When purchasing building materials, it is important to accurately calculate their quantity. Both lack and excess bring no joy. It is usually believed that “overshoot” is better than “undershoot,” but not in the case of cement. This material cannot be stored for a long time and therefore it is necessary to accurately calculate the required quantity. How much cement is needed per 1 m³ of concrete can be determined in kilograms and bags. In principle, it is better to know both, because the packaging may be different.
Advertisement
How much cement is needed per cube of concrete?
Cement is a type of building material that should not be stored for a long time. Even if it is stored warm and dry, after three months it loses 20% of its strength, after six months - 30%, and after a year - 50%. So for critical areas it is better not to use stale ones. To be sure of “freshness,” it is better to purchase in the original packaging, which is marked with the production date. If you put it into action right away, it might be two months old. If you also have it for some time, a fresher one is better.
The quality of cement depends on compliance with the proportions
In order not to store it, you need to know how much cement is in a cube of concrete. For this purpose, there are tables that show the consumption of cement in kilograms per cubic meter of solution. The most popular are Portland cement grades M400 (new designation CEM I 32.5N) and M500 (new designation CEM I 42.5N). They are used to prepare concrete up to grade M500. For less durable ones, you can use the cheaper M300.
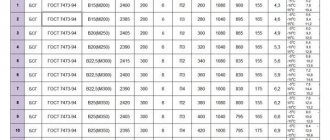
Table of cement consumption M400, M500 and M300 per 1 cubic meter of concrete of different grades
Based on these data, it is easy to calculate how much cement is needed for the amount of concrete you require. For example, 5.7 cubic meters are required to fill the foundation. The concrete will be M300 grade, we will make it from PC400. There are 290 kg per cubic meter. This means that 5.7 m³ * 290 kg/m³ = 1653 kg will be used for everything.
Amount of cement per 1 m³ of concrete depending on hardness
Above is the table "on average". In general, the specific amount of binder depends on its quality, aggregates (sand and crushed stone), and also on the required hardness of the concrete solution. At factories, a specific ratio is selected for each delivery of cement, sand or crushed stone. They brought another batch of sand and are conducting tests. New binder arrived - everything is done again. At least that's how it should be. For meticulous house builders, we present a table that shows the cement consumption per cubic meter of mortar depending on the required rigidity (fluidity) of the composition.
How much cement is in a cube of concrete of varying hardness
Also keep in mind that the use of additives that increase the workability of the solution (flowability) allows you to use less binder. But it’s better not to reduce it “by eye”. If you decide to add the same “Fairy”, add cement according to the norm. By the way, an additive too. Because if there is excess, the concrete simply will not set and even after a month it will be soft.
How many bags of cement are needed to prepare one cube of concrete?
It is better to buy building material in containers, packaged in bags weighing 50 kg. This will greatly facilitate any calculations related to the amount of material required.
The amount of cement depends on its brand , which differ in their characteristics. The higher the cement index, the less it is needed to produce 1 cubic meter of concrete solution. To produce high-grade concrete, a larger amount of cement is required.
Let's look at some examples of the cement content in 1 cubic meter of concrete:
- Concrete M 100 contains 160−200 kg (3−4 bags) of cement and is used for pouring road bases, constructing small buildings, and curbs.
- Concrete M 150 contains 220 kg (4-5 bags) of cement and is used for general construction work and the construction of small buildings.
- Concrete M 200 consists of 240−280 kg (5−6 bags) of cement, used for pouring foundations and for the construction of buildings and structures.
- Concrete M 250 contains 300−330 kg of cement (6−7 bags) and is used for the construction of monolithic foundations and flights of stairs.
In conclusion, I would like to remind you that when choosing a concrete solution for a certain type of work, you should take into account its brand and class , because these two criteria are interrelated. It is also important to remember that there are different grades of concrete - frost-resistant, waterproof and others. The main thing is that all parameters comply with standards that will ensure the strength of the structure or structure.
How many bags of cement are there in a cube of concrete?
Cement is sold in bags and therefore it is better to know how many bags of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete will be required. There are also reference tables for this, but you can calculate it yourself. Counting is more accurate than using tables. Firstly, there are bags of 40 kg and 50 kg. This is a standard container. But there are also 25 kg and there are also a lot of such packaging. The table shows how many bags of cement are in the most popular brands of concrete.
How many bags of cement goes into 1 cubic meter of concrete?
In addition, it is rare that a whole number of bags are required per cubic meter. For example, M150 concrete requires 215 kg of PC400. Let's calculate the amount of binder in kilograms that will be needed to make 4.6 cubic meters of concrete. 4.6 m³ * 215 kg = 989 kg. Now we calculate the number of bags of cement that will need to be purchased:
- 25 kg each - 898 kg / 25 kg = 35.92 pcs. That is, you will need 36 pieces of 25 kg each;
- in 40 kg packaging: 898 kg / 40 kg = 22.45 pieces, rounded up, it turns out that you will need to buy 23 forty kilogram bags;
- 50 kg each - 898 kg / 50 kg = 17.96 pcs; You need 18 bags of 50 kg each.
Now let’s calculate how many bags of cement are needed per 1 m³ of concrete using the second table. Let's take the same example - 4.6 cubic meters of M150 concrete from M400 cement. According to the table, one cubic meter requires 4.3 bags of 50 kg and 5.4 pieces of 40 kg. Total, the entire volume will go:
- 40kg bags: 4.6 cubes * 5.4 pcs = 24.84 pcs or 25 bags.
- in 50 kg packaging: 4.6 cubes * 4.3 pcs = 19.78 pcs or 20 pcs.
The consumption of cement per cube of concrete is not so high, but the proportions must be strictly observed
The table does not indicate the number of 25 kilogram bags. You can calculate it yourself - you need to divide the number of 50 kg bags by 2.
What determines the amount of cement per cubic meter?
How much cement is needed for 1 cubic meter of concrete? Every builder should know the answer to this question.
In order to make a concrete mixture for the foundation, the best option would be a ratio of 1:3:5 - respectively, 1 part cement, 3 sand and 5 crushed stone. To determine the required amount of ingredients, their characteristics should be taken into account.
Necessary characteristics that need to be taken into account for a particular material:
- For cement: weight, activity, setting time.
- For concrete mix: volume, strength, workability, water resistance and water release.
- For sand: fraction, weight, volume, humidity, amount of impurities.
- For crushed stone: weight, strength, moisture content, fraction and shape.
Such mixing of concrete mortar will make it possible to obtain a high-quality mixture - strong, namely, with the required rigidity, with a certain plasticity, which, after hardening, will not crumble from external influences in a short period of time.
The consumption of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete depends on what grade of concrete is needed, that is, for what purpose the concrete solution is planned to be used.
How much cement is needed for 1 cubic meter of mortar?
To determine how much sand and cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of mortar, it is important to know its purpose. To prepare masonry, plaster, foundation and other types of mixtures, different ratios of dry materials are used. The consumption of sand and cement per 1 m3 of mortar varies for each type of work, and often other dry or liquid compositions are added to the composition, increasing moisture resistance, strength, changing the rate of hardening of the mixture, etc.
What determines cement consumption for different solutions?
The preparation of cement mortar, the proportions of which may differ, requires strict adherence to technology and the correct determination of the ratio of components. To use different grades of concrete, different amounts of cement and sand are used. Remembering the proportions of cement and sand is not enough for high-quality construction; it is better to understand the principle.
Main factors influencing consumption:
- the amount of fillers in the mixture. The greater the proportion of crushed stone and sand, the higher the cement consumption per 1 m3 of solution. Cement is the binder of the components, which is responsible for holding all the fillers together. The ratio of bulk mixtures determines the amount of cement;
- brand of cement. As the grade increases, the strength of the final structure increases. It is worth remembering that the grade of the final mixture is significantly lower than dry cement, since sand is added to the composition, and gravel or slag can also be added;
- brand of solution. The cement-sand mortar is also divided by grade. For all types of work, GOST has recommended brands. After determining the desired brand of construction mixture, you can choose the right brand of cement. For example, to obtain an M100 mixture from M500 cement, you will need to mix 1 part Portland cement, 5.8 parts sand and 8.1 parts crushed stone. If the final goal is M450 solution, a proportion of M500 cement (C:P:SH) will be required: 1:1.4:2.9;
Rules for calculating the amount of cement
If your concrete does not contain enough binder, it will be unacceptably flexible. This is a consequence of the fact that when mixing concrete, calculating the number of components, it is permissible to make an error of plus or minus 1 kg of binder and plus or minus 5 kg of crushed stone and sand.
In other words, if there is little cement in concrete, it cannot cope with retaining the filler (crushed stone and sand), but if there is a lot of it, then, given the high cost of this material, it is not economically feasible. At the same time, experts in the field of construction technologies advise not to save money, and to prepare concrete with the amount of cement - “calculated plus 1 kg.”
Types and brands of mixtures
The introduction of the concept of “cement grade” helps to calculate the cement consumption per cube of mortar if the input parameters are known. To prepare a mortar with the same construction characteristics from different brands of cement mixture, different proportions of fillers will be required. Cement is produced in production, starting from grade M100, but due to the low structural strength, the material is practically not used.
The most popular cements are M400 and M500, but some other types have also become widespread. The choice of mixture depends on the scope of application of the material.
The main areas of use of cement grade:
- M300 cement is used in installation construction, as well as during the manufacture of monolithic structures;
- M400 cement is successfully used in monolithic construction and during the preparation of reinforced concrete;
- M500 cement is actively used in the construction of buildings or slabs that must be resistant to moisture or located in water. The scope of application of this concrete mixture is quite wide: the creation of sidewalks, the construction of asbestos-cement structures, the formation of large concrete masses and all kinds of foundations;
M400 and M500 cements are the most popular
- M600 cement is used to create prefabricated structures and foundations that are subject to high loads;
- M700 is a suitable grade of cement for the construction of highly loaded and stressed structures.
So how much does it weigh in grams?
For your convenience, just in case, we will also name the necessary proportions when making M250 and M300 mortars from M400 cement. Since this is one of the most commonly used brands in foundations. In the first case, the parts of cement, crushed stone and sand will have a ratio of 1/3.9/2.1, and 300 kg of cement will be needed per cube of concrete. In the second - 1/3.7/1.9 and consumption 320 kg.
But in other cases, it is advisable for us to calculate the consumption of cement for preparing the mortar not in buckets and abstract “parts”, but in mass weight. So that you can do this yourself, we will calculate a formula by which you can determine in advance how much cement you need to buy to pour the foundation. Let us recall that for these purposes we will take the already known proportion of 1/3/5 and a grade of cement that is twice the strength grade of the finished material. In this case, the consumption of cement for concrete can be calculated based on the fact that we used 9 parts of materials (5+3+1) for the mortar. There are 1 million cm3 in one cubic meter. Divide by 9 and get the volume of one ninth part - 111111 cubic centimeters. 1cm3 is approximately 3 grams of cement. We multiply and get cement consumption equal to 333 kilograms per cubic meter of finished concrete.
Please note that all calculations given are approximate. The exact composition of concrete for the foundation and the mass of cement and aggregates must comply with SNiP 82-02-95 (which replaced SNiP 5.01.23-83).
Material consumption rates per cubic meter of different solutions
Today there are 4 main areas of use of concrete: foundation, masonry, screed and plaster. In each case, special requirements are imposed on the building mixture, which makes the choice of cement and its consumption different. The greatest consumption of cement per cube of concrete occurs when it is necessary to make masonry or plaster. The consumption of materials per 1 m3 of foundation mortar is slightly lower due to the use of a large filler fraction: slag, crushed stone or gravel.
GOST has records of cement consumption rates per 1m3 of mortar, taking into account the purpose of the mortar. Designation of concrete per cubic meter. meters is a generally accepted system of measurement.
Consumption standards per 1 m3 using M500 cement:
- on M100 – 170 kg;
- on M150 – 200 kg;
- on M200 – 240 kg;
- on M250 - 300 kg;
- on M300 – 350 kg;
- on M400 – 400 kg;
- on M500 – 450 kg.
Consumption rates for cement and sand per cube of foundation mortar
Calculating cement for a foundation calculator is the easiest way to understand how much material is required and the number of necessary components. Concrete calculations can be done with high accuracy and manually.
To determine how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of solution, we recommend following simple instructions:
How many kg of cement in 1 m3 of solution:
- in M50 when using M400 – 380 kg;
- in M100 when preparing concrete from M300 cement – 214 kg;
- in M200 with cement M400 – 286 kg;
- in M300 at M500 – 382 kg.
The data is presented if the cube contains 2-4 parts of sand and 3 parts of crushed stone.
Consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of masonry mortar
To prepare cement mortar for wall construction, a proportion of 1 to 4 is most often used. Thus, the cement consumption per cubic meter will be 0.25 m3 or 325 kg, and the sand consumption per 1 m3 of mortar will be 0.75 m3 or 1200 kg.
Cement consumption rates for masonry
Table 1: Mortar consumption for walls of different thicknesses
| Thickness in bricks | Consumption, m3 |
| 0,5 | 0,189 |
| 1 | 0,221 |
| 1,5 | 0,234 |
| 2 | 0,24 |
| 2,5 | 0,245 |
To calculate how many bags of cement are needed, just multiply 325 kg by the consumption per cubic meter, for example, walls of one brick - 0.221. You will get 72 kg of cement for laying 1 m3 of wall, provided that the composition does not contain other components (lime, clay, etc.).
Consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of screed mortar
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution is calculated according to similar rules as in previous mixtures. The recommended mixing ratio is 1 to 3. Difficulties in calculations often appear at the stage of determining the volume of the solution, so let’s look at an illustrative example. It is necessary to fill a surface of 3x4 m or 12 m2. The layer thickness will be 30 mm.
Cement consumption rates for screed
Calculation of cement for screed from the example:
- We calculate the required volume of solution: 12 m2 * 0.03 m = 0.36 m3.
- We determine the brand of cement, M200 solution is often used, and we use it as an example. We will cook from M500, and according to the standards, the consumption will be 410 kg.
- We calculate the required number of bags of cement: 410 kg * 0.36 m3 = 148 kg - this is 6 small or 3 standard bags of 50 kg each.
- We determine the cost of sand. To do this, we multiply the specific gravity of 1 m3 of sand by the required amount of the finished mixture: 1600 kg/m3 * 0.36 m3 = 576 kg, and since the share of sand in the total solution is 75%, we also multiply by 0.75 - 432 kg of sand. Sand consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution is approximately 1200 kg/m3.
Consumption rates of cement and sand per cube of plaster mortar
Cement consumption per 1 m2 of plaster greatly depends on the quality of the wall covering, the required layer thickness and the number of large holes. Again, for clarity, we will give an example of a calculation, remembering that a mixture of 1 to 4 is usually used. Input parameters: it is necessary to cover 60 m2 of walls with plaster 2.5 cm thick.
Calculations of cement and sand consumption per 1 m3:
- Amount of materials in cubes. For 1 m2 you will need 1 * 0.025 = 0.025 m3 of solution, where a fifth is cement and the rest is sand. Using elementary mathematics, we determine that 0.02 m3 of sand and 0.005 m3 of cement will be required.
- For the entire area of the wall you will need: 0.02 * 60 = 1.2 m3 of sand and 0.005 * 60 = 0.3 m3 of cement.
- The specific density of cement is on average 1400 kg/m3 (fresh 1100-1200 kg/m3, and compacted 1500-1600 kg/m3). We determine the cement consumption: 0.3 * 1400 = 350 kg.
- Required weight of sand: 1.2 * 1600 = 1920 kg, we remind you that 1600 kg/m3 is the specific gravity of sand.
All calculations are simple; it is only important to choose the right brand of the initial mixture and the desired brand of output solution. Everything else can be easily calculated in a few mathematical steps.
What does consumption depend on?
The main requirement for concrete is to achieve the required strength after hardening. Based on this, in accordance with construction standards describing the quality of components, their ratio and technical characteristics are selected. This is done taking into account the strength grade of the composition; the recommended ratio of ingredients is indicated in specialized reference books. To calculate how much cement will be contained in 1 m³ of concrete, the following factors are taken into account:
- brand, density, required setting time;
- plasticity of the solution and its mobility;
- type of sand, fraction, presence of impurities, the proportion of which does not exceed 15%, otherwise this filler is subjected to pre-treatment - sifting or washing;
- fraction, type and other technical characteristics of crushed stone - flakiness, density, contamination, if it exceeds the norm, the crushed stone is cleaned;
- the presence of additional components that improve characteristics - hardeners or plasticizers.
Cement consumption per 1 m3 of concrete (M100, M200, M300, M400, M500).
To calculate how much cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of concrete, you need to know what it will be used for. On average, 1 m3 of concrete will require from 240 to 320 kg of cement, depending on the brand of cement. Next, we will consider which brand of concrete should be chosen for what purposes and what cement consumption will be in the manufacture of each of them.
Calculation rules.
When performing calculations, it is necessary to take into account the mobility of the finished solution. If the volume of cement is less than required, it will not be able to hold the binder and filler. As a result, after drying, concrete may crack under the influence of the external environment.
However, it is also not worth significantly exceeding the recommended value. This can also cause cracking. That is why each cube of the finished mixture can contain only one kilogram of hardener less or more than that obtained as a result of the calculation.
Let's find out how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of M200 concrete.
As a rule, M200 concrete is used for floor screed and foundation construction. The reason is that this brand is characterized by high strength and frost resistance. In addition, the material combines perfectly with the reinforcement frame. If we consider concrete in terms of load perception, then M200 is considered a medium-strength material.
But to prepare a high-quality product, it is necessary not only to select all the components correctly, but also to combine them in the correct ratio. Let us give the required quantities of all ingredients for concrete M200.
How much cement and other components does it contain:
- Portland cement – 265 kg;
- sand – 860 kg;
- gravel or crushed stone – 1050 kg;
- water – 180 l;
- plasticizer – 4.8.
If you decide to prepare the solution with your own hands, then using this proportion is not convenient. It is best to use the parts ratio approach.
In this case, the required amount of ingredients will look like this:
- cement – 1 part;
- sand – 2.8 parts;
- crushed stone - 2.8 parts;
- 20% of the total mass of the mixture should be removed from the water.
We calculate how much cement is needed per 1 m3 of M300 concrete.
In order to get 1 cubic meter. of high-quality M300 concrete, you need to use 366 kilograms or 244 liters or 5.88 bags of M400 cement, and in the case of using M500 cement, respectively: 319 kilograms or 213 liters or 4.26 bags of M500 cement.
When performing calculations, it was taken into account that the density of cement is about 1500 kg/m3. This indicator corresponds to the average looseness of cement - typical for material supplied in 50 kg bags. Compliance with the specified proportions of the content and quality of cement in concrete during its preparation will allow us to obtain ready-mix concrete of the M300 grade, which meets all construction requirements.
Consumption of cement grades M400 and M500 per 1 cubic meter of concrete.
If in order to obtain the necessary technical characteristics it is necessary to know the proportions of sand and crushed stone, then in order to calculate the financial costs of construction it is necessary to calculate the cost of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete. This data has been calculated and summarized in the appropriate tables:
| Concrete grade | Weight of cement, kg |
| 100 | 166 |
| 150 | 205 |
| 200 | 241 |
| 250 | 313 |
| 300 | 329 |
| 400 | 417 |
| 450 | 469 |
Similar reference data have been developed for M500; if necessary, this indicator is calculated using figures for the proportions of the components for preparing the mixture.
Drawing up proportions.
To calculate the amount of cement spent on a cube of concrete, you need to know the brand of the mixture; in addition, the brand of the binder used is also taken into account. The proportional ratio of the components is indicated in special tables. In construction, M400-M500 are more often used, and the proportion is calculated in mass parts.
| Concrete grade | Proportion by weight cement/sand/crushed stone |
| 100 | 1/4.6/7 |
| 150 | 1/3.5/5.7 |
| 200 | 1/2.8/4.8 |
| 250 | 1/2.1/3.9 |
| 300 | 1/1.9/3.7 |
| 400 | 1/1.2/2.7 |
| 450 | 1/1.1/2.5 |
| Concrete grade | Proportion by weight cement/sand/crushed stone |
| 100 | 1/5.8/8.1 |
| 150 | 1/4.5/6.6 |
| 200 | 1/3.5/5.6 |
| 250 | 1/2.6/4.5 |
| 300 | 1/2.4/4.3 |
| 400 | 1/1.6/3.2 |
| 450 | 1/1.4/2.9 |
This means that to prepare M300 concrete from M400 cement you will need to take 10 kg of cement, 19 kg of sand, 37 kg of crushed stone. The result will be 66 kg of finished material. The average density of the mixture is 2200 kg/m³, so the mass of the binder component consumed is 2200/66*10≈330 kg. Such calculations have already been compiled into special tables to facilitate the work of designers and builders.
Selecting the required class of concrete.
The required grade of concrete must be indicated in the design documentation for the construction site. If the construction is carried out independently, you should decide on the brand of the mixture, since this will decisively affect the strength and cost of the building or structure being constructed.
The purpose of the most common grades of concrete is given below:
- M100 - used for constructing concrete footings, installing parquets, and small architectural forms;
- M150 – used for constructing paths and sealing fence supports;
- M200 – for the construction of walls, porches;
- M250 – production of monolithic foundations, grillages, foundation slabs, light-loaded floor slabs, stairs, retaining walls;
- M300 – for any loaded structures: walls, ceilings, foundations;
- M350 – load-bearing walls, columns, floors, beams, monolithic foundations.
Additives for concrete mortar.
- Modifiers. Designed to increase the strength and frost resistance of concrete.
- Plasticizers. Increases the mobility and water resistance of the mixture.
- Mobility regulators. Allows you to extend the setting period and maintain mobility during transportation.
- Anti-frost additives. Ensure normal setting of the solution at low temperatures, down to minus 20 degrees.
- Setting accelerators. They increase the setting speed, ensuring the fastest possible strength gain in the first day.
When using additives, the consumption of materials per 1 m3 of concrete should be determined taking into account the manufacturer’s recommendations. Violation of the instructions for use can have the completely opposite effect.
Determining the weight and volume of cement for the concrete mixture
Both experienced and novice builders are often interested in how much cement is needed per cube of concrete. Considering several grades of strength of cement and concrete mixture, remembering the quantitative indicators of cement and other components of concrete is not easy, and it is not necessary. It is enough to have this article before your eyes, which indicates how to correctly calculate the optimal amount of cement per cubic meter of concrete mortar.
The composition of concrete includes:
- cement;
- sand;
- crushed stone (gravel);
- water;
- optionally - plasticizers, reinforcing additives.
The required grade of concrete is determined based on future loads on the structure and construction purposes. If large loads on concrete are envisaged, then the grade of cement and grade of concrete required is higher. The higher the grade of cement, the less it will need to be added to the mixture. The permissible error for the inclusion of cement is 1 kg, and for crushed stone it is 5 kg.
Even before purchasing building materials, it is advisable to calculate how many bags of cement per 1 cubic meter of concrete will be required.
Using convenient packaging of 50 kg, we will decide on the quantity.
- Concrete mixture M100 requires 166 kg of cement, that is, 4 bags. We always round up.
- M150 → 205 kg of cement = 4 bags + 5 kg of cement.
- M200 → 241 kg of cement = 5 bags of 50 kg.
- M250 → 300 kg of cement = 6 bags of 50 kg.
- M 300 → 319 kg of cement = 6 and a half bags.
- M 400 → 417 kg of cement = 8 and a half bags.
- M 450 → 469 kg of cement = 10 bags of cement, 50 kg each.
If, when purchasing building materials, it is convenient to determine how many bags of cement will go to 1 cubic meter of concrete, another method is also used during the construction process. Practicing builders find it convenient to measure the amount of cement and other components in bulk parts, such as buckets or shovels. To do this, you need to know the ratio of cement, sand and crushed stone.
So, how much cement M 400 is used per cubic meter of concrete in the following proportions:
- Concrete M100 - 1 part cement (C) + 4.1 parts sand (P) + 6.1 parts crushed stone (Sch). 1 liter of cement produces 7.8 liters of concrete.
- Concrete M 150 - 1 tsp C + 3.2 tsp P + 5.0 tsp Sh. 1 liter of cement yields 6.4 liters of concrete.
- Concrete M200 - 1 tsp C + 2.5 tsp P + 4.2 tsp Sh. From 1 liter of cement you can produce 5.4 liters of concrete mixture.
- Concrete M 250 - 1 tsp C + 1.9 tsp P + 3.4 tsp Sh. From 1 liter of cement we get 4.3 liters of concrete.
- Concrete M 300 - 1 C + 1.7 P + 3.2 Sh. 1 liter of cement gives 4.1 liter of concrete.
- Concrete M 400 - 1 C + 1.1 P + 2.4 Sh. We produce 3.1 liters of concrete from a liter of cement.
- Concrete M 450 - we take the proportion of cement, sand, crushed stone 1: 1: 2.2, respectively. 1 liter of cement = 2.9 liters of concrete mixture.
It’s clear how to calculate the amount of cement per cube of concrete, now let’s look at the purpose of the main concrete strength grades. M 100 concrete is used to fill road bases and curbs. For general construction work and the construction of small buildings, a concrete mixture of grade 150 is used. Pouring foundations and the construction of buildings and structures requires a special approach and a more durable grade of concrete 200. Monolithic foundations and flights of stairs are constructed from concrete 250. When creating a high-quality concrete mixture, pay attention to such characteristics as density, rigidity, and plasticity of the mixture. Use clean, homogeneous building materials in dry form without impurities. Accurate calculation of the amount of cement, sand and crushed stone makes it possible to save money, prevent overuse of materials and avoid purchasing missing components during the construction process.
Consumption rates for cement and sand for concrete and other mortars
Looking at bags of cement and a pile of sand, not every developer feels calm and confident. He is tormented by the question: what proportion should be chosen for the solution so that it turns out strong enough and does not “eat up” extra money?
Sprinkling “by eye” is stupid and dangerous, especially when it comes to critical concrete work on the foundation or brickwork. Following the principle “the more the merrier” is also not an option. When it comes to cubes, such a rule can ruin the developer.
Another question that arises in this regard: how to control the work of the builders who are tasked with preparing the mortar and concrete? You can’t keep track of everything, so there is no guarantee that the cement will not go “to the left”, and the foundation and masonry will not soon collapse.
How much material is needed
We often encounter problems such as low-quality solutions. It can end up either too runny or too thick, and this leads to a whole host of problems down the road. Therefore, before starting work, you need to clearly calculate how many bags of cement. There are several basic rules for counting, in particular, you need to pay attention to the following nuances.
- The less cement you add, the higher the mobility of the concrete. Therefore, the calculation is made as accurately as possible, plus or minus 1 kg. As for crushed stone, in this case an error of plus or minus 5 kg is allowed. Please note that if there is a lack of materials, the solution will quickly become unusable, so calculate exactly how many bags of cement and crushed stone you need.
- Brand. It is worth remembering that cement can be different and it must be selected based on this indicator. The grade of material must be twice the value of the grade of solution. At the same time, each type of cement requires a different amount to obtain high-quality concrete.
- The calculation of building materials for making the mortar requires the presence of 9 parts, of which 1 part is cement, 3 parts are sand and another 5 are crushed stone. But again, a lot depends on the brand. For example, the ratio of M-400 grade to sand is approximately 1:2, and M-600 grade is 1:3. It is believed that for one cubic meter of concrete approximately 0.8 cubic meters of crushed stone and 0.5 cubic meters of sand should be used. However, we must not forget that for 1 m3 of solution you cannot use more than 350 kg of cement (7 bags of 50 kg or 14 of 25 kg), otherwise it may quickly crack.
“Old-father method” or current SNiP?
Experience is a good thing, but we should not forget about building regulations. They take into account all the factors associated with the preparation of mortars and concrete (purity, coarseness, moisture content of sand and crushed stone, cement activity and water quality).
Therefore, when preparing for work on pouring a foundation, screed or laying walls, do not be lazy to look at the GOST tables. You only need one or two lines in them. They clearly describe what the cement consumption per cube of mortar should be to obtain the required strength (grade).
Here is a simple “squeeze” from SNiP, which will help prepare a high-quality mortar for masonry and screed . After studying it, remember that the given consumption rates differ slightly from practical values.
Cement brand
Brand of solution
Cement consumption rate for making 1 m3 of mortar
The reason is that they are produced from standard preparation conditions (air temperature +23C, medium-grained sand, ideally clean, its humidity no more than 7%, etc.). It is not realistic to ensure standard parameters for mixing at a construction site, so it is better to purchase cement with a small reserve (10-15%).
The answer to the question of how much cement and sand you need per cube of concrete will be given by the following standards:
Concrete grade
Cement consumption M500 kg/1m3
When making concrete, it is important to know not only the amount of cement, but also the standard volume of sand and crushed stone. The following table will be useful for calculations.
Volumetric proportions for various grades of concrete
Concrete, brand
Ratio of cement/sand/crushed stone in liters
cement M 400
cement M 500
The required sand consumption per 1 m3 of solution is 1 cubic meter . Some developers are mistaken in believing that the volume of cement increases the volume of the finished mixture. This is wrong. The cement is very finely ground, so it is distributed in the voids between the sand, without increasing the total volume of concrete and mortar. Therefore, for 1 m3 of sand we can add 200 and 400 kg of cement, obtaining the same 1 cubic meter of solution.
Water is added to the mixture according to a simple proportion - half of the total weight (not volume!) of cement . In this case, you need to take into account the actual moisture content of the sand and pour water in small portions so that the solution or concrete does not turn out to be too liquid.
The consistency of the solution according to the standards is determined by the amount of sediment of a standard metal cone lowered into the mixture. You are unlikely to be able to conduct such a test on a construction site. Therefore, just remember that the thickness of the masonry mortar should be such that it is not too hard, but rather flexible and does not leak out of the seams. For the screed, the mortar and concrete must be of medium thickness so that they can be easily compacted and leveled according to the rule.
Cement calculation method
Known methods for calculating volume are based on the total amount of concrete required and are not very complex. To use them, you should carefully study the project and become familiar with the main dimensions of the future concrete structure. Knowing the proportion in which the concrete mass is mixed, you can easily calculate the required amount of cement.
In this case, packages or sacks are taken as the calculation unit, containing, as a rule, from 40 to 50 kg of dry composition.
In more detail this process looks like this:
- First of all, the volume of concrete that is needed to build the foundation is calculated (see the article “Proportions of concrete for the foundation”). At this stage, the calculation comes down to summing up the volumes of all elements of the monolithic structure. For slab-type foundations, a simple multiplication of the main dimensions is carried out (in accordance with the project data).
- After this, you should decide on the qualitative composition of the future concrete mass, the characteristics of which are selected based on the calculated loads on the foundation, as well as taking into account the composition of the soil.
- Based on all the data listed above, the required grade of concrete is selected, which determines the percentage of cement per cubic meter of the structure. At the same time, the question of the need to use special additives that significantly simplify the work with the mixture under specific conditions is being investigated.
- At the final stage of the calculations, the required amount of aggregates (sand and crushed stone) is determined.
Cement consumption for masonry
When preparing cement-sand mortar for brickwork, take into account that the construction of 1 m2 of a wall with a thickness of 1 brick (250 mm) will require at least 75 liters of M100 grade mortar. The proportion of cement (M400) - sand here is 1:4. Cement consumption for bricklaying with this ratio will be 250 kg per 1 cubic meter of sand.
Water, as we have already said, is taken at the rate of 1/2 of the total weight of the cement used.
Translating into “bucket standards” that everyone can understand, let’s say that for one 10-liter bucket of cement (M500) we need four buckets of sand and 7 liters of water. We calculate the amount of water based on the weight of the cement in the bucket (10 liters x 1.4 kg x 0.5 = 7 liters).
To quickly determine the need for cement masonry mortar for walls of different thicknesses (per 1 m3), you can use the following table:
Wall thickness in bricks
Cement consumption for the foundation: calculation technology
Quite often, for certain reasons, private developers prefer to prepare concrete themselves. Of course, you need to calculate in advance the required volume of the mixture, which is done using a fairly simple arithmetic operation. But due to the differences in the types of foundation structures, the calculation formulas also differ. If you have practice preparing a cement-sand mixture , for example, for brickwork, then the process will be more fun.
Those who are especially lazy can calculate the amount of cement required to build a foundation using a calculator that is available online on specialized sites. The amount of material can only be determined approximately in this way, which is not entirely acceptable for a small construction site.
Volume calculation formulas for certain types of foundation structures:
- Slab - just multiply the area and height of the planned slab V = S x H.
- Tape - the product of the total length of the structure and the cross-sectional area V = S x L.
- Pile - determine the cross-section of one support and multiply the result by the number of piles V = S x H x N, if the pillars are cylindrical, then the cross-section is calculated using the formula 3.14 x R².
Now you can directly begin to calculate the volumes of the cement mixture. It should be taken into account that the recommended Portland cement is grades M400 and M500. Depending on the design marking of the finished concrete, certain masses of components are used for its preparation.
Below is a table of the W/C ratio (water/cement) in order to ultimately obtain a certain brand of concrete mortar.
If the hydraulic solution is planned without the use of crushed stone, then the B\C coefficient should be reduced by 0.1. But this is not all the data, for example, the amount of water depends on the volume of sand and the size of the crushed stone fraction. Basic proportions 1:3:5 or 1:4:4 (Portland cement: sand: crushed stone) do not take these factors into account, so the calculation of cement for the foundation will not be reliable. The required ratios are presented in the table:
Calculation example
Let's say we have the following material at our disposal:
- Crushed stone fraction 25 mm (ρ = 2700 kg/m³).
- Fine-grained sand (ρ = 2500 kg/m³).
- Portland cement M400 (ρ = 3000 kg/m³).
The technology for further actions is as follows:
- From Table 1 of water-cement (W/C) values, we find out that for the M300 brand of mortar (and we need such a mixture) the coefficient is 0.53.
- Using table 2 of water consumption, we determine that for 1 m³ of solution, 195 liters of water (0.195 m³) will be needed, from here we calculate the required mass of Portland cement: 195/0.53 = 368 kg.
- Now we calculate the volume of fillers (sand and crushed stone) per 1 m³ of mixture: 1-((368/3000)+0.195) = 0.682 m³ (682 l).
- Next, according to Table 2, we determine the percentage of sand - 46% (0.46), from which it follows that its volume: 682 × 0.46 = 313.7 l (0.314 m³).
- To find out the amount of crushed stone, you need to subtract the amount of sand from the total volume of fillers: 682-313.7 = 368.3 l (0.368 m³).
- Taking into account the density and volume of fillers, you can calculate their weight: sand - 0.314 × 2500 = 785 kg; crushed stone – 0.368×2700 = 993.6 kg.
As a result, to prepare 1 cube of concrete mortar grade 300 from Portland cement M400 you need:
- 195 l of water;
- 368 kg of Portland cement;
- 785 kg of sand;
- 993.6 kg of crushed stone.
For a complete calculation, you should multiply the resulting numbers by the number of cubes of solution required for work. As you can see, the procedure for counting components is no more complicated than connecting a pass-through switch , so it will take little time.
How many bags of cement should I buy?
Before things get to the point of mixing, it is important for the developer to know how many bags of cement will have to be purchased. Here you should also build on standard consumption rates.
Let's say we need to calculate the cement consumption for floor screed . The optimal proportion to ensure high strength is 1:4. For this work we will need ¼ cubic meter of cement. To convert cubes into kilograms, use the average bulk density of the binder: in 1 liter - 1.4 kg of cement.
1/4 of a cube is 250 liters. Multiplying them by 1.4 kg, we get 350 kg of cement. So, in total we will have to purchase 350/50 = 7 bags of cement (50 kg each) or 14 bags of 25 kg each.
You can calculate the binder consumption per 1 m2 of screed using the “reverse” method . With a thickness of 10 cm, filling one “square” will require 0.1 m3 of solution. It contains 10 times less cement than 1 cubic meter: 350 kg/10 = 35 kg. For a screed 5 cm thick we need 35/2 = 17.5 kg of M500 cement.
The rate of cement consumption is greatly influenced by its activity. It is determined experimentally by mixing control samples and testing them for strength. This method is not suitable for the average developer. A rule of thumb to follow when purchasing and before using is shelf life.
The loss of activity by cement can reach 20% in one month. Therefore, after keeping this material in the garage for three months, instead of grade 500 indicated on the label, you will receive grade 400. When using such a binder for mortar or concrete, take the consumption rate specifically for this (lower) grade. If cement waits for its “finest hour” for six months, then it is not suitable for anything other than disposal to a landfill.
Vigilance should also be exercised when purchasing binders, requiring the seller to provide a certificate for the purchased batch, which indicates the factory production date.
How to correctly determine the volume of cement for the foundation?
Exceeding or decreasing the norm of constituent rocks increases the time interval for complete maturation of concrete. Basic mathematical knowledge and a calculator will help you correctly calculate cement consumption. Incorrectly calculated material can be costly for the developer. To calculate exact numbers, you need to measure the volume of concrete mixture being poured. Cement costs are determined in 1 kg/1 m. How much cement is needed for the foundation depends on the type of material used. For concreting the frame, a binder component with indicators from 200 to 500 is used. The most popular cement is M 300, which can be calculated using an online calculator. Its physical and technical characteristics fully comply with safety standards. It is irrational to use grades 600 - 800 for concreting the foundation. They have high strength, which is justified in using for multi-story buildings, the construction of dams, bomb shelters, military complexes, and not for home construction.
Knowledge of the types of building materials will help you accurately calculate how much cement is needed for the frame. This will allow you to evaluate and calculate the costs of building materials using estimates.
Article Rating