Functional, durable and easy to process materials most preferred in the construction industry. Unfortunately, achieving such a combination of performance properties is not easy. Cellular concrete and in particular aerated concrete blocks can be considered as the building material closest to such requirements.
Its unique porous structure allows the construction of warm houses, which at the same time have a high margin of safety . Cellular concrete also has disadvantages, so when choosing such a construction tool, you need to familiarize yourself with all the nuances of operation.
There are many offers on the modern market for aerated concrete of different brands, which allows you to make the best decision when purchasing.
General information about aerated concrete
As already noted, aerated concrete blocks are included in the group of cellular concrete. The material is ready-made elements for laying walls and other structures .
A special feature of the blocks is the presence of pores in the structure , the diameter of which reaches 3 mm . It was the cellular structure that determined one of the main positive qualities of aerated concrete - its effective thermal insulation function.
The blocks are based on components such as cement, lime, gypsum and quartz sand . Gas formers are added separately , on which the quality of aerated concrete blocks largely depends, since during their action the formation of a cellular structure occurs. Some manufacturers also introduce industrial waste, including slag and ash.
Return to content
Classification by size
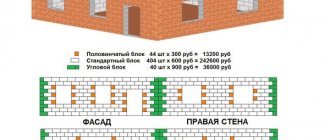
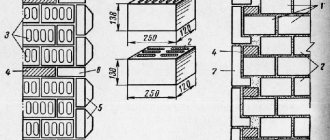
The thinnest aerated concrete block that can be found on the market today is 75 mm thick. Of course, it is not intended for the construction of load-bearing structures, like all other blocks whose thickness does not reach 200 mm. All of them are designed for the construction of partitions. But blocks thicker than 200 mm can already be used for walls.
When calculating the material for construction, be sure to carefully consider the required thickness of the blocks, since the difference in the cost of thin and thick blocks is very noticeable. Therefore, by choosing the thickness wisely, you can optimize your costs. The standard choice for the construction of structures are 240 and 300 mm blocks. If you consider that the characteristics of these types of blocks are almost identical, then it is worth choosing blocks with a thickness of 240 mm, since they will cost less.
This also determines the thickness of the walls that are built from aerated concrete: 24 - single block, 48 - double block.
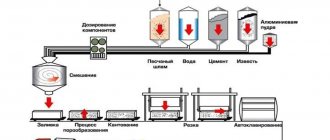
Manufacturing technology
At the first stage, the components of the base composition are mixed with water . In this way, a primary solution is prepared, which is subsequently poured into special molds.
Reactions with the release of hydrogen follow . It is provoked by the introduced gas-forming agent and calcium hydroxide. This is how the mass swells , resulting in an increase in its volume. When the mixture has hardened sufficiently, it is removed from the mold and processed mechanically .
At this stage, the same aerated concrete blocks or panels are obtained from the monolithic base. In the future, manufacturing technologies involve different operations - for example, blocks can be treated with water vapor or dried in special chambers.
Final processing can be carried out using an autoclave or non-autoclave method. In essence, these are varieties of hardening .
Russian companies produce autoclaved aerated concrete blocks based on lime, and non-autoclaved ones - from cement . The differences between hardening technologies are that autoclave materials undergo this process in autoclave chambers at elevated pressure and temperature. Non-autoclave blocks are not treated with special media and harden under natural conditions, but when exposed to heat and moisture.
Return to content
Aerated concrete, gas silicate and safety
Security is a term that is interpreted very broadly in the modern world. Security is protection from threats and risks. Aerated concrete walls help increase security.
The main advantage of aerated concrete is that this material allows you to build an energy-saving house with single-layer external walls - without a layer of effective insulation on the facade.
A single-layer wall is least susceptible to the risk of accidental or deliberate damage.
A single-layer wall is the key to the absence of hidden defects:
- It is impossible to place insulation poorly in it, since the insulation is the masonry material itself;
- It is impossible to perform a bad vapor barrier in it, since it does not need a vapor barrier. The entire wall is in front of your eyes and you don’t have to worry about the condition of the foam or mineral wool hidden in its depths - nothing is hidden in the wall.
Read: What is the best material to make an external single-layer wall from?
Aerated concrete is a 100% mineral material - therefore it is not flammable and fire resistant. Aerated concrete is a non-combustible building material and belongs to the NG class - non-combustible material . After fires in houses built from aerated concrete, the material itself remains intact. Structures made from aerated concrete blocks have the first degree of fire resistance (the highest) and do not emit toxic or other harmful gases in the event of a fire. Tests have shown that the fire resistance limit of load-bearing walls made of blocks with a uniformly distributed load of 7.5 t/linear meter is at least REI 240. This means that after 240 minutes (4 hours) of testing, a load-bearing wall with one-sided continuous exposure to flame does not lost its load-bearing capacity (R), integrity (E) and thermal insulation capacity (I).
The given limits of fire resistance of aerated concrete structures characterize it as a material from which fire walls can be erected and used to protect building structures from fire in order to increase the degree of their fire resistance.
Where is it used?
Aerated concrete blocks are used in almost all areas of construction . Another thing is that its physical and technical qualities impose certain restrictions during the installation process. One way or another, the material is used in the construction of residential buildings, commercial buildings, industrial and production facilities.
In the construction of multi-storey residential buildings, load-bearing combined walls and internal partitions are constructed from aerated concrete. By the way, flexibility in processing allows you to diversify architectural ideas when building walls .
In low-rise construction, aerated concrete blocks, the pros and cons of which have been correctly calculated, can also be used as a material for external walls . As a rule, these are one- and two-story buildings, but if we are talking about frame-monolithic projects, then the number of storeys is unlimited - in such cases, partitions and facades .
Based on the above, we can summarize that aerated concrete blocks are mainly used as a basis for walls. However, depending on the design and standard size, this material can act as a thermal insulation barrier in the finishing of the same walls and partitions.
Return to content
Types of aerated concrete
One of the key divisions into types of aerated concrete is determined by production technology. These are the already noted autoclave and non-autoclave blocks . These building materials are distinguished by two qualities: thermal conductivity and compressive strength. The autoclave post-processing method is improved and produces a material with increased thermal insulation and durability.
No less significant is the classification by purpose , which should be taken into account primarily when choosing a material for certain purposes.
Aerated concrete blocks are structural, thermal insulating and combined, in which the first two functions are combined. Accordingly, structural ones are used for laying walls, combined ones are used to form walls and partitions with insulation, and thermal insulation ones are designed purely for solving the problems of insulating building structures.
The following classification involves a more in-depth analysis of the characteristics of aerated concrete. In this case, we consider the properties of the binder component , which is used in the process of creating blocks. This additive can be boiled lime, gypsum, slag, cement with a certain proportion of Portland cement, ash and siliceous elements.
Return to content
Aerated concrete, gas silicate and ecology
Aerated concrete products do not contain toxic or organic compounds, therefore they do not emit harmful gases or other emissions during operation.
Sometimes you can come across statements that during production, harmful gas remains in the pores of aerated concrete. But aerated concrete has an internal structure with open pores, unlike, for example, foam plastic, in which the pores are closed. The open pores of aerated concrete cannot contain anything other than ordinary air.
In terms of radioactivity, aerated concrete belongs to the first class (low level) with reduced radiation Aeff less than 54 Bq/kg (Becquerels/kg) mass. Among its “neighbors” in this indicator are wood and gypsum.
The reduced radioactive radiation Aeff of heavy concrete and expanded clay concrete ranges from 54 to 120 Bq/kg, clay brick - from 120 to 153 Bq/kg.
The group of materials with relatively high radioactivity - from 153 to 380 Bq/kg includes expanded clay and ceramic tiles. If we recalculate Aeff from mass to volume, then 1 m2 of aerated concrete or wooden wall has a reduced radioactivity of less than 2,000 Bq (Becquerels), and of a brick wall - from 10,000 to 18,000 Bq.
Aerated concrete (gas silicate) is the friendliest building material.
Brands of aerated concrete blocks
Among the most popular brands are D350, D400, D500 and D600 . The material under the D350 brand is quite rare, since many other building materials can provide its performance characteristics. However, its lightness, low thermal conductivity and ease of processing allow the blocks to be used as a good heat insulator.
Brand D400 has higher strength values (up to 1.5 MPa), which makes it possible to use this material when laying walls with light loads. The heat insulator function in such blocks is also preserved, so with their help you can create durable protection against heat loss.
The most popular brands of aerated concrete blocks in construction are those with the designation D500 . Such blocks have optimal characteristics of strength, fire resistance and frost resistance for their class. In particular, compressive strength of up to 3 MPa allows the construction of floors in monolithic buildings and external walls in low-rise buildings. Compared to grade 350, this aerated concrete also has increased noise insulation , although in terms of thermal conductivity it is slightly inferior to its lighter counterpart.
Aerated concrete blocks marked D600 demonstrate strength up to 4.5 MPa. This indicator makes it difficult to use blocks in the construction of walls and partitions of residential buildings of different heights, but also to provide for higher loads. In particular, a ventilated facade can be attached to walls made of this brand of material.
Return to content
Composition and properties
Components included in the mixture for the production of non-autoclaved aerated concrete:
- Portland cement grade not lower than M300, not less than 50% of the total weight;
- sand;
- ash, chalk, gypsum, blast furnace slag;
- aluminum powder for foaming;
- lime;
- water;
- calcium chloride - to speed up the hardening process of the mixture;
- additives and additives to improve the performance characteristics of the material.
In the production of non-autoclaved aerated concrete, sand without impurities and water without salts are used.
The mortar recipe for non-autoclaved concrete requires the use of sand without admixtures of clay or silt, and water without salt content. The following additives are recommended to improve the strength of aerated concrete: semi-hydrous gypsum, microsilica, acidic fly ash. For the same purpose, reinforcing fibers can be added, which will improve the characteristics of the material. For better foaming, washing powders and table salt can be added.
Advantages of aerated concrete blocks
Aerated concrete material is very attractive both in terms of ease of installation and performance. The following qualities contribute to this:
- Heat capacity . Aerated concrete is good not only when used as a heat insulator, but also in general as an energy-saving material. It is the porous structure that allows for heat saving, which is several times higher than the similar qualities of traditional concrete and brick;
- Low weight with high strength . Of course, compared to stone and brick, an aerated concrete block is not as strong, however, in its field of application these indicators are sufficient. The average density, which is due to the porous structure, gives the material a modest mass. As a result, transportation and work of builders are facilitated;
- Environmental friendliness . The recipe for the production of aerated concrete blocks contains mainly mineral, environmentally friendly components. These include sand, water, lime, cement, various slags, etc. Among artificial elements, only binding components , but their percentage is insignificant from the point of view of causing harm to humans. Autoclave blocks are especially safe in this regard, since the forced hardening procedure allows you to rid the material of harmful impurities.
Return to content
Pros and cons of using
The compositions of concrete blocks used in construction are similar, while non-autoclaved aerated concrete has its own advantages. These include: light weight; heat resistance; moisture and frost resistance; energy saving properties; high sound insulation characteristics; seismic resistance; pliability to any electric and hand tools; the ability to fill blocks of any shape; simple manufacturing process. At the same time, the strength indicators are lower than other similar materials. Other disadvantages include a tendency to destruction under the influence of mechanical loads, large shrinkage, and a long period of waiting for the material to harden during the production process.
Disadvantages of aerated concrete blocks
Considering all the advantages described above, we can conclude that cellular concrete has no analogues at all in the modern building materials market . However, aerated concrete blocks, whose pros and cons make them a rather specific material, also have serious limitations in use. This is due to, albeit few, serious shortcomings, including the following:
- Low moisture resistance . Despite the fact that the pores of autoclave blocks are not filled with water, this does not exclude the harmful effects of the latter on the structure of the material. As a result, houses, walls and partitions made of aerated blocks require high-quality independent waterproofing ;
- Shrinkage susceptibility . Shrinkage processes are characteristic of almost all materials that form the basis of buildings of any type. But in the case of aerated concrete blocks, it is important to take into account the consequences of shrinkage in the form of cracking. Manufacturers strive to minimize them, but small displacements of up to 3 mm still occur . You can get rid of shrinkage only by properly drying the blocks before using them.
Return to content
Conclusion
Aerated concrete blocks can be classified as controversial building materials . This means that such blocks have quite significant advantages, but if used incorrectly, they can nullify all the efforts of builders.
On the other hand, it is a lightweight and economical material . For example, finishing of aerated concrete blocks is optional, which reduces costs, as is the case with transporting the material.
Due to insufficient strength, even slight shrinkage can trigger the formation of cracks in the blocks . Therefore, a mandatory measure during the design process should be a scrupulous calculation of the characteristics of cellular blocks and, what is especially important, an assessment of their strength indicators.
Inexpensive roofing
Roofing should be inexpensive. But!
When assessing the cost of roofing, there is no point in paying attention to the “bare” price per square meter. Find out how much additional elements cost - a snow retention system, aeration devices, ridge and end elements, stairs and ladders. Calculate the cost of the material for installing exactly your roofing configuration in the complex, add to this the cost of the insulation cake and rafter system corresponding to the selected type of roofing. You will see that the difference in the cost per square meter of one type of coating from another against the general background of the cost of the entire roofing system with insulation cake is small. And there are often situations when a more expensive type of coating in the total cost of a complex of materials and work turns out to be more profitable to use than a cheaper one.