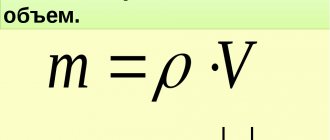It is also worth adding that a variety of techniques and equipment are used in the installation process.
What types exist
Therefore, it is not enough to simply attract experienced specialists and study the technology in detail. You also need to have a license confirming that the company has the right to provide the relevant services. In addition, the contractor must know how to correctly calculate the thickness of the future coating, how to mark it, and carry out all the necessary work. He is also obliged to guarantee quality. This is very important, because each of us knows perfectly well how much domestic companies like to save on this process.
As a result, the road surface crumbles in just one season. So, laying asphalt is a multi-stage technological process. It is not easy to perform, especially in the cold season. It is important to show utmost precision and scrupulousness.
This article explains what an asphalt pavement is and in what cases the use of single-layer asphalt is justified. Asphalt is a mixture of various resins and bitumen - asphalt with filler - sand, gravel, crushed stone and various additives that change the properties of the finished mixture.
If the standards are violated, the consumption of materials will increase significantly, and the coating will quickly become unusable. But first, let's figure out what asphalt pavement consists of. And it contains the following components:. Each of these components is taken in strictly defined proportions. Under no circumstances should you replace clean crushed stone and sand with stone crushing products.
The work process begins with the area being carefully marked. The asphalt must be level with the ground. That is why the soil itself is prepared first. The loosest part is removed using a bulldozer.
It turns out like a bathtub for laying the material. Its bottom is covered with sand, which is compacted using a vibrating roller and covered with a special material. It's called geotextile. Its function is to prevent crushed stone from falling into the sand layer.
Due to this, the level of strength increases. The asphalt itself is laid either on a rigid concrete base or on a crushed stone bed. To prepare it, three types of crushed stone are used. The largest type is poured first, and then the medium and small ones. As each layer is poured, it is also compacted using a roller. When the pillow is ready, it must be watered with bitumen emulsion. The final stage is laying asphalt, which is thoroughly mixed with fine sand and stone flour.
This mixture is heated to the desired temperature and laid in layers. Each of them should be approximately seven centimeters thick. An asphalt paver is used during the laying process.
What are the compositions?
This serious equipment is equipped with many sensors and its own computer. Upon completion of the process, the finished coating is again watered with bitumen emulsion. Please note that technology may change.
It all depends on what type of material will be used in the process. For example, hot asphalt is laid completely differently than cold asphalt. Updating the existing coating is also carried out using a different technology. In this case, there is no need to make a new base. You either need to simply remove the old coating, or ensure high-quality adhesion between the old and new layers.
A very important parameter is the evenness of the coating, that is, the absence of waves. It also happens the other way around.
Trends New items My channel Blog Rutube. Subscribe to our social networks. Download our apps. Login for partners. Decorative asphalt - color coating technology.
At the Fuji Circuit in Japan before its reconstruction, marks on the asphalt from cars were a normal occurrence. To obtain such an even coating, there is a technology in which the top layer of crushed stone, which is located under the first layer of asphalt, is laid using an asphalt paver.
About methods for laying asphalt on rainy and snowy days
"Drowned" asphalt. Photo by Peter Magera, Quto.Ru
From time to time, I previously came across messages online that here and there passers-by noticed how road workers were laying asphalt in the snow and rain. People were indignant, but every year history repeated itself. Now, it seems, they have even gotten used to it.
Recently, I even saw in one of the conferences a completely coherent justification: they say, it’s no big deal, they’ve laid it in snow and rain a million times, and the coating holds up even better than when laid in traditional conditions. Is this possible or not? I looked at the standards, called experts, and studied the background of the problem. Now I can put it in order.
In the good old days, when we lived in the USSR, asphalt plants closed on October 15 and started working again on April 15. There was a SNIP that prohibited laying the mixture on a wet or cold base. A lot of time has passed.
SNIP remains old, but asphalt plants operate almost all year round. At first it was due to a financing mess. It took a long time to create the budget and money for road repairs only came in the fall. We had to urgently master the budget.
Then we got so used to it that we made it a good tradition.
No matter what they say, today there is not a single document allowing the laying of asphalt mixture on a wet base. There has never been such a standard, and it may never exist. No regulatory authority will give permission for such work.
However, this happens even at serious facilities.
In 2002, for example, during the repair of the Krylatsky Bridge, they did not meet the deadline and could not wait for normal dry weather, and meanwhile indignation grew in the press, since the protracted repairs paralyzed all traffic from Rublyovka to Leningradskoye.
It was necessary to finish the work as soon as possible at any cost. As a result, we laid the experimental material - a cast sulfur-asphalt concrete mixture, partly in moisture, partly in frosty temperatures of minus 26 degrees. Well, the material endured this and worked quite successfully. But it was force majeure.
The only thing that is allowed to be done during the cold (or rainy) period is pothole repair. There are special cast and cold mixtures for this. Although this is also considered as a temporary measure until the onset of normal conditions for repairs with traditional mixtures.
However, all of the above can be forgotten if we take into account the document released by the Moscow government a few months ago. It establishes the capital's transition to a three-year road repair cycle (previously it was five and six years). In fact, this negates any standards.
At the very least, any asphalt will last three years or it will be replaced by a contractor under warranty. In such a situation, there is no point in focusing on the quality of the coating, its strength, or waiting for dry and warm weather...
Meanwhile, back in 2006, Moscow authorities ordered ten mobile laboratories to regularly monitor the condition of roads in the city. In accordance with the monitoring results, it was planned to predict the situation and make appropriate decisions.
In 2008, a decree was signed so that such monitoring would be carried out twice a year. Today these laboratories are laid up and do not fulfill their function. For what? Such serious work is needed for more or less long-term operation of asphalt.
With a three-year cycle, it makes no sense. Asphalt should not be laid in rain or snow, but given the current situation, it turns out that no one cares.
Scriptio: director Dmitry Leontyev.
Pages
← previous next →
Page 3
- Alpina gave itself two powerful sports cars for its anniversary. The famous tuning studio Alpina, which made its name on the construction of charged BMW sports cars, turned half a century old. German engineers celebrated the holiday with dignity by rolling out to the public two special modifications of the B5 and B6 models, which became the most powerful road Alpins in history. March 29, 2020 16:00:00 / Avto.Vesti.Ru
- The British auction house will sell the rare Alpina B12 5.7 Coupe. A unique car is the Alpina B12 5.7 Coupe, which once graced the collection of the Sultan of Brunei. Launched in 1993, the supercar remains a benchmark for speed and elegance even more than twenty years later; The price matches the product, of course. July 16, 2014 09:00:00 / Top Gear Russia
- The new Alpina B6 xDrive Gran Coupe debuted in New York. The so-called four-door coupe, according to Alpina tradition, is based on the charged modification of the M6 Gran Coupe and is driven by the same 4.4-liter V8 Twin Turbo. April 21, 2014 07 :27:00 / Auto.Vesti.Ru
- Alpina has declassified the diesel D3 Bi-Turbo. The modified “treshka” has been prepared in both a regular four-door and a more practical version (station wagon), and boasts a 350-horsepower diesel engine along with a completely revised suspension. September 11, 2013 23:44:00 /Top Gear Russia
Page 4
Pages
← previous next →
Page 5
Pages
← previous next →
Page 6
Pages
← previous next →
Page 7
Pages
← previous next →
Page 8
- Bugatti tested a caliper printed on a printer. The world's first brake caliper printed from titanium on a printer was successfully tested on the bench. December 24, 2020 16:45:00 /
- Bugatti hinted at the creation of a hybrid crossover. The company believes that Chiron alone is not enough for them. October 4, 2020 12:00:00 /
- Lego built a plastic Bugatti Chiron, and it drives A full-size working replica of the famous French hypercar Bugatti Chiron was created by Lego.30 August 2020 14:55:00 /
- The delivery dates for the Bugatti Chiron worth €3.1 million have been announced. The luxury division of the group has specified the delivery dates for the Bugatti Chiron hypercar worth €3.1 million to Russia. August 20, 2020 13:40:00 /
- The craftsmen removed the all-wheel drive from the Bugatti Veyron. The owner decided to make the Veyron rear-wheel drive in order to make better circles and give it the ability to enter into an evil drift. July 30, 2020 11:45:00 /
- Mechanics showed how to change the oil on a Bugatti: it's not for the faint of heart. The Camaro has two of them. The Lamborghini Huracan has eight. And the Bugatti Veyron has sixteen. Yes, we are talking about drain plugs, which still need to be reached. July 19, 2020 16:45:00 /
When was asphalt invented?
Asphalt is one of the oldest substances used by man; its history of invention goes back centuries. The ancient Greeks used rock resin, which they called "asphaltos". But they only applied the knowledge and discoveries made long before them by the ancient Sumerians, and then by the ancient Egyptians.
Asphalt provided waterproofing for the famous Hanging Gardens of Babylon. And the Egyptians 3000 BC. They provided waterproofing in their granaries using asphalt: a layer of asphalt covered the floor and the lower part of the walls. Where did they get it from? Herodotus described asphalt lakes in Mesopotamia and Egypt.
In Ancient Babylon, asphalt was used in the construction of stone walls as a binder. True, in Babylon they called it “earth resin.”
The historian Xenophon argued that in Media 500 BC. built by holding bricks together with natural bitumen. Even the Chinese did this - in some sections of the Great Wall of China, the bricks are held together with asphalt.
But the natives of America were the first to use it to cover roads. Of the Europeans, the first to see an asphalt road was the conquistador Francisco Pizarro in 1532 on the territory subject to the Incas. True, these roads were not paved by the Incas, but by those peoples who lived in these places before them. Asphalt roads survived these now nameless empires, the Inca Empire - and survived until the era of the Conquest, the seizure of these territories by the Spaniards.
John Everett Millais, “Pizarro captures the Peruvian Incas” Photo: Source
Asphalt road surfaces began to come to Europe in the 19th century. The industrial era had arrived, and it was necessary to quickly build communications. But making a road stone and then laying it so that the road comes out smooth takes a lot of time and human labor. In addition - skilled labor, which means expensive. Artificial asphalt roads have proven to be an excellent solution to the problem. So great that asphalt is still the main road surface around the world.
At the very beginning, it was very expensive, and therefore it was used, as a trial, to “beautify” pedestrian sidewalks and embankments. In 1832, the first sections of streets paved with asphalt appeared in Paris. People immediately noticed that in these areas the noise from moving carriages is much less than where the streets are paved with stone. I liked the new product, and Lyon followed the example of Paris, followed by London, Vienna, Philadelphia...
And the promotion of asphalt roads around the world began. The development of industrial society required the rapid construction of a huge number of roads.
An experiment illustrating the viscosity of asphalt: a piece of asphalt was placed in a funnel in 1927 and left; by 2007, a significant part of the asphalt had flowed into the glass Photo: Amada44, ru.wikipedia.org
Asphalt pavement came to Russia at the end of the 19th century. In 1873, the plant in Syzran began producing asphalt. Despite the fact that back in 1839 in St. Petersburg, 45.5 linear fathoms of asphalt were laid near the Tuchkov Bridge. Apparently, it didn’t catch on, it was a bit expensive, the cost of one square meter of asphalt was then 14 rubles (then rubles!).
In 1876, the Moscow City Duma allocated 50 thousand rubles to conduct an experiment on the construction of asphalt concrete pavement. Several sections of the new material were built on Tverskaya Street. Things didn't go any further.
As a result, until the flood of 1924 in St. Petersburg, even Nevsky Prospekt was covered with “trimming” and had a wooden covering. The sawn ends of wooden beams dampened traffic noise much better than asphalt. And only after the flood, when the entire pavement on the flooded streets of Leningrad (that year the city changed its name) simply floated on the waves, the question arose about replacing the street surfaces.
Where does asphalt come from?
In ancient times it was taken from asphalt lakes. Among the active asphalt lakes known today, for example, Peach Lake on the island of Trinidad. Once upon a time, the Indians soaked their canoes with bitumen from this lake, making them waterproof. Today, bitumen is extracted from this lake on an industrial basis; natural bitumen is a very valuable chemical raw material. It is calculated that at the current rate of production (about 200,000 tons per year), the lake’s reserves will last for about 400 years.
Peach Lake Photo: Martina Jackson, ru.wikipedia.org
In Syria and the Middle East, asphalt was taken from the Dead Sea. The Romans even called it Palus Asphaltites (Asphalt Lake). Once upon a time, blocks of natural asphalt floated to its surface from the bottom. The last case of the appearance of such a block was documented. This happened in the 60s of the last century; the weight of the block exceeded 1 ton.
Nowadays, the demand for asphalt is very high. Millions of tons of asphalt are needed every year to repair roads and lay new tracks. This asphalt is made at asphalt plants using bitumen, which is the final product of oil refining. Cars all over the world need a lot of gasoline, which is why a lot of bitumen is also produced.
So it turns out that although today there are many types of asphalt (asphalts for various climatic conditions, low-wear, even asphalts with built-in markings), but if you look in general terms, it turns out that we are still actively using the discovery of some indigenous civilization of America , even whose name we do not know. Only that they existed before the Inca civilization.
What else to read on the topic?
How much money does it take to bury in sand to make asphalt? Did you know that?.. Asphalt can be natural Pavements of St. Petersburg. Are there two troubles in Russia?
Tags: history of invention, road surface, asphalt
Is it possible to lay asphalt in the rain?
In any city you can watch road workers laying asphalt during rain or snowfall. Many are sure that this is a gross violation of all norms. But is it possible to lay asphalt in the rain?
Is it possible to lay asphalt in rain and snow?
To understand whether it is possible to lay asphalt in rain and snow, you need to know about the methods of laying it. And there are only three of them:
- hot;
- cold;
- cast.
The hot method is relevant for the construction of new roads, repair work involving the removal of old asphalt or small sections of roads in warm weather.
The method involves the use of a bitumen mixture, which must be rolled until completely cooled.
The peculiarity of installation is that certain conditions must be met: the air temperature outside must be above + 5 °C and there is no precipitation.
We draw on the asphalt, we draw... with asphalt. Non-obvious uses
The most famous way to use asphalt is described above: in the creation of road surfaces. It is also an excellent roofing, electrical and waterproofing material. In the chemical industry, asphalt is used to prepare varnishes, adhesives, etc.
- Asphalt-bitumen varnish is a solution of asphalt with various additives in organic solvents such as gasoline. Additives can include rosin, plasticizers, the types of bitumen and the amount of mineral dust, and aluminum powder can be changed. Elastic for a long time due to bitumen in the composition. Disadvantages: oxidation when exposed to light, loss of water resistance, cracking, hardening. Heat resistance is low, up to 100-130 ° C, depending on the brand. They are used for anti-corrosion vapor and waterproofing coatings, for the protection of metal structures, asbestos-cement pipes, finishing of stoves, painting of gas stoves and other surfaces.
- In various construction works, plaster asphalt waterproofing is used, in three different modifications: cast, hot or cold
- In the regions of the Far North, asphalt-polymer concrete prepared with tars and heavy oil fractions, and various synthetic polymers is used for various purposes.
- Natural asphalt has other, less obvious uses, such as painting and printmaking.
For example, Dead Sea asphalt, or Syrian as it is also called, is of the highest quality. Since it contains almost no mineral impurities, it is used to create oil paints, as well as lithographs. Gives a beautiful brown-golden color, perfect transparency, easy to apply. When combined with other paints, this asphalt is, as it were, forced out into the top layer of the picture. Craquelure: blackening and cracking of the paint layer - a fashionable effect in the 21st century for various interior solutions
The invention of photography also began with the use of Syrian asphalt, namely its ability to oxidize in light, losing light transmission. It was on a tin plate with a thin layer of asphalt that the oldest photograph from 1826 (J. Niepce “View from the window at Le Gras”) was preserved.
Milling cutters
The first step is to prepare the repair site. Previously, this was done by several workers with shovels and jackhammers. Now road milling machines have come to their aid. Their “weapon” is a rotating milling drum, with which they “gnaw” through old asphalt to a specified depth.
The productivity and dimensions of the milling cutter depend on the width of this drum. The most common sizes: 350, 500, 600, 1000, 1200, 1300, 2000, 2100 and 2200 mm. Compare, for example, the small Dynapac PL500T milling cutter, which has a cutter width of 500 mm, and the large Caterpillar PM200 with a milling drum width of 2010 mm:
Modern self-propelled milling machines are very complex units with an advanced control system and many monitoring sensors. But each manufacturer tries to supplement its equipment with new functions that competitors do not have. The same Dynapac can work normally in conditions where the front wheels are at different heights (for example, one is rolling along the road, and the second is along the edge of the curb). Even under these conditions, the cutter will be aligned horizontally and the depth of the cut will be the same across the entire cutting width. Large Caterpillar milling cutters are equipped with another useful option: they can lift the cutter assembly even if the engine is faulty. For this purpose, a separate electric pump powered by a battery is provided. This was done so that the broken car could be dragged onto the platform and transported to the repair site.
Conclusion
As you can see, road decking has a complex structure and also requires a special approach during installation. The operation of the road surface includes a number of activities that must be carried out regularly. Only in this case will it be possible to talk about the long service life of the road surface. Pothole repairs of road decks are allowed in cases where damage to the road deck is minimal. If extensive intervention is required to repair the road deck, part of the pavement is completely cut out and a new road deck is laid.