How to make formwork from OSB boards with your own hands?
Formwork is an integral part on a construction site. It is used not only for the construction of strip foundations, but also stairs, armored belts, floor slabs, columns, and wall structures. Allows you to create products from concrete mortar of a certain shape. Often the main elements for its manufacture are wooden boards or metal plates. One of the most practical options is OSB.
Oriented strand panel is a type of engineered lumber that resembles chipboard in its wood structure. It is formed using special adhesives and pressing several layers of wood chips oriented in the required manner. It has a somewhat rough surface, where small chips of wood measuring approximately 2.5x10 or 2.5x15 cm are visible. They are located chaotically, while their thickness and appearance differ from each other.
To create OSB, three thin layers of shavings are used, with the two outermost ones opposite each other being laid lengthwise, and the middle one perpendicularly. It is this oriented arrangement that ensures proper strength. Water-resistant synthetic resins and high-temperature pressure molding are also used to improve performance. Due to their homogeneous structure, they work well in bending and tearing.
OSB formwork has:
- Low hygroscopicity. The material is particularly resistant to swelling or delamination.
- Easy to process. Easy to saw and drill.
- Reusable. OSB-3 does not lose its qualities, since one of the sides is laminated.
- Light weight. It simplifies installation work, which is why it is in demand among private developers.
- The possibility of using large-sized slabs, which allows you to create large-panel formwork with a small number of joints.
Oriented Strand Board
OSB/OSB board is easily recognized by its characteristic wood structure. Oriented strand board (OSB) is a type of engineered lumber, similar to chipboard, that is formed by adding adhesives and then pressing layers of wood strands oriented in a specific way. The OSB surface is rough and variegated, with individual shavings (chips) about 2.5 cm * 15 cm, located unevenly to each other and having different appearance and thickness.
Usage
OSB boards are widely used in residential construction. The mechanical properties of this building material allow it to be used for a variety of purposes. Most commonly used as sheathing for walls, floors, roof decks and formwork for foundations and other concrete (reinforced concrete) building elements. For external walls, panels are produced pre-laminated on one side; this simplifies installation and increases the energy efficiency of the building envelope. OSB is also used in furniture production.
Production
The board is made in the form of wide mats, from layers of differently oriented chips, compressed and glued together with adhesives made of wax and synthetic resins (95% wood, 5% wax and resin). Commonly used types of resins include phenol formaldehyde, melamine-molded urea formaldehyde, or isocyanate. All these binders are resistant to moisture. A combination of binders is often used, typically isocyanate in the core and urea formaldehyde in the face layers. This has the advantage of reducing pressing cycles while imparting a vibrant appearance to the panel surface.
The layers are created by chopping wood into strips, which are sieved and then oriented using various devices as they are fed to the forming line. For outer layers, the chips are aligned along the strength axis of the panel, while the inner layers are perpendicular. The number of layers placed depends in part on the thickness of the panel to be produced, but is limited by the equipment installed in the plant. Individual layers can also vary in thickness to give different thicknesses to the finished panel (usually a 15cm layer produces a 15mm thick panel). The mat is placed in a thermal press to compress the raw material and bind it together through heat activation and curing of the resin coating the wood. The individual panels are then cut from the mats to the required dimensions.
Wood OSB panels can be cut and installed with the same ease and tools as real wood.
Properties and types
Adjustments during the manufacturing process may introduce differences in thickness, panel size, strength and rigidity. OSB boards have no internal voids and are water resistant, although they require additional sheathing to achieve water tightness and are not recommended for exterior use. The finished product has properties similar to plywood, but is more uniform and cheaper. When tested to fracture, OSB has a greater load-bearing capacity than milled wood panels.
Four types of OSB are defined in terms of their mechanical characteristics and relative resistance to moisture:
- OSB/1 – general purpose boards for interior decoration (including furniture) for use in dry conditions;
- OSB/2 – load-bearing boards for use in dry conditions;
- OSB/3 – load-bearing boards for use in wet conditions;
- OSB/4 – load-bearing boards (for heavy loads) for use in wet conditions.
Although OSB does not have a continuous grain like natural wood, it does have an axis along which the resistance force is greatest.
It is the strength of OSB boards that makes their use as a formwork material expedient, and the ease of processing makes it possible to do the work yourself.
Advantages and disadvantages of such formwork
The production of OSB is carried out by pressing large chips (50-80 cm) under high temperature. At the same time, waterproof resins and chemical additives are added, which eliminate damage by fungal microorganisms or mold. Under the influence of moisture, the products are not able to warp and collapse for a long time, due to which they are effectively used in the construction of formwork for the foundation.
Compared to wooden boards, slabs do not deform due to external factors and precipitation, therefore they are used several times without loss of performance characteristics. They have perfectly smooth edges, which is not always possible to achieve from ordinary wood.
Since OSB is easy to saw, you can create panels of any size, which makes it easy to select the necessary elements. The material is quite elastic, so it is less susceptible to destruction under bending loads. Also, this and its low weight makes it possible to easily and quickly create formwork, saving time on construction.
OSB boards have some disadvantages:
- Poor resistance to high concentrated loads.
- They contain phenol in adhesive compositions, which is harmful to human health.
- Panels of types 3 and 4 can only be placed outside the building.
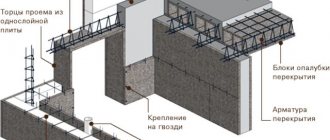
Formwork made of plywood and OSB is often used in the construction of buildings and structures for various purposes. Due to their mechanical properties, they are widely used for wall cladding, roofing floors, foundation frames, floor slabs and other reinforced concrete monolithic structures. There are elements with a laminated surface, which greatly simplifies their installation and increases their effectiveness as fencing products. The panels are also used in the manufacture of furniture products.
Calculation of formwork for a strip foundation is carried out only after the installation of trenches. In this case, the height of the building’s base and the specific density of the concrete solution, which places a certain load on the panels, must be taken into account. For its manufacture the following are used:
- Wooden blocks as stiffeners.
- Hardware for connecting the structure (bolts with nuts, washers, studs).
- Metal corners for reliable fastening of plates.
- Plastic pipe for fastening oppositely located panels.
- Reinforcing bars.
- Plywood or slats to cover gaps.
- Self-tapping screws for connecting OSB and glassine.
At the preparatory stage, slabs of the required sizes, plastic pipes and fittings are cut, and the dimensions of the panels are calculated.
Installation technology step by step
The assembly of the fence begins after excavation work and laying a sand cushion under the strip foundation. The most practical option is to install removable formwork. Prefabricated panel systems allow you to quickly and easily assemble panels of the required size with correction of corner sections.
Provide places for laying engineering and plumbing communications that will be located on the construction site.
Installation is carried out in the following sequence:
1. OSB boards are cut to fit the dimensions of the foundation edges, with the height being made slightly larger than the clean level by 15 cm.
2. Frames for the walls are made. The budget option is wooden, but for repeated use you will need panels made of bent-welded metal profiles.
3. The OSB blank is attached to the frame with self-tapping screws, the heads of which should be on the inside and slightly recessed.
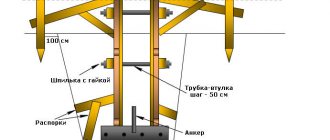
4. Each side of the formwork is reinforced with transverse bars in increments of 40 cm. This will allow the geometry of the structure being created to be maintained.
5. Opposite elements are connected by metal pins, which are threaded through previously drilled holes with a diameter of 16 mm. Fasteners should extend beyond the shields by 3-4 cm on each side to ensure reliable fastening with washers and nuts. The lateral plane of the fasteners is chosen to be wide so that under the pressure of the mixture they do not push through the OSB.
6. Plastic pipes are threaded, which will allow maintaining the accuracy of the width on any section of the strip foundation. After pouring the solution and hardening, they remain in the body of the concrete, and work well as ventilation.
7. If there are no pipes, fastening can be done using nuts. Then there are about 4 pieces with washers per side. When dismantling, they are removed and the ends of the studs are cut off flush.
8. When pouring the concrete mixture, the corner areas absorb the greatest forces, so they are reinforced with wooden blocks driven vertically into the ground. For additional reinforcement, steel corners are used to connect the shields to the pegs.
To give maximum rigidity, holes are made in the panels into which embedded reinforcement products are inserted in the shape of the letter “T”. The long side is welded to the reinforcement frame of the foundation and the solution is poured. After hardening, excess parts are cut off with a grinder.
Inclined beams on the outside of the structure in increments of 1 m make it possible to keep it in a vertical position until the very end of construction. Spacers should be attached to the boards at an angle of 30-45°, then the possibility of them collapsing is eliminated. Upon completion of the formwork installation, a control check of the parallelism of the side faces is carried out. To do this you will need a piece of timber and a water level.
Concrete work can be carried out in layers, taking short breaks between pouring. Then the solution will set and the expansion pressure will decrease. However, if the foundation area is small, it is recommended to lay the mixture in full, excluding the appearance of cold seams.
Materials used
To prepare OSB formwork for the foundation with your own hands, you need to prepare everything you need for the work.
The necessary calculations are performed when the foundation ditch is prepared. The height of the plinth and the specific density of the concrete solution should be taken into account.
To work you will need:
- OSB boards;
- bars for the manufacture of stiffening elements on OSB boards;
- fasteners for assembling the structure. This will require nuts with washers, studs and bolts;
- tubes made of plastic material, with the help of which the opposite formwork panels are connected;
- metal corners. They are installed on the corner sections of the formwork to increase the reliability of the OSB structure;
- reinforcing bars for pegs;
- plywood material or glassine. They lay the slotted areas in the formwork;
- self-tapping screws They are used to fix boards, plywood and glassine.
At the preparatory stage, the slab material is cut into the necessary elements, the dimensions of which correspond to the calculations performed.