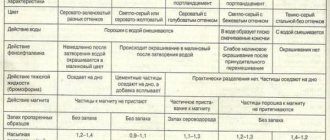
What is cement?
Cement
(which means “broken stone” in Latin) is the most famous, popular and indispensable building material. It is a gray finely ground free-flowing powder. Mixing with water, salt solutions or other liquids forms a plastic mass, as a result of which hardening a stone-like material is formed. Cement is most often used to make concrete and mortars. Unlike mineral binders (air lime and gypsum), which harden only in air, cement gains strength in humid conditions.
Portland cement
– one of the most popular types of cement, obtained by annealing the material in special furnaces at high temperatures (up to 1500 degrees). It, in turn, comes in several types:
- aluminous;
- pozzolanic;
- Romancement;
- expanding;
- white cement;
- slag;
- cement with fillers.
Any cement is marked. Its grade is determined by compressing and bending a specially made test sample, 4x4x16 cm in size, made of sand and cement (in proportions 3:1). The higher the grade (the value can be from 100-600, 700 is less common), the stronger the cement. The most popular are cement materials of grade 350-500, the most durable of them is M600, also called “military”, as it is excellent for the construction of missile silos, shelters, etc.
Cement has been known and successfully used in construction practice for 160 years. And over the past few years, its quality indicator has increased significantly, and new types of this material have also appeared.
Scope of application of cement
The purpose of cement is determined by its marking, which is usually indicated on the bags in which it is packaged. The designation “M” tells you how much load the cement will withstand when fully cured. And the letter value “D” shows the percentage of additives present in cement. Their content in the material determines strength and some other properties.
For example, cement M400 D20 can withstand a load of no more than 400 kg per m3, and the impurity content in it is 20%. Cement material with this marking is used in construction and for the production of reinforced concrete.
PC400 D20 cement has high frost and moisture resistance (PC, like M, is a universal brand). It is successfully used in agricultural, industrial, residential construction, as well as for foundations, wall panels, beams and floor slabs.
The main uses of cement are:
- production of various mixtures necessary for leveling walls and plastering work;
- construction of house foundations;
- strengthening facades;
- finishing facilities;
- laying the walls of buildings from various building materials;
- construction of roads and bridges;
- floor arrangement;
- production of various reinforced concrete structures.
Of all the building materials known to us, cement rightfully occupies a leading position. It is truly the most necessary in any direction of construction. Today it is difficult to imagine that any structure was erected without the use of cement.
To understand the reasons for its great success, let's consider all the properties of this material.
Main characteristics of cement
Cement has been known in the building materials market for more than 150 years. Of course, over the many years of its existence, this material has changed somewhat, or rather, its characteristics. One very important detail should be noted: the properties of cement depend on its type. Considering the fact that there are quite a lot of varieties, it is very difficult to highlight the qualities inherent in all types of cement to the same extent.
As a rule, when purchasing cement, the following qualities are taken into account:
- Frost resistance
is one of the most important indicators for regions with a northern climate. The ability of cement to withstand changing climates, with frequent periods of freezing and thawing, is essential for Russian climatic conditions. In order for the frost resistance indicator to meet these requirements, it is recommended to choose hydrophobic cement, designated by the letters “GF”, plasticized, marked “PL” (strength 42.5), or marked M500.
- Durability
. Cement is considered a fairly durable material, which is important for the durability of the entire structure being built. There are several strength classes of cement material:
- 22.5 (M300);
- 32.5 (the most popular M400);
- 42.5 is considered an increased strength class (M500), most often used for residential and industrial construction;
- 52.5 (M600) – the highest strength indicator.
- Resistance to corrosion
is a property that indicates the ability of a material to withstand various environmental influences. M400 cement copes well with this task.
- Sulfate resistance
or resistance to sulfate ions found in some aqueous solutions. A high level of resistance to sulfates is present in cements M300 and M400.
- Water resistance
is a fairly important property, especially when filling seams and joints. Some types of cement are not resistant to moisture, which can negatively affect the durability of the building and its quality.
- Grinding fineness
is a characteristic that affects the setting and hardening time. As a rule, the hardening time of cement depends on the strength class of the cement. Thus, material with a strength index of 32.5 and 42.5 begins to harden after at least 60 minutes, with an index of 52.5 - after 45-50 minutes.
- Durability
. Houses built using cement serve the owner for many years, provided that the proportions in the process of preparing the cement mortar and the technology of laying wall material are strictly observed.
- Versatility
. Cement is used in all areas of construction, and is even included in some binding materials, such as tile adhesive.
- Relatively low price of some types of cement
(compared to other materials).
Modern technologies make it possible to produce cement of various colors, which is an effective element in the architectural and decorative design of buildings.
So, if you are planning construction or renovation, then be sure to turn to cement for help. We offer simple instructions for preparing cement mortar with your own hands.
Instructions for preparing cement mortar
A properly prepared and thoroughly mixed mortar guarantees reliable bonding of the material used (brick, tile, etc.). To obtain such a solution, it is necessary to strictly observe the proportions of all components.
Cement and cement mortars
Cement and cement mortars
Today, delivered cement remains the best-selling binding material, far ahead of dry building mixtures in terms of sales volumes.
Cement mortar prepared on site is significantly cheaper than a similar mortar made from a dry mixture, and the difference in quality for many types of work is practically indistinguishable. The main volumes of cement mortar during construction are used for bricklaying, floor screeding and wall plastering - work that does not require the use of high-performance mortars. Therefore, the standard cement-sand mortar does an excellent job here.
The most commonly found cement brands on sale are M500 D0, M500 D20, M400 D0 and M400 D20. Where M500 (or M400) is the brand of binder in terms of strength, and D0 (or D20) is the percentage of foreign impurities.
Many people believe that high-quality cement mortar can only be obtained using M500 D0 cement. This is the biggest consumer misconception. All brands of cement (even M400 D20) allow you to obtain a solution of the highest quality, just the proportion of cement and sand in these solutions will be different.
Based on strength, mortars are divided into grades: M75, M100, M150, M200 and M300. They are made by mixing cement, sand, lime and water. Cement is a binder that is responsible for the strength of the solution, sand is a filler that creates the mass and volume of the solution, lime is a plasticizer that simplifies the process of applying the solution and increases its resistance to cracking.
Floor screed
For floor screeding, a solution of grade M150 is used, for the preparation of which the following proportion of cement-lime-sand is used: - Cement M500 D0: 1 : 0.3 : 4
- Cement M500 D20: 1 : 0.25 : 3.2 - Cement M400 D0 : 1 : 0.2 : 3 — Cement M400 D20: 1 : 0.15 : 2.4
Mix the solution in an open container or using a concrete mixer:
- Pour water into the container. The volume of water in the solution should be approximately equal to the volume of cement.
- Mix the required amount of lime (or other plasticizer) in water.
- Pour in half the volume of sand required for one batch and mix again.
- Pour the entire volume of cement into one batch. Mix.
- After complete mixing, add the remaining half of the sand.
- If necessary, add water to the solution, adjusting its thickness. The cement mortar of the correct consistency should have the appearance of rich sour cream.
Instead of lime, many people prefer to use special plasticizers. Others use dishwashing detergent (50g per 25kg of cement) or PVA glue (200g per 25kg of cement) as plasticizers. Many people also believe that you need to mix sand and cement first, and only then add water. It doesn't really matter. Do what is convenient. It is only important that the water is added with a plasticizer already dissolved in it.
You can also add crushed stone or expanded clay to the screed solution. Crushed stone allows you to reduce the cost of the solution without losing strength characteristics. Expanded clay - increases the heat resistance of the screed. Everything here is for everyone. The main thing is not to add expanded clay to the screed over the heated floor.
Masonry mortar
For masonry work, the most commonly used mortar is M100: - Cement M500 D0: 1 : 0.5 : 5.5
- Cement M500 D20: 1 : 0.4 : 4.5 - Cement M400 D0: 1 : 0.4 : 4 .5 - Cement M400 D20: 1 : 0.3 : 3.5
Prepared similarly to the mixture for screeds. Only without crushed stone and expanded clay.
Plastering works
For plastering work, a mortar of grade M100 is used, with a proportion similar to that of masonry mortar. The only difference is that it is advisable to use river sand, and be sure to sift it thoroughly. In addition, it is especially important to strictly observe the proportion of components. So, if you overdo it with cement, the solution will be greasy and will quickly crack. If you overdo it with sand, the solution will be less durable and not convenient to work with.
In conclusion, it must be borne in mind that the finished cement mortar must be used within one hour, otherwise it will begin to set.
In addition, the cement mortar does not immediately gain its strength. So, after three days its strength is only 33%. It reaches its design strength of 100% after 28 days. And after 90 days it has a strength of 130%.
Binding building materials grades M400 and M500
When carrying out construction work, cement remains an indispensable material. Cement is a powdered building binder material consisting of:
- clinker (an intermediate product in the production of cement);
- additives;
- plaster (if necessary).
Interacting with water or with special solutions, after mixing, cement forms a plastic mass, which after time hardens and turns into solid stone.
There are many types of cement. They are distinguished by marking (name) and properties (technical characteristics). Each type of cement is marked with reference to regulatory documents, such as State Standard 10178 of 1985. Some of the most popular brands are M400 and M500.
Material marking
Important information about the properties of cement is contained in the labeling. As an example, M400 cement stands for:
- “M” is the maximum permissible degree of load that cement can withstand after hardening. Instead of “M” there may be “PC” (PTs400).
- 400 is the maximum load per 1 cubic meter. Measured in kg/m. cube
There is this type of marking M400 D20. The marking means the following:
- “D” - there are additives in the cement.
- 20 is the percentage of additives present.
Additives affect technical characteristics, such as: strength, frost resistance, water resistance, etc.
Specifications
Let us consider in more detail the composition and properties of the binder material.
M400 is manufactured in accordance with GOST 10178-85 and includes:
- clinker;
- gypsum - no more than 5%;
- additives (active minerals) - 0 to 20% of the total mass (marked D).
Figure 1 — M400 packaging
It is used for the construction of reinforced concrete structures that are resistant to moisture (hydroelectric power plants, underwater structures), in above-ground, underground and transport construction. M400 grade cement has the following characteristics:
- resistance to corrosion;
- high strength;
- water resistance;
- frost resistance;
- durability.
Read more in the article about the properties and technical characteristics of M400 cement.
M500 is manufactured in accordance with GOST 10178-85. It contains the same components as the M400. Cement is mainly used in above-ground, underground, transport construction and in repair and restoration work.
Figure 2 — M500 packaging
M500 grade cement has the following characteristics:
- resistance to low temperatures;
- sulfate resistance;
- minor deformation changes during shrinkage;
- good elasticity
- high strength;
- water resistance;
- frost resistance;
- durability.
Read more about M500 cement in the article by following the link.
Differences between M400 and M500
To find out which is better to use cement M400 or M500, you need to determine for what purpose you will use it. Let's compare the composition and characteristics of the M400 D20 and M500 D0 brands.
Table 1 - Specifications
| Brand | M400 D20 | M500 D0 | ||
| Indicators | Standard according to GOST | Values | Standard according to GOST | Values |
| Tensile strength of cement at 28 days under compression | not less than 32.5 not more than 52.5 | 40,7 (±) 2,5 | not less than 42.5 not more than 62.5 | 52,6 (±) 2,8 |
| Start of setting, min | no earlier than 75 | 200 (±) 20 | no earlier than 60 | 168 (±) 35 |
| End of setting, min | not standardized | 200 (±) 20 | not standardized | 262 (±) 65 |
| Uniformity of volume change, mm | no more than 10.0 | 0,5 (±) 0,5 | no more than 10.0 | |
| Weight loss on ignition, % | — | — | no more than 5.0 | 1,06 (±) 0,39 |
| Insoluble residue,% | — | — | no more than 5.0 | 0,42 (±) 0,21 |
| Sulfur oxide (VI)SO3 content, % | no more than 3.5 | 2,67 (±) 0,30 | no more than 3.5 | 2,5 (±) 0,2 |
| Content of oxide ion ST, % | no more than 0.1 | 0,001 (±) 0,001 | no more than 0.1 | |
| Mineral supplement content | not less than 6.0 | 18,1 (±) 1,5 | — | — |
| Granulated slag + flask, % | no more than 20.0 | 18,1 (±) 1,5 | — | — |
| Specific effective activity of natural radionuclides Aeff. Bq/kg | no more than 370 | 78 (±) 11 | no more than 370 | 41 |
| Mineralogical composition of clinker, % | ||||
| Tricalcium silicate (C3S) | С3S | 57,2 (±) 3,0 | not standardized | 65,35 (±) 4,65 |
| Dicalcium silicate (C2S) | C2S | 17,5 (±) 2,0 | not standardized | 13,81 (±) 4,1 |
| Tricalcium aluminate | not standardized | 6,9 (±) 1,0 | not standardized | 9,54 (±) 1,72 |
| Tetracalcium aluminoferite | not standardized | 13,3 (±) 1,0 | not standardized | 11,3 (±) 2,5 |
Based on the table, it can be seen that the same clinker components are used to make cement, only in different proportions. This affects the physical and mechanical properties of cement. These brands differ:
- Strength (maximum load indicator in M400 and M500 - 400 and 500 kg/m3, respectively).
- By setting (M500 begins to harden faster, which is why it is popular in repair and restoration work).
Figure 3 - Sealed cement bags
For the construction of walls, the construction of reinforced concrete products and slabs, grade 400 cement is popular in construction.
For heavy loads and for the construction of foundations, a product with increased durability (M500), which is also used in the manufacture of paving slabs and tiles, has become very popular.
It is not recommended to use M500 for structures located in highly aggressive environments. For these purposes, it is better to use sulfate-resistant cement.
Cement grades, GOST standards, main differences
The most common brands of cement:
Cement PC 500 D0 (M 500 D0) Cement grade PC 500 D0 is used in the production of critical concrete and reinforced concrete structures in industrial construction, where high demands are placed on water resistance, frost resistance, and durability. Cement of this brand is effective when carrying out emergency repair and restoration work due to the high initial strength of concrete.
Cement PC 500 D20 (M 500 D20) Cement grade PC 500 D20 is used in industrial, residential and agricultural construction for the production of prefabricated reinforced concrete, foundations, beams, floor slabs, etc., and is also successfully used for the production of concrete and mortars, plaster , masonry and other repair and construction works. Cement of this brand has water resistance, frost resistance, and reduced resistance to corrosion compared to ordinary Portland cement.
Cement PC 400 D0 (M 400 D0) Cement grade PC 400 D0 is used for the production of prefabricated concrete and reinforced concrete structures using thermal and moisture treatment, as well as for concrete, reinforced concrete underground, above-ground and underwater structures exposed to fresh and mineralized water. Cement of this brand has successfully proven itself for the production of concrete and mortars.
Cement PC 400 D20 (M 400 D20) Cement grade PC 400 D20 is used in industrial, residential and agricultural construction for the production of precast reinforced concrete, foundations, beams, floor slabs, wall panels, etc. Cement of this brand has good water resistance and frost resistance. GOST 10178-85 Cement, like any other material used in construction, differs in its physical and technical characteristics depending on the conditions under which it is intended to be used. According to GOST 10178-85, the symbol of cement must consist of: - name of the type of cement - Portland cement, Portland slag cement. It is allowed to use an abbreviated designation of the name - PTs and ShPTs, respectively; — grades of cement; — designations of the maximum content of additives in Portland cement: D0, D5, D20; - designation of fast-hardening cement - B; - designations for plasticization and hydrophobization of cement - PL, GF; - designation of cement obtained from clinker of standardized composition - N; - designation of the standard to which the cement complies. An example of a symbol for Portland cement grade 400, with additives up to 20%, quick-hardening, plasticized: Portland cement 400-D20-B-PL GOST 10178-85. GOST 31108-2003 From January 1, 2008, some Russian cement plants, in particular those belonging to the EUROCEMENT concern, switch to cement production in accordance with GOST 31108-2003. One of the advantages of the GOST 31108-2003 standard is its harmonization with the European standard EN 197-1, which establishes a uniform classification, technical requirements and methods for establishing compliance of cement quality with the requirements of the standard for all countries of the European Union (EU). The GOST 31108-2003 standard does not cancel the currently valid GOST 10178-85, which can be used in all cases if it is technically and economically feasible. At the same time, it is promising for the development of new regulatory documentation in construction, based on the characteristics of cements harmonized with the requirements of EN 197-1. When cement production switches to GOST 31108-2003, it is possible to obtain an adequate assessment of the quality of cements produced in the CIS and EU countries. The main differences between GOST 31108-2003 and the current GOST 10178-85: - compressive strength classes similar to those established by EN 197-1 have been introduced instead of grades; - for cements of all strength classes, in addition to the requirements for strength at the age of 28 days, additional standards for strength at the age of two days are established, with the exception of classes 22.5N and 32.5N, and for cements of classes 22.5N and 32.5N - in age 7 days; — for all strength classes, except for class 22.5, a division of cements according to hardening speed has been introduced into normal-hardening and fast-hardening, which will minimize cement consumption in construction due to its optimal selection according to hardening speed. According to GOST 31108-2003, the designations of cements will change. The symbol of cement will consist of: - the name of the cement (CEM I - Portland cement, CEM II - Portland cement with mineral additives) - Portland cement with mineral additives is divided into subtypes A and B - for subtype A the amount of mineral additives is limited from 6% to 20%, for type B – from 21% to 35%; - abbreviated designation of cement, including the designation of the type and subtype of cement and the type of additive (granulated slag is designated by the letter Ш; pozzolana - P; composition of slag and pozzolana (tripoli, opoka) - K (Ш-П)); — strength class (22.5; 32.5; 42.5 and 52.5, which means the minimum compressive strength at 28 days, MPa); - subclass designations (compressive strength at the age of 2 (7) days - N (normally hardening) and B (fast-hardening), except for class 22.5); - designation of the standard to which the cement complies. Examples of symbols: 1. Portland cement class 42.5, normal hardening: Portland cement TsEM I 42.5N GOST 31108-2003; 2. Portland cement with slag from 6% to 20%, strength class 32.5, quick-hardening: Portland cement with slag TsEM II/A-Sh 32.5B GOST 31108-2003; 3. Portland cement with slag from 21% to 35%, strength class 32.5, normal hardening: Portland cement with slag TsEM II/V-Sh 32.5N GOST 31108-2003; 4. Composite Portland cement with a total content of granulated blast furnace slag and pozzolana from 6% to 20%, strength class 32.5, normal hardening: Composite Portland cement with slag TsEM II/A-K (Sh-P) 32.5N GOST 31108-2003. When producing cement according to GOST 31108-2003, auxiliary components can be added in an amount of 5% to all types of cements (including CEM I). Any mineral or inert additives regulated by GOST 31108-2003 can be used as auxiliary components of cement. Auxiliary components should not significantly increase the water demand of cement, nor reduce the durability of concrete or the protection of reinforcement from corrosion. The correspondence of cement designations (by plant) according to GOST 10178-85 and GOST 31108-2003 is relative due to differences in material compositions and differences in test methods, however, the construction and technical properties of cement produced according to GOST 31108-2003 are comparable to cement produced according to GOST 10178-85.
Choosing construction material when purchasing
When purchasing cement, carefully study the packaging. Pay attention to:
- date of manufacture (in order to preserve all its properties, cement must be stored in intact, undamaged packaging for 6 months in a dry place);
- labeling (it will indicate the strength and the presence or absence of additives);
- integrity of the packaging.
It is preferable to buy cement in bags rather than in bulk, since you yourself can control the quality of the purchased product.
Definition and composition of cement
This building material is crushed clinker powder , which in turn contains modifying additives and fillers. In simple terms, cement is the most popular building material, which is used for the construction of various types of structures and for the production of high-strength products. At the same time, cement looks like a gray powder consisting of small grains. The grains, when combined with water, turn into a homogeneous mixture.
Types of cement
Cement is divided into several types:
- Portland cement.
- Slag cement.
- Pozzolanic.
- White type of cement.
- Hydrophobic.
- Magnesian.
- Special (acid-resistant, colored).
The main technical characteristic of any type of cement is its grade . The grade of cement is conventionally designated by the letter “M” and a digital indicator. The numbers, in turn, indicate the digital maximum load in kilograms per certain volume of hardened cement, that is, its compressive strength. In other words, in practice this means the weight that the cement can hold without breaking. So, for example, the well-known cement brand M400 is capable of bearing a mass weighing 400 kg, and M500, respectively, a mass weighing 500 kg.
So what is the difference, besides the weight category, between the two brands of cement M400 and M500?!
Features of cement M400
To produce M400 cement, three components are needed: clinker, gypsum (up to 5%) and mineral additives in amounts from 0 to 20%. Moderately high compressive strength allows the use of the finished composition for the construction of underground or above-ground objects.
Scope of application of M400 cement:
- Creating a subfloor.
- Construction of reinforced concrete structures for power plants and underwater structures.
- The needs of transport construction are the creation of paving slabs or beams.
- Production of floor slabs.
The volumetric weight of the M400 grade composition is determined by the degree of compaction and shelf life. Density affects the quality of the finished concrete solution.
Features of cement M400:
- high frost resistance - F100;
- sufficient strength;
- water resistance;
- ability to resist corrosion;
- salt water resistance;
- durability.
However, this brand of cement is not suitable for the construction of high-rise buildings. The finished composition is not able to cope with such a large load.
Cement grade M400
This brand of cement has fairly high strength and anti-corrosion properties . This brand is considered one of the most common, both in industrial and domestic construction. M400 cement is used as a base in building concrete or concrete mortar. Also, the strength of this cement allows it to be used in the construction of reinforced concrete products.
This brand of cement is used in the following sectors of construction work:
- During the construction of reinforced concrete products, reinforced concrete underground, above-ground and underwater structures.
- For industrial and agricultural construction.
- In the manufacture of foundations and beams.
The main and first advantageous factor of this cement is its low requirements for hardening and construction regulations . Also, the absence of cracks with some deviations from the technology, which is another advantage of this brand of cement. And of course, that indisputable fact is the price. Cement of this brand is much cheaper than higher brands, which will significantly save your budget. It is also worth mentioning such advantages as frost resistance.
Comparing cement brands M-400 and M-500 | Determining the best
The product is used in the construction of structures for various purposes, as well as in the creation of high-strength products. Externally, cement is presented in the form of a powdery gray mass, which, when combined with water, is transformed into a thick synthetic mixture, characterized by plasticity, and when hardened, it is highly durable.
Modern industry does not stand still, constantly improving the material, refining and modifying its structure. Despite such diversity, all types of cement have one constant characteristic - brand. The latter speaks of the maximum load, expressed in kilograms, that a certain volume of cement can withstand without the appearance of traces of deformation on it.
In fact, we are talking about the strength of the material when it is compressed. M grade cement is deservedly one of the most popular.
It is characterized by high strength and excellent anti-corrosion properties. The product is actively used both in industry and in everyday life as a base for concrete mortar. The use of M is especially relevant in the following industries: Construction of above-ground, underground and underwater structures made of reinforced concrete, as well as reinforced concrete products; Among the shortcomings of the material, perhaps only insufficient strength can be noted, which is why M is never used in the construction of high-rise buildings.
M is best suited for creating concrete slabs and constructing reinforced concrete structures. Cement grade M is available in two varieties: M D0 is a pure cement mixture that does not contain any additives. It has found wide application in industrial construction due to its unique characteristics: when mixed with concrete, it improves its water and frost resistance, as well as strength.
The design is incredibly stable, able to withstand significant loads. Due to its ability to quickly harden, cement M is actively used in emergency and repair work.
So, what industries often use M? This building material is indispensable for building foundations, creating paving slabs, roof tiles, etc. Experts do not recommend the use of M for products that are located in an aggressive environment.
It is better to prefer sulfate-resistant cement. Of course, both brands under consideration are valued in construction for their high strength and resistance to corrosion, but this does not make them identical. Let's look at the main differences between the two products:.
What is the difference between cement M400 and M500?
Their quantity directly affects the ductility and strength of the material. Many people think that the numbers in the marking indicate the amount of sand that is necessary to prepare a high-quality mortar. In fact, this is far from true - numbers, etc.
They are given when testing cement at the factory, when a cube molded from cement is subjected to gravity tests - if it breaks under pressure of a kilogram, then such cement is assigned the grade , - accordingly M. The name of the product, trademark and relevant GOST standards must be indicated on the front side of the bag. On the back, look for the weight, density and other technical characteristics of the product, as well as the address and telephone number of the manufacturer.
The first has increased frost and water resistance. It is usually used in the manufacture of precast reinforced concrete, wall slabs, foundations, etc. The second is ideal for plastering, masonry, other repair and construction work and the preparation of various mortars.
In addition to good water and frost resistance, this type of cement has reduced resistance to corrosion. Before purchasing cement, carefully study the packaging in which the material is packaged. In addition to the brand and weight, it must indicate the manufacturer - company name, country and city. Remember that when buying a wholesale batch of loose cement, you risk purchasing low-quality or expired goods.
Also ask about the conditions under which the material was transported and stored: the quality of cement is greatly influenced by the environment, especially high humidity.
We offer some practical tips that will help you choose really high-quality cement, as well as transport and store it correctly.
Cement grade M500
This brand of cement is a quickly hardening building material. This cement is able to withstand loads of up to 500 kg per cm. Due to its quickly hardening property, this brand of cement is used during emergency restoration and repair work. There are two types of cement of this brand, these are:
- M500 D0 is a mixture without impurities or additives. Used in industrial construction.
- M500 D20, in this case the additive content is 20%. This type of cement is used for repair and construction work.
This brand is used for the production of various concrete and reinforced concrete structures. This cement is also used to produce prefabricated reinforced concrete, foundations, beams and prepare the following types of mortars:
- Masonry mortars.
- Plaster solutions.
- Construction cement mortars.
Of course, speaking about cement of this brand, we should also talk about the significant advantages available, namely:
- High water resistance.
- High frost resistance.
- High level strength indicators.
- When shrinkage occurs, the deformation change indicators are low.
- High resistance to prolonged exposure to low temperatures.
In addition to the above, due to the presence of active mineral additives in the cement mixture, it should also be said about the increased anti-corrosion quality.
The difference between cement grades M400 and M500
These brands of cement consist of almost the same materials. Their main difference is their ability to withstand a load of 1 cubic meter. For M400 cement, this number is 400 kilograms, respectively, for M500 cement – 500 kilograms.
For a detailed comparison, it is necessary to consider each brand separately.
Cement m400
This brand is intended for both household and professional work. The scope of application extends to reinforced concrete structures, which are often placed under water.
This is due to the water resistance of this brand. It is also used in ground work. Another important difference is the hardening time. In M400 cement it ranges from ten to twelve hours.
Cement m500
Despite the almost identical composition, this type is more elastic than M400. Thus, it is resistant to more aggressive conditions. The scope of application includes the construction of load-bearing structures and work with the foundation of a building.
Depending on the amount of additives, properties such as corrosion and frost resistance may change. Hardening time ranges from five to eight hours.
conclusions
Thus, cement grade M500 is more durable. The difference between the above two brands is in strength per cubic meter, curing time and ability to withstand various environmental conditions.
These brands are interchangeable, unless we are talking about fundamental work. For long-lasting results, it is advisable to use each of them for their intended purpose.
Differences between M400 and M500
Considering the two options, it is clear that M500 wins in benefits, since in addition to the production of paving slabs and paving stones, it is also used in the construction of multi-storey monolithic residential buildings. Strength is also a distinguishing feature between the two types of cement.
| Brand | M 400 | M 500 |
| Water resistance | 22-25% | 25-28% |
| Hardening | 10-12 hours | 8-9 hours |
| Strength (pressure, according to the latest indicators according to GOST) | 38,0 | 47,5 |
| Maximum permissible % of impurities | 15-20% | 10-15% |
| Content of harmful chemical compounds | 4,0 | 4,5 |
- The water resistance of cement is an indicator of how much a particular brand is exposed to water, any cement absorbs moisture, there is a certain standard for each brand
- Hardening. The hardening time for each brand is also different, it depends on the purity and quality of the clay rocks; the higher the brand, the faster the process.
- The strength of cement is determined using ready-made concrete blocks, necessarily identical in volume, by compression until they completely collapse. This way they determine what load the concrete can withstand.
- Each cement powder contains an acceptable amount of impurities according to GOST; this is done in order to reduce the cost of the finished product.
- Cement also contains hazardous chemical compounds such as chromium, nickel, benzene, ethylbenzene, and formaldehyde.
Specifications
Cement M400 and M500 is crushed clinker powder with the addition of modifying additives and gypsum of no more than 5%. According to its material composition, it is divided into the following types:
- Portland cement. Pure mass without impurities.
- Portland cement with active fillers with a share of no more than 20%.
- Portland slag cement. Contains granulated slag above 20%.
This building material has high qualities:
- anti-corrosion;
- moisture resistance;
- frost resistance;
- elasticity;
- resistance to low temperatures and aggressive environments;
- high crystallization rate;
- reliability;
- durability.
The mass fraction of fillers ranges from 0 to 20% and is indicated as follows:
- D0 - pure cement;
- D5 - 5% amount of mineral additives;
- D20 is a mixture with a high content of fillers, up to 20%.
The letter M means the maximum load that a building material is ready to bear without destruction.
The marking may also contain the following designations:
- B - adding components that affect rapid hardening;
- PL - the use of plasticizers for the solution;
- GF - hydrophobization, introduction of water-repellent fillers;
- N - obtaining a solution based on the standardized clinker composition.
Brand M400 has the following technical characteristics:
- Tensile strength in bending - 5.4 MPa (55 kgf/cm²).
- Ultimate compressive strength - 39.2 MPa (400 kgf/cm²).
- Setting time: 60 minutes.
- Final hardening is 28 days.
- Density:
- in a loosened state - 900-1100 kg/m³;
- in the solid state - 1400-1700 kg/m³.
- Uniformity of volume change - up to 10 mm.
- The cycle of complete freezing or thawing is 70 cycles.
- Operating temperature range -60…+300°С.
Technical and operational parameters of M500 cement:
- Compressive strength - 59.9 MPa (500 kgf/cm²).
- Bending strength is 5.9-6.4 MPa.
- Setting time: 45 minutes.
- Complete drying - 8 hours.
- Bulk density - 1100-1700 kg/m³.
- The actual density is 3000-3200 kg/m³.
- The uniformity of volume change is no more than 10 mm.
- Weight loss during piercing is up to 5%.
- The volume of insoluble residue is up to 5%.
General characteristics
M500 cement, the price of which is relatively low, is produced in accordance with GOST 10178-85.
The following raw materials are used for its production:
- Gypsum stone.
- Clinker. This is a mineral that is obtained by sintering limestone and clay.
- Blast furnace charge.
- Various active additives that are used to improve the properties of cement. They can be hydrophobic, plasticizing, acid-resistant.
All components are finely ground and mixed in a certain proportion. Index 500 in cement marking means that the material can withstand a weight of 500 kg per 1 square centimeter. Solutions made on the basis of this brand are quite resistant to low temperatures, and upon hardening their shrinkage is insignificant, which significantly reduces the risk of cracks in the body of the structure.
Cement M500 technical characteristics have the following:
- Frost resistance - F70. This is a very important parameter. The ability of M500 cement to withstand repeated freezing and thawing is achieved by adding various modifying additives to its composition.
- Flexural strength 6.4 MPa.
- Setting period is approximately 50 minutes.
- Compressive strength 59.9 MPa.
- Expansion during setting - 10 mm.
- Grinding fineness 92%. This characteristic can have a direct impact on the setting and hardening time of the solution, as well as its strength.
- Radioactivity is 370 BC/kg.
- M500 cement has the most positive technical characteristics. Concrete and mortars based on cement 500 are highly resistant to corrosion and aggressive environments. Such mixtures are recommended for winter concreting. M500 cement has the following proportions when used in domestic construction: 1: 3: 6, where there is 1 part of cement, 3 sand and 6 aggregates
. It should be remembered that you cannot mix M500 cement with other brands, as the characteristics of this material will sharply change for the worse.