SMD LEDs - what are they?
LED SMD – surface mount LED lamps. Their main difference from conventional diodes is the installation method, which determines the design features. The standard output version has long leads for installing the lamp through holes in the board. An SMD device has only contact pads - planer leads, so the product is attached directly to the board. This method is called surface mounting. Installation of diodes is very simple and can be done by a non-specialist.
This solution has another significant advantage. The characteristics of SMD LEDs include high light output with low electricity consumption. However, the realization of this advantage requires very good heat dissipation. Massive short leads are more efficient and dissipate heat better. In addition, the diode practically sits on the board and transfers heat to it.
SMD LEDs are more resistant to vibrations and mechanical damage due to their tighter fit.
Explanation of SMD LED markings
LED brands are designated in order to make their use more convenient. Only 4 digits are used for this, so it’s not difficult to “unravel” the designation.
Devices are classified by size, and the marking essentially indicates the size of the product. The numbers indicate the length and width in millimeters. For example, model 3528 has dimensions of 3.5 * 2.8 mm. Other information about the device can be obtained from the instructions.
Important! It is useful to study the instructions, since many Chinese manufacturers install lower-power chips in a typical case. At the same time, it is easy to purchase an LED with a power of 0.1 W instead of 1 W.
What types of LEDs are there?
Let's consider the classification of LED devices depending on their purpose and technical characteristics.
Properties and parameters of indicator models
Indicator LEDs can have a diameter of 3, 5, 10 or 8 mm. Their voltage varies from 2.5 to 5 Volts. At the same time, they consume electric current from 10 to 25 milliamps. The average brightness of such a diode is only from 100 to 1000 millicandellas. These devices have round or rectangular lenses.
Lighting diodes
Diodes are most actively used in lighting. Lighting diodes are made by coating a blue LED with a layer of phosphor. COB LEDs are a substrate with semiconductors located on it. The crystals are filled with a phosphor of the desired colors. The density of the crystals placed provides increased brightness of the emitted light.
SMD LED Dimensions
The standard sizes of SMD LEDs to some extent determine the parameters of the product. There are many types of them, but the following 6 are among the most popular.
| Type | Dimensions, mm | Number of crystals | Power, W | Luminous flux, Lm | Current, mA | Operating temperature, C |
| 3528 | 3,5*2,8 | 1, 3 | 0,06, 0,2 | 0,6–5,0 | 20 | -40 — +85 |
| 5050 | 5,0*1,6 | 3, 4 | 0.2 or 0.26 | 2–14 | 60 or 80 | -20 — +60 |
| 5630 | 5,6*3,0 | 1 | 0,5 | 57 | 150 | -25 — +85 |
| 5730 | 5,7*3,0 | 1, 2 | 0.5 or 1 | 50 or 158 | 150 or 300 | -40 — +65 |
| 3014 | 3,0*1,4 | 1 | 0,12 | 9–11 | 30 | -40 — +85 |
| 2835 | 2,8*3,5 | 1 | 0,2, 0,5, 1 | 20, 50, 100 | 60, 150, 300 | -40 — +85 |
The table includes only the basic parameters, but allows you to compare the luminous flux and power of the device.
Important! The power of the luminous flux depends on the color of the LED.
In addition to those listed, they also produce a variety of 3 and 6 volt LEDs, which are used to backlight LED TVs, computer monitors, tablets, and smartphones.
Advantages and disadvantages
LEDs - LED (light emitting diode) or LED, from the English Light Emitting Diode - as sources of electric artificial light have many advantages. Compared to traditional incandescent lamps LN, incl. and halogen, they are more energy efficient. This is confirmed by such a parameter as light output. For example, light output, i.e. The ratio of the amount of light that a light source produces to the power consumed for different sources has the following values, in Lm/W:
- for ordinary incandescent lamps - from 4-5 to 12-13;
- for halogen ones - from 14 to 17-18;
- for luminescent ones - from 45-50 to 70;
- for discharge metal halide – from 75-80 to 100-105;
- for LEDs and high-power discharge sodium lamps - about 110-115;
- for promising LEDs - about 250-270.
Other advantages include:
- long service life, which is 10-100 times longer than the nominal service life of incandescent lamps;
- efficiency significantly larger than other light sources;
- the highest reliability is ensured by the mechanical strength of the solid-state crystal, soldering on large planes of contact pads, small size and weight of the device housing, etc.;
- electrical safety - operating voltage does not exceed 12-18 V and only some LED products are powered directly from a 230 V network;
- safety for human health and nature - the materials used in the design are neutral or low-hazard, while in other energy-efficient light sources - discharge lamps, fluorescent tubes, compact, induction, etc. mercury is used - a material of the 1st hazard group, which has the ability to accumulate in the body of humans and animals;
- sufficiently high quality of light: different color temperatures, accurate color reproduction, low level of light flux pulsations, etc.;
- work in different climatic conditions: with high humidity and dust in the air, at a temperature of minus 50-60℃;
- instant return to operating mode. Discharge lamps require from 30 seconds to several minutes to do this;
- unlimited number of inclusions. Fluorescent light sources have from 7-8 to 20-25 thousand inclusions;
- high stability of parameters over time.
Thematic video
White LEDs with a three-component phosphor have 3-5 spectral lines in the emission spectrum, and modern gas-discharge lamps have 2-3. Therefore, LEDs have a higher color rendering index than fluorescent lamps.
But LEDs also have disadvantages:
- limitation on the upper operating temperature not exceeding 80-100℃;
- high cost, but it is compensated by long-term operation and a minimum of maintenance.
Some varieties of LEDs provide the desired shade of white light during production - from super warm to very cool, or almost any color. Adjustable LEDs - RGB triads, triplets of multi-colored crystals in one housing, allow you to get any white or color shade. In lamps, strips and rulers, LED-based modules, these possibilities are even greater.
Characteristics of SMD LEDs
Each type of SMD LED is characterized not only by the amount of radiation and the amount of current consumed, but also by other parameters. The type of product determines the application of the device and installation features.
3528 LED Specifications
As can be seen from the table, the SMD 3528 LED can be single-chip or triple-chip. In the first case, it can generate white neutral and warm light, as well as yellow, blue, green and red. In the second, it serves several flowers at once. The single-chip version is equipped with 2 terminals for connection, and the three-chip version is equipped with 4 (1 cathode and 3 anodes). To prevent environmental influences, the crystals are filled with a transparent compound. The material may include a phosphor: this is how the color parameters of the device are equalized.
The luminous flux that the device emits is small. But SMD 3528 has miniature dimensions and regenerates different colors. Due to this, LEDs are used in lighting strips and inexpensive decorative lamps.
5050 LED Specifications
The SMD 5050 LED can include 3 or 4 crystals. For a single-color lamp, crystals of the same or similar shade are chosen. 5050 has a higher brightness - 3 times more than 3528. The diodes provide the same protection: a transparent compound or phosphor.
The device has the best power-to-price ratio and provides any color of light output. As a rule, 5050 is installed on decorative lighting strips - single-channel, RGB, RGBW. If you increase the mounting density - up to 60 pieces per 1 m, the LED strip can be used not only as decoration, but also to illuminate interior elements. The strips are equipped with controllers that allow you to adjust the shade and intensity of the light.
5630 LED Specifications
Element 5630 has only a single-chip design, but is distinguished by high power: it generates a luminous flux of 57 lumens. The color is white, with different temperatures: cold, daytime, warm. The device is protected by 2 antistasors and can withstand a current pulse of up to 400 mA.
The LED has 4 pins, but only 2 provide operation of the element. The other 2, together with the substrate, are required for heat removal. Diodes are used in the manufacture of powerful lamps and spotlights.
Important! The brightness of the diode depends on the air temperature. At +85 degrees the indicator drops by 25%.
5730 LED Specifications
The single-chip version has the same power as the 5630, but the three-chip SMD LED 5730 is three times more powerful: it produces light with a brightness of up to 158 lumens. Also designed to produce a white luminous flux, but with different color temperatures.
The modification has a very low thermal resistance, which makes it possible to do without two additional pins, as in the 5630. At the same time, it can also withstand pulse current.
The element is characterized by high performance and is used in the same way as 5630 - in the production of high-power LED lamps.
Characteristics of LED 3014
Single-chip element of moderate power - up to 11 lumens, and very small sizes. A compound is used as protection. The LED produces white light - warm, cool, primary colors, as well as orange. This relatively recently appeared modification is classified as low-current.
When installing the product, you need to take into account its peculiarity: its leads are atypically long and reach the bottom of the case. Thus, heat dissipation is improved.
The main purpose of 3014 is modules and strips of decorative lighting. Diodes are often used in the production of automobile lamps and tabletop devices.
2835 LED Specifications
Of all types of SMD LEDs, this model is the most powerful: it emits about 20% more light than 5730. This can reduce power consumption. The single-chip device is produced in three versions of different power. It emits white light of different temperatures. It is similar in size to element 3528, but has a round lens.
This option is the most popular, as it is used in the manufacture of literally any lighting fixtures: outdoor lamps, spotlights, household LED lamps. And this means a large number of fakes, where instead of a one-watt diode they install an element of lower power.
What is an LED and the history of its invention
How an LED works
An LED is a semiconductor device that emits photons of a certain frequency when an electric current is passed through it.
Often the term “LED” is replaced by the English abbreviation LED from “led emitting diode” - light-emitting diode. The Russian-language analogue of this phrase - SID - is used much less frequently.
The effect of photon emission is achieved due to the presence in these devices of an electron-hole transition, the recombination of electrons and holes in which is accompanied by the transition of electrons from one energy level to another, as a result of which excess energy is released in the form of free photon radiation.
Oleg Losev, Soviet scientist, inventor, one of the forefathers of the LED
A similar phenomenon was first discovered back in 1907 by the English researcher Henry Round. Later, independently of him, the Soviet scientist Oleg Losev in 1923 also recorded electroluminescence at the point of contact of silicon carbide and steel under the influence of electric current and was even able to patent his invention called “Light Relay” in 1927. But, as often happens, the discovery was not properly appreciated by contemporaries and many decades remained before the victorious march of LEDs.
The technology for creating infrared LEDs was mastered in the USA only in 1961, and the first actually applicable LED in the visible range of the spectrum (red) was created in 1962 by Nick Holonyak. Later research led to the creation of a blue LED in 1971, and in 1972 the first yellow LED was created and methods were developed to increase the brightness of red LEDs tenfold.
However, despite the obvious progress in the development of LED technology, LEDs remained prohibitively expensive until the late 60s of the twentieth century. Their widespread industrial production and use began only in the 70s of the twentieth century, and the production of cheap blue LEDs began only after 1990, when Japanese scientists, who later received the Nobel Prize for this, managed to critically improve the technology for their creation.
Application of SMD LEDs
LED lamps are used so widely that it is impossible to list all areas of application.
Most often, devices of this kind are found in the following products:
- pocket and tactical flashlights - 6 volt LED lamps are installed here;
- lamps and turn signals on cars;
- household lighting products of various types;
- decorative lighting, mounted both inside and outside the building, uses crystals that generate different colors;
- signs, indicators, traffic lights, billboards;
- SMD LEDs are extremely popular in landscape design; the elements are not afraid of vibration and low temperature, which allows you to organize the most interesting lighting options;
- Low-current modifications are actively used for indication.
In each case, diodes of the required power are selected. In this case, the color of the light flux is taken into account.
LED design
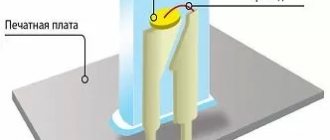
LED design in vertical section.
The heat-removing substrate is shown in lilac. Gray trapezoids are sections of a reflective reflector-reflector of a ring configuration made of aluminum. In the blue center is an LED chip with connected gold or silver wires soldered to the anode and cathode terminals.
Connection requirements
You can install diodes on any surface: on a concrete ceiling covered with wallpaper, on a plastic panel, next to tension films. Thanks to good heat dissipation, the possibility of damaging the material is eliminated. But although the installation of devices is very simple compared to output devices, installation requires the implementation of several recommendations:
- to connect the product to a power source, you need to use a driver, otherwise the LED may fail or operate incorrectly;
- if only 1 resistor is used, the elements should be connected in series to avoid variations in parameters;
- It is forbidden to connect diodes with different operating current values in series, in this case some of the elements will glow dimly;
- if the current is too high, the LED overheats and burns out; accordingly, it is permissible to install a resistor only with sufficient resistance.
If you plan to install garden lighting, you should choose products that are protected from moisture and dust.
Connecting LEDs to an electrical circuit
LED designation on the electrical diagram
Normal operation of light-emitting diodes is possible only when a positive potential is applied to the anode and a negative potential to the cathode, i.e. when current passes through it only in the forward direction.
Since the pn junction has a sharply increasing current-voltage characteristic, the LED must be connected to a current source. When connecting an LED to a voltage source, provision must be made for the installation of current-limiting elements (for example, resistors). The role of such elements can be performed by the electrical circuit itself. LED models from some manufacturers come with built-in current-limiting elements. In such cases, the technical description for the LEDs indicates the maximum and minimum permissible values of the voltage supplied to the light-emitting diode.
Current-voltage characteristic of pn junction in LEDs
Failure of an LED may be due to the supply of voltage to its contacts that exceeds the limits stated by the manufacturer. In this case, the LED generates an amount of heat that cannot be removed by the heat sink elements, which leads to overheating of the SMD LED and its irreversible failure.
The current-limiting circuit for low-power LEDs (the simplest option) can be an elementary resistor connected in series with the LED. In more complex cases, when there is a need to protect high-power LEDs, pulse-width modulation circuits are used. This option allows you to solve two problems at once: firstly, it maintains the average value of the current flowing through the LED at a safe level and, secondly, it allows you to dim the LED, i.e. adjust the brightness of its glow.
It must be remembered that when using power supplies with low internal resistance, it is not allowed to apply reverse polarity voltage to the LED, since most LEDs have a reverse breakdown voltage of only a few volts.
If the LED is used in a circuit where there is a possibility of reverse voltage, the LED should be protected by installing a conventional diode in parallel with it in reverse polarity. Options for protecting LEDs from reverse voltage (using the example of connecting to a 220V AC network)
| Protecting LEDs from reverse voltage with a diode | Back-to-back connection of LED and diode | Back-to-back connection of two LEDs |