies depending on the weather and largely on what part of the stack it is in, the moisture content should be determined quite often. Many methods have been developed for determining humidity. The oldest method is to determine the weight loss of a sample of aggregate as a result of drying it on a tray over a heat source. In this case, it is necessary to avoid overdrying in every possible way. The sand should be dried until it becomes free-flowing, and then stop heating it. This test method is quite lengthy and requires great care in operation, for example, it is necessary to completely remove air bubbles from the pycnometer. However, it gives very accurate results. Aggregate moisture content can also be determined by measuring the volume of water displaced by a specified amount of aggregate. In this case, it is necessary to know the specific gravity of the rock. The equipment used for this method may vary. The moisture content of an aggregate of known specific gravity can be determined by the amount of weight lost by the aggregate when it is immersed in water. This is a fairly fast method; it allows you to determine humidity with an accuracy of 0.5%. Numerous other methods for determining moisture have also been developed, for example, moisture can be removed by burning the aggregate with methyl alcohol, and the loss in weight of the test sample is measured. There are also patented measuring instruments, the principle of which is based on measuring the gas pressure generated in a closed vessel as a result of the reaction of calcium carbide with the moisture of the aggregate. Electrical devices have been developed to periodically or continuously record the moisture content of aggregate in a storage bin. The operating principle of these devices is based on a change in resistance or capacitance when the moisture content of the aggregate changes. In some concrete plants, measuring instruments of this type are used in automatic devices that regulate the amount of water introduced into the concrete mixer. It should be noted that although there are many different methods for determining aggregate moisture content, test results will only be accurate if a properly selected average sample is used. In addition, adjusting the composition of the concrete mixture is made difficult by the inconsistent moisture content of the aggregate in different parts of the stack. Humidity in a stack varies primarily in the vertical direction from high humidity at the bottom of the stack to the top drying or dry surface. Therefore, care must be taken to properly store the aggregate in stacks that should reduce moisture fluctuations to a minimum. It is preferable to store in horizontal layers, have at least two stacks and provide conditions for moisture drainage in each stack; do not use a bottom layer 30 cm high, etc. Coarse aggregate contains much less water than sand and has more constant moisture values.