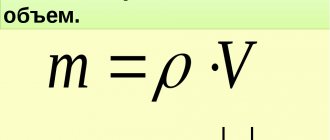Coating features
Cold asphalt is produced and sold in the form of asphalt concrete mixture, packaged in 50 or 15 kg. For large volumes of work, packaging weighing up to a ton is provided.
The finished material includes:
Composition of cold asphalt
- bitumen;
- polymer and elastic additives;
- plasticizers;
- fine crushed stone.
All components are mixed and at the last stage of production undergo heat treatment. The special additives included in the mixture form a protective film on the surface. A special manufacturing technology allows the material to retain its properties and not set until it leaves the packaging in an open environment. Upon contact with air, the protective properties are lost, and the bitumen begins to harden.
Thanks to these characteristics, cold asphalt can be used in the most unfavorable conditions and at any time of the year.
It is advisable to use the material for minor road repairs. This is a very convenient tool for filling holes - there is no need to transport heavy equipment and prepare hot asphalt mixtures.
Shelf life.
The ready-mixed cold asphalt has a long shelf life of 10 months to 1 year.
When working, no special surface preparation or use of tools and equipment for repairs is required.
Restoration of road surfaces can be carried out in subzero temperatures.
This property allows it to be used in areas with cold climates.
The mixture is made using high-strength fine-grained crushed stone, previously cleaned and subjected to intensive drying.
A mixture of cold asphalt is prepared on special equipment at asphalt concrete plants.
Crushed stone of a certain fraction is mixed in mixers with bitumen added in portions.
The duration of mixing the components of cold asphalt is 20...25 seconds.
Crushed stone fractions are preheated to a certain temperature, but not higher than 100 C.
The volume of bitumen added to the mixture should be from 4.2 to 4.5% of the mass of crushed stone.
Advantages
The cold method of laying asphalt is incredibly simple. It can easily be used for road repairs or landscaping in the yard. Moreover, this can be done not only by a utility worker, but also by an ordinary site owner.
Advantages of modern material:
The advantage of cold asphalt is its ease of installation.
- quick installation. Fill, level and compact - the whole process takes no more than an hour;
- ready-to-use material;
- no need for special equipment for installation;
- can be used in winter at temperatures down to -25 degrees;
- transportation and storage in any conditions, shelf life in original packaging - from 2 to 10 years.
There is no need to fear that the cold asphalt coating will be fragile and short-lived. It can be used immediately after installation, while maintaining high strength for a long time.
Composition and preparation of cold asphalt
Cold asphalt consists of many components, it includes crushed stone, sand, bitumen, kerosene or other type of fuel, and various additives. Additives provide the viscosity of the mixture, and the ability to use it at different temperatures. The composition of cold asphalt is almost identical to that of conventional hot asphalt; it consists of mineral filler, specially shaped crushed stone, bitumen and plasticizers. Crushed stone in cold asphalt is washed and cube-shaped, which allows for a tighter fit of the filler fragments to each other. Also, bitumen allows you to achieve a greater sealing density and the color of crushed stone affects adhesion; gray and black improve adhesion to bitumen.
Plasticizers provide the formation of a film that prevents the evaporation of hydrocarbons from bitumen before it adheres to the base surface.
This material is produced using several technologies:
1. Without heating, adding bitumen additives as a binder allows you to produce a mixture without heating; the composition made using this technology gives better adhesion to the surface, even when wet, and does not require cooling after preparation. 2. With heating, in this case the mixture is made using the same technology as hot asphalt. Mineral fillers undergo a drying process and are heated to 110 degrees, then bitumen is added to the mixture, after mixing, the finished composition with a temperature of 105 degrees is sent for cooling to 25 degrees and then packaged in containers for sale. The finished mixture can be stored, depending on storage conditions and the types of bitumen used, from two weeks to six months. At positive temperatures, the mixture can be stored in the open air, outdoors.
Scope of application
The main purpose of the material is rapid partial repair of roads and restoration of their technical functions. There are several areas of its application:
Application of cold asphalt
- elimination of holes and potholes on the road surface;
- creating a blind area;
- arrangement of garden paths;
- paving the entrance to a house or cottage;
- preventive measures for road improvement.
All these activities can be carried out regardless of the weather - in severe frost, if it rains or snows.
Most often, laying dry asphalt is carried out on those sections of roads where urgent repairs are required, and it is not possible to stop or limit the traffic flow. It is also advisable to use it in areas where it is difficult to deliver heavy special equipment. This also includes hard-to-reach areas, hatches, recreation areas and courtyards of high-rise buildings. They can restore parts of the foundation.
For owners of suburban areas and private houses, laying cold asphalt can be useful for making a parking lot or driveway to a garage. They lay out the floors in gazebos and verandas. Summer residents also find a use for it and use it to lay paths in their gardens.
Although its price is high, this is compensated by the convenience and durability of the coating - it will last for a long time without heavy loads. This is an excellent option for minor repairs and landscaping.
Laying technology
The process is similar to laying regular hot asphalt, but with some nuances. Laying cold asphalt includes several stages. They are simple and take little time, but all are required. When all stages are completed correctly, vehicles can immediately move on the new surface. Here is an example of road repair, but for use in a country house or in the yard of a private house, you should follow the same algorithm.
Cold asphalt laying technology
Preparatory
At this stage, markings are carried out, the old road surface is removed, and seams are cut. The area to be treated is marked with lines around the perimeter, with a margin of 5 cm on each side. If there are several pits nearby, they should be combined.
Dismantling of the old canvas is carried out with a jackhammer or cutter. The seams are cut with a grinder or a special cutting tool along the entire depth. It is necessary to ensure that the sides of the pit are maintained vertically.
Preparing a road hole for laying cold asphalt
Cleaning
It is necessary to get rid of large parts of the old coating and remove asphalt chips. All small debris and moisture are also removed. This is a very important stage - if, when laying cold asphalt, foreign inclusions get into it, this will complicate the process of setting the two materials.
Treating a prepared pothole with bitumen emulsion. This procedure is not mandatory, but it is highly advisable to perform it to increase the service life of the restored area. The product can be purchased at a hardware store. This is a sticky liquid that consists of bitumen, water and other components.
Laying
The asphalt is poured onto the prepared surface and leveled. If there are stuck together lumps in the mixture, they must be broken up with any convenient tool.
The layer should not exceed 5 cm. If this thickness is not enough and the depth of the base is greater, you can add the required amount of crushed stone to the bottom. But this will reduce the quality of adhesion to the surface. Therefore, it is better to carry out the laying procedure in several layers, compacting each of them well.
The new coating should protrude 2 cm from the main surface - cold asphalt tends to compact and sag under the influence of passing cars.
Technological scheme for laying cold asphalt
Tamping
You can use the manual method for this, but a vibrating plate is more suitable. Compaction is carried out in a spiral. You need to work out the joints especially carefully.
Before use, fresh coating should be sprinkled with sand or cement - this way it will not stick to the wheels of cars.
Compacting cold asphalt
Technology of working with cold asphalt
For use in small quantities, it is necessary to determine how much of the mixture needs to be purchased, for this you should know that 1 cubic meter of the mixture weighs from 1,100 kilograms to one and a half tons, dismantled old asphalt weighs 1,400 kilograms per cubic meter. The technological process for repairing road surfaces using cold asphalt consists of the following stages:
- The damaged area is marked so as to cover an area at a distance of 5 centimeters from the boundaries of the damage, seams are cut and materials from the damaged area of the coating are removed with a milling cutter or jackhammer.
- The dismantled area is cleaned of coating residues and dust.
- The edges and bottom of the area prepared for repair are treated with bitumen.
- The asphalt layer should not exceed 5 centimeters in thickness; if the depth of the repaired area is greater, it is necessary to add a layer of crushed stone. It is necessary to pour a layer of asphalt so that it protrudes 2 centimeters above the level of the road surface, this is the so-called compaction reserve.
- Compaction is carried out manually or with a vibrating plate, starting from the edges to the middle.
- Upon completion of compaction, the repaired area should be sprinkled with cement or sand to prevent the mixture from sticking to car wheels.
Disadvantages of cold asphalt
Even such modern and easy-to-use materials have their drawbacks:
Cold asphalt
- the price of this foreign innovation is 3 times higher than that of ordinary asphalt;
- laying cold asphalt is not suitable for highways, highways and other areas with heavy traffic - it will not withstand such loads and will quickly collapse;
- moisture resistance is lower than that of its traditional counterpart;
- the surface must be thoroughly cleaned, otherwise if any dust gets into the asphalt mixture, its properties will be impaired.
In terms of cost, in practice it is not that expensive, considering that they only carry out minor repairs and fill holes. In addition, it requires less labor and does not require the use of technology.
It is not used for complete laying of the road surface, not only because of its high cost. The point is in its properties - the material must be placed in a recess. Otherwise, under the weight of the cars, it will simply crawl apart, and it will certainly not withstand a loaded truck.
Related video: Cold asphalt laying technology
Publications on the topic
How to properly lay asphalt in your yard
Technology for laying paving slabs on concrete
DIY paving guide
Artificial asphalt
Main article: Asphalt concrete
Artificial asphalt
or
asphalt concrete mixture
is a building material in the form of a compacted mixture of crushed stone, sand, mineral powder and bitumen. A distinction is made between hot bitumen containing viscous bitumen, laid and compacted at a temperature not lower than 120 °C; warm - with low-viscosity bitumen and compaction temperature 40-80 °C; cold - with liquid bitumen, compacted at low ambient temperatures, up to −30 ° C.
Asphalt concrete is used for covering roads, airfields, playgrounds, etc. Modifying additives are also used, including those that are a product of processing car tires.
Properties
Asphalt turned out to be the most suitable material for road surfaces. Its layer is more even and therefore less noisy. Asphalt concrete pavement is easy to repair, wash and clean; it has the necessary roughness and any markings adhere well to it. Once laid asphalt concrete can be used for traffic immediately (unlike cement concrete, which gains the necessary strength only on the 28th day).
History of application
Initially, in the 19th century, city streets were paved with stones (cobblestones). Starting from the mid-19th century, in France, Switzerland, the USA and a number of other countries, road surfaces began to be made from bitumen-mineral mixtures. In the 1830s, asphalt concrete pavement was first used to cover the sidewalks of the Royal Bridge in Paris. Around the same time, the sidewalks on Lyon's Moran Bridge over the Rhone River were covered.
In the summer of 1839 in St. Petersburg, sidewalks were covered for 45.5 linear fathoms with a width of 5 feet (97.08 × 1.52 m) and part of a bridge 8.5 feet long and 6.5 feet wide (2.59 × 1. 98 m) at the Tuchkov Bridge dam. In 1876, the Moscow City Duma allocated 50 thousand rubles to conduct an experiment on the construction of asphalt concrete pavement: several sections of the new material were built on Tverskaya Street.
The rapidly developing road network required new types of road surfaces that could be constructed as quickly as subgrades. In 1876, cast asphalt prepared using petroleum bitumen was first used in the United States. In 1892, the first concrete road structure with a width of 3 m was built in the USA using the industrial method. 12 years later, a 29 km road was built using a tarmacrator with the free flow of hot bitumen.
In Russia, the production of asphalt was first established by engineer and architect Ivan Buttats - asphalt began to be mined in 1873 at the Syzran plant, on the right bank of the Volga, 20 km above Syzran.