What is asphalt made from?
Crushed stone used for the production of asphalt: granite, volcanic
For the production of asphalt, granite or volcanic crushed stone, minerals, bitumen and sand are purchased. After arriving at the plant, they are loaded into special drying devices. The operator feeds sand and crushed stone separately into the rotating drum via a conveyor belt. At the end of the installation there is a gas or diesel burner that heats the walls of the drum.
Interesting: How is amber mined? Extraction methods, description, photos and videos
Drum installation "Roar"
In this way, the components of the future asphalt inside are dried. An electrically heated unit can also be used for drying. Once the process is complete, the crushed stone and sand are sent to a drum machine called a “Screech” for cleaning.
Dryer drum
During cleaning, the components pass through grates and filters and are screened out from debris, foreign inclusions, large and small stones. After processing, they are loaded into bunkers. These bins store the components for the required amount of time until the next step. Using computer remote control and electric valves, it is possible to measure the required amount of ingredients for the production of different types of asphalt.
Asphalt recycling
Home – Technology – Asphalt recycling
Fig. 1 Version with a hopper-doser on a subframe structure
In the field of road construction, it is a well-known fact that when constructing a road, the most expensive expense item is the purchase of raw materials for the production of asphalt concrete. This is due to the high cost of materials, which in turn is due to the high costs of extraction and transportation.
Obviously, reusing old milled asphalt would result in a significant reduction in the cost of producing new asphalt and savings in aggregates and binders. In order to reuse old asphalt concrete, it is crushed. In this form, asphalt is called reclaimed asphalt (RA).
In many countries, especially those where the raw materials necessary for the production of asphalt concrete are limited, this technology has been used for decades. For example, in the USA, asphalt concrete is the most recycled material. At least 90% of all asphalt removed from the road is reused. Road construction companies in the United States are constantly looking for ways to increase the amount of PA relative to the mass of new inert materials, as they understand the economic potential of its use.
One of the important and complex processes when using RA is its drying. The fact is that RA contains a relatively large amount of moisture. There are various ways to introduce and dry PA, but the most cost-effective method is to inject it directly into the asphalt plant mixer. When using this method, new inert materials are heated to a higher temperature than usual in order to dry the material while mixing it with PA in the mixer. In this case, abundant moisture is released from the RA in the form of steam. There is a need to take into account the humidity of the RA and the rate of its introduction during the mixing process. It is also necessary to weigh it with high accuracy.
The line offered for supply for feeding, weighing and dispensing material into the mixer is intended for the reuse of old crushed asphalt concrete as a raw material for the production of new one. The use of RA reduces the cost of inert materials and binders. Using this equipment, it is possible to use up to 25% PA relative to the total mass of the asphalt concrete mixture being produced. This means that 25% less new inert materials will be used in the production of asphalt concrete.
Operating principle of the equipment
Fig.2 Option for a dosing hopper mounted on the plant frame
This set of equipment is a separate material supply line with its own weighing and mixer dispensing system. Fundamentally, this material supply line is similar to the feed unit of an asphalt concrete plant, but, nevertheless, it has its own characteristics.
The RA power supply unit consists of a feeder hopper with a grid installed on its upper part to prevent oversized and foreign materials from entering the hopper. From a belt feeder installed under the hopper, the PA enters an inclined conveyor, which lifts it to the level of the asphalt plant mixer. Next, the material is poured into a dosing hopper with a strain gauge weighing system. After the material has been weighed, the RA falls from the dosing hopper onto a belt conveyor, which, in turn, gradually pours the dosed material into the inlet pipe, through which it enters the mixer. It should be noted that the feeder installed under the dosing hopper has a speed control and supplies PA gradually so that the amount of steam released during drying is moderate.
Peculiarities
Fig3. Technical drawing of the PA supply line as part of the asphalt plant
Of course, the fundamental composition of the equipment for supplying PA remains unchanged, but, nevertheless, there is a need for individual selection of the layout for each plant. When choosing each unit for a specific plant, Rotor plant specialists take into account many factors, such as plant size, productivity, design features, free space, etc. This type of equipment is suitable for any cyclic asphalt concrete plant, regardless of brand.
Today in Russia ODM 218.2.034-2013 issued by Rosavtodor has been put into effect and is being actively implemented: “Methodological recommendations for the preparation and use of asphalt concrete mixtures using recycled asphalt concrete.” The document allows us to be confident that in the near future technologies for reusing asphalt concrete mixtures will be actively used in Russia. Despite the fact that there is a fairly large supply of inert materials on our territory, transporting them over long distances is very expensive, and reusing old asphalt concrete allows us to save huge amounts of money when producing new ones.
Bitumen preparation
Bitumen
Bitumen is produced at specialized factories, and is delivered ready-made to asphalt production. It is placed in huge boiler tanks with electrical heating, where it is gradually heated to a temperature of 110 - 120°C. Before production, it is transferred to another boiler, where it is melted to an operating temperature of 150°C. Bitumen is the result of petrochemical production, therefore safety precautions are strictly observed when heating it. At a temperature of 150 – 160°C it can ignite and lead to a long fire.
Making asphalt at home
The production of road surfaces is considered to be difficult and inaccessible. But, nevertheless, there are enthusiasts who are ready to experiment. Of course, such compounds are not designed for federal highways, but at the dacha it is quite possible to prepare such asphalt with your own hands.
Advice: from experience, we can say that a mixture prepared in a homemade way is, of course, suitable for arranging, but more often it is used for repairing potholes on an already finished surface.
Classic recipe
For preparation, we will need ordinary river or quarry sand, bitumen resin or bitumen and fine crushed stone. Equipment you will need is a metal barrel and a bucket.
It is better to cook asphalt over a fire, since using gas is unsafe and expensive.
- Initially, add crushed stone and sand in a 2:1 ratio and mix well. All this should be filled with water and hung over the fire.
- At the same time we prepare the bitumen base. To do this, take a metal bucket and heat the bitumen in it until it boils. You can add synthetic polymers as a plasticizer, but it’s cheaper to use shampoo or any detergent.
- When the resin has warmed up and the water in the barrel with crushed stone has also boiled, they need to be combined. Water is needed to ensure that the crushed stone and sand do not heat up above 100ºС. Next, this broth must be stirred, maintaining a boil until all the water has boiled away. While the solution is hot, it can be poured.
Important: be careful, bitumen melts at 80 ºС, and boils at 100 - 120 ºС. But already at 170 ºС bitumen can ignite. Actually, to prevent such a fire, we use water.
Using old road surfaces
Dismantling asphalt pavements and bases can provide good material for preparing new asphalt.
The technology is partly similar to the previous version, but with some amendments.
- The dismantling of the asphalt concrete pavement itself is carried out using the old-fashioned method, using a sledgehammer and other impact tools. Only the top layer of asphalt bound with bitumen is used; the road cushion can be left untouched.
- The old road surface is broken into pieces with a fraction of no more than 40 mm. For 100 kg of old asphalt, take 10 kg of bitumen.
- After this, the crushed substance must be poured with water and boiled in a barrel until melted. The technology then repeats the option described above. The heated bitumen combines with the molten asphalt and the water evaporates.
Cold asphalt
The two methods described above are well suited for economical repair of damaged asphalt in or near the yard. If you need to cover a large area, we recommend using cold asphalt.
This coating appeared on the market in our country about 5 years ago. The principle of operation here is similar to the well-known cold welding. Modified bitumen is used for the binder, so it can be laid even at sub-zero temperatures. Instructions are included on the packaging.
The only disadvantage of this material is its significant price. But, as you know, asphalt is shipped hot from the factory and must also be laid hot. Therefore, for remote locations, cold polymer asphalt is the only alternative.
Important: when repairing road surfaces, the problem is the quality of the joint in the asphalt concrete pavement. Cold polymer-based asphalt completely solves this problem, since it reliably adheres to any bitumen-based composition.
Asphalt production
Bunkers and asphalt mixing plant
The prepared components enter special bunkers, from which they enter the mixing apparatus via a conveyor belt. Due to its specific properties, bitumen is delivered separately via pipeline. Sometimes, to maintain temperature, the pipeline is equipped with an insulating coating or a heating system.
Stabilizing cellulose additive for asphalt
Some types of asphalt have a cellulose stabilizing additive added to increase their strength. All toxic fumes are removed by a ventilation system with installed filters for purifying polluted air. All production control occurs remotely from a computerized control panel.
Interesting fact: the first paved road appeared in the 1830s in England. Then it was first used for the sidewalks of the Royal Bridge in Paris.
All components are mixed while rotating in a heated drum. Under the influence of rotational movements and high temperature, the asphalt is completely mixed until the required properties and consistency are obtained.
Interesting: Why is coffee served with a glass of water in Turkey? Reasons, photos and videos
How to make asphalt concrete
It's hard to believe that this huge structure periodically migrates from place to place. The entire plant, which produces 200-240 tons of asphalt concrete per hour, can be transported and reassembled in one and a half to two months. Now it is located near the Minsk-Gomel highway, the reconstruction of which is actively underway. The company is serviced by only 14 people (not counting drivers), fortunately the technology is German and automation replaces a large number of workers. Dump trucks barely have time to pick up freshly prepared material for our routes. Onliner.by correspondents studied the asphalt concrete production process in detail. We offer a photo report from one of the most modern enterprises in the road industry in Belarus.
First stage. Our report begins 17 kilometers from the asphalt concrete plant,” explains the head of the enterprise, Pavel Yakimov. The elevated one is a section of the railway track where trains with crushed granite from Mikashevichi arrive. It is located 1.5-2 meters above ground level (this makes it easier to unload) - hence the name.
The supply of crushed stone is of utmost importance. Work on this site is carried out around the clock during the season. Loaders and dump trucks constantly maneuver between mountains of rubble. It also comes in different sizes - large fractions, medium, small. It is crushed stone, forming a kind of mosaic of the roadway, that takes the main load of cars.
And here is the so-called screening, reminiscent of cement. Like sand, this material also acts as a filler. After all, crushed stone of even the smallest fractions is not able to completely fill the entire space of the canvas. Screenings and sand fill the voids, preventing the appearance of a network of microcracks.
— Logistics is of utmost importance. It’s not profitable to drive 30-ton dump trucks 300 kilometers to Mikashevichi,” explains Pavel Yakimov on the way to the plant. — It is more profitable and faster to transport crushed stone by rail. Therefore, when choosing a site to locate a plant, a reconnaissance of the area is always carried out.
Second phase. Dump trucks deliver crushed stone to the plant. At the same time, sand is brought from the quarry, and bitumen and mineral additives are brought from different parts of Belarus.
“The composition of asphalt concrete includes: firstly, crushed stone of different fractions, secondly, sand, thirdly, bitumen as the most important material, and fourthly, mineral additives,” say road workers. — In all reference books, the resulting material is listed as asphalt concrete. Although, if you look at it, there is no concrete in it.
Third stage. A sand and gravel mixture containing cobblestones and boulders is transported from the quarry to the plant. She is sent to the “rumble” - a sonorous installation for sifting out stones, which fully corresponds to the name given to it by the workers. The technology is simple: sand, poured into a receiving hopper, gets into a “rumble” along a conveyor belt and passes through two sieves, eventually becoming clean and yellow. Like on a playground!
Fourth stage. Crushed stone is stacked using a bulldozer. Mountains of clean, filtered sand and screenings are located nearby. Everything is ready for loading into special bunkers, from which the most important process begins - the direct production of asphalt concrete.
On the site of the plant (it occupies about two and a half hectares), cars drive non-stop, and there is a column of dust. By the way, is there any opportunity here to clean up after a hard day? It turned out that the factory workers live here - a construction camp was built in the corner. Of course, it’s not a three-star hotel, but life for temporary housing is decently organized: there is a shower (a special well was drilled), some kind of kitchen, sleeping trailers.
Fifth stage. Attention! Bitumen arrived at the plant, which in asphalt concrete serves as a binder between crushed stone, sand, and screenings. Like glue! It is this that crumbles as it ages and cracks appear in the coating. In the spring, water enters them and turns into ice. During temperature transitions through zero, a constant process of loosening of the canvas occurs. So the quality of bitumen is of utmost importance. After all, if the glue is bad, then in bad weather the soles of the shoes will scoop up water.
“Before bitumen is poured into tanks, samples are taken and examined - we check compliance with the declared brands (bitumen has several of them),” explains Pavel Yakimov. — All this is called input control. For example, viscosity is determined using a penetrometer. The softening temperature is also measured. The sample is poured into special rings, kept in air for half an hour, then cooled to +5 degrees Celsius. Then the bitumen is placed in an electronic mixer and a certain rotation speed and heating temperature are set. After this, they place a metal ball on the bitumen and see how long it takes for it to touch the lower level of the site.
Drivers often wonder how much oil is in asphalt? As it turned out, a fraction of a percent. For example, asphalt concrete uses only 4.5-6% bitumen, which, as is known, is a residual product of oil refining. “And plus or minus one tenth matters. If there is more bitumen than necessary, the asphalt concrete will turn out greasy and will melt in the heat. If you add less than required, it will become dry and crack in severe frosts. Scientists are constantly working on the ideal formula for our climatic conditions,” experts explain.
Sixth stage. Loaders send sand and crushed stone to the receiving hopper. This is where human intervention could not have happened. The worker makes sure that boards, pieces of iron and other large debris do not get inside. Otherwise, it may damage the conveyor belt. In some ways, the process is reminiscent of preparing a kind of industrial cocktail.
Seventh stage. Three tanks are filled with bitumen, which is found to meet the standards. This process also takes place in parallel with the preparation of crushed stone, sand, and screenings. The temperature in the tanks is maintained at about +160 degrees Celsius.
Bitumen is in three white tanks - Bitumen is produced by both of our refineries. But during hot times the demand for it is very high. To get it, you have to wait in line overnight,” says the plant manager. — Drivers come, spend the night and load up in the morning so that the asphalt concrete production process is continuous.
Eighth stage. Since the enterprise is automated, no one, of course, manually starts the installation. This process takes place in the control room, which houses the control cabinets - the brains of the plant. Here the operator (as instructed by the wizard) sets the necessary algorithms. The entire technological process is clearly visible on the monitor.
“The German plant Benninghoven is a brand! He’s the best,” the company’s employees were even surprised at our ignorance when we decided to clarify the information about the logo. Before working on equipment that replaces dozens of people, many underwent special training.
Ninth stage. Each bunker, depending on the algorithms set by the operator, releases a portion of crushed stone, sand or screenings at a certain speed. All this moves along the conveyor belt straight into the drying drum. What is happening at this stage can still be seen.
Tenth stage. In the drying drum, the burner heats the resulting mixture to +170-180 degrees Celsius. Firstly, to get rid of moisture. And secondly, in order to prepare the material for mixing with bitumen and mineral additives, enveloping must occur evenly, without temperature fluctuations.
It should be noted that an asphalt concrete plant is a fairly energy-intensive production that requires the installation of a high-voltage power line. This is a lengthy process, which is why the plant has a diesel generator with two engines. One provides lighting in the construction site. The second is capable of maintaining the entire plant in working order. And this is at a consumption of about 60 liters of diesel fuel per hour.
Eleventh stage. There is a roar on the site. The hot material elevator, using special buckets, delivers the hot mixture to the very top to pass it through 5 rows of sieves.
This will ensure the material is evenly distributed. Each “portion” must contain all the necessary fractions of materials - from small to large.
At the same time, bitumen and mineral powder are added. Everything happens in a pipe system and is hidden from view.
Twelfth stage. The resulting asphalt concrete is mixed by two shafts with blades. It is weighed and sent to a skip car. You can hear the characteristic smell of hot asphalt. Even in hot weather, a wave of heat emanates from the plant.
Thirteenth stage. After weighing, the skip trolley delivers the asphalt concrete upstairs to the bunker. It takes literally a few seconds. The cart moves back and forth tirelessly. The bunker can store up to 180 tons, a kind of reserve. “This is a big plus, because even before the first cars arrive at the plant, we can already start working,” say plant employees. — There is no downtime, which means the enterprise operates more efficiently. By the way, our record is 2,269 tons of asphalt concrete in a 10-hour shift.”
Fourteenth stage. We return to the laboratory again, where the composition of the resulting asphalt concrete is checked. This is done quite simply: a container with a sample is placed in a special oven. The bitumen burns out. Then they take three sieves and sift the crushed stone. The resulting portions are weighed. Nothing complicated. A common mathematical operation.
Fifteenth stage. Finally, the asphalt concrete is unloaded from the bunker into a dump truck. The quantity can be adjusted by both the operator and the driver himself. MAZ can take away about 20 tons, and Volvo, for example, took 30 tons.
Sixteenth stage. Now the loaded car remains to be weighed (it had already gone through this procedure when arriving at the plant). A worker helps cover asphalt concrete with a thermal blanket. These are the requirements of technical supervision. Laying is carried out at a temperature of +110 degrees Celsius. All! A line of dump trucks is moving onto the road to unload the asphalt in the hot weather and return for the next batch.
If you have a production or service that you would like to tell our readers about, please write to ( [email protected]
) and we will make the best report, which will be seen by thousands of readers of the site.
How it was done.
Individual photos from my reports can be viewed on Instagram Instagram
. Click on the links, subscribe and comment, if you have questions about the matter, I always answer.
My most interesting videos are also published on YouTube, support it by subscribing by clicking on this link - How it’s done
or according to this picture. Thanks to everyone who signed up!
Completion of production
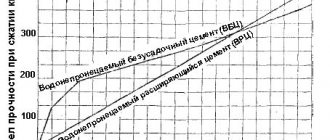
The finished product enters a container, where a small part of it is selected for test control. Samples are tested for strength under pressure from a press and its composition is examined. After passing the quality control department, the hot asphalt is sent for road construction using special trucks.
The finished asphalt will delight everyone who drives or walks on it. Its hard and shock-absorbing surface will keep more than one pair of legs and wheels intact.
What it is
This composition is used everywhere, from laying federal highways to arranging city squares and garden paths in private construction.
According to GOST and SNiP, the design of asphalt concrete pavement can be different.
But the general composition of the mixture has remained unchanged for more than 100 years:
- First of all, bitumen is included as a binder.
. - Sand and large mineral fillers must be present to one degree or another.
. - The list is completed by various mineral or synthetic additives
.
At the time when the composition was developed, natural bitumen was used, but since there is little of it in nature, an artificial analogue was synthesized based on petroleum products, which is still successfully used by road workers around the world.
Quarry sand is taken, as for coarse filler, along with various types of sand, crushed rocks and some crystallized slags are widely used.
Natural mineral or synthetic additives are used to increase certain beneficial properties of the coating. In particular, frost resistance, road adhesion level, viscosity coefficient and much more increase.
What formulations are produced
The range of presented types is quite wide, depending on the percentage of components, as well as what additives were used, experts divide asphalt into the following varieties.
- Sand compounds are used to arrange sidewalks, garden paths or the interior space of city courtyards.
- Fine-grained compounds cover city streets with medium and high traffic intensity.
- Coarse-grained asphalt is used as a base layer in multi-layer laying technology.
- Polymer-bitumen coatings are used for the installation of bridges, large parking lots or road junctions. They have increased strength and durability.
- Crushed stone-mastic types of asphalt are considered the strongest; they are used to lay federal highways and expressways with increased traffic load.
- For stadiums, jogging or cycling tracks, as well as other sports facilities, there is a rubber-bitumen coating.
Technology for recycling asphalt pavements
The need to save money when repairing and building new asphalt roads led to the development of an effective recycling system (reuse of materials). In this case, the asphalt removed from the road surface is processed, both in stationary factory conditions and in mobile equipment at the work site.
Using this technology, the asphalt concrete coating is removed using a special mechanism with a mechanical cutter - a remixer. Next, the removed material is crushed into a crushed stone fraction and can be used to prepare dry mixtures for the construction of road bases and fills for suburban highways and roads.
Asphalt base.
According to the second technology, the collected and crushed material is placed in a furnace and heated without fire to 170°C with the addition of the required amount of fresh bitumen and additives. This processing method is widely used when repairing city streets and courtyards, since the price, production and laying of asphalt in this case is much lower.
Recycling asphalt at home
An old road surface made from an asphalt mixture allows a home craftsman to arrange comfortable and neat asphalt pedestrian paths on his or her plot, which can easily replace paving slabs. This DIY asphalt can also be used, for example, to cover the floor in a garage or in front of it.
Only the top bitumen layer needs to be removed. The removed material must be broken into pieces as small as possible. The maximum fraction should not exceed 40 mm.
Start of using asphalt for road construction
The first mention of the use of natural asphalt for laying roads dates back to the 16th century and South America. The production of artificial cast asphalt mixtures appeared in the USA only at the end of the 19th century; bitumen-mineral compositions came to the streets of Europe a little earlier - in 1830-40. paved sidewalks and roadways in cities in France, Austria, Great Britain and Russia began to be replaced by asphalt surfaces.
The first trial and larger-scale asphalt paving experiment was carried out in St. Petersburg, but only by 1980. the new road material spread to other major cities. At the same time, our own plant was not built in Russia right away - for three decades, the then progressive product was purchased abroad.
America was again the pioneer in mechanized laying. It was here that a tarmacrator, from which hot bitumen poured, was first used to build a road.
Composition of natural and artificial asphalt
Natural asphalt is extracted from rare deposits - Peach Lake in Trinidad, the Dead Sea in Israel, Alberta in Canada, the Orinoco Belt in Venezuela, US states, Iran, and Cuba. The composition includes a mixture of bitumen up to 70%, inorganic inclusions and organic compounds.
Artificial asphalt concrete mixtures consist of two main components. The role of the binding component is viscous, low-viscosity or liquid petroleum, modified bitumen and PBB (polymer-bitumen binders). Crushed stone/gravel of different fractions from 5-10 mm to 20-40 mm, sand and mineral powder are used as fillers to improve strength, toughness and fill voids.
Asphalt concrete is a monolithic road surface obtained by laying and compacting an asphalt concrete mixture.