When planning to make repairs or decoration in their own home, every novice master understands perfectly well that they cannot do without cement.
Cement is sold in special packages
Without it, it is impossible to level the floor, plaster the wall, and generally cope with the finishing. How to make the right choice and not make any mistakes when buying cement? Which brand should you prefer, since the specific gravity of cement M400 and M500 can be completely different? Let's first look at the labeling of this building material.
Brief description of heavy concrete
Reinforced concrete products for construction are manufactured not only at specialized enterprises, but are also very often cast directly at the site being constructed. Not a single construction site is complete without concrete. To create a reliable structure with specified technical characteristics, heavy concrete is used, which, in accordance with building codes, has a volumetric mass of over 1,800 kg/m3.
Distinctive features of heavy concrete
The production of building materials is carried out in two categories: light and heavy concrete products. They differ significantly in physical and technological characteristics and, accordingly, in scope:
- Lightweight concrete is produced on the basis of “light” fillers, which significantly reduce the bulk density and increase thermal insulation properties. In addition, the lighter the concrete, the greater its porosity, which means low hydraulic resistance, so products made from lightweight concrete are used for internal non-critical structures without a strong dynamic destructive effect.
- Heavy concretes are characterized by high strength and low porosity, which guarantees excellent resistance to any mechanical and chemical influences. Building materials made from heavy concrete are applicable for especially critical structures with open (natural) operation, including for the construction of foundations, walls, and pouring floors.
Characteristics of heavy concrete
Calculation and selection of the composition and proportions of heavy concrete is carried out taking into account the required characteristics (properties):
- Strength is the main indicator of the ability of reinforced concrete products to withstand destructive loads. It is this indicator that indicates the area of application of concrete in high-rise buildings, foundations or hydraulic structures. The indicator is classified from B3.5 to B60, which corresponds to the tensile strength marking from M50 to M1000 (from 5 to 100 MPa).
- Thermal expansion and fire resistance of heavy concrete is an indicator of the possibility of using building products in temperature affected areas. Thus, pouring a floor made of heavy concrete has an expansion coefficient of no more than 0.5 mm per linear meter. Concrete can withstand temperatures up to 500 degrees (higher destruction occurs), and at a temperature of about 200 degrees its strength is lost by no more than 30%.
- Porosity, water resistance and frost resistance are related indicators, the amount of which determines the operational resistance of reinforced concrete products. The porosity of heavy concrete should not exceed 15%. Frost resistance is marked by its ability to withstand cyclic freezing from F50 to F1000. Heavy concrete is used in the construction of canals and bridges, so their water resistance is within the marking range W2 - W20 (the number is an indicator of the impact of water in kgf/cm2).
Application of heavy concrete
It is very important to correctly calculate and select the composition and proportions of heavy concrete, because The brand of concrete produced and its areas of application depend on this:
– Particularly critical structures and hydraulic structures must be erected from concrete of a grade not lower than M500.
– Critical structures, foundations and walls of high-rise buildings, slab foundations are made of M250 – M350 concrete.
– Individual construction can be carried out using M150 – M200 concrete.
– Non-critical concrete products for paths, blind areas and elements of road or landscape design can be cast with strength M50 - M150.
Structural features of heavy concrete
The composition and proportion of the components used for heavy concrete directly affects its technological and physical characteristics, so the calculation must be carried out quite accurately, which is more convenient to do using an online calculator. To cast high-quality concrete products with suitable technical characteristics, it is necessary to take into account a number of features of the production of heavy concrete:
- There are always two types of fillers used: large-format and small-format. Large-format aggregates (crushed stone or gravel) ensure the strength of concrete, and small-format aggregates, due to compacted distribution, increase the density and reduce the porosity of concrete. Filler of large formats with angular shapes provides less shrinkage of the casting and high operational dynamic strength. The fraction of fine aggregate also affects the characteristics of the concrete product: the finer it is, the higher the density and water resistance. It is worth considering that the strength of the concrete casting itself depends on the strength of the large-format aggregate.
- Plasticity of concrete or workability is the ability of a concrete mixture to completely fill a poured form with sufficient compaction to guarantee its design strength. Plasticity is marked from P1 (minimum) to P5 (maximum). To fill open areas using compaction (vibration) technology, you can take P1 concrete, but for complex structures it is necessary to use highly plastic concrete solutions from P3 to P5.
It is a mistake to think that adding water can increase the plasticity of concrete without harming its quality, because its uniformity and strength decrease and shrinkage increases. To increase the plasticity of concrete, plasticizers are used, which improve the ability to move fillers, which guarantees high-quality filling of the mold and easy release of air from the casting with a uniform structure of the entire concrete. Professional construction necessarily uses plasticizers.
Which brand of cement should you prefer?
This is what all modern construction is based on!
If you decide to do only interior finishing work, then there is absolutely no point in buying frost-resistant cement, which is used only for exterior work. In such a situation, it is better to look at another indicator - cement marking.
High-strength grades marked with symbols above 400 are not used in construction and finishing work carried out inside the house. Except for those cases when you need to build something super strong. An acceptable grade of cement for finishing a house is M300.
For repair and construction work, for the production of concrete, and construction of foundations, markings from 350 to 500 are suitable. M400 D0 is also very common, it is used for heat and moisture resistant processing. In addition, it hardens quite quickly. M-400 D20 and M-500 have excellent water resistance and frost resistance.
Such a variety of markings helps to choose the best option for the intended purposes, thereby ensuring the strength of the structure and the durability of its operation.
Weight of a cubic meter of concrete
| Type of concrete | Weight 1 cu. m, t |
| On crushed stone or gravel | 2,4 |
| On volcanic slag | 8–1,6 |
| On quartz sand | 8–1,2 |
| On expanded clay sand | 5–1,8 |
| On perlite | 6–1,2 |
| On blast furnace slag | 1,2–1,8 |
The specific gravity fluctuates over a wide range. This is due to differences in the characteristics of concrete: the materials have different grades of density and strength, which depends on the ratio of the components in the composition and the mixing method. Mixes prepared by hand are significantly lighter compared to concrete produced by deep compaction. The amount of water added to the mixture also affects the final results.
Basic performance qualities of cement M400
Portland cement of the described brand is a rather complex composition of mineral components that are in a solid state of aggregation, with a mass fraction of up to 98%. There are aluminum oxides, calcium, magnesium and iron oxides, silicon compounds and other components. In accordance with state standard 31108-2003, Portland cement M400 must have the following basic operational parameters:
- compressive strength after 28 days - more than 30 MPa;
- the setting period of the mixture is more than 60 minutes. upon reaching 98% strength on the 28th day of hardening;
- density with loosened consistency - 1000-1200 kg/m. cubic;
- complete thawing/freezing cycles - at least 70 at an operating temperature range of -60 - +300 degrees C;
- cement that has fully reached its final density must have guaranteed water resistance.
Under storage conditions recommended by the manufacturer (sealed packaging), the material should not lose its working qualities for at least a year.
Mass of a cube of concrete of different brands
| Brand | Weight 1 cu. m, t |
| M100 | 2,494 |
| M200 | 2,432 |
| M250 | 2,348 |
| M300 | 2,389 |
| M350 | 2,502 |
| M400 | 2,376 |
| M500 | 2,298 |
The grade of concrete is an indicator of its compressive strength. It is designated by the letter M and a number from 50 to 1000, which indicates the compressive strength. The indicator is expressed in kgf/sq. cm and depends mainly on the quality of the cement used in the preparation of the concrete mixture. The higher the strength grade, the shorter the hardening period of the material, so it is more difficult to work with. But high-grade concrete is also more durable, and therefore suitable for the construction of monolithic frame industrial buildings, hydraulic structures, etc.
The strength grade affects the weight of a cubic meter of concrete. This is due not only to the characteristics of the components, but also to their ratio. The more water in a concrete solution, the more pores are formed, which reduce the strength of the material in a frozen state. Therefore, high-grade concrete has a lower mass for the same volume.
It is possible to determine exactly how much 1 cubic meter of concrete weighs only experimentally. To do this, manufacturers conduct laboratory tests and weigh materials in order to enter the data obtained in the accompanying documentation for the batch of material: in the declaration, certificate, passport. The weighing procedure must be carried out every time, since the results vary greatly from batch to batch. The specific gravity can be affected by the moisture content of the components, the fraction of fillers, the quality of cement, the type of sand, etc.
What does the M400 marking mean?
The grade of cement determines the grade of finished concrete when it is produced in strict accordance with technical documentation and compliance with technical processes in accordance with GOST. The grade of Portland cement is a conventional value, which is expressed in numbers (in this case - 400) and indicates the strength of the finished product after curing for 28 days. The number 400 indicates that the compressive strength of this material is at least 400 kg per square centimeter.
The marking of cement also reflects the presence/absence of modifier additives in the mixture, which change the characteristics of the solution (improve anti-corrosion characteristics, increase the moisture resistance of the mixture, increase the rate of hardening, etc.).
In accordance with approved standards, Portland cement brand M400 can be produced in pure form (in this case, the index “D0” is indicated on the packaging and in the accompanying documentation), or with special modifying additives (the index is indicated on the packaging – D5-D20). The letter “D” indicates the presence of additives in the cement, and the numerical designation indicates their quantity (D5 - 5% additives, D15 - 15%, etc.).
The main function of modifying additives and plasticizers is to impart additional characteristics to the mortar and concrete. This may be increased resistance to the aggressive effects of sea water, an increased number of frost resistance cycles, rapid or delayed hardening, etc. The manufacturer can also introduce technological additives into the cement composition, for example, to facilitate the grinding process of Portland cement clinker and gypsum stone, improve cement transportation, etc.
In accordance with the rules adopted several years ago, the labeling indicates one of two designations:
The new standard does not have the concept of brand, but there is the concept of strength class. If, according to Soviet standards, the strength of Portland cement was indicated in kg per square centimeter, then according to the new rules it is indicated in megapascals (MPa). The M400 brand corresponds to the designation - 32.5.
Next in the marking follows the subclass: N - normal-hardening or B - rapid-hardening. An example of PC decoding according to the modern notation standard:
CEM II 32.5B - Portland cement with modifying additives, the strength of this type of cement corresponds to the M400 grade, quick-hardening.
Weight of dry and wet concrete
Humidity indicators affect the specific gravity of any materials: sand, gravel, cement. The presence of water in the concrete solution also increases its mass, but when making calculations it is important to remember: it evaporates during the hardening process of the material. The more liquid there was initially, the more significant the difference in the mass of a cubic meter of wet and liquid concrete will be.
| Brand | Weight of dry concrete, t | Mass of liquid concrete, t |
| M100 | 2,18 | 2,366 |
| M150 | 2,181 | 2,36 |
| M200 | 2,182 | 2,362 |
| M300 | 2,183 | 2,358 |
| M400 | 2,170 | 2,35 |
| M500 | 2,180 | 2,355 |
Recipe for preparing cement mortar
Before you start preparing a concrete product, you need to familiarize yourself with some useful tips:
- The cement used is of a grade
that exceeds the required concrete class value by at least 2 times; - To make 1 cube of solution
, much more dry materials are needed than in the calculations, because when the mixture is obtained, it noticeably decreases in volume; - The strength of crushed stone
should be 2 times higher than the design grade of the finished product; - When mixing sand and cement,
you should use a measuring bucket, not a shovel; - concrete for the foundation
using a concrete mixer; - The process of preparing the solution itself comes down to the following algorithm
: pour water into the concrete mixer; - add the remaining components;
- add liquid;
- mix the solution;
no more than two hours from the moment of preparation.
The production of cement-lime mortar occurs as follows:
- 2/3 of water is poured into the concrete mixer;
- pour lime, then cement, doing this alternately;
- add sand;
- fill with remaining water.
This solution is used no later than 5 hours after production. At temperatures above 25 degrees, the application time is significantly reduced.
For greater contact of the solution with the previously laid masonry, it must be wetted. If the solution is applied with a trowel, there is no need to press the finished mixture into the cracks of blocks that have voids. Otherwise, the thermal insulation of the wall will be significantly reduced. During long breaks in the construction of walls, the masonry is covered with a film, which prevents precipitation from entering it.
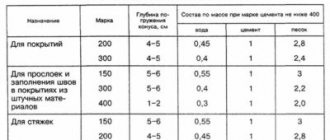
The table shows the main brands of solution and raw material consumption
Cement-sand mixture is used quite widely in construction. It is used for making brickwork, leveling the floor using screed, and also for plastering. The components will be the same. Only the consumption of cement and sand per 1 m3 of solution differs. At first glance, it may seem that everything is quite simple here - you should use a ratio of 1:3 or 1:4, depending on the requirements for the strength of the composition. But what proportion should be used and in what cases?
| Proportions of cement and sand for the production of cement mortar of various grades | ||||
| Cement | Cement mortar grade “100” | Cement mortar grade “50” | Cement mortar grade “25” | Cement mortar grade “10” |
| Part ratio, cement:sand | ||||
| Brand M-400 | 1:3,5 | 1:6 | — | — |
| Brand M-300 | 1:2,5 | 1:5 | — | — |
| Brand M-200 | — | 1:3,5 | 1:6 | — |
| Brand M150 | — | 1:2,5 | 1:4 | 1:6 |
How much does a cube of concrete weigh?
The use of cement mortar for construction purposes can be found much more often than most other known materials. That is why quite often it is necessary to find out the mass of one cubic meter of the mixture - the weight of finished concrete and reinforced concrete structures plays an important role in the design of structures. Next we will talk about how much a cube of concrete weighs and what affects this characteristic.
What affects the consumption of cement when making a cube of mortar?
The selection of components of the finished concrete mixture is subject to certain features. For example, you need to know that as the grade of cement increases, the amount of binder will decrease. Also, in some cases, stone dust is added to the solution. This reliably preserves its structure.
Cement consumption per 1 cubic meter meter of finished product depends on:
- Brand of mortar
- it shows the degree of strength of the resulting product. Its value is selected depending on the final purpose of using the resulting material. Mortars of maximum strength are used in the manufacture of building supports. Interior walls require less binder content. - Type of mortar
- sand, clay or limestone. They differ in the final purpose of using the resulting product, and as a result, require different ratios in the solution. So, in the case of using clay, cement is used in a ratio of 1:9. - The composition of the solution
is the specific ratio of binder and filler.
How much cement will be needed per cube of mortar?
Approximate amount of cement consumed per cubic meter. A meter of the resulting solution, according to the standards for the manufacture of building materials, is equal to 200 kg of binder. This volume is required if grade 100 cement is used.
How many bags of cement should I buy?
Preparation of the optimal mortar for the foundation, screed and other construction work requires an accurate calculation of the ratio of cement and other components of the finished product. This value must be determined based on the brand of binder.
For example, for masonry mortar you need to use 1 cubic meter. meter of sand with a third cubic. meter of cement. Here the number of components of the solution is indicated without taking into account the inclusion of water in its composition. The volume of sand should be equal to the final volume of the product.
Depending on the purpose, a certain amount of mortar and, accordingly, cement is used.
The finished concrete product consists of the main components:
- Binder
– the solution is mixed on its basis. It is a powder material that quickly hardens and crystallizes after moistening. - Ballast
is sand mixed with gravel. - Crushed stone
is a material that consists of large, loose grains. - Construction additives
– improve the properties of the finished product.
In most cases, cement is used in a ratio of 1:3, 1:4 and 1:5.
Classification by weight
The use of concrete mass has become quite widespread: from finishing purposes to the construction of dams. That is why the characteristics of the mixture are displayed by dividing them into classes and brands. This makes it possible to make precise choices for specific purposes. For example, B25 grade of concrete is much stronger than B10 and, naturally, its mass will be greater. There is also a division depending on mass. The table will help you see exactly the weight of concrete in 1m3, but more on that a little later, but for now let’s look at the division by “weight categories”:
| types | stamps | specific gravity, kg |
| especially light | M50 - M75 | up to 500 |
| lungs | M100 - M200 | 500-1800 |
| heavy | M200 – M400 | 1800-2500 |
| especially heavy | M 450 and above | 2500-3000 |
Weight directly depends on the density of all elements and can be in the range of 300-3000 kg.
Thermal insulation (extra light)
This material is made from cement and fillers, which when mixed, produces a structure with about 85% voids. Used for the manufacture of structures with special requirements for thermal conductivity (they are not able to withstand significant load-bearing loads). This category includes mixtures weighing up to 500 kg per cubic meter. In some cases, a plasticizer for concrete is used to increase their strength.
It is worth considering the low resistance of porous structures to frost. When installing them, it is necessary to install waterproofing protection.
Easy
This is how a solution with a mass in the range of 500-1800 kg is classified. It is mainly used to create special building blocks, the structure of which contains pores - they can be formed with the help of foaming agents or due to the use of cellular fillers (expanded clay, for example).
Only ready-mixed concrete can exactly match the specified weight and grade.
Heavy
Heavy concrete is one of the most common in construction. It is ideal for the construction of structural components that perform a load-bearing function. The weight of the cube in this case can be 1800-2500 kg - this figure depends entirely on the percentage of sand and coarse filler, as well as the density of the latter (even when using granite and gravel filler in the same quantity, the final weight of one cubic meter will be different).
Super heavy (extra heavy)
For its manufacture, metal fillers are used, which increases the weight characteristics to a maximum limit of 1 cubic meter - a little more than 3000 kg. Such mixtures are used to prevent the spread of radioactive radiation through walls.
The production of super-heavy mixtures involves the use of materials quite specific to construction, the cost of which will make the construction of a house quite expensive. That is why they are used exclusively in the construction of objects with increased requirements for radiation protection.
Table Weight of 1 cube of solution depending on the type of binder and fillers
| Name of solutions | Weight of 1 cube |
| Cement-sand mortar | 1800 |
| Complex mortar (sand, lime, cement) | 1700 |
| Lime-sand mortar | 1600 |
| Cement-slag mortar | 1400 |
| Cement-perlite mortar | 1000 |
| Gypsum perlite solution | |
| Porous gypsum perlite solution |
Cement is one of the building materials that is used to prepare a binder mortar. There are various brands that differ in the strength of the final product, which also has some classification.
High-quality construction requires that the brand of mortar be identical to the brand of building material (cement). Determine how much cement powder is needed to obtain 1 cubic meter. meter of mixture at a ratio of 1/4 (binder and filler) is very simple.
Determining the quality level of a solution is very simple. To do this, you need to divide the brand of cement by the number of buckets with sand used.
You just need to know:
- The percentage of aggregate is the amount of sand in the solution.
The optimal solution is to use sand of different grain sizes. This is necessary for better mixing of them with each other. - Amount of binder element.
- The density of cement
varies depending on the storage time. Fresh cement has an average density of 1100-1200 kg/cub.m. After long-term storage it rises to 1500-1600 kg/cub.m. The average density of cement is 1300.
If you use a ratio of binder to aggregate of 1:4, then the composition will contain 20% cement.
If we take into account its density, then its consumption per 1 cubic meter of solution can be easily calculated as follows:
Average density (1300)/number of parts in solution (5) = 260 kg. This equals 5 bags of cement. With a similar formula, you can carry out the necessary calculations using an online counter specially developed for this on the Internet.
The use of cement is very wide, so it has to be calculated in many cases:
- Foundation work
- in this case, high quality mortar is required; - For subsequent production of reinforced concrete
and other construction products; - Bricklaying;
- For the production of asbestos-cement products
.
The main thing when calculating the required volume of a binder is not to make mistakes in the notation and not to confuse kilograms with grams, for example.
Depending on the application, the percentage of elements may vary. For example, for the manufacture of brickwork, the ratio of 1:3 and 1:4 is used.
In practice, the amount of cement when making the mortar turns out to be slightly higher than expected. This is due to the fact that sand has a larger particle size.
As a result, cement fills voids very well when mixed with aggregate.
Using the example of calculating the required volume of cement powder in a 1/3 solution, we will consider another calculation method.
To do this you need to know the following information:
- In 1 cubic a meter of space contains 1000 liters;
- The weight of a bag of cement is 50 kilograms;
- 1 bag contains 36 liters;
Also, in order to know how many cubes are in 1 bag of cement, you need to understand its “filling”.
Cement contains:
- Clinker is an intermediate element.
It is obtained by heating lime and clay quite strongly. It is then crushed and mixed with gypsum. It makes up 85% of cement. - Various additives
that determine the properties of the final product.
A solution with a ratio of 1:3 is calculated according to the following steps:
- 1 cu. meter of sand + 1/3 cubic. meter of binder (333 liters);
- 333 liters *1.4 kg/l. This turns out to be 466 kg of cement, which is necessary to obtain 1 cubic meter of solution.
In a similar way, you can calculate the required amount of cement powder at any ratio with sand. So, calculate the price of 1 cubic meter. meters of solution in general, and the binder in particular, is not at all difficult. 1 bag of cement how many cubes of mortar
There is such a thing as a water-cement ratio. It characterizes the percentage of water content in the final product. This parameter is determined depending on the volume of the binder. This is what characterizes the quality of the resulting concrete. If the water-cement ratio is 0.50, this means that the volume of water required will be equal to 50% of the amount of binder.
This indicator can characterize concrete, defining it:
- Brand
is the main indicator that draws attention to itself when purchasing construction products. The grade of concrete is designated as follows: m 70, or m 75. These numbers characterize the compressive strength of the finished product. - Class
- also characterizes the strength of the material and is directly proportional to the brand. The higher it is, the greater the class value. It is designated as B 10. - Frost resistance
– resistance to the destructive effects of low temperatures. - Consistency
; - Plasticity
and other characteristics.
Relying on the calculations described above, you can determine how much concrete is produced from 1 bag of cement. First you need to decide on the proportions.
If you adhere to the classic ratio, then the proportions will be as follows - 1: 2: 3 (cement, sand and crushed stone, respectively).
A simple calculation leads to the formula - 50*(50*2)*(50*3)=300 kg. The density of the concrete obtained at this ratio is 2400 kg/cubic. meters. To determine the volume of a product, you need to divide the mass by the density. The result will be 0.125 cc. meters.
Volumetric weight table
| Cement brand | Liquid state (t/m³) | Dry condition (t/m³) |
| M100 | 2 366 | 2 180 |
| M150 | 2 360 | 2 181 |
| M200 | 2 362 | 2 182 |
| M300 | 2 358 | 2 183 |
| M400 | 2 350 | 2 170 |
| M500 | 2 355 | 2 180 |
If we compare weight indicators in volumetric and specific ratios, it turns out that volumetrically M200 weighs the same as actual concrete M250.
Basic moments
Before proceeding with detailed calculations, you should consider the main factors influencing the consumption of cement and sand. There are several of them:
Interesting! Qualified builders claim that to obtain a cubic meter of solution it is necessary to use a cube of sand. The cement and water will simply fill the space between the grains of sand.
In most cases, the composition is prepared according to the principle identical to the previous version. But professionals additionally use plasticizers that improve the performance properties of the mixture, as well as polypropylene fiber. Such components will allow you to obtain a high-quality coating that can last for decades.
| Cement consumption, kg per 1 m³ of sand or mortar | ||||||
| Cement brand | Brand of solution | |||||
| 150 | 100 | 75 | 50 | 25 | 10 | |
| 400 | 350 | 255 | 100 | 140 | — | — |
| 400 | 300 | 240 | 175 | — | — | |
| 300 | 470 | 340 | 270 | 185 | 105 | — |
| 510 | 385 | 310 | 225 | 135 | — | |
| 200 | — | — | 405 | 280 | 155 | 25 |
| — | — | 445 | 325 | 190 | 95 | |
| Note: the top line is cement consumption per 1 m³ of sand, the bottom line is per 1 m³ of solution | ||||||
When preparing a solution, the best option is a hardener of the M150, M200, M300, M400 brands. The consumption of cement and sand for screed is represented by the ratio 1:3. Simply put, for 50 kg of the latter, take 15-16 kg of hardener.
Important! Much attention should be paid to the consistency of the resulting composition. It should be like thick sour cream, slightly spreading on a flat surface. If there is too much water, the mixture turns out to be very liquid - its performance characteristics will decrease, and the screed will be defective.
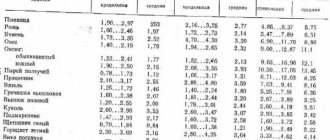
Specific gravity table
| Concrete grade | Specific gravity of 1m 3 concrete |
| Concrete M100 | 2494 kg |
| Concrete M200 | 2432 kg |
| Concrete M250 | 2348 kg |
| Concrete M300 | 2389 kg |
| Concrete M350 | 2502 kg |
| Concrete M400 | 2376 kg |
| Concrete M500 | 2298 kg |
Now you know how much a cube of concrete of a particular brand weighs. Just keep in mind that it is possible to achieve exact compliance with the characteristics during its factory production.
Plastering surfaces
Plastering the base when performing external finishing work requires the use of a component of no less quality than the screed. The best option would be cement grades M300 and M400. For one part you should take 3 parts of sand. To prepare a cement-lime mortar you will need one part of Portland cement M400 or M500, ½ lime paste, 2 volumes of washed sand. These are the optimal consumption rates of cement and sand for plaster.
Looking at bags of cement and a pile of sand, not every developer feels calm and confident. He is tormented by the question: what proportion should be chosen for the solution so that it turns out strong enough and does not “eat up” extra money?
Sprinkling “by eye” is stupid and dangerous, especially when it comes to critical concrete work on the foundation or brickwork. Following the principle “the more the merrier” is also not an option. When it comes to cubes, such a rule can ruin the developer.
Another question that arises in this regard: how to control the work of the builders who are tasked with preparing the mortar and concrete? You can’t keep track of everything, so there is no guarantee that the cement will not go “to the left”, and the foundation and masonry will not soon collapse.
If the customer knows exactly what the standard consumption of cement and sand is for the mortar, it is easier for him to control his costs and monitor the use of purchased materials.
How much does a cube of concrete weigh - weight table for all brands!
Often, when planning construction work, you need to know how much a cube of concrete weighs m300, m400, m500. Let's see how much a cubic meter of concrete mixture will weigh, depending on its type. The mass of the concrete mixture is determined by the mass of the aggregates used.
Weight m3 of concrete grades M100, M200, M300, M400, M500.
According to the specific gravity, the concrete mixture can be:
- especially light up to 500 kg;
- light 1000 to 1800 kg;
- heavy 1800 - 2500 kg;
- especially heavy 2500 to 3000 kg.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated when calculating the mass of concrete mortar, and then we will consider in more detail the question of what the mass of concrete is for different brands, and we will also provide a detailed table.
Specifications
Portland cement Grade M-400 is a complex composition of components of mineral origin that are in an aggregate state. The composition of the mixture is dominated by oxides of calcium, magnesium, oxides of aluminum, iron, and silicon. The share of mineral components reaches 98%.
M400 cement, in accordance with the requirements of GOST 31108-2003, must meet the following characteristics:
- Compressive strength (after 28 days) - not less than 30 MPa;
- The onset (time) of setting is at least 60 minutes, strength (up to 98%) is achieved after 28 days;
- Density in a loosened state - 1000-1200 kg per cubic meter;
- Uniformity of volume change - no more than 10 mm;
- Frost resistance - operating temperature range -60 - +300 degrees, 70 cycles of complete freezing/thawing;
- The water resistance of cement that has fully gained strength is high;
- Shelf life in sealed packaging is up to one year.
Specific and volumetric weight of concrete in 1m3, table of weights of all brands.
Concrete is the main component of any construction work, be it ordinary repairs or the construction of pits and structures. It has high strength initially, but with the use of additives it can improve its characteristics.
During construction, first of all, how much concrete weighs is calculated, since based on this characteristic it is determined by the specifics of its use and application. The weight of the solution depends directly on the components added as filling. These can be materials such as crushed stone, expanded clay, pebbles and many others.
Also, when kneading, the volume of water spent is taken into account. Based on these characteristics, concrete is divided into four types: light and heavy, especially light and especially heavy.
Weight of 1 cube of concrete of all brands and classes, table:
Detailed weight table.
| Concrete grade | Concrete class | Weight of 1 m3 of concrete (kg) |
| M100 | B7.5 | 2494 |
| M200 | B15 | 2432 |
| M250 | IN 20 | 2348 |
| M300 | B22.5 | 2502 |
| M350 | B25 | 2502 |
| M400 | B30 | 2376 |
Types of specific gravity of 1 cube of concrete.
The most common way to classify the mass of a cube of composition is by dividing it according to specific gravity.
According to the volumetric mass, the following types of concrete are distinguished:
- Particularly light: Weight 500 kg maximum per cubic meter. Characterized by the content of air cells with a diameter of 1-1.5 mm and a porous base. These are the familiar foam and gas blocks, which are based not only on classic cement and sand, but also on a foaming agent that creates cells with air. This allows for low weight and good thermal insulation properties.
- Lightweight - concrete compositions filled with lightweight porous aggregates, such as expanded clay or without aggregates, but having a porous structure, such as foam concrete or aerated concrete. A cube (cubic meter) of lightweight concrete weighs from 500 to 1800 kg. A cubic meter of concrete includes about 600 kg of sand - the main and essential component. Lightweight concrete is usually used in the form of ready-made building blocks.
- Heavy. This is the most common (classic) type of mortar. It is best suited for the construction of the main elements of load-bearing structures, pouring screeds, erecting fences, etc. The composition of heavy concrete includes large-sized and massive fillers: coarse sand, gravel, crushed stone. They occupy the bulk of the mixture. A cubic meter of such material weighs 1800-2500 kg.
- Particularly heavy . Metal fillers are used in production, giving the finished product a massive appearance. The weight of a cube of concrete is 2500-3000 kg. Super-heavy mixtures necessarily contain high-strength cement. They are not used in private housing construction. They are usually used to make protective structures for special purposes, for example, for nuclear reactors.
| types | stamps | specific gravity, kg |
| especially light | M50 - M75 | up to 500 |
| lungs | M100 - M200 | 500-1800 |
| heavy | M200 – M400 | 1800-2500 |
| especially heavy | M 450 and above | 2500-3000 |
Application area
Sand-cement mixtures are used in various branches of construction:
- For plastering walls and exterior work. In the process of producing mixtures for plaster, lime and plasticizers are introduced into the composition, which can impart specific properties to the mixture.
The cement-sand mixture for plaster is prepared in a ratio of cement and sand of 1 to 3, which is the most optimal proportion in construction. To increase the plasticity and adhesion of the solution, you can add a little lime or clay. You can purchase ready-made mixtures in the store if the amount of work is small. In this case, the solution will cost several times more than all the components separately.
- For masonry mortar. This mixture has the greatest strength. You can prepare it yourself if you have M200 cement. At sub-zero temperatures, special components are added to the mixture to ensure frost resistance of the material. If you remove crushed stone from the composition, then the ratio of cement and sand will be 1 to 3. In this case, the volume of liquid to obtain the finished solution will be half the volume of cement.
If the solution turns out to be too thick, it will quickly harden, and it will be very difficult to work with such a solution, since its ability to adhesion will be much reduced. For example, it will be difficult to adjust the bricks; aligning them will require more effort.
- For screeding floors. The screed is carried out to level the floor surface. It usually happens in multi-storey buildings that one concrete floor slab is laid slightly higher than the second, resulting in an unevenness at their junction.
The mixture can be prepared either independently or purchased at a hardware store. At factories, fillers are usually added to the solution: fine crushed stone or gravel. Thanks to these components, the coating acquires higher strength and low shrinkage ability.
“Old-father method” or current SNiP?
Experience is a good thing, but we should not forget about building regulations. They take into account all the factors associated with the preparation of mortars and concrete (purity, coarseness, moisture content of sand and crushed stone, cement activity and water quality).
Therefore, when preparing for work on pouring a foundation, screed or laying walls, do not be lazy to look at the GOST tables. You only need one or two lines in them. They clearly describe what the cement consumption per cube of mortar should be to obtain the required strength (grade).
Here is a simple “squeeze” from SNiP, which will help you prepare a high-quality mortar for masonry and screed. After studying it, remember that the given consumption rates differ slightly from practical values.
The reason is that they are produced from standard preparation conditions (air temperature +23C, medium-grained sand, ideally clean, its humidity no more than 7%, etc.).
It is not realistic to ensure standard parameters for mixing at a construction site, so it is better to purchase cement with a small reserve (10-15%).
The answer to the question of how much cement and sand you need per cube of concrete will be given by the following standards:
| Concrete grade | Cement consumption M500 kg/1m3 |
When making concrete, it is important to know not only the amount of cement, but also the standard volume of sand and crushed stone. The following table will be useful for calculations.
Volumetric proportions for various grades of concrete
| Concrete, brand | Ratio of cement/sand/crushed stone in liters | |
| cement M 400 | cement M 500 | |
The required sand consumption per 1 m3 of solution is 1 cubic meter. Some developers are mistaken in believing that the volume of cement increases the volume of the finished mixture. This is wrong.
The cement is very finely ground, so it is distributed in the voids between the sand, without increasing the total volume of concrete and mortar. Therefore, for 1 m3 of sand we can add 200 and 400 kg of cement, obtaining the same 1 cubic meter of solution.
Water is added to the mixture according to a simple proportion - half of the total weight (not volume!) of cement. In this case, you need to take into account the actual moisture content of the sand and pour water in small portions so that the solution or concrete does not turn out to be too liquid.
The consistency of the solution according to the standards is determined by the amount of sediment of a standard metal cone lowered into the mixture. You are unlikely to be able to conduct such a test on a construction site.
Therefore, just remember that the thickness of the masonry mortar should be such that it is not too hard, but rather flexible and does not leak out of the seams.
For the screed, the mortar and concrete must be of medium thickness so that they can be easily compacted and leveled according to the rule.
How many bags of cement should I buy?
Before things get to the point of mixing, it is important for the developer to know how many bags of cement will have to be purchased. Here you should also build on standard consumption rates.
To convert cubes into kilograms, use the average bulk density of the binder: in 1 liter - 1.4 kg of cement.
1/4 of a cube is 250 liters. Multiplying them by 1.4 kg, we get 350 kg of cement. So, in total we will have to purchase 350/50 = 7 bags of cement (50 kg each) or 14 bags of 25 kg each.
You can calculate the binder consumption per 1 m2 of screed using the “reverse” method. With a thickness of 10 cm, filling one “square” will require 0.1 m3 of solution. It contains 10 times less cement than 1 cubic meter: 350 kg/10 = 35 kg. For a screed 5 cm thick we need 35/2 = 17.5 kg of M500 cement.
The rate of cement consumption is greatly influenced by its activity. It is determined experimentally by mixing control samples and testing them for strength.
This method is not suitable for the average developer. A rule of thumb to follow when purchasing and before using is shelf life.
The loss of activity by cement can reach 20% in one month. Therefore, after keeping this material in the garage for three months, you will receive a 400 grade instead of the 500 grade indicated on the label.
When using such a binder for mortar or concrete, take the consumption rate specifically for this (reduced) grade. If cement waits for its “finest hour” for six months, then it is not suitable for anything other than disposal to a landfill.
Vigilance should also be exercised when purchasing binders, requiring the seller to provide a certificate for the purchased batch, which indicates the factory production date.
To determine how much sand and cement is needed per 1 cubic meter of mortar, it is important to know its purpose. To prepare masonry, plaster, foundation and other types of mixtures, different ratios of dry materials are used. The consumption of sand and cement per 1 m3 of mortar varies for each type of work, and often other dry or liquid compositions are added to the composition, increasing moisture resistance, strength, changing the rate of hardening of the mixture, etc.
Weight of a cube of concrete 1m3 - grades and table.
To accurately determine the weight of concrete, you need to know its brand and type. Based on specific gravity, mixtures are distinguished:
- lungs;
- heavy;
- especially heavy.
Lightweight concrete
The basis of mixtures of this type is porous aggregates, which is why they weigh less. Expanded clay, shell rock, and tuff are used as fillers. There is concrete without them, but with a foaming agent (gas, foam concrete). The weight of a cube of light concrete is 500-1800 kg. The main component is sand, of which 1 cube contains up to 600 kg.
Varieties of these mixtures are used as ready-made wall blocks and distributed according to density (D-parameter), which characterizes the specific gravity of 1 m3 of concrete. The weight of the D600 foam block is, for example, 600 kg/cubic.
Heavy concrete
Classic mixture with crushed stone or gravel. The weight of concrete is 1800-2500 kg per cube of the finished composition. The bulk of the average distribution is as follows:
- crushed stone – 1250 kg;
- sand – 650 kg;
- cement – 300 kg;
- water – 200 l.
Extra heavy concrete
A rare type, on barite, magnetite and various types of scrap metal and similar compounds. Such concrete has a heavy weight - 2500-3000 kg/m3. coarse aggregate has the highest specific gravity.
Reference. Weight limits vary depending on the type and can have a wide range. The most common type of concrete used for monolithic work is cement. Its weight is 2300-2500 kg per cubic meter.
Concrete weight by grade
How much does concrete weigh, based on its grade? To do this, specialists carried out repeated weighings and displayed the average concrete weight values in a table.
So, if you calculate based on the type of concrete, the average weight is 2400 kg/cubic meter. This
similar to the calculated indicators for various parameters. Concrete of such strength will ensure frost resistance, reliability and water resistance of finished products. It is used for foundations without fear of any climatic and weather conditions. The error may be experimental. In addition, filler fractions and manufacturer also matter, even for concrete of the same brand, but from different sources. Components, such as sand, can be of different densities and structures - fine, larger river sand, sifted. The cooking method also affects the weight. The composition prepared using equipment and manually will differ in weight.
Expert advice! Don’t have a table, manufacturer, brand of concrete at hand? Focus on the value 2500 kg/m3. It is true for most designs and is most often found in reporting.
Why know the specific gravity of concrete?
Most often, weight information is needed in order to calculate the cost of concrete needed for pouring. In addition, this information is important for determining the density and amount of building mixture required. The price of concrete per 1m3 directly depends on the amount of cement and its strength, which also needs to be taken into account.
Concrete delivery in Moscow and some areas of the Moscow region is carried out using concrete mixer trucks with a volume of 7 to 12 cubic meters. These vehicles retain the properties of concrete and make the pouring process convenient and not dependent on the year and weather conditions.
What determines the weight of a cubic meter of concrete?
No one will give a definite answer to this question without first asking several clarifying questions. The weight of concrete is a value that depends on a combination of indicators such as:
- brand of cement;
- type of aggregates;
- the amount of water used for mixing.
Depending on the above factors, the following types of concrete are distinguished, differing from each other in their specific gravity, that is, the mass of a cubic meter:
Extra light
Most often these are cement mortars filled with small air bubbles or pieces of perlite, vermiculite and other light minerals. They are used as heat insulators, when sealing various seams, joints, and to eliminate cracks. They are not suitable for the manufacture of load-bearing structures. In this case, the weight of a cube of concrete does not exceed 500 kg.
Lightweight, grade M 100 or 150
The fillers in them are porous materials, for example, tuff, expanded clay or shell rock. There are types of mortars that do not contain either heavy or light stones. Their low weight is explained by the presence of pores in the cement mortar itself. These include foam and aerated concrete.
A cubic meter of such mixtures can have a mass from 500 to 1800 kilograms. A significant proportion of them is occupied by sand, which can be up to 600 kg in a cube of the finished solution. Such concrete mixtures are used to make wall blocks.
Heavy, grades M 200, 250, 300
These are classic concretes in which gravel or crushed stone acts as fillers. They are prepared using the proportion 1:2:4:0.5 or 1:3:5:0.5, where the first number is the volumetric content of the binder component - cement, and the rest are sand, crushed stone and water, respectively.
For example, to prepare a cubic meter of such concrete mortar it will be necessary to spend from 250 to 400 kg of cement, depending on its brand, 600 - 700 kg of sand, 1200 - 1300 kg of gravel or crushed stone and fill this mixture with 170 - 200 liters of water.
These values are imprecise and can vary widely. However, concrete is produced in large volumes, so a few kilograms lost and added during calculations will not play a significant role.
A cube of such concrete has a mass of 1800 to 2500 kg. The range of areas of its application is very wide. This includes pouring foundations, building monolithic walls, and manufacturing reinforced concrete slabs and blocks. This solution is suitable for pouring screeds, paths, platforms, making fences and stairs. The concrete grades indicated are the most in demand.
Extra heavy, grades M400 or 500
Here, waste from the metallurgical industry (metal scrap), as well as magnetite, barite, and hematite are used as fillers. Such concrete is not used in the construction of residential buildings. The main areas of their application are the creation of protective structures at nuclear power plants, in bunkers for storing radioactive waste and other similar structures.
The weight of a cubic meter of such concrete is from 2500 to 3000 kg, most of which is accounted for by large aggregates.
Weight determination
Reference data on the volumetric weight of concrete are defined in SNiP No. II-3. This standard specifies the design weight of concrete varieties depending on the type of filler. It contains a table of concrete weight, from which you can find out that reinforced concrete products are characterized by a volumetric weight (in kg/m3) of 2500, concrete using filler in the form of gravel or crushed stone - 2400, expanded clay concrete based - 500-1800, based on perlite sand - 800-1000. In turn, aerated concrete is characterized by a volumetric weight of 300-1000 kg/m3. Naturally, the weight of 1 m3 of concrete is approximate, but these data are quite suitable for calculation purposes. After all, the accuracy of data up to several kilograms cannot be ensured by any calculation.
How to calculate the mass of a cubic meter of concrete
All the above parameters are regulated by SNiP standards No. II-3, established back in 1979. This document also provides more precise values for concrete using specific aggregates (all values in kg/cubic meter):
- reinforced concrete structures - 2500;
- crushed stone, gravel - 2400;
- tuff - from 1200 to 1600;
- pumice and other fractions of volcanic origin - from 800 to 1600;
- expanded clay - from 500 to 1800;
- foam and aerated concrete - from 300 to 1000.
You can also determine the mass of a cubic meter of ready-made concrete based on its brand. The specific gravity of concrete in kg/cubic meter is given below:
Table “Specific gravity of concrete (1m3) of various grades”
If you need data specifically for your concrete, and not average indicators, you can make the calculations yourself. To do this, you need to know the content and brand of each component of the mixture.
Characteristics of concrete
Compressive strength is used as the main indicator characterizing concrete. This characteristic defines o (Latin) and numbers indicating (in kg/sq.cm) the permissible load. For example, the value B25 shows that this class of concrete is designed for a load of 25 kg/sq.cm. When calculating the strength indicators of structures, coefficients should be taken into account. Example: a structure made of class B25 concrete at a rate of 13.5 percent can withstand a load of 327 kg/sq.cm, and this is equivalent to strength grade M350. Strength class B3.5 corresponds to strength grade M50, B10 - M150, B30 - M400, and B60 - M800.
Other important indicators of concrete include frost resistance, flexural strength and water resistance. Frost resistance is designated by the letter “F” and a number from 50 to 500, indicating the number of transitions from freezing to thawing and back that the concrete will withstand. For the water resistance indicator, the letter “W” and a number from 2 to 12 are used, which shows what a sample of a given brand of concrete in the form of a cylinder will withstand.
What determines the mass of concrete?
First of all, it should be noted that builders do not use such a concept as “specific gravity of concrete.” This is due to the fact that this building material may contain a variety of components with different weights. So, the following can be used as a filler: . Crushed stone. . Gravel. . Expanded clay, etc. Even if the same composition is used to prepare a concrete solution, the weight of 1 m3 of concrete may be different in cases where the filler has different fractions. The larger the fraction size, the more voids in the material and, accordingly, the less its mass.
But builders are still interested in weight characteristics, since many characteristics of the objects being completed depend on the value of this indicator. For example, based on this data, the type of foundations for different types of soil is made and selected. The same applies to other load-bearing elements.
In practice, builders use a parameter called “volumetric weight”. But this characteristic does not have a permanent meaning. In addition, the calculations must take into account the weight of the liquid used in preparing the solution.
Cement consumption for masonry
When preparing cement-sand mortar for brickwork, take into account that the construction of 1 m2 of a wall with a thickness of 1 brick (250 mm) will require at least 75 liters of M100 grade mortar.
The proportion of cement (M400) - sand here is 1:4. Cement consumption for bricklaying with this ratio will be 250 kg per 1 cubic meter of sand.
Water, as we have already said, is taken at the rate of 1/2 of the total weight of the cement used.
Translating into “bucket standards” that everyone can understand, let’s say that for one 10-liter bucket of cement (M500) we need four buckets of sand and 7 liters of water. We calculate the amount of water based on the weight of the cement in the bucket (10 liters x 1.4 kg x 0.5 = 7 liters).
To quickly determine the need for cement masonry mortar for walls of different thicknesses (per 1 m3), you can use the following table:
| Type of brick | Wall thickness in bricks | |||||
| (250x120x65mm) | Brick, pcs. | |||||
| Solution, m3 | ||||||
| Modulated (250x120x88mm) | Brick, pcs. | |||||
| Solution, m3 | ||||||