Asphalt is one of the most popular road surfaces. The technology of laying asphalt on soft soil to ensure the reliability and durability of pavements includes the use of innovative geosynthetic materials, which can be purchased from our company GeoSM, which specializes in the production and sale of these materials in a full range at the best prices. Our asphalt paving materials are developed using a unique, patented technology.
We specialize in the development and production of Geoflax geosynthetics:
— geotextile fabric Geoflax; — Geoflax geogrids; — Geoflax geogrids; — dornita Geoflax.
We guarantee that all materials comply with regulatory requirements and national standards.
Recommended materials:
Flat geogridGeogrid volumetric Geotextiles
What should be the thickness of crushed stone for asphalt?
If we talk about roads on which cars drive, including multi-ton trucks, and not about pedestrian paths, then the preparation technology before laying asphalt is much more complicated. If the fertile layer of soil has already been removed and the sand cushion has already been compacted, then the next stage will be crushed stone flooring. Crushed stone will be required in different fractions. The total layer should be 25-35 cm. The first layer of crushed stone should be from a fraction of 40-70 mm. It will also serve as drainage from groundwater. It will be about 20 cm. The next layer of the 20-40 mm fraction is 5-10 cm thick. This smaller crushed stone will ensure even distribution of the load when rolling the road. Many builders also lay down a third layer from a fraction of 5-20 mm up to 5 cm thick. Now you can lay the asphalt.
The thickness of the cushion of crushed stone and asphalt layer depends on the expected load on the road surface. If the asphalt path is for pedestrians and cyclists, then a thickness of a layer of crushed stone (middle fraction) of 15 centimeters is sufficient, on which only one layer of asphalt is laid.
How roads are built in Russia (ideally)
Rushing in a car along an asphalt highway, we rarely think about the fact that the road, although made mainly of simple natural materials, is a very complex engineering structure. In road construction today, high-tech rules the roost - technology that navigates by GPS and understands CAD models works here. What is the reason that most of our roads still, as they say, “leave much to be desired”?
Oleg Makarov
November 3, 2020 09:00
Hearing the phrase “travel clothes,” the uninitiated will immediately think of some unpretentious and not too easily soiled wardrobe items. Meanwhile, this is a professional term denoting a set of structural layers of the roadway. The term accurately reflects reality - during the construction of highways and highways, a piece of land is actually “dressed,” and the quality of those “clothes” that are hidden under the asphalt concrete surface is decisive for the quality of the entire road.
Road construction requires an extensive fleet of machines that are used at all stages of creating road pavements. These are excavators, bulldozers, graders, mining and articulated dump trucks, asphalt pavers, various rollers and, finally, machines for applying road markings and installing curbs and bumpers. Many of them today operate under electronic control and are geo-referenced using GPS.
Victory over clay
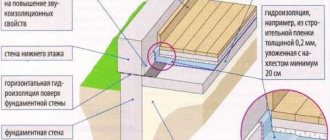
What and how will be laid under the asphalt is decided during geological surveys. At the site of the future road, wells and pits are made, and soil samples are taken to study its physical and mechanical properties. The groundwater level is also determined. As you know, water is the main enemy of the road surface, because, going through cycles of thawing and freezing, it can turn the smallest crack into a huge hole. If there is water under the road surface, then when it is impacted by car wheels, this water “lens” can cause heaving of the asphalt and ultimately destroy it. To remove, expel, and remove harmful moisture is one of the main tasks of road workers, the successful solution of which determines the quality and durability of the road. It is good if the area where the highway is being laid has sandy soil. Then the task is greatly simplified, since sand is an excellent drainage material. But in the Moscow region, for example, there is almost no such luxury: there is heavy clay and loam underfoot. On such soils, for drainage, it is necessary to lay an impressive thickness of underlying layer of sand.
The first stage of road construction is soil preparation. A special roller for soil compaction uses both smooth and cam rollers. Their surface has special protrusions).
However, sand is not simply poured onto the ground: most often, preliminary work is required to stabilize the soil. A machine called a recycler is used for this. This word brings to mind the idea of reusing something, and indeed, recyclers are used in the reconstruction of old roads, in cases where a new surface is made by recycling the old one. However, when stabilizing soils, the recycler simply mixes soil taken on site in a bunker with various kinds of organic and inorganic additives, such as cement, lime, fly ash, foamed bitumen, etc. Having laid the resulting mixture on the site of the future road and compacted it, the builders get a well prepared base. Now you can lay the underlying layer of sand. Medium and coarse sand is used - the coarser the sand and the fewer clay particles it contains, the faster and easier it will be to drain water through it into the ditch. The thickness of the underlying layer varies in the range of 50−60 cm. The sand is leveled by graders and bulldozers and compacted using rollers.
Creating the foundation. Using bulldozers and graders, a drainage layer in the form of sand is laid on the ground, and then a base of crushed stone of different fractions is laid. Both sand and crushed stone are compacted by rollers.
Stone bed
Now comes the time to lay the base, which is usually crushed stone. There are also many technological subtleties here. Crushed stone varies both in granulometric parameters (size and shape) and in strength grade. Grades 600 and 800 are crushed stone from relatively soft calcareous dolomite rocks, and crushed stone grades 1000 and 1200 come from granites mined in Karelia. It is clear that crushed limestone is less durable and can withstand fewer thawing-freezing cycles. But it is still used in the construction of roads of lower categories with low loads and low traffic intensity. In roads of the first technical category, granite crushed stone of grades 1000 and 1200 is used. To pour “mixed-sized” crushed stone onto the underlying layer means to hopelessly ruin the road.
The asphalt paver places an already compacted layer of asphalt concrete mixture on the base. In one pass, a modern machine is capable of covering a strip of more than 10 m with asphalt. Typically, three layers of asphalt concrete are laid.
In reality, crushed stone is delivered to the construction site in the form of fractions, within which the dimensions of an individual stone cannot go beyond a given range, for example 40-70 mm. This is the largest fraction, which is placed directly on the compacted drainage layer. Next, a finer fraction (20−40 mm) is poured, then an even finer one (5−20 mm). The point of all this action is that the crushed stone of the lower layer is wedged into smaller ones, or, in other words, the small fraction fills the voids among the stones of the large fraction. This ensures the strength of the base. At the same time, the shape of the crushed stone is also of considerable importance. Modern crushing and screening equipment gives it a cubic shape; on the contrary, if the crushed stone is “flaky”, that is, elongated and thin (similar to bream), it is almost impossible to wedge it. On a road whose base is made of flaky crushed stone, the asphalt concrete surface will break under the wheels like chocolate.
The laid asphalt concrete requires additional compaction. Modern rollers, using automated control systems, are able to vary the compaction effect in different areas.
However, simply laying crushed stone fractionally (the thickness of the base is approximately 24-28 cm) and compacting it with rollers is sometimes not enough. For roads of the first technical category, which are subject to the most intense loads, so-called “skinny” cement concrete is laid in the base. It is lean because it contains a smaller amount of binders compared to concrete used in construction and industry. For this reason, pavement concrete is less durable, but for foundation purposes this strength is quite sufficient.
“The most difficult thing is to make a high-quality subgrade and a high-quality base,” explains Sergei Kulichkov, general director of a road construction company near Moscow. — Those who lay asphalt can be called “white bones” among road workers - it’s easier for them, they always walk on a clean, level base. And those who build the subgrade and lower layers of road pavement have to deal with groundwater, with soils, not all of which are suitable for constructing a foundation or embankment, with huge masses of sand and crushed stone. And it is the quality of this work that is often given insufficient attention in our country.”
At the final stage, road workers equip the constructed highway: install signs, put up fences and apply markings. For large volumes of work, all these operations are also mechanized and automated.
Paving technology
The final stage is laying asphalt, which is thoroughly mixed with fine sand and stone flour. This mixture is heated to the desired temperature and laid in layers. Each of them should be approximately seven centimeters thick. An asphalt paver is used during the laying process. This serious equipment is equipped with many sensors and its own computer. Upon completion of the process, the finished coating is again watered with bitumen emulsion.
- Hot type coatings. They are laid at temperatures above 140 degrees. This requires special equipment. Hot asphalt pavement is highly durable, so it is used for laying roads, city streets and squares.
- Cold asphalt. This type of mixture is also called warm, and it is prepared using bitumen, which has a reduced viscosity. Cold material is laid at a temperature of 80 to 120 degrees. Asphalt coatings of this kind are most often used in courtyards, playgrounds, sidewalks and other places that are not subject to heavy loads.
Road works technologies
Proportions and manufacturing standards are regulated by GOST, but many manufacturers ignore this rule and use cheap substitutes. This does not reflect well on the quality of the asphalt mixture, so it is preferable to order this product from truly trusted companies, for example, representative offices.
- First class coatings. They are used for laying routes and can withstand heavy loads. The technology involves the use of mineral filler up to four centimeters in size. Such coatings can withstand the weight of loaded vehicles and intensive use.
- Second class coatings. They are used for paving squares, sidewalks and pedestrian roads. The largest inclusions of the asphalt mixture reach 25 mm.
- Third class coatings. The priority in this case will be the plasticity of the mixture. Mineral particles of minimal size (up to 15 mm), which allows for a tight fit of the composition. This type of coating is used for non-vehicular use (private courtyards, institutional areas, sports grounds).
We recommend reading: I bought an apartment with a mortgage, further steps
Laying asphalt
As soon as the asphalt is delivered to you by dump truck, you must immediately begin laying it. You can use an asphalt paver for these purposes. Narrow paths are covered with asphalt using a shovel, and then compacted using a vibrating plate. Based on the thickness of the asphalt, immediately after spreading it over the surface, compaction should immediately begin with self-propelled or manual devices.
2. Preparing the base for laying asphalt. In order to do a good asphalt laying with your own hands, you need to lay a solid foundation. The base for the road surface can be rigid (road slabs) or flexible (sand, crushed stone or gravel). If the load on the coating is low with low traffic intensity, these base parameters will suit you. In the area of the entrance to the house, pour crushed granite stone of a fraction of 40 - 60 mm . (layer thickness 15 cm). For pedestrian paths and areas, an embankment of 5-10 cm will be sufficient. Crushed stone requires compaction and compaction, as well as uniform distribution. It is important to note that laying a larger layer is not advisable. After laying coarse crushed stone, it is followed by laying granite crushed stone of a smaller fraction of 20 - 40 mm. Its thickness is about 10 cm, the last layer is river sand. It is advisable to spill the entire flooring with water so that it settles and becomes more durable.
Application of asphalt, technology of its laying and repair
20 5
Environmental friendliness
16 5
Ease of manufacture
16 5
Labor intensive to use
Currently, asphalt is considered the most popular material used for road surfaces. It's quite reliable. At the same time, asphalt markings with the best performance indicators, for example, such as M1200, are intended for heavy loads. A slightly lower density material (M1000) is no longer able to withstand the weight of numerous vehicles, so it is usually used only for laying paths and sidewalks.
Initially, you should mark the area where asphalt is to be laid. All work will depend on the purpose for which the coating is intended to be used. So, for an “easy” route, along which a large flow of traffic is not expected, only one layer of crushed stone will be needed, but when building a highway it will be necessary to use at least three layers of it.
The fractions are stacked from largest to smallest and rolled very carefully with a roller. At the first stage, it is necessary to form a special cushion on which the asphalt will be located.
If it is necessary for the coating to be level with the surrounding area, then you will first need to dig a pit of the required depth, and after laying crushed stone in it, proceed directly to pouring the asphalt mixture. All road work on laying asphalt is carried out in accordance with the requirements of SNIP and GOST.
There are two main ways to construct asphalt roads:
- Cold. It is usually used for repairs, since it sets very quickly and soon it will be possible to use the coating to its full extent;
- Hot. Can be used when laying a new road. In this case, the bitumen mixture must be rolled before it begins to cool.
The bitumen consumption when repairing the coating should be at least 0.5 liters. But the asphalt consumption when laying a new route is calculated separately. Here it is necessary to take into account not only the size of the road, but also its structure, as well as other additional factors.
When working, you must use a special thermometer that allows you to determine the temperature of the building material. Constant monitoring of this indicator is important, since after cooling the bitumen will no longer be suitable for laying a road.
The video shows the technology for laying cold asphalt:
At the moment, there are three types of impregnations included in the road surface:
- Based on acrylic polymer. One of the expensive coatings that is used only in limited areas. For example, such as tennis courts. They provide the highest quality protection and are also available in several colors.
- Coal tar. A modified coating that is resistant to petroleum products. Thanks to special components, not only long-term service is ensured, but also high-quality color.
- Asphalt emulsion. It is quite common and accessible, but does not provide adequate protection, which is why the canvas may soon require repair.
When cracks form on the paved asphalt, the bitumen mixture is no longer used as a fill. For this purpose, a sealant is used, which is then sprinkled with fine crumbs of cement. The use of special meshes for asphalt can prevent their occurrence and ensure the best strength. With their help, reliable adhesion of the coating is produced, the performance qualities of asphalt are improved and its service life is extended.
Compaction is a very important step in laying pavement. For this purpose, it is possible to use special paving machines: a roller, vibrating plate or asphalt paver. Each of these types of equipment is quite mobile, but has some advantages over other types of rolling. Thus, a vibrating plate has the best maneuverability, and an asphalt paver can carry out at least two types of work.
The photo shows the process of compacting the coating when laying asphalt
Do-it-yourself asphalt laying
In private construction, using asphalt, they make blind areas, arrange paths and sidewalks. In addition, asphalt can be used to form roofing and carry out yard work.
When laying paths yourself, the work is done in stages:
- Initially, up to 30 cm of soil is removed and all debris is removed;
- Next, curbs are installed, which will not only serve as an additional decoration, but will also prevent the bitumen from spreading;
- At this stage, a pillow is created. The crushed stone layer should reach 15 cm, after rolling which you can pour a finer fraction of crushed stone and roll it again. The last layer will be sand. 5 cm will be enough. After creating such a pillow, you will need to fill it with water and roll it with a hand roller;
- Hot asphalt must be spread evenly around the entire perimeter of the path. Next, to level out the bumps, you need to use a motor mop, gradually filling all the holes with new portions of asphalt. Since the material hardens quite quickly, several workers are needed to carry out all the work;
- When the road section is filled with asphalt and leveled, it is necessary to compact it with a hand roller. You will first need to lubricate the roller with diesel fuel to prevent sticking and ensure uniform coverage. It is important to cover all the tools used to perform the work with diesel fuel.
The temperature of the asphalt during laying is very important. It should not fall below 120C, otherwise the coating will soon become completely unusable.
When laying, it is important to make only direct movements; reverse movements are strictly prohibited. Bitumen consumption in this case is calculated individually and can be either 5 or 10 kg. At the end of the work, instead of impregnation, you can use special paint for asphalt. It will give the necessary shade. In addition, you can use white paint to mark asphalt.
The video will tell you how to properly lay (lay) asphalt with your own hands:
After some time, the bitumen will need repairs. If it is carried out on time, replacing the most worn areas, then it will last a much longer period. The most important thing at the repair stage is milling. It involves removing the old coating using a cutter.
After this, the surface is textured. The hot milling method involves first heating the asphalt surface, while with the cold method this is not considered necessary. The latter is practically indistinguishable in quality from hot, but can make the work several times easier.
The seam cutter is also designed for removing coatings, as well as for cutting seams. To transport asphalt mass, a Kocher is used, which is specially manufactured for this purpose. It can be either mobile or stationary.
Popular about asphalt laying technology
The work itself begins with a device, the so-called earthen trough. New asphalt pavement should generally be flush with the rest of the surface, so all layers of crushed stone and asphalt should go deeper. Therefore, throughout the entire territory, soil is selected to a depth equal to the total thickness of the future coating. After the soil has been selected, it is advisable to compact the bottom of the trough by walking over it with a road roller or vibrating plate.
Landscaping is a serious matter. And although it will almost certainly be asphalt concrete specialists who will be paving your yard, it will be useful for you, as the owner-customer, to familiarize yourself with the basics of asphalt laying technology in order to assess the professional level of your contractors and to simply navigate the process.
Application of asphalt, technology of its laying and repair. Asphalt thickness according to GOST
MiscellaneousAsphalt thickness according to GOST
Asphalt road surfaces are common and extremely popular. This is due, first of all, to the durability and strength of this option. For these conditions to be fully met, a number of conditions must be met. The technology of laying asphalt has certain difficulties, but if everything is done correctly, the costs will be recouped with impeccable coverage and trouble-free operation.
Other materials from the reference book on this topic:
Source: https://starimpex.ru/raznoe/tolcshina-asfalta-po-gostu.html
Asphalting the yard of a private house: more about the process
When the base is ready for asphalting, the asphalt mass must be poured into several small piles. This is done to ensure uniform distribution over the paved area of the yard. Next, the mass needs to be scattered with a shovel and distributed evenly on all sides: 5 cm thick in the yard and pedestrian paths, 10 cm in places of car passages.
We recommend reading: If a Pregnant Woman Doesn’t Work What Payments Are She Entitled to in 2020
For example, if an area near a house is being prepared for parking and driving a car, then it is necessary to asphalt it in two layers, and the crushed stone base should reach from 25 cm to half a meter. And when paving pedestrian paths, you don’t have to build a serious foundation; only 10 cm of crushed stone is enough, so asphalt paths will cost several times less.
Roads in the courtyards of apartment buildings: who should repair them
It is no secret that state and municipal authorities in Russia work extremely slowly, and road surface repairs often drag on for months, or even more. It happens that your request to repair the road, sent to the competent authority, will be completely ignored.
So, first you need to find the entity whose property is the road, the section of which needs repair. If the road is included in the local area, then it belongs to the common shared ownership of the house, i.e. the management company will be responsible for its operation, and therefore repairs (see Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 491).
European method in Russian conditions
The poor condition of roads in Russia is, unfortunately, not a myth. The huge populated territory requires active construction, and the state is trying to implement this. But, as can be seen in some cities, they do not always succeed.
First of all, it is worth learning from America in terms of quality. The quality of roads is a favorite topic of jokes among citizens of the Russian Federation. Purchasing the cheapest equipment does not have a very good effect on the longevity of roads, so over time, you again have to look for money for repairs. In addition, the speed of construction also suffers. You can often see funny pictures of asphalt being laid directly on grass or snow. For the most part, the construction of roads in the photo, where the laying is done around a car or on top of grass, is all a joke, but it often happens that the strange actions of the builders still have to be observed from the sidelines. Such a road can hardly be considered complete. But sometimes deadlines force us to create not the most reliable coatings.
You can talk and think for a long time about why it turns out that in Europe everything is not so bad with roads, but in Russia, despite using the same time-tested method, road construction is not carried out to a very high quality. But one thing is for sure - the problem must be approached comprehensively and the origins of the problem must be sought from the very first stages of this area.
You can often see funny pictures of asphalt being laid directly on grass or snow.
Thus, we can conclude that road construction has not yet found an ideal method, although the American one is more effective. However, some may argue even with this. But one thing can be said for sure - technology has room to develop, and perhaps in the near future something fundamentally new will appear that will take road construction to another level.
Technology for laying asphalt (road surface)
In the case of asphalt concrete pavement intended for high loads, rollers of 6-10 tons or higher must be used to compact the base and then the asphalt concrete. For smaller loads, rollers of 2-4 tons are sufficient. It should be remembered that in modern rollers the vibration function significantly increases the compaction ability (about 3-4 times!). Vibrating plates and vibrating rammers can also be used for compaction in hard-to-reach places. To improve the quality of compaction, the base should be moistened. At large facilities, watering machines are used for this.
So, it all starts with marking or breaking down the territory - you need to determine where the asphalt will lie, where the curbs will be, where and how the drainage and collection of rainwater will be arranged. It is also necessary to determine the composition of the asphalt concrete pavement from the very beginning. Depending on the upcoming operating mode, the thickness of the crushed stone base and the number of asphalt layers are selected. If only pedestrian loads and occasional passenger traffic (sidewalks, courtyards, parking lots) are expected in the landscaped area, then you can limit yourself to a crushed stone base with a thickness of 10–15 cm and one layer of asphalt 4–5 cm. If the traffic movement is systematic and even possible movement of heavy trucks (road sections, gas stations, industrial areas), then the crushed stone base should be 25 - 35 cm, asphalt 2 - 3 layers.
TR 103-07 technical recommendations for the construction of road structures using asphalt concrete
| THE GOVERNMENT OF MOSCOW DEPARTMENT OF URBAN POLICY, DEVELOPMENT AND RECONSTRUCTION OF THE CITY DEPARTMENT OF SCIENTIFIC AND TECHNICAL POLICY IN THE CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY STATE UNITARY ENTERPRISE RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF MOSCOW CONSTRUCTION State Unitary Enterprise NIIMosstroy TECHNICAL RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CONSTRUCTING ROAD STRUCTURES USING ASPHALT CONCRETE TR 103-07 Moscow - 2007 These technical recommendations provide practical guidance for road construction organizations carrying out work on constructing road structures using asphalt concrete. Technical recommendations were developed by the State Unitary Enterprise "NIIMosstroy" (Doctor of Technical Sciences A.V. Rudensky, Candidate of Technical Sciences L.V. Gorodetsky). The recommendations were prepared taking into account domestic and foreign experience in the design, construction and operation of urban road structures with asphalt concrete pavements. The recommendations were agreed upon with Inzhdorstroy OJSC and Asphalt Plant No. 1 OJSC. PREFACERoad structures with asphalt concrete pavements are the main type of roadway structures for streets and highways in Moscow. Increasing the efficiency of the construction of asphalt concrete pavements, ensuring their high transport and operational performance, and extending their service life is an important technical and economic task, since the condition of asphalt concrete pavements has a significant impact on the efficiency of road transport and on the reliability of the city road network. The technology for constructing asphalt concrete pavements includes the following main stages: preparation of raw materials and preparation of asphalt concrete mixtures, delivery of asphalt concrete mixtures to the work site, laying and compaction of the asphalt concrete mixture, quality control of materials and finished asphalt concrete pavement. Technological features of the process of constructing an asphalt concrete pavement are determined by the requirements of construction conditions and the characteristics of the technological equipment used. For the construction of asphalt concrete pavements of highways and airfields, along with standard mixtures (i.e., those that meet the requirements of the standard), various special compositions of asphalt concrete mixtures are used, the use of which may be justified by special requirements or technical and economic considerations. Special asphalt concrete mixtures are usually used in accordance with specially developed technical specifications that reflect the characteristics of the mixtures or their components used. For example, the use of cast asphalt concrete mixtures (cast asphalt), which have practically zero residual porosity and do not require compaction after laying, is widely known. The use of such mixtures has become widespread in a number of countries. Another type of asphalt concrete mixtures that have recently been widely used abroad are the so-called crushed stone-mastic asphalt concretes and asphalt concretes with a high crushed stone content of more than 65% (up to 75 - 90%).
There is known experience of using various types of powdered industrial waste (rock crushing screenings, fly ash from thermal power plants, fly dust from cement factories) as part of asphalt concrete mixtures instead of carbonate mineral powder, as well as various types of fibrous fillers. Non-standard artificial stone materials (expanded clay, agloporite, etc.), low-strength crushed stone obtained by crushing limestone, shell rock or bitumen-containing rocks, cement concrete, broken glass and other materials are used as crushed stone or gravel. The choice of one or another type of asphalt concrete for the road surface, its composition and components is determined by the requirements depending on the category of the road, climatic and operational conditions, technical and economic factors (availability of resources, construction time, reliability requirements, etc.). The thickness of the asphalt concrete pavement laid in one layer is 3 - 6 cm. Coatings of greater thickness are usually laid in 2 - 3 layers of asphalt concrete mixture with separate compaction of each layer. In this case, the thickness of the top layer is taken to be within 3 - 5 cm, and the thickness of each of the lower layers of asphalt concrete pavement is 4 - 8 cm. Along with the traditional technology of layer-by-layer construction of asphalt concrete pavement, the technology of construction of a single-layer coating with a layer thickness of 9 - 20 cm or more is known. Thin-layer coatings with a thickness of 1.5 - 2.5 cm are usually made from asphalt concrete mixtures of a special composition to ensure surface roughness. The variety of types of asphalt concrete and bitumen-mineral (asphalt) mixtures, as well as materials used for the construction of road bases, determines a significant variety of road pavement designs. To increase the durability of asphalt roads, asphalt concrete bases are installed, because structural layers made from mineral materials treated with organic binders have greater stability compared to layers made from materials not bound by binders. These “Technical Recommendations” are intended for use by road construction organizations when carrying out work on constructing road structures using asphalt concrete. 1. GENERAL PROVISIONS1.1 Work on the installation of road structures with asphalt concrete pavements of city streets and highways is carried out in accordance with the regulatory documents in force on the territory of the Russian Federation. When carrying out work, you should be guided by SNiP 3.06.03-85 “Highways” 1.2 Technical recommendations for the construction of road structures with asphalt concrete pavements include instructions for performing a set of preparatory work, ensuring industrial, sanitary and fire safety, environmental protection requirements, rational choice of asphalt concrete composition taking into account the category of the road and operating conditions, technology for the production of asphalt concrete mixtures, their laying and compaction, quality control of work and acceptance of the finished coating. 1.4 The design of pavement with asphalt concrete pavement and the thickness of the structural layers are determined by the project depending on the category of streets and roads. The development of the project is carried out taking into account an album of standard structures for the city of Moscow, current SNiP and TR. Developed State Unitary Enterprise "NIIMosstroy" | Approved Head of the Department of Scientific and Technical Policy in the Construction Industry "" Dmitriev AN. | Date of introduction into action "01" June 2007 |
1.5 The road structure is formed by sequentially laying a sand drainage layer on a compacted and prepared subgrade, on which layers of the road base and coating are laid.
1.6 Asphalt concrete pavement is the upper part of the road structure, consisting of one or several layers laid on a prepared road base, incl. asphalt concrete. Asphalt concrete pavements, depending on the asphalt concrete mixtures used, belong to permanent or lightweight types of road structures.
1.7 The main types of road structures with asphalt concrete pavements are as follows:
— option 1 includes an asphalt concrete pavement laid on a layer of crushed stone (or gravel) base, or directly on a prepared subgrade;
— option 2 includes an asphalt concrete pavement laid on a base, the bottom layer of which is made of crushed stone or gravel untreated with binder, and the top layer is made of crushed stone or gravel treated with an organic binder;
— option 3 includes an asphalt concrete pavement laid on a base made of crushed stone materials reinforced with inorganic binders or on a concrete base
What thickness of asphalt should be in the yard
Next, the base is prepared, for which crushed stone corresponding to the thickness of the layer is used (for a layer of 10-15 cm, for example, crushed stone of a 20-40mm fraction is used). When preparing a fairly serious base, a multi-layer laying method is used - the bottom layer is laid with crushed stone of a fraction of 40-70 mm, the top layer is laid with smaller ones, for the correct and uniform distribution of loads over the entire base. For the third layer, fine crushed stone, fractions 5-20 mm, is used. Each layer must be thoroughly compacted with an asphalt roller, running it over each area 5-6 times.
The asphalt laying technology also involves the use of various rollers - for pavements designed for high loads, rollers weighing 6-10 tons are used; for pavements with lower endurance requirements, a roller weighing 2-4 tons is sufficient. Also, do not forget about modern rollers equipped with a vibration function, which increases compaction efficiency several times.
06 Aug 2020 consurist 6100
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Is it possible to obtain an Inn with temporary registration?
- Sample withdrawal application
- Is it possible to temporarily register a newborn child?
- Adoption of children by foreign citizens thesis