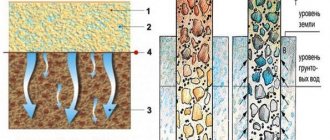
In its structure and properties, sandy loam is close to sand. It contains only 3-10% clay particles of the kaolin or montmorillonite group. The material is mined in quarries or directly on construction sites. It may contain large impurities (pebbles, gravel) and organic matter.
It is not difficult to distinguish sandy loam from other clayey soils. In appearance it looks more like sand and crumbles easily. When wet, sandy loam, unlike clay, does not hold its shape.
Sandy loam is used in very different areas. Sometimes it is used as a cheaper substitute for sand, although it is not suitable for critical work. A high percentage of clay particles can cause swelling and frost heaving of the soil.
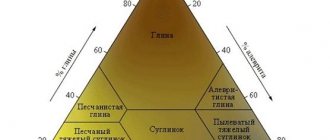
Sandy loam is divided into light (3-5% clay) and heavy (5-10% clay particles). In addition, they are coarse-grained, fine-grained and dusty (depending on the diameter of the sand grains). This classification affects the areas of use of the material.
Basic properties of sandy loam:
- Low ductility
- Good water permeability (in this indicator, sandy loam is superior to loam, but inferior to sand)
- Low load-bearing capacity (2-3 kg/m³)
- Slight tendency to swelling and frost heaving
- Low price
The material is used in the following areas:
- Construction
- Men at work
- Landscaping
- Agriculture
You will learn more about them in the next part of the text.
Construction
In construction, sandy loam is used for:
- Leveling and raising areas
- Backfilling of foundations
Next we will tell you how specifically sandy loam is used in construction.
Leveling and raising areas
Sandy loam is a fairly good and affordable leveling soil. With its help, you can level or raise the site before starting construction. This material is easy to work with: it does not stick to tools, generates almost no dust and spreads less throughout the area than ordinary sand. In addition, sandy loam is cheaper.
After construction, sandy loam can be used to fill in areas where a lawn or vegetable garden will be laid out in the future. It is covered with a layer of black soil or other fertile soil on top. You can also make the bottom layer of the base from sandy loam before laying asphalt or paving slabs. On top you need to make a layer of gravel or crushed stone.
Instead of sandy loam, loam, clay, gruss, overburden and construction soil are also used to level and raise areas.
Backfilling of foundations
In the cold season, sandy loam heaves less than clay and loam. When backfilling, there is virtually no risk that such soil will cause deformation of the foundation of the house and provoke the formation of cracks.
On the other hand, sandy loam will not be able to provide waterproofing, although it will quickly pass water from the upper to the lower layers. If groundwater is low, this can ensure dry foundations and basements. If the aquifer is high, it is better to install a full-fledged drainage system near the house with waterproofing treatment of the foundation.
Sand is better suited for filling the foundation cavities. The material is similar in properties to sandy loam, but is more expensive. But the number of hydrophilic clay particles capable of swelling is lower, and water permeability is higher.
Specifications
• the extracted material varies in weight from 1.5 to 5 mm; • a small content of dust, clay and other additives in the base material.
The division of alluvial material into the following groups depends on the fraction of granular grains: small fraction, medium and large. Bulk density, specific gravity, filtration and compaction coefficient also depend on the fraction of grains.
Sand comes in a variety of shades that may vary. The color palette ranges from amber yellow to the darkest shades, it all depends on the location of the quarry and its features.
Men at work
The use of sandy loam in road construction is slightly limited. Not all types of material are used in this area.
Most often, soil is purchased for the following work:
- Equipment for dirt road foundations
- Construction of embankments
- Backfilling of roadsides
Next we will tell you what kind of sandy loam is used on roads and under what conditions.
Equipment for dirt road foundations
Sandy loam can be used to make the bottom layer of the base of a temporary or permanent dirt road. It is mixed with the main soil (clay or loam) to increase its permeability or reduce heaving.
Sandy loam is also used to make a cushion under the top layer of a dirt road. It creates a stable base and evenly distributes the load transmitted from above. But it is also necessary to use geotextiles.
Instead of sandy loam, sand is often used for the bottom layer of the base; it contains fewer clay impurities. But this material is always more expensive than sandy loam. It can also be replaced by screening out crushed stone or gruss.
Embankment equipment
Sandy loam embankments are made under low-traffic roads. For these purposes, it is recommended to use coarse-grained light sandy loam (clay impurities do not exceed 5%). When moistened, fine-grained material acquires the properties of floaters and loses its stability. It is not recommended for use on roads where the groundwater level is higher than 2m. Dusty sandy loams are not suitable for embankments.
Backfilling of roadsides
Sandy loam is conditionally suitable for roadsides. You can make a bottom layer out of it, and gravel or crushed stone can be poured on top. Sandy loam soil with organic matter can be used on roadsides that will be sown with grass.
Description
• road construction;
Road construction
• used as a special filter for buildings to level sites for the construction process; • GOST 8736 sand is added to dry mixtures that are intended for puttying or arranging self-leveling floors;
Already from the name you can understand that this type of matter is extracted from quarries.
Also, certain properties are affected by the method of sand extraction; there are several methods: washing, sifting and open mining.
In order to obtain high-quality sand for construction work, the moisture coefficient should not be more than 7%. Impurities and other components should be about 3%, sulfur no more than 1%.
Landscaping
Sandy loam is widely used in municipal services, in landscaping areas around residential buildings and private buildings.
It is suitable for the following work:
- Reclamation
- Backfilling of trenches and pits
- Filling foundations under lawns and flower beds
- Equipment for the lower layers of garden paths
- Ice control
You can read further about each application area.
Reclamation
In areas where there used to be quarries, landfills or construction sites, it is necessary to restore the ecology. Over time, the land can be converted into arable land, hayfields, public parks or forest plantations. To do this, quarries are filled in, and soil is partially or completely replaced in landfills.
Sandy loam is successfully used in reclamation. The material is inexpensive and serves as a base under fertile soil. Peaty sandy loam soil itself becomes a substrate for plants. Coniferous trees and shrubs grow well on such soil.
In addition to sandy loam, other materials are also used for reclamation. Deep quarries are first filled with overburden and debris. The top layers are made of loam, clay or plant soil. Peat soil is suitable for these purposes, but it is highly flammable. If the land will be used in agriculture in the future, they are covered with black soil.
Backfilling of trenches and pits
It is more convenient to fill pits and trenches with sandy loam than with loam or clay. This material does not stick to shovels or bulldozer buckets. It drains water well, and the site does not turn into a swamp in the future. Sandy loam soil can be used to fill trenches with communications. It does not heave much and swells slightly, cables and pipes are not in danger of deformation.
Sandy loam can also be used to fill drainage. It filters liquid well and prevents contamination of drainage holes. It is best to choose a light type of material, the clay content of which does not exceed 5%. Sand is more often used in drainage systems; it is better purified. But sandy loam is cheaper and is more accessible in our region.
Filling foundations under flower beds and lawns
Sandy loam allows rain and melt water to pass through well, and it will not stagnate on the surface of the lawn. At the same time, clay particles are able to retain some of the moisture along with nutrients so that they do not wash out into deep soil horizons. It is recommended to lay black soil, peat soil or another type of fertile soil on top of the sandy loam.
Equipment for the lower layers of garden paths
According to recommendations, the bottom layer of the path should be made of sand. It creates a barrier to the growth of weeds, prevents soil contamination of crushed stone, and allows water to pass through well. But to save money, sand can be replaced with sandy loam.
Temporary paths or passages between beds are often simply covered with sandy loam soil. This is a simple and cheap solution. In addition, the material can be used to mark a future path.
Ice control
Sandy loam is one of the cheapest options for combating ice. It costs less than sand, and performs its function no worse. The only drawback is the high clay content. It can contaminate shoes and get into car tires. When the ice melts, a swampy slurry forms in its place.
Nowadays many more modern means of combating ice are being produced. But they have their drawbacks. The substances are expensive and are not always environmentally friendly. Therefore, in many cities, in the old fashioned way, they use screenings, sand or sandy loam, sometimes mixed with table salt - in order to more effectively combat ice.
Mining Features
Sand is present in all soils, but the percentage of the total share differs among areas of different climates and topography. If the content is above 90%, then the surface is considered sandy. Such a territory is characterized by certain properties that affect productivity and the ability to grow certain crops:
- high degree of moisture transmission;
- wide amplitude of heating and cooling.
Moisture absorption capabilities can be checked without the use of special means. It is enough to moisten the clod of earth: if it does not stick together, then the sand content is high. The development of vegetation in such areas is limited due to the passage of water to the deeper depths of the soil. The structure of the rock does not retain the moisture necessary to nourish the roots.
A wide temperature range during the day is more typical for desert areas, where the concentration of sand is maximum. But even in the climate of the Russian central zone, the upper sand layer heats up more during the day and gets colder at night. For plants in the middle zone, sharp fluctuations negatively affect the comfortable microenvironment. Excessive heating can lead to planting burns, lowering the temperature can lead to excessive cooling.
The most common method is the open method, because thanks to it, specialists can make do with ordinary technical equipment: bulldozers, excavators, and more. This method is quite economical and does not require special costs; therefore, the extracted sand cannot be used for all applications.
Open way
Quarries that were flooded with water are destroyed using a suction dredger and sand is extracted. This device has a powerful pump, which allows you to unload sand to the very bottom.
The unit is installed on a floating pontoon (dredger), then secured with anchors and strong ropes or left on the surface of a specialized vessel.
The presented method of sand extraction is called hydromechanized; it has gained wide popularity among other similar methods.
Hydromechanized method
In some cases, it is possible to use other specially equipped devices that perform the same functions and are used for their intended purpose. An example is a sieve - it cleans the sand from excess stones and other substances that were mined using the open method.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to grow anemones in open ground
Also, instead of a sieve, a regular metal mesh can be used, which can sift sand with two hands.
Agriculture
In agriculture, sandy loam soil can be used for the following purposes:
- Improving the structure of clay and loamy soils
- Creation of soil mixtures
You will learn more about this further.
Improving the structure of clay and loamy soils
Clay and loamy soils have low fertility. They are difficult to process. They are heavy and stick to tools. This type of soil is bad for plants. In numerous closed pores, water accumulates and is retained, which leads to rotting of the roots. When the soil dries out, it becomes dense and hard, and the root system lacks air.
Sandy loam has better water permeability and has more open pores. When it is added to loam or clay, the soil becomes looser and allows water and air to pass through better.
Instead of sandy loam, peat can be used to improve the soil structure. This material has high porosity, but also contains a lot of organic matter. Peat retains water. It contains a lot of undecomposed remains of herbs and mosses, which absorb liquid like a sponge.
Creation of soil mixtures
Sandy loam is used to make soil mixtures for seedlings, growing indoor flowers and greenhouse plants. It is mixed with plant humus, peat, turf or leaf soil, and black soil.
For seeds, it is best to take a mixture of sandy loam and plant humus in a ratio of 1:2. You can add 2 more parts of garden or turf soil or black soil to the soil. The material is well suited for growing orchids; pine needles, tree bark, and high-moor peat are added to it.
In greenhouses, sandy loam is mixed with peat or peat soil. It can be used as an independent soil when growing onions and herbs, if you water the plants with nutritious fertilizers.
Adding topsoil
The main way to enrich sandy soil is to add a layer of fertile soil. The methods used to form the surface and the types of soil added differ in the conditions under which the plants will develop. The choice is based on a number of characteristics:
- nutrient content;
- possibility of moisture accumulation;
- acidity.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Quick shortbread pie with apples
Each plant needs its own conditions to promote its development. Most are adapted to a neutral environment, some to a slightly acidic or slightly alkaline environment. Saturating the earth with nutrients contained in fertile soil allows for a comprehensive approach to solving the problem of growth of different crops.
The surface layer is: peat, black soil, manure, humus, turf, silt, humus, compost. The introduction of additives into the sand structure is carried out in compliance with the technology: thickness determined for each type of soil, loosening or compaction, and the use of minerals. Before choosing a specific biosoil for mixing with rock, it is necessary to consider what vegetation will grow on the site. With the right approach, it is possible to increase fertility in 1-2 years.
Rocky soils
The most reliable, but also the rarest soils in the North-West region.
The rock base is durable, resistant to erosion and deformation, durable and safe for construction. Such soils lie in a continuous mass, so the foundation can be built without additional deepening, immediately on the surface of the soil base. Rocky soils are monolithic rocks or in the form of a fractured layer with rigid structural connections, occurring in the form of a continuous massif or separated by cracks. These include igneous (granites, diorites, etc.), metamorphic (gneisses, quartzites, schists, etc.), cemented sedimentary (sandstones, conglomerates, etc.) and artificial.
They hold compressive loads well even in a water-saturated state and at subzero temperatures, and are also insoluble and do not soften in water.
They are a good base for foundations. The only difficulty is the development of rocky soil. The foundation can be erected directly on the surface of such soil, without any opening or deepening.
Coarse clastic - loose fragments of rocks with a predominance of fragments larger than 2 mm in size (over 50%).
Based on their granulometric composition, coarse soils are divided into:
- boulder d{amp}gt;200 mm (with a predominance of unrounded particles - blocky),
- pebble d{amp}gt;10 mm (with unrounded edges - crushed stone)
- gravel d{amp}gt; 2 mm (with unrounded edges - wood). These include gravel, crushed stone, pebbles, and debris.
These soils are a good foundation if there is a dense layer underneath them. They shrink slightly and are reliable foundations.
If coarse-grained soils contain sand filler of more than 40% or clay filler of more than 30% of the total mass of air-dry soil, the name of the type of filler is added to the name of the coarse-grained soil and the characteristics of its condition are indicated. The type of filler is determined after removing particles larger than 2 mm from coarse soil.
Coarse soil can be heaving if the fine component is silty sand or clay.
Conglomerates
Conglomerates are coarse-grained rocks, a group of rocky destroyed rocks, consisting of individual stones of different fractions, containing more than 50% fragments of crystalline or sedimentary rocks, not interconnected or cemented by foreign impurities.
As a rule, the bearing capacity of such soils is quite high and can support the weight of a house of several floors.
Cartilaginous soils
Cartilaginous soils are a mixture of clay, sand, broken stones, crushed stone and gravel. They are poorly washed out by water, are not subject to swelling and are quite reliable.
They don't shrink or blur. In this case, it is recommended to lay a foundation with a depth of at least 0.5 meters.
Rocks, which are solid igneous crystalline rocks, are distinguished by high resistance, negligible compressibility, resistance to water and water resistance, since the layers are not broken by cracks. Rocks, which are sedimentary rocks, are layered formations. These include sandstones, siliceous rocks, carbonic rocks, marls, and shales. The material itself is mostly practically waterproof, since the layers are not broken by cracks. Sedimentary rocks are usually fractured.
Advantages and disadvantages
The most important material in enterprises involved in the extraction of sand, as well as the sale of its various types, is the use of quarry sand itself.
This is explained by the following factors:
- enterprises do not use their own reserves to clean the resulting sand. Based on the fact that quarry sand cannot be processed and resort to other methods, production saves money on cleaning and sifting the extracted material.
- It is not at all difficult to obtain sand using special devices. The open method is the most accurate and inexpensive, so most enterprises resort to using this mining method.
- Delivery of quarry sand also does not involve large financial costs. There are a large number of sand deposits in quarries today, so at any time you can find the right amount of sand nearby.
The norms and coefficient ratio of this sand are not always equal to alluvial or seeded sand, however, the low cost and a number of other characteristics that indicate high-quality material make the sand more popular and in demand than similar types of quarry sand.
Clay
Clay is a product of the destruction and chemical decomposition of crystalline feldspathic rocks, and the particles that make up clays are tiny flakes. Clay can absorb large amounts of water and, depending on humidity, can be solid, plastic or fluid. Clays are practically waterproof. Clay swells when moistened and decreases in volume when dried.
Pebbles. . …………….. ………5.00 m/mGravel ………………… ……..5.00–2.00 m/m Very coarse sand ……2.00–1.00 m/ The sand is coarse. . . . ………1.00—0.50 m/m Average sand ……………. 0.50–0.20 m/m Fine sand……………… 0.20–0.10 m/m Fine sand…………………
Wet clay is highly compressible. Settlement under load takes a long time. Shear resistance depends on humidity and is insignificant at high humidity; in the solid state, clay has a high shear resistance, which is explained by cohesion (capillary tension of water filling the pores). Loams are mixtures of clay and sand.
Loess represents aeolian deposits, i.e. deposits of particles transported by the wind. The smallest particles of dust could only linger on spaces covered with grass; otherwise they would be carried away further. The dying roots of vegetation caused the structure of the loess to be porous in the vertical direction.
The amount of dust particles in loess reaches 75%, the rest is mainly clay, lime and iron. Porosity - up to 50%. Loess is permeable to water in the vertical direction, much less permeable in the horizontal direction, and disintegrates in water, which explains its ability to produce significant precipitation when moistened.
Stone crushed stone
Stone rubble, rolling down from the mountains, accumulates in some place and is then cemented by substances released by the water that washes it, forming breccias. The compressibility of breccias is low; The shear resistance due to the acute angle of the crushed stone and the cement connection is significant, but the type of cementing agent is of great importance.
When filling with clay, water has a softening effect. Conglomerates are similar to breccias, but are an accumulation of pebbles and gravels; due to the roundness of the stone material, they are less resistant to shear than breccias. Loose mountain crushed stone, pebbles and gravelly rocks are characterized by greater mobility and water permeability than cemented ones; they are dangerous foundations in seismic areas when they are inclined.
Sandstones
Sandstones are sands whose grains are cemented by some substance. Depending on the cementing substance, they are distinguished: siliceous sandstones and quartzites, calcareous clayey, bituminous, mica and sandstones with gypsum. Depending on the density and type of cement, the properties of sandstones in relation to water are determined.
Of the siliceous rocks, the most common are siliceous shales, which are insoluble in water, and tripoli, which disintegrate into powder in water. Carbon dioxide rocks are represented by a wide group of limestones, chalk, marble and dolomite. The weakest varieties are chalk and clayey limestone, which disintegrate in water.
Bulk
Bulk materials are the result of human activity and are characterized by an uncertain composition, being almost always very loose. Recently, due to the rapid development of industrial and residential construction in Russia, bulk soils are used as foundations with preliminary compaction or the adoption of constructive measures in the structures themselves.
One of the types of bulk soils - refilled sand - is a good base, because in this case the sand is compacted by the action of water filtering through it from top to bottom.
The main types of soil foundations and their properties.
| Group designation | After drying | When shaking a dried sample with water | After drying and soaking with water again | On an open flame |
| Fibrous organic masses | — | — | Shrinks and swells | Burns out |
| Dense stable rock | — | Without change | Without change | Without change |
| crumbling rock | — | — | Breaks down into smaller pieces | — |
| Partially cemented accumulation of grains | Forms a connected b. or m. solid mass | Only partially breaks down into smaller pieces | — | — |
| Uncemented. cluster of grains connected by cohesion | — | Breaks down completely into individual grains | — | Without change |
| Amorphous organic masses | — | — | — | Burns out completely or partially |
| Accumulation of grains not connected by cohesion | Consists of individual grains | — | — | — |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with DIY soil for pelargonium
The main differences between quarry and river sand
As such, there are no obvious differences between the two species presented; the essence lies in the different costs of these breeds. River sand costs twice as much as quarry sand. In the process of comparing these types of sand, we can conclude that the percentage of purity is higher for river sand than for quarry sand.
There are slight differences in density between river and quarry sand. They also differ from the density of construction sand.
River sand
It is mined immediately without various impurities and third-party components, and the second type has clay, which is often useful. From these characteristics we can conclude that it is impossible to say unambiguously which type of sand is better. It all depends on the enterprise and its goals for using sand.
Peat
Peat is characterized by very high compressibility, and in a dry state - flammability. In exceptional cases, structures are erected on soils with wet peat layers; but as a rule, these soils are unsuitable for natural foundations of structures.
Peat soils consist of clay and sand particles with an admixture of plant residues and organic humus. Wet peat easily compresses under load; it often develops sediment with a composition that is aggressive to building materials, so building on such soils without preliminary preparation of the foundation is strictly prohibited.
Coarse soils
Coarse soil consists of unconsolidated particles, among which sand predominates (50% of the composition) and large rocks more than 2 mm. Coarse-grained soils practically do not deform under load, so the foundation can be buried only 0.5 - 1 m. Depending on the size of the stone particles, such soils are divided into two types:
- crushed stone (pebble) soil: the soil composition is dominated by large components larger than 10 mm in size (rounded pebbles and/or sharp-angled crushed stone), between which there is a fine filling of sand or other inert material of natural origin;
- gritty (gravel) soil: the composition of the soil is dominated by large components larger than 2 mm in size (rounded gravel and/or sharp-angled grit with grains of 5-12 mm), between which there is a fine filling of sand or other inert material of natural origin.