About terminology: what are HDF and MDF - decoding of abbreviations, what are the differences and differences
Fiberboard refers to all products made from fluffed wood, regardless of their density. But fiberboard is also often referred to as a specific type of wood pulp product.
This is one that is characterized by low (or rather, not increased) density. The reason for the ambiguity of one term obviously lies in the production process.
Articles on the topic (click to view)
- Metal kitchen rack for appliances
- Instructions for the electric stove “classic plus”
- How to choose an electric stove with 4 burners and an oven for the kitchen
- Sofa in the bay window for the kitchen
- Lighters for gas stoves
- Small enamel kitchen sink
- Electric Turk with automatic shut-off when boiling
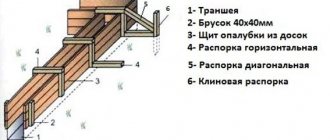
The technology for manufacturing loose slabs is the simplest: the stage of forming the “body” of the product is limited to drying the molding mixture on a fine metal mesh.
Denser slabs are, strictly speaking, a modification of conventional ones. The manufacturing process for them is somewhat complicated. Therefore, probably, MDF and HDF have separate names, while the loose ones have a common name. It is convenient if, when talking about loose fiberboard, they add: “low density”, “insulating”, “light” or “obtained by dry method”.
MDF, what kind of material is it? There is another trend: all fiber boards are called MDF . Perhaps the reason is the popularity of products that are compacted, but not too much, with an optimal price-quality ratio, with the widest possible application.
How to care for the material?
Housewives often complain about MDF panels, as stains from hands, grease and water remain on laminated and varnished materials. How to clean them without harm and effectively?
- Soapy water will do. But there is one trick, do not wipe in sunlight, close the curtains. When water heats up, it quickly evaporates and leaves stains. Wipe with a dry cloth.
- Do not use products with chlorine; it can dull glossy surfaces.
- You can’t take ammonia either.
- Do not polish with furniture wax. The panels sometimes swell from it.
- If the contamination is severe, you can take regular alcohol and treat it with it.
To reduce dust settling, use a regular antistatic agent.
Now you can choose a product made from MDF, knowing what it is and how to care for it, you won’t be confused in the store.
Manufacturing of fiberboard
Main components of fiberboard:
- binders - polymer or mineral.
Expert opinion
Smirnova Ekaterina Anatolevna
7 years of experience in interior design, professional architect
The slabs are formed after fluffing the wood to a fiber state. Such fine mechanical grinding is not possible without first cutting and softening the wood (with hot water or steam).
Fluffing is one of the ways of porousization of a material (that is, the inclusion of very small voids evenly distributed throughout the volume into its body). Relatively dense raw materials (sawdust, shavings, wood chips, slabs) after fluffing become fibrous material.
Forming of products begins with mixing a mass of wood fibers with water and additives (fire retardants, antiseptics, water repellents). The raw material suspended in water is poured onto the fine copper mesh of the casting machine.
After the water is filtered (this process is accelerated by a vacuum unit), a carpet of wet fiber remains on the mesh.
The next stage of board production is different for light fiberboard, MDF and HDF:
- to create a soft, low-strength, highly porous slab, the fiber is only dried (in a roller dryer);
- the result of compaction on a hot press (t = 150–165 °C, p = 1–5 MPa) is a fine-fiber material and, at the same time, hard and durable: medium- and high-density fiberboard.
The difference in density and physicochemical properties of solid slabs is achieved by changing the hot pressing time. Soft and semi-hard slabs are lightly pressed, and final drying occurs without compaction.
The same mass, completely dried under high pressure, becomes a solid finishing fiberboard. When making superhard slabs, the suspension is enriched with phenol-formaldehyde polymer (synthetic resin) before dehydration.
Fiberboard - wood fiber boards.
Fibreboard is a sheet material made by hot pressing a mass of wood fibers formed into a carpet. These fibers are obtained by steaming and grinding wood raw materials. They are individual tissue cells, their fragments or groups of wood cells.
The raw materials are sawmill and woodworking waste, technological chips and firewood. To improve the performance properties, strengthening substances (for example, synthetic resins), water repellents (paraffin, ceresin), antiseptics, etc. are added to the mass. The formation of a carpet can be carried out in an aqueous environment to obtain slabs of one-sided smoothness (wet production method) or in an air environment to obtain slabs of double-sided smoothness (dry method).
Types of fiberboard produced
The mechanical and performance qualities of wood composites significantly depend on their density (ρ). The greater the weight per unit volume, the higher the strength and rigidity of the material.
Depending on density, hardness and weight, wood fiber boards are divided into types by state authorities and manufacturers - if they rely on technical specifications when producing products.
The most common gradation is:
- light fiberboards are those boards whose density does not exceed 500 kg ⁄ m3. They are divided into semi-hard (ρ = 400–500 kg ⁄ m3) and soft (ρ 950 (hdf).
In Austria, fibreboards have been developed and are awaiting the start of industrial production, the density of which changes in waves in volume. The strength of such plates is higher than that of homogeneous products with the same thickness and average density (and, accordingly, the same weight).
From hard slabs:
- form partitions;
- ceilings are hemmed. Here about finishing the MDF ceiling;
- lay floors;
- make doors;
- built-in furniture.
Walls and ceilings are lined with finishing products.
Insulating fibreboards form a heat- and sound-insulating layer of walls and ceilings, and an underlying layer in the floor structure.
These are soft and semi-hard, with the lowest bending strength of the slab. The use of insulating fiberboards is especially widespread in prefabricated panel construction.
For more information about MDF and HDF, watch the video:
Installation methods
Installation of MDF panels on the ceiling or walls can be done in two ways - glue or frame. Let's take a closer look at them.
Adhesive
This is the simplest and fastest method. In this case, preliminary preparation of the material is very important - it must be perfectly clean and accurately measured. Using the glue method, you can lay out both the walls and the ceiling from MDF panels - if you do all the work yourself, this option is preferable. It will take less time and effort, and will not require special construction skills.
When purchasing liquid nails for attaching MDF boards, carefully check the color matching of the glue.
Frame
This method is more labor-intensive, but preferable for the kitchen. Before attaching the panels, you need to make a frame. It is assembled from metal profiles that must be secured to the wall with hangers or self-tapping screws. The sheathing strip should be perpendicular to the length of the panels, the fastening pitch should be medium (approximately 40 cm).
If the walls are uneven, choose galvanized profiles - they are more elastic, which is very important in this case.
You can also use wooden beams, especially if this is a private house. They are installed in the same way around the perimeter of the room. Horizontal panels are attached to vertical beams, and vice versa. The frame is pre-treated with an antiseptic or olive oil.
Material characteristics
Product dimensions
Finished products are obtained after cutting dry wood fiber carpet into slabs. The length of the slabs is 1.2–12 m, width 0.6–2 m. Thickness depends on hardness :
- 3–8 mm - hard;
- 8–25 mm (38 mm - “Extra Light”) - insulating.
There are no fundamental differences in the dimensions of MDF and HDF.
Soundproofing
To isolate the room from sound propagated by shock transfer, the structures of the internal walls of interfloor ceilings are provided with a cushioning layer of sound-proofing material.
The porous-fibrous structure allows fluffed wood materials to act as a sound insulator.
But only those fiberboards that are called insulating are effective in absorbing impact noise. MDF and HDF are too rigid and not deformable enough to dampen the vibrational movements of the structure caused by the sound wave.
As insulation for doors
To rightfully be called a thermal insulation material, the thermal conductivity of fiberboard should not exceed 0.175 W / (m × °C) . Only soft fiberboard can serve as an organic fibrous piece heat insulator - with parameters in a dry state:
- ρ avg. = 0.15–0.35 t ⁄ m3;
- thermal conductivity - 0.064–0.1 W ⁄ (m × °C).
Such products can cover a wall, ceiling, cover a floor, insulate a roof, or a loggia. Here is the installation of MDF ceiling.
In sandwich panels
Expert opinion
Smirnova Ekaterina Anatolevna
7 years of experience in interior design, professional architect
Fibreboards with sufficient rigidity - MDF and HDF - can serve as cladding for flat three-layer structures with a polymer core of heat and sound insulation.
Lightweight fiberboards are used as an outer layer, not for structural purposes, but for insulating multilayer products, with polyurethane foam in the middle.
Thanks to the qualities of the fibreboard (only a few millimeters thick), covering both sides with a light and fragile layer. Wall panels for interior decoration have good physical and mechanical properties. By changing the thickness of the outer layers, manufacturers vary the strength of the entire product.
In public and industrial buildings, sandwich panels are used to insulate external walls and partitions, and they are used to form suspended MDF ceilings. For residential premises, polymer material, even hidden in the casing, is not suitable: it is flammable and toxic.
An alternative to synthetics is honeycomb core (cardboard, paper). Its advantages include safety and the ability to increase the thickness of the product without adding weight.
Corrugated strips of three-layer plywood, profiled solid wood bars inside HDF sheathing are heavier than other cores, but do not impart carcinogenic properties to the product. Are the substances that bind wood fibers together harmless?
Migration of formaldehyde
fiberboard is the most popular material for the manufacture of furniture, interior doors, baseboards, trim, and other items used inside residential premises. Here about the laminated MDF plinth. What solid wood cannot boast of, but which is typical for fiberboards:
- homogeneity – identical properties throughout the entire volume of the product;
- relatively light weight;
- lower heat and sound conductivity.
MDF and HDF differ from particle boards by more than half the content of synthetic resins. The concentration of formaldehyde in fiberboard, according to the domestic standard, should not exceed 8 mg ⁄ g of an absolutely dry board. But this figure significantly exceeds Western European requirements.
Chipboards have gained fame as a building material with increased toxicity . The problem with particle boards is the migration of poisonous formaldehyde gas from them. Limiting carcinogen emissions from products by state standards did not eliminate the problem.
180 domestic enterprises surveyed by the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision Service and the Forest Products Certification Center produce board materials that emit formaldehyde significantly exceeding the maximum permissible values.
Domestic manufacturers of board products need to reduce the content of harmful resin, change its type, and improve production technology. In terms of formaldehyde concentration, HDF and MDF boards are not fundamentally different from each other.
The intensity of its release into the atmosphere, obviously, depends on the density of the wood-fiber material (then HDF is better than MDF). But this difference is hardly so significant that it should be taken into account as a difference between these types of fiberboard.
MDF - history of creation
MDF – Medium Density Fiberboard, which translated from English means “medium-density fiber coating.” MDF is a board material made by dry pressing of fine wood chips at high pressure and temperature.
The prototype of fibreboard was first obtained by William Henry Mason, an inventive engineer from the USA. In 1924, he persistently worked on creating a technology for the production of cardboard or, at least, plywood from waste from sawmills - sawdust, shavings and wood chips. The first task - separating waste wood fragments into fibers - was more or less successful for him. Mason created a “steam gun”, later named after him - a pipe made of steel alloy, completely welded at one end, and with a sliding lid at the other, which could be removed remotely. William Mason's cannon worked like this - after putting small chips and shavings inside, pouring several liters of water, the free hole was tightly closed with a lid. Closer to the “welded” end of the pipe, the inventor placed a gas burner - the flame heated the water, turning it into steam. Having waited until the pressure reached a certain value, Mason pulled the handle and moved the lid - trying to equalize the pressure, steam, along with wood particles, was thrown out of the “gun” barrel in a powerful stream onto a receiving hopper previously positioned opposite. As a result, a significant part of the shavings, etc., was separated into fibers.
Encouraged by the success, Mason began working on paper production. However, it was not possible to create either paper or even cardboard from wood fibers - even in the exfoliated state, the wood particles were excessively large. Not used to giving up just like that, William Mason refocused on obtaining a wood board that could be adapted as a building material. Renting an old model steam press, the American inventor placed wood fibers on its bottom plate, carefully spreading them into a carpet shape. Since the experiment was carried out from fibers obtained using a “gun” in the morning, Mason planned to lay them out by lunchtime. He expected to run the press for an hour and a half to two hours, no more, but hunger forced him to leave the experiment and go home for lunch. And if it weren’t for two mistakes made that day by William Mason, the fibreboards would have been created much later - the engineer did not check all the components of the old press for serviceability (the steam valve on the upper pressure plate was leaking) and forgot to turn off the press before heading to the dinner table. And the path from the sawmill where the research was carried out to the engineer’s house was not close...
The wood fiber carpet was kept in the press under pressure and steam for a long period of time. After a hearty lunch, Mason returned to the sawmill and noticed that the steam press was still working, that steam was coming out of the gap between the plates, but what he saw after turning off the device and lifting the slider (the upper, movable plate) delighted the inventor. Under the influence of hot steam and pressure, wood lignin glued the fibers together into a fairly dense slab that did not collapse when lifted by one of the edges. William Mason soon patented “Masonite,” as he called the manufactured fiberboard. By the way, masonite is still produced to this day - in Russia such slabs, smooth on one side and rough on the other, are called hardboard (fibreboard).
Until the middle of the 20th century, there was no need for wood fiber boards, although their technological components - the same Masonite and the first phenol-formaldehyde resin "Bakelite" by the chemist Leo Baekeland - were already known to industrialists. Serial production of MDF boards started in the USA towards the end of the 60s, simultaneously at several enterprises owned by different companies. All manufacturers in those years used similar technology for the production of fiberboards; it is not possible to confidently name the first manufacturing company among them.
In the Soviet Union, “thick” boards from wood fibers were not produced - it was believed that chipboards (chipboards) were more than enough. With a focus on the Russian furniture industry, the first production of domestic fiberboards started in the village of Sheksna (Volgograd region) in 1997. Since the beginning of the 21st century, China has been a world leader in the production of MDF boards, as well as furniture and other products made from this material.
MDF board production technology
The first and most common method of making wood fiber boards was “wet” and was not much different from the technique of producing cardboard sheets. Subsequently, technology was developed that made it possible to do without water - this is what MDF manufacturers use today. Let's consider the stages of “dry” production of medium-strength fiberboards.
Preparation of woodchips. The species of tree trunks supplied to the production of MDF boards can be different - as a rule, the same board contains fibers from several trees. The round timber is placed in drum-type machines, during the rotation of which the built-in knives completely cut off and remove the bark. Further, in disintegration machines equipped with massive chopping knives, the debarked round timber becomes wood chips. In addition to cutting wood into chips, logging reduces the bonds between fibers that the wood polymer lignin provides. The chopped chips enter a conveyor belt and follow several electromagnets that extract metal particles from it. Next, the chips are sorted in vibrating sieves - the excessively large chips go back to cutting, the excessively small chips go to the waste storage bin and will then be burned in the boiler room furnaces. Wood particles of the required size range are sent for washing into vertically installed cyclones - they remove debris and mineral impurities from the chips. Prepared for the next operation – steam treatment – the chips go into a bunker, where they are heated to a temperature of 100°C, bringing their humidity level to 80% throughout the entire volume.
Obtaining wood fiber. Hot and wet wood chips are loaded into a special installation - a defibrator (also known as a refinator) - a disk-type grinding apparatus. The feeder auger drives wood particles through a cascade of disc and conical blades, separating them into fibers. The division operation is repeated two or three times; for this, the required number of defibrator units are placed one after another in a single cascade. To more effectively break down wood chips into fibers, phenol-formaldehyde resins, paraffin, binders and hardeners are placed in the defibrator container.
The wood fibers obtained in the defibrators are sent to the dryer, and during the process they are constantly treated with steam. Inside the dryer, the fibers are no longer exposed to steam, but to dry air with a temperature ranging from 170 to 240°C - the drying time is short, does not exceed 5 seconds. Dried wood fibers (humidity no more than 9%) are loaded into a cyclone, whose task is to remove excess air from the mass of fibers. Fibers ready for the production of fibreboards are accumulated in a hopper.
Carpet formation and pressing of MDF boards. When moving along a conveyor, wood fibers are shaped into a continuous carpet, for which the flow of fibers is rolled by rollers (see photo).
Primary pressing of the fiber carpet is carried out using a conventional press and has one goal - to completely eliminate air from the future MDF board. At the end of this operation, the main pressing (hot) is performed, taking place in three stages:
imparting surface rigidity to the slab . Under a pressure of about 350 MPa developed by the slider plate and at a temperature of 200-230°C, the wood fiber carpet acquires the primary properties of an MDF board;
strengthening the inner layer of the slab. The pressure in the press is reduced to 50-120 MPa, the heating temperature is reduced to 190-210°C, as a result, the binding components in the compacted wood fiber carpet form strong bonds inside the product;
fiberboard calibration . The formed plate must be brought to the required thickness, for which it is pressed under pressure of 60-150 MPa without heating.
The finished MDF board emerges from the sizing press in a continuous strip, then it is cut into blocks of specified sizes using circular saws. The cut slabs are placed on racks for cooling; this operation takes about 25 minutes. Despite a series of pressing works, MDF boards still have some surface flaws and a small difference in thickness, a few millimeters. They are removed on surface grinding machines. Finished products are marked and placed in a warehouse, or go to a workshop where the surfaces of the slabs are given a decorative finish.
Characteristics of MDF
There is no Russian state standard for medium-density fiberboards; MDF manufacturers either develop their own technical specifications or produce boards according to the European standard ANSI A208.2. We produce MDF boards of the first and second grade, with a thickness from 6 to 24 mm. Gluing of wood fibers is carried out using urea-formaldehyde resins and wood lignin. Many manufacturers claim only lignin as a binding element: they say that there are no environmentally harmful components present - this is not true, MDF panels and slabs created only with lignin do not actually exist. Standard sizes of MDF panels: 1650 by 1650 mm, 2800 by 1650 mm, 2750 by 1650 mm, 2250 by 1650 mm and 2440 by 1650 mm. Panels of “additional” sizes are also produced - 3660 by 1650 mm, 3050 by 1650 mm, 2100 by 1650 mm and 1850 by 1650 mm. The surfaces of grade I MDF panels have absolutely no defects - they are perfectly smooth, without chips, scratches or any stains. Class II slabs may have scratches no more than 0.3 mm deep and no longer than 20 mm, small chips on the edges, and small polishing defects. Grade III MDF is only suitable for construction needs, because... has multiple chips and surface defects. The density of produced MDF boards ranges from 600 to 1200 kg/m3. The emission class (emission of free formaldehyde from 100 g of mass) for any type of MDF is E1, i.e. does not exceed 10 mg. Any MDF panel has high moisture resistance, and the thicker the panel, the higher its moisture resistance - the maximum swelling for slabs 6-8 mm thick does not exceed 17% of the original volume of MDF. During the production process, MDF boards can be given higher quality properties in terms of water resistance, fire resistance and biostability than serial boards.
Application of MDF
MDF is a very dense and homogeneous material, which makes it resistant to moisture and hot steam, fungi and microorganisms. That is why MDF boards are widely used in the manufacture of kitchen furniture, because they withstand the effects of kitchen steam very well, do not swell, and do not warp. The developed technique of bending structural elements from glued wood fibers made it possible to create armchairs and stools, elegant headboards from this material. As a rule, all furniture for rooms with high atmospheric humidity (bathrooms, kitchens) is made from veneered or laminated MDF. MDF boards can also be used to construct interior partitions, but they are not suitable for flooring due to their mechanical vulnerability. Panels made from this material are widely used in interior decoration - in finishing ceilings and constructing air ducts. MDF is used for the manufacture of door blocks along with frames and trim from the same material. Laminated platbands and linings for entrance doors are made from MDF. In construction, T-beams made of MDF are popular, used as the core of interfloor floor beams in monolithic construction. Waterproof MDF is used for roof lathing; elements of such lathing are painted with oil paint for longer service.
Advantages of MDF
The advantages of MDF include the ability to maintain geometric parameters for a long time, which allows us to talk about a long service life. Products made from MDF can be used in rooms with high air humidity - impregnations protect the boards from the development of mold and mildew, and from insect activity. However, MDF panels are not recommended for installation in rooms with constantly high levels of air humidity, with the exception of their waterproof modifications. MDF is a good insulation and sound insulator. You can enhance these properties by laying insulating material underneath. The biggest advantage of MDF is its favorable ratio between thickness and hardness. This material has a uniform, dense, even, smooth surface, which makes processing the slabs quick and easy. The density of the material ranges from 600 kg/m³ to 800 kg/m³, which is quite a lot. The strength of MDF is 1.8-2 times higher than the strength of particle boards. Thanks to their smooth and hard surface, MDF boards are ideal for finishing with advanced methods of lamination, lamination, thin veneer veneering, imitation printing, coating with varnishes and enamels. If you have the necessary tools, you can cut out any patterns into the panels and decorate them with decorative cuttings. This eliminates the known disadvantages of solid wood: anisotropy of properties depending on the direction of wood fibers, tendency to crack when operating temperature and humidity conditions change, etc. MDF is perfectly cut with carbide saws. When drilling MDF, the same tools are used that are used for plywood and chipboard. Excellent results are achieved when milling edges and surfaces. The MDF structure guarantees exceptionally high quality at high processing speeds. All available brands of wood adhesives are suitable for gluing MDF. During the production process, MDF can be given special properties: fire resistance, biostability, water resistance. It is also worth noting the relatively low cost of MDF. MDF panels require minimal and simple care - it is enough to occasionally wipe the boards with a damp cloth or one of the special products that are sold in abundance in stores today.
Disadvantages of MDF
The disadvantages of MDF boards include their easy flammability when in contact with an open fire. It is also worth noting that the resistance to mechanical damage is not very high: an accidental fall of a heavy object onto the MDF surface can leave a dent. As for working with MDF, it should be noted that it will be almost impossible to drive a nail or screw into MDF; preliminary drilling of a hole for fastening is required. During processing and milling of slabs, a lot of dust is generated - the use of a respirator is mandatory. MDF boards weigh an order of magnitude more than wood boards of the same size. Despite the environmental friendliness claimed by some manufacturers, this is not entirely true. Yes, the emission class of MDF is low and almost equal to natural wood, but the emission of formaldehyde is still present. That is, although MDF boards are compared to wood, they are not so environmentally friendly.
MDF in Russia
Today, the Russian market of sheet construction and finishing materials offers medium-density fiberboards from both domestic and foreign manufacturers. The most widely used products are the following brands: Kronospan (Russia, Yegoryevsk), Kronostar (Russia, Sharya), Shekninsky KDP (Russia, Vologda region), Glunz AG (Germany), EGGER (Austria), Korostensky plant MDF (Ukraine).
Decorative finishing of fibreboards
Coatings protect the slabs from moisture and abrasion :
- enamel. The products become the most moisture-resistant, suitable for cladding the walls of grocery stores and medical institutions. Here about moisture-resistant MDF;
- polymer films for rooms with high humidity in the bathroom and kitchen. Here about bathroom furniture;
- paper impregnated with resins;
- paint - water-based polyvinyl acetate;
- plywood.
Abrasion of the varnish film occurs to a greater extent on the inside of furniture made of MDF and HDF.
Microclimatic factors (mainly the difference in humidity that accompanies the change of seasons) affect wear and tear 3–4 times less than the use of the contents of cabinets and chests of drawers.
However, the coating on the back side of furniture is thinner than on the front side. Lamination of slabs with synthetic film is carried out on textured paper that imitates the cut of solid wood of a valuable species. This is how laminated wall panels are made.
MDF wall panels for finishing the apron and kitchen walls
In the kitchen, MDF wall panels are most often used to finish the apron, but often also for partial or complete wall cladding. In this article we will talk about how to choose the right material, as well as how to install an MDF kitchen apron with your own hands. In addition, here you will find 25 photo examples of the use of MDF in the interior.
Is the type of wood important in fiberboard?
The microstructure of coniferous and deciduous wood is different. Thus, only deciduous trees have tubes running along the trunk - vessels through which moisture rises from the roots to the crown. But in the trunks of coniferous trees there are intercellular spaces filled with resin (resin passages). The properties of specific breeds also vary.
The performance of most wood composites depends on the properties of the wood from which they are made. For example, the density of chipboard, poplar plywood is 450 kg/m3, birch is 650, and coniferous plywood is 550. Paulownia plywood is 1.7 times lighter than birch plywood.
The properties of products made from wood separated into fibers retain a connection with the species, but less significant. The macrostructure of the initial solid raw material has a weaker effect on the quality indicators of MDF and HDF.
It has been experimentally established that slabs made from coniferous tree fibers are the most durable . The reason for this is the peculiarities of the fractional composition of wood pulp and the shape of the particles. As for specific hardwoods, birch MDF and HDF are stronger than others, alder and aspen are “weaker”.
The inclusion of deciduous wood in the raw composition of a building material is fraught with a decrease in its physical and mechanical characteristics. Density and swelling are almost not affected, and the bending strength is reduced.
HDF: what is it, abbreviation, size
Everyone is familiar with the building material, which is denoted by the abbreviation MDF (finely dispersed fraction) - this is a medium-density board made from fine wood chips.
Relatively recently, the innovative material HDF or HDF (High Density Fiberboard) appeared on the construction markets. In everyday life, it has another name: “HDF sheet” - it is also a high-density fibreboard.
What is the definition of MDF and what is it, you can find out from this article.
HDF is produced from waste that remains in sawmills. But not all waste from wood processing plants can be used, but only those that do not contain phenol-formaldehyde resins, i.e., are environmentally friendly. Therefore, in terms of environmental friendliness, this material can be compared with natural wood.
Sanitary felling wood is also suitable for HDF (this is when trees are forced to be cut down, for example, because they are in disrepair or are in the way due to their location). At the enterprise, sawdust is crushed and steamed.
In this case, a binding adhesive substance (ligin) is released. Then the fibers are dried with a stream of hot air and pressed under high temperature and pressure to form panels of specified thickness and dimensions.
In principle, MDF is produced in the same way.
The difference between MDF and chipboard can be seen in the photo in this article.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let us dwell in more detail on the advantages and disadvantages of this finishing material. There are more of the first, so let's start with them.
Advantages of fibreboards:
- attractive appearance;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- moisture resistance (do not swell or warp);
- easy to process - drilling, gluing, milling and grinding, decorative cutting, etc.;
- easy to install, MDF panels can be attached using any wood glue;
- have excellent sound insulation;
- keep the room warm in cold weather;
- the material is static - does not attract dust, easy to clean.
Another undoubted advantage that a kitchen wall panel made of MDF has is its undemanding nature on the wall surface. Before attaching this material, they do not need to be plastered, puttyed or primed - you don’t even have to remove the previous coating.
It is convenient to hide cables and other unnecessary communications under the frame of such slabs, after making sure that they are well insulated.
There are no ideal materials, and MDF coating is no exception. Its disadvantages include the following:
- installation requires caution - after sawing, the edges of the panels must be treated with a special agent against moisture and dampness (otherwise their swelling and deformation cannot be avoided);
- Deflections may be noticeable at the joints of such slabs;
- low fire safety - MDF panels are highly flammable.
The advantages in this case significantly outweigh the disadvantages. If you are careful and careful when processing and fastening them, then unpleasant moments can be completely avoided.
What are the differences
The difference is in density. The density of HDF is from 800 to 1000 kg/m3, and MDF is only up to 800 kg/m3. Due to the higher density, the characteristics of the materials differ slightly. HDF is stronger and more reliable. Decoding fiberboard implies other density indicators.
MDF is produced with a thickness of 6 mm, and HDF can be much thinner - 2 mm, 3 mm, 4 mm (up to 8 mm). In terms of performance, HDF boards are very close to natural wood, although their price is more than half the price. The differences between MDF and laminated chipboard are approximately the same, but the latter also has a different top coating.
What MDF plinth looks like before painting is indicated in this article.
Where is MDF used?
The technological properties of MDF boards have made this material incredibly widespread, especially in the furniture industry. The boards are used to make carved facades, and facades pressed into PVC film are not inferior in their characteristics to furniture made of natural wood. MDF is used to create many products:
- Floor coverings. Laminate floors made from MDV boards look stylish and last a long time due to their moisture resistance and durability.
- Wall panels. An economical and practical option, ideal for decorating an apartment, home, or office.
- Interior doors. Doors made of MDF are easy to process, and therefore are characterized by a variety of design solutions.
- Decorative elements, cornices, frame profiles, platbands.
- Electronics. MDF is used in the production of acoustic systems for cabinet decoration, as well as for the production of packaging.
Conclusion: if you need products that are as good as natural wood or chipboard, choose MDF. It fits all parameters, looks great and lasts a long time.
The article uses materials from the site mebel.ru. More details - https://www.mebel.ru/blog/mdf-ili-dsp-chto-luchshe/
Technical characteristics and material properties
HDF boards are available in 2800 x 2500 mm and 2800 x 2070 mm formats. Varnished - only in sizes 2800 x 2070 mm. Thickness can be 2.5 / 3 / 4 / 5 / 6 mm. Deviation from dimensions can be minimal for this type of product: from 0.2 to 0.5 mm. Density 800 – 1000 kg/m3.
Basic properties:
- the material is environmentally friendly, which means it is safe for health;
- has increased strength;
- horizontal surface – flat, with minimal permissible deviations.
- wear-resistant to abrasion;
- characterized by good sound insulation;
- perfectly amenable to processing, without chipping or breaking;
- resistant to aggressive substances;
- durable.
You can find out what is the best material to choose for a children’s room: chipboard or MDF by reading this article.
In the photo - an apron for the kitchen made of MDF HDF:
Varieties and their characteristics
Finishing the kitchen with MDF panels, varying in texture, shape and size, will help you create a stylish, original and at the same time practical interior.
Let's look at what they are.
According to physical characteristics
- Rack - strips of different widths that are connected to each other using grooves and ridges. These are the most popular MDF panels for walls and ceilings. Can be mounted both horizontally and vertically.
They are convenient to use for visual play with space - increasing the height of the room or making it wider.
- Tile - made in the shape of rectangles or squares, in appearance they most resemble ceramic tiles, but of larger dimensions. They are mounted in the same way - a ridge in a groove.
Various ways of combining them allow you to create original effects, even when using plain slabs.
- Sheet – decorative sheets of various sizes. A wall finished with them will be pleasing to the eye, and the installation process will take the least time (the design of such panels is very diverse).
Each variety is good and interesting in its own way. It will not be difficult for you to choose the option that suits your kitchen, no matter what interior style you choose.
By the method of decorating their surface
- Laminated - covered with polyvinyl chloride film. They come in a wide variety of patterns, colors and textures. Glossy PVC film makes the room respectable and stylish.
- Veneered - as close as possible to natural wood, both in color and texture. They are lined with the thinnest layer of wood veneer - less than 3 mm.
- Painted - coated with a special paint that creates a uniform and smooth coating without roughness. They have a wide variety of colors; mother-of-pearl and silver effects have recently become popular.
- With photo printing - any image or photograph can be applied to their surface, and the design is coated with water-repellent acrylic varnish on top.
- With a 3D effect - three-dimensional images are applied to the finishing material by painting the panels in different colors (shapes, waves, relief, etc.). This know-how coating allows you to implement the most diverse and daring ideas in the interior.
Various MDF panels for ceilings and walls differ in their quality characteristics. Laminated ones are more resistant to scratches and abrasion. Painted ones have better moisture resistance, veneered ones are a natural, but more expensive option.
Types of HDF
Sanded slabs . Produced by hot pressing of wood pulp. In appearance they are very similar to MDF boards, the only difference is in density. The compressed material is not initially processed in any way. In further use, it is coated with varnish and paint.
Decorated slabs (their second name is “varnished”). The base is polished products, which are additionally coated with primer paint, then they are given texture and a base color.
Using certain rollers, you can imitate the texture of different woods. It turns out to be an ideal material for furniture.
This is the industry that uses it the most. Although decorative HDF boards are also ideal for interior doors.
You can learn in detail about what MDF panels for walls are from our article.
Expert opinion
Smirnova Ekaterina Anatolevna
7 years of experience in interior design, professional architect
HDF boards are well coated with almost all common paints. This can be done at home with a roller or brush, but on an industrial scale they use various paint and varnish systems.
You can find out what size corner for MDF panels is needed in this article.
Application
The material is well suited for veneering and lamination. Due to its excellent characteristics, it is widely used in various fields:
- Furniture industry . To reduce the cost of products, hidden parts of structures are made of HDF (bottoms of drawers, back walls of cabinets, etc.). The material is adjusted to the standard size of kitchen countertops from other samples. The material is also used under natural veneer. Perforated HDF panels are also popular in the furniture business (inserts in upholstered and cabinet furniture, trade and exhibition equipment, partitions, etc.).
- Repair of premises and construction . HDF is used for flooring (subfloor and not only), as a base for laminate and parquet. These thin slabs are easy to cover, level walls, and hide communications and ventilation behind them. They are often used for suspended ceilings.
- Carriage building . It is used for interior decoration of train cars and trams.
- Production of exhibition stands (wall elements, partitions).
- Making doors . HDF board is suitable for making door panels.
- Other: picture frames, trade stands, decorative elements, car interior lining, etc.
MDF ceiling panels, price and application features are indicated in the article.
The video explains the difference between HDF and MDF:
Advantages compared to some other materials
From the very name of the material it is clear that it is denser, harder and stronger than other similar plates. Here are a few more of its advantages:
- HDF is environmentally friendly , because there are no chemical additives in its production. Wood fibers contain the natural component ligin. At high temperatures it melts, producing an organic glue that binds the fibers into a dense layer. It turns out that the naturalness of HDF is very close to solid wood. But the structure of the slab is homogeneous, without compactions and voids, which happens in natural boards.
- Same sizes . After all, the thickness and horizontalness of the same plywood can be different in one sheet.
- The material can be easily processed . It can be sawed, drilled, cut. Chips and cracks do not form.
- Affordable price . The cost of HDF is less than the price of natural wood.
You can read more about other types of cladding panels in our article.
It is also useful to read about the dimensions of 16 mm chipboard.
Use in the kitchen
Kitchen wall panels that imitate stone or tile are made from HDF boards. They serve as excellent wall decor and are also suitable for kitchen aprons.
Wall finishing is possible without guides, but in each specific case you need to consult with a specialist. Sometimes lathing is required for the installation of sheets to avoid sagging and bending during operation.
Flaws
This material has few significant disadvantages. First of all, this is insufficient moisture resistance for damp and damp rooms. However, this is not typical for moisture-resistant particle board. To increase resistance to water, the slabs are treated with special compounds.
PVC wall panels dimensions and prices are indicated in the article.
You can find out what brick-like pvc panels for interior decoration look like in the article.
Read about what technical characteristics a fiberboard sheet has.
On photo-sheet HDF panels under tiles:
As a kitchen apron, you need to take panels with a moisture-resistant coating; they are usually laminated with PVC film or MDF film. This increases their wear resistance, but abrasive products must be used with caution, and it is better to avoid such care.
It’s also useful to read about the pros and cons of 2-2 plywood.
HDF is a fairly new material, but in many respects it has appealed to consumers and, perhaps, will soon seriously displace its analogues.
Chipboard - chipboard
Oh, who among us doesn’t know chipboard! Who hasn’t said in disappointment: “Well, this is deespe...” But let’s get to the point. Chipboard is made from sawdust and shavings impregnated with a binder, namely formaldehyde resins. This is the most common material for cabinet furniture, interior design, construction (roofs, partitions, etc.).
Pros: water resistance, strength, ease of processing. Chipboard “holds” nails and screws holding the structure together well. Another advantage of chipboard is its low price. That is why chipboard is the most widely used material for economy class furniture; Most office furniture is made from chipboard.
For kitchens and baths, a special type of chipboard is used - with increased moisture resistance.
Cons: the presence of those very formaldehyde resins that hold wood particles together. The fact is that chipboard releases a certain amount of formaldehyde into the air - not the most healthy product, it should be noted. But it's not all that scary. There are two types of chipboard: E1 and E2. E1 is more environmentally friendly; its formaldehyde emission rate is noticeably lower. But E2 is prohibited from being used in the production of children's furniture: draw your own conclusions. The most environmentally friendly are chipboards made in Austria and Germany.
Chipboard is a very hard material that does not allow fine processing (deep milling, all kinds of shaped parts).
MDF: main characteristics
MDF is produced by grinding and steaming wood waste into fine shavings. Then pressing occurs under pressure and the formation of plates having a certain size and thickness.
The final stage of manufacturing is coating with binders. This process occurs under high temperature conditions, most often lignin is used as a binder.
- High resistance to steam (deformation, swelling of the panel is not observed);
- Easily amenable to mechanical processing, which makes it possible to change the shape of corners and apply decorative elements;
- Simple hygienic care, allowing you to safely use MDF for the kitchen and bathroom;
- Good heat and sound insulation;
- Safety for human health;
- High quality material;
HDF panels - what is it?
HDF wall panels not only perform an aesthetic function, but also protect the surface of the kitchen working wall. Decoding the abbreviation HDF - High Density Fiberboard , translated from English - high-density fiberboard.
LHDF means lacquered or laminated panel. The material is quite new, it is used in the production of furniture, wall cladding, and for the manufacture of kitchen aprons.
The boards are compressed wood fibers coated with a transparent water-based varnish.
If your budget is limited, then your choice is environmentally friendly and safe HDF sheets. Due to the absence of toxic emissions, they received a certificate of the European hygiene class E1. This allows them to be used in any living space and even in children's rooms.
On the construction market, HDF boards are presented in the following sizes: 2070 x 695 mm, 2440 x 847 mm, 2400 x 650 mm, 3000 x 600 mm. The most common thickness is 3 mm.
The main advantages of a kitchen apron made of HDF are its performance characteristics: resistance to abrasion, scratches, humidity, and the use of aggressive detergents .
To prevent the formation of fungus and mold under the influence of moisture, the reverse side is covered with a protective layer. Externally, such panels are very similar to glass “skins”, but their cost is several times less.
High-density fiberboards have appeared on the construction market quite recently, but have already gained enormous popularity among buyers. The reason for this popularity is the low price, simple and quick installation, higher quality than analogues made from fiberboard and MDF.
Expert opinion
Smirnova Ekaterina Anatolevna
7 years of experience in interior design, professional architect
Photo printing on the panel will allow you to create a bright and exclusive interior of your kitchen. And the protective layer of varnish that covers the outside of the panel will protect the design from damage and moisture, and will also make it easy to care for the apron.
The panels are installed on pre-prepared walls using any mounting adhesive. After installation, you will not be afraid of any drops of water or splashes of grease.
In addition to the protective functions, you immediately get a stylish interior element. 3D drawing creates a feeling of incredible reality. Thanks to the ability to apply any image, you can choose an apron to suit any style of kitchen. With the help of such a surface it is possible to implement the most unimaginable design solution.
Don't forget about the ease of maintenance of the panel. Every housewife will appreciate this property. The protective layer of high-quality varnish that covers the sheet ensures absolute smoothness of the product. This allows you to quickly and easily get rid of any dirt, and the design is protected from the effects of detergents.
Kitchen aprons have gained enormous popularity due to their advantages:
- ease and speed of installation - installation is carried out directly on the wall, which does not require special preparation;
- the ability to hide the imperfections of uneven walls;
- the laminated surface is resistant to heat and moisture;
- resistance to detergents;
- protection of the drawing from erasure or other damage;
- the ability to quickly and easily cut holes for sockets after installation;
- comfort and practicality;
- the most acceptable ratio of price for material and resulting quality.
Thus, an apron made from HDF panels is a budget option that combines high performance and design characteristics.
Material advantages
There are many reasons to use such a panel; there are many more advantages than disadvantages.
- strength;
- sufficient hardness;
- low cost;
- ease of care;
- resistance to fungus formation;
- ease of installation (especially since there is no need to specially prepare and level the surface before installation).
The material itself does not differ in a particular variety of colors, but today it can no longer be called boring, since manufacturers laminate the surface and also apply various images to it. This variety allows you to use an MDF wall panel for a backsplash in the kitchen, harmonizing with almost any interior.
Separately, it should be emphasized that this type of finishing is economical: if necessary, it will not be difficult to replace wall panels that have been used in the kitchen with new ones of a slightly different shade; for this, you will not need to renovate the entire room and incur significant costs. At the same time, the interior will look completely different.
Applications and properties of HDF
HDF is mainly used in the same places as MDF.
Due to its high density and strength, HDF is used as floor panels and subfloors are made from it. Due to the fact that these boards withstand mechanical stress well, they are suitable for a base under laminate or natural veneer.
High-density board is widely used in the furniture industry. Due to its low cost, HDF is often used to make parts and parts of structures that are hidden behind the facade of the housing. For example, this could be the back wall of furniture, the doors of wardrobes, the base of drawers, and so on.
Minimal deviations in thickness make HDF an ideal material for leveling walls and floors. In non-residential premises, suspended ceilings are made from HDF, which allow you to hide communications, ventilation and everything that needs to be hidden from view, for a more aesthetic appearance of the room.
In the carriage and automotive industries, HDF is used as a material for the interior decoration of carriages, buses, trams, etc. In industrial production, packaging or reusable containers for non-food products are made from these wood boards.
HDF is widely used in various fields due to its beneficial properties:
- Environmentally friendly material. No chemical additives are used in the production of boards. Bonding of raw materials provides a natural component that is contained in the wood itself. It is called lignin, under the influence of high temperatures, it turns into an organic glue that reliably holds everything together into a single system;
- The decoding of the name HDF indicates that this material has high density and hardness, which distinguishes it from other fiberboards;
- Uniformity of the structure, which is achieved by production technology, since the raw materials are crushed into a single mass without voids and defects characteristic of natural wood;
- High dimensional stability and good horizontality. This distinguishes HDF from ordinary plywood, which can have different thicknesses;
- Good tolerance to mechanical processing. HDF can be sawed, drilled, perforated, and bent modules can be created, all of which significantly expands the range of applications of high-density fiberboard;
There are two types of HDF boards: sanded and decorated:
- Sanded boards are produced by sanding the surface of finished boards; they are not coated with anything and serve as a good base for paints and varnishes;
- Decorated slabs can come in a variety of colors and textures. They are coated with dispersion colored varnishes in several layers, using different rollers, you can create the texture of different types of wood. The final clear varnish protects against scratches, weather conditions and chemicals.
Now you know what kind of miracle material HDF is, which costs several times less than natural wood, but is no worse in quality, and in some cases even better. HDF is easy and convenient to install; it allows you to give free rein to your imagination and create something new and unusual in your interior. If you are limited in finances, then you can safely replace natural wood with HDF board.
Types of MDF panels
Manufacturers present multiple options for MDF boards for decorating a kitchen backsplash. They can now be selected according to the most suitable parameters:
The most common thickness is 7 mm, but can be from 6 to 9 mm. Some manufacturers also offer more durable options of 12-14 mm. The standard length of products is 1300 mm and 2600 mm, which makes it possible to cut them in the most compact manner and without unnecessary waste (into two or four parts). First of all, the price is influenced by the length, as well as the choice of the manufacturer (German ones are one of the most expensive, domestic ones are much cheaper).
An interesting design option for an apron in combination with a tabletop
The variety of colors and textures today amazes. Modern materials with a combination of color and pattern can imitate:
- natural wood (beech, oak, cherry, pear);
- natural stone (granite, marble);
- bamboo.
A completely new trend - MDF panels with photo printing. This apron becomes a wonderful accent to the interior and makes it stylish.
What is HDF?
The abbreviation HDF comes from the English name of the product and stands for High Density Fiberboard, which means high-density fiberboard. Therefore, it is often confused with MDF, but such products have slightly different characteristics.
HDF is produced by sampling rejected wood or raw materials left over from wood processing. The technology involves drying, cleaning and thoroughly grinding the components.
The resulting mixture is molded and pressed under high pressure and temperature, due to which the product acquires the desired performance properties. Further processing consists of sanding on both sides and decorating (if necessary).
Application of panels
Thanks to its excellent parameters, the area of use of HDF boards is quite wide:
- Furniture manufacturing. The product is gradually replacing hardboard, because it can be used as the back wall of interior items, the bottom of drawers and inserts of frame and MDF facades. A special technology makes it possible to produce radius parts.
The material is also used as spacers when transporting goods, to create shaped elements and the basis for Hand Made.
Types of material
Currently, products are divided into two categories:
- Sanded on both sides. There are middle and high class parts on sale. The first are sheets in which one part is smoother, which is clearly noticeable to the touch. The second variety has a higher density and identical surfaces.
Laminated material has an affordable price and high wear resistance
- Treated with paints and varnishes. They are used as the back wall of furniture in the “economy” segment or to create partitions. The most common ones are white and black, but you can choose sheet products of the desired shade. Poor quality products become contaminated.
- Veneered. They are used for interior items and decoration of areas of the room.