Double hollow porous brick is a four-kilogram ceramic or clay cement building material, the height of which is 14 cm, width - 12 cm, length - 25 cm. The product has twenty-one square pores to reduce its weight, increase its functional use in the construction of tall buildings and structures .
Features and characteristics of double hollow bricks
Hollow porous (containing pores) brick has several other names. For example, slotted (that is, containing slits), perforated (that is, having holes in its design) or effective (that is, effectively performing many construction functions). The last of the given names most fully reflects the essence and purpose of using this brick, since its effectiveness when compared with other types of standing blocks increases significantly. This happens thanks to:
- Savings in the bonding solution, which is applied to fewer faces (the total area of the faces spread or covered with the solution is significantly reduced);
- The durability of the material used (double hollow brick, when properly laid, will last at least fifty years, and in the absence of constant destructive factors for such building materials - a much longer period);
- Retention of additional heat in winter and release of cold air in summer, which eliminates the need to use additional thermal insulation materials and, therefore, save on their purchase and installation;
- Savings on the original material, which is consumed in less quantity during production than for the solid version;
- The lightness of the structure being built from double hollow bricks (the main role is played by internal voids);
- Regulation of the microclimate inside a brick room without the use of additional costs and special building materials due to the unique vapor-permeable properties of the material.
Advantages and disadvantages
Solid artificial stone has great strength and frost resistance. You can find this type of brick with technical voids. They are necessary to reduce internal stress during the firing process.
The full-bodied, low-porosity look is manufactured without voids. Thanks to this, it has low moisture absorption (within 8%) and high thermal conductivity.
Its disadvantage can be called its low heat-protective performance. To reduce heat loss and brick consumption, it is best to use well masonry when constructing walls. This type of masonry means that the masonry of the walls looks like two independent walls, having a thickness of half a brick. To connect them, vertical and horizontal bridges are laid out, forming closed wells. Next, the resulting wells must be filled with slag, lightweight concrete and expanded clay.
Another disadvantage is the unattractive appearance of the walls. The surface laid out on it will be rough. Therefore, internal and external walls will need to be plastered.
A common brand of solid brick is M125. The brand indicates the degree of strength of the product; the higher it is, the stronger the material.
Production Features
This type of ceramic material is characterized by particularly high strength, density and frost resistance. It is made from refractory clays using special technology. The firing process involves sintering raw materials at temperatures much higher than those required to produce conventional bricks.
The price of such material is quite high, but its use in difficult operating conditions is quite justified. For example, facades finished with it practically do not allow contamination to enter the surface structure, due to which they retain an attractive appearance for a long time and do not require repairs.
Ceramic materials are made in two ways. Most often - plastic, in which products are squeezed out using a belt press from a clay mass with a moisture content of about 30%, followed by drying and firing. The second method involves semi-dry pressing of raw clay with a moisture content of up to 10%, which is advisable in the production of building materials for wet conditions.
Basic material classification
Hollow bricks are classified according to the shape of their holes:
- with oval shaped holes;
- with rectangular;
- with round;
- with square.
By purpose:
- if the material on the front side has a textured pattern, then it can be used for laying decorative fencing;
- if the product has beveled corners or rounded edges, then it is used for the construction of vaulted structures and arches in a building.
By firing method:
- in tunnel kilns;
- in ring furnaces.
By type of material:
- cement;
- clay.
According to characteristics:
- thermal efficiency. This is achieved thanks to a design feature, namely the presence of voids;
- degree of porosity;
- firing temperature.
Advantages of hollow bricks
The advantage of bricks with different shapes of holes is that during operation there is less chance of cracks forming in such material. The optimal void ratio should be 1:1 or 50%.
During the laying process, this building material must be laid on a thick mortar. Another advantage of this material is its attractive aesthetic appearance. If the seams are done correctly, further finishing may not be necessary.
General characteristics of hollow bricks
If you try to create a generalized “portrait” of an ordinary hollow brick of a standard size, then its technical parameters will look like this:
- average material density 1000-1450 kg/m³,
- coefficient of working thermal conductivity of the material is 0.3-0.5 W/m°C,
- degree of frost resistance 15-50 cycles,
- specific porosity 6-8%,
- strength grade 75-250,
- color shades from light brown to dark red.
And this is what the corresponding technical parameters for ultra-efficient hollow bricks look like:
- average material density 1100-1150 kg/m³,
- coefficient of working thermal conductivity of the material is 0.25-0.26 W/m°C,
- degree of frost resistance 15-50 cycles,
- specific porosity 6-10%,
- strength grade 50-160,
- shades of color various variants of red.
Thus, currently, a demanding consumer has the opportunity to choose from a huge array of brick products a building material that, in terms of its physical and aesthetic qualities, is ideal for the customer and his future home. And among this “sea of bricks” we can very well distinguish, with its excellent properties, hollow brick, a faithful assistant to a person in creating harmonious home comfort.
Hollow sand-lime brick
According to GOST, both silicate stones and bricks can be hollow. A distinctive feature of the latter is the presence of holes.
Concept and features
Regulates the properties of both solid and hollow SK GOST 379-95. The brick is made in the form of a parallelepiped; the holes are assumed to be non-through and should be located perpendicular to the bed. The wall thickness must be at least 10 mm. However, by agreement with the customer, the number and shape of holes can be changed if this does not contradict established standards.
Hollow brick is characterized by the following features:
- less weight - voids make it possible to lighten the product without a large loss in strength, which is very important when constructing storey buildings;
- lower thermal conductivity - voids filled with air increase the thermal insulation properties of the product. Thermal conductivity is 0.56–0.81 W/(m*C);
- ease of installation due to the lighter material;
- The density of the product is lower - 1450–1550 kg/cubic. m. In general, hollow concrete is used in the construction of lower buildings;
- however, thanks to the voids, the water absorption of the brick also increases to 8–11%, which means less frost resistance.
The following video is dedicated to the features and concept of solid sand-lime brick:
Product types
GOST allows for different hollowness of the product. The classification is as follows:
- the degree of hollowness is 28–31%, that is, there are 14 holes in the brick measuring 30–32 mm;
- the degree of hollowness reaches 22–25% - the product has 11 cells with a diameter of 27–31 mm;
- 15% - implies 3 cells measuring 52 mm.
The thickness of different types is as follows:
- single sand-lime hollow brick – 65 mm. These sizes are called standard. This briquette weighs 3.2 kg;
- thickened or one-and-a-half silicate hollow brick has a thickness of 88 mm. Weight of one block – 3.7 kg;
- double - according to GOST it is called silicate stone. Its thickness is 138 mm, weight reaches 5.4 kg
Front and private SK
Material is produced for ordinary wall masonry, where some other finishing layer is expected, and material that creates a fairly attractive surface that does not need cladding. Accordingly, the products are called ordinary and facial.
Their requirements for appearance differ, but otherwise their characteristics are completely identical.
- The facial SC has a relatively smooth outer surface and very precise geometric parameters. The surface may be painted or unpainted. In any case, the shade must match the template, and color spots or color changes are not allowed. In the case of facial KS, this is considered a serious defect.
- Products according to GOST must have two front planes - a splice and a spoon. However, with the customer’s consent, bricks with one front surface can be produced. Rounding of ribs no more than 6 mm is allowed.
- Cracks, dull ribs, chips, as well as swelling, peeling or fine cracks are not allowed.
The requirements for ordinary products are much lower. However, here too there are very specific standards: defects in any case should not affect the strength characteristics.
- An ordinary SC can change color, and in a very wide range. Swelling and peeling are acceptable.
- Cracks up to 40 mm long are allowed - no more than 1, chips at corners up to 15 mm - no more than 3, broken edges up to 15 mm - up to 3.
- There should be no fractures or inclusions of other materials with a diameter of more than 5 mm.
We talk about the application and prices of hollow silicate bricks of different sizes below.
Application and cost of material
- SK is used in multi-story construction, since the strength of sand-lime brick allows pressure up to 2.5 MPa. However, other properties of the product somewhat limit its use.
- The thermal conductivity of hollow SC is lower than usual. However, it is by no means a thermal insulation material. Its use is based precisely on the greater lightness of the blocks.
- Load-bearing, self-supporting walls, interior partitions, unloaded structures, and so on are erected from SF.
The cost of the material depends on the type:
- single facing costs from 10 to 26 rubles. per piece;
- thickened facial – up to 29 rubles;
- an ordinary single will cost 9.5 rubles;
- thickened – from 10 rub. per piece;
- double brick or stone costs from 17 rubles.
Types of hollow bricks
Like other material options, hollow brick has several types depending on the appearance, some characteristics and production method:
- Clay (ceramic, clinker, dry pressed).
- Limestone (silicate, brick based on crushing rocks and cement).
Depending on the scope and purpose, hollow bricks can also be divided into:
- Private. Used during construction and renovation. It has the highest strength, as it is expected to withstand the main load. It is created only by firing, which prevents deformation of the raw material and ensures the appearance of additional pores for effective heat retention.
- Facial or pouring. Used for external decoration of walls and facades of residential, industrial, industrial premises. It has an attractive appearance (in addition to the main materials, various dyes can be added to the composition, which give the finished product a special shade).
- Foam diatomite. A type of hollow brick that is characterized by maximum resistance to elevated temperatures. Suitable for the construction of structures in hot climates, as well as for the design of some sections of pipes and chimneys.
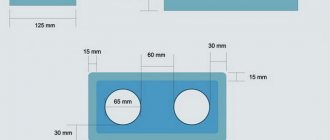
Hollow bricks are manufactured according to GOST standards and have standard dimensions: 250x120x65 mm. There are also thicker versions - one-and-a-half hollow bricks have a thickness of 88 mm, double ones - 138 mm. The dimensions of hollow bricks are suitable for the construction of various buildings. Due to its high performance characteristics, it is enough to use one and a half masonry to ensure the strength of the structure.
Solid sand-lime brick
Solid¸, as the name suggests, does not contain voids and is a monolithic silicate block. The weight of such material is correspondingly higher, but the strength is also higher.
We will tell you in more detail and in detail later in our article how much white sand-lime solid brick weighs, what dimensions and density it has.
Concept and features
The same GOST 379-95 regulates the products. Most of the requirements are the same for both hollow and solid modules, but there are differences.
The corpulent one has the following features:
- has higher strength - M300 grade material can withstand pressure up to 30 MPa when compressed, and up to 4 MPa when bending;
- water absorption reaches 7.7%;
- The frost resistance of solid stone is higher - grade material up to F 50 is produced, which means 50 cycles of complete freezing and thawing.
Varieties and characteristics
There are no voids in a solid module, however, a classification by density exists, since during manufacturing, by adding sand of different sizes, more or less porous blocks can be obtained.
- Bricks with a density of less than 1500 kg/cubic meter are classified as porous. m.
- Dense - material with a density higher than 1500 kg/cu m. The latter is selected for load-bearing walls of multi-story buildings.
Product sizes are standardized. The weight will accordingly be greater due to the higher density.
- Single - length is 250 mm, width is 120 mm, and thickness is 65 mm. The weight of such a block reaches 3.7 kg.
- One and a half - with the same length and width, it has a thickness of 88 mm. The weight of one-and-a-half silicate bricks (solid, hollow) ranges from 4.2 to 5 kg.
There are solid facing (facing) and ordinary sand-lime bricks. The requirements for them are completely identical to the requirements for a hollow SC.
This video will tell you why solid brick should be chosen for building a house:
Application and price of materials
Solid SK is, if not the basis of modern construction, then a very popular material. Its strength and durability guarantee the reliability of the building, and a multi-story one at that.
- However, its use in regions with cold climates is less justified, since despite all its good strength characteristics, the frost resistance of the material may be insufficient.
- Another limitation is the rather high water absorption. Although the properties of a solid SS in this sense are better than a hollow one, nevertheless, the foundation is not built from it, and it is not suitable for cladding underground floors.
The use of SK is standard - walls of all possible types, load-bearing and unloaded structures, any architectural details that can be formed from standardized blocks.
The cost of the material is more than affordable:
- A single facial will cost 17–36 rubles. for 1 piece A brick with one front surface may be cheaper. The color of the product significantly affects the cost;
- one and a half - from 15.50 rubles;
- the price of a single ordinary “starts” from 10 rubles.
- a one-and-a-half private costs from 9.35 rubles.
stroyres.net
Material Specifications
Thus, the dimensions, weight, and characteristics of ceramic bricks are regulated by GOST 530-2012, which, depending on them, divides these products into bricks and stones. The first are the well-known rectangular parallelepipeds, which, as a rule, easily fit in the hand, the production of which is possible both in a solid version and with voids.
The second are large and necessarily hollow products, starting from the size of a “double” brick, twice the usual size, and ending with stones 15 times the nominal value. It is taken to be an ordinary single ceramic brick; hollow or solid, it has unchanged geometric parameters: 250x120x65 mm, in relation to which the dimensions of other bricks and stones are determined.
The weight of these building materials, in addition to their size, largely depends on the presence of voids in them. Based on this criterion, solid products are distinguished - those in which there are no pores at all or their volume does not exceed 13%, and hollow ones, produced with voids of different sizes and shapes. The attitude towards one of these types is determined not only by the weight of the bricks, which affects the overall pressure of the building on the foundation, but also by a number of other characteristics of the material.
For example, a thickened (one and a half) hollow ceramic brick may not exceed a single solid brick in weight. Larger material with voids will exert approximately the same load on the foundation as a standard one without pores, and the construction period of the building and mortar consumption will be significantly reduced.
And this does not exhaust the advantages of hollow stones and bricks. In addition to economic benefits, their use allows you to simultaneously improve the sound and thermal insulation of the walls being built. They will be higher, the greater the volume of voids in the material. The most “warm” buildings are erected from special porous bricks, which have many small pores, or are more than half hollow.
Ordinary solid brick
As a rule, it is used for the construction of basement floors, foundations, pillars, basements, construction of external and internal walls and other structures. It is also quite often used in the construction of stoves, chimneys, and fireplaces. Ordinary corrugated bricks are used to build walls and partitions, which will then be plastered.
Solid brick must have greater compressive strength and be frost-resistant. It is sometimes produced with technical voids. This is done in order to reduce internal stress during firing. It is made without voids and with low porosity, so it has characteristics such as low moisture absorption (about 8%) and high thermal conductivity. If the outer walls of the house are made of this building material, then it will be necessary to make additional insulation.
Ordinary solid brick varies in size:
- single;
- one and a half;
- double;
- restoration;
- quadruple;
- Euro size, etc.
Ordinary hollow brick
Hollow brick is used to construct internal and external walls of buildings and structures. It cannot be used for the construction of basements, basements or foundations. This is explained by the fact that if water gets into its voids and freezes in the cold winter season, this will most likely lead to destruction or deformation of the structure. Hollow bricks vary in the shape of their holes:
- oval hole shape;
- rectangular;
- round;
- square.
Oval and round hole shapes reduce the likelihood that cracks will form during the manufacturing process. The production of this building material requires less raw materials than the sample described above (by 13%). Due to the dry air, which is closed in the volumes of the holes, the thermal insulation of this material increases. When using hollow bricks, you need to remember that the masonry mortar must be so thick that it does not fill the voids.
Even at the production stage, in order to improve the thermal characteristics of this material, it is made more porous. This is achieved by adding coal, sawdust, peat and straw to the clay. When fired, these materials burn out and form voids, making holey bricks. Builders also call them “light”.
Today, hollow bricks are more often used in construction. This is due to its better performance characteristics, lower cost and less load on the foundation. Walls built using this material can be twice as thin and still maintain the same high level of heat and sound insulation. The optimal void ratio is 1 to 1, that is, about 50%.
Loading and unloading of packages with finished products is carried out mechanically using load-handling devices. Under no circumstances should unloading be carried out by dumping or loading by bulk method.
The choice of a particular building material will primarily depend on the structure for which it is intended. For help in determining the final option, it is better to contact an experienced specialist.
1pokirpichy.ru
Brick grade 150: size matters
Compared to conventional single bricks, double bricks (grade 150) have a clear advantage in size. This positive difference allows the construction of large (tall and/or wide) buildings, including high-rise residential buildings, in a shorter time. The double brick is more than twice the standard height. Thus, laying each double hollow brick is much faster, more economical and easier than laying two regular bricks. In this case, savings are achieved both in time and in the consumable fixing solution.
Where are solid ceramic bricks used?
Due to its high density and frost resistance, artificial stone is necessary for the foundation, walls, columns, vault, and plinth. Used for masonry wherever high strength is required. The main component of red brick is clay, which is a fire-resistant material. Therefore, from time immemorial, chimneys, pipes, fireplaces, and stoves were built from ceramic materials. The silicate type is significantly inferior in fire and water resistance. Therefore, on beautiful, light-colored houses, it is the red chimney that can stand out, and wells are never made of white masonry.
Despite significant frost resistance, which is essential in the conditions of the Russian winter, the full-bodied version loses in heat resistance to the hollow one. High density serves as a conductor of cold. To ensure that housing always loses expensive heat, they practice well masonry (in two walls), use insulation, or increase the thickness of the walls. But massive walls must be placed on a reinforced foundation. And such bills do not please the owners. The weight of a full-bodied product is 3–4 kg. For 1 m2 you need to take 52 pieces, and this is already 150–200 kg. Taking into account the area of the external walls, which is additionally increased due to the thickness, the cost of the necessary materials soars significantly.
A good way to reduce construction costs is to buy ordinary bricks
Using the term “solid” often means ordinary brick, which does not differ in aesthetic characteristics and does not have facing edges. Although, in fact, the full-bodied appearance represents almost all varieties of facing, clinker and decorative stones. The color and texture of ordinary products leave much to be desired. But the lack of costs for creating a neat appearance allows manufacturers to set the lowest prices for this product.
It can be used without restrictions: foundations, walls, arches and openings, wells, fireplaces, cellars. At their own discretion, developers additionally decorate buildings made of unsightly material with plaster. Industrial and utility buildings are often left without decorative treatment.
Purpose of ceramic bricks
According to their purpose, ceramic materials are also divided into types, of which there are basically two: ordinary (otherwise called construction or ordinary) and facial (finishing, facing). There are several more subtypes, such as shaped, facade, glazed, figured and others. Moreover, they can belong to both the first type and the second.
For example, figured brick, which allows the construction of complex architectural forms (arches, columns, etc.), is used both for construction and finishing work. The same applies to the texture of the edges of the poke and spoon. It can be smooth or corrugated, regardless of whether the brick is ordinary or facing, ceramic, hollow or solid, the price depends more on the technical characteristics of the products than on their type.
It is customary to classify clay materials as a separate type, specifically intended for the construction of stoves and fireplaces. Contact with open fire requires the use of a special fire-resistant brick called fireclay for the internal surfaces of the stove. Made from special flame-resistant clay, it can withstand maximum temperatures of up to 1600°C. It is recommended to add the same clay to the solution when laying.
For cladding and external finishing of stoves and fireplaces, traditional ceramic facing hollow single brick, for example, in a shaped design, is suitable. Special material is also required when paving courtyards, streets or roads. For this purpose, as well as for cladding facades, plinths and finishing floors in production workshops of enterprises, clinker bricks are used.
Why can you buy ceramic hollow bricks?
The presence of voids significantly reduces:
- weight of the building;
- cost of materials;
- possible places of application.
And significantly increases energy efficiency. The minimum number of slots is 13%, and the maximum is 50% of the total surface of the rectangle. The air cushion in the openings ensures low thermal conductivity. The same effect is present in porous expanded clay, aerated concrete and similar materials. Most often, the average ratio of voids and ceramics is taken into account during production. The minimum does not provide the necessary thermal insulation, and the maximum makes the stone less durable. A hollow single weighs 2.3–2.5 kg.
Ceramic hollow bricks are used only for laying walls in houses up to 3 floors high and constructing partitions. For example, for interior walls in high-rise buildings, where the weight of the structure is of fundamental importance.
In addition to low strength, this material is not suitable for the construction of cellars, foundations and plinths because the voids collect water. According to all the laws of physics, water freezes at sub-zero temperatures, increasing its volume. This process destroys the artificial stone from the inside.