When building a house on heaving soil, it is better to use a strip, shallow foundation. Of course, in this case the house should be low-rise and made of the lightest possible materials. If the house stands on rocky ground, brick and stone houses can be built using a shallow strip foundation.
The non-buried strip foundation has several variations: in the form of a lattice, a monolithic slab and a columnar one.
The non-buried strip type is ideal for building a low-rise building made of lightweight materials on heaving soil.
Let's look at all the types, for which buildings it can be used and how to fill it with your own hands without the help of specialists.
Features of a non-buried strip foundation
The foundation tape may be poured over non-heaving and non-floating soils. A sand cushion with a thickness of twenty to forty centimeters is first placed under it. The monolith must pass under each load-bearing wall of the facility and the frame of all extensions, which include a veranda, porch, etc.
This type of base is approved for use when the wall length is no more than seven meters. Longer sections are susceptible to failure due to uneven shrinkage of the object. The reason is insufficient mechanical strength.
One of the main differences between a shallow foundation and a shallow foundation is that the walls are not affected by the soil, which is prone to movement. Frost heaving has a slight effect on the sole of the base.
Structurally, the base looks like this:
- reinforced concrete strip 0.2 – 0.5 m high, 0.3 – 0.5 m wide;
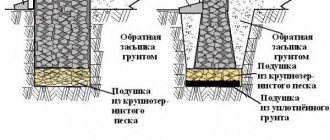
- a pillow whose materials are not prone to heaving. The optimal solution is sand and gravel. The latter can be replaced with slag or crushed stone.
The height of the cushion of a non-buried foundation depends on the tendency of the soil to heave, on the level of groundwater, on the building materials used from which the object is being built.
The properties of a pillow to suppress heaving decrease when moistened, followed by freezing. To prevent moisture from getting into the sole, a blind area with a heat-insulating layer and a waterproofing base is installed along the outer walls along the entire length of the foundation strip.
Recessed foundation
Home > Articles > Construction and repair > Construction of a house
The type of foundation is selected depending on the soil and the load transferred to it. Thus, the foundation can be dispersed throughout the building or concentrated in certain places. Depending on the design of the foundation, its cost also changes. So what kind of foundation should you choose for your home? The most reliable foundation for building a cottage is a buried foundation .
Since in some geographical areas soils can often change their properties, i.e. groundwater appears. The house, in this case, may give uneven settlement when building a house on a strip or columnar foundation. To avoid this, it is recommended to build a house on a deep foundation.
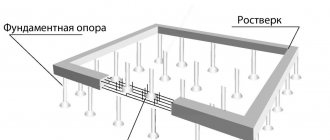
The buried foundation combines two types of foundations - solid and strip. The material used for the construction of a buried foundation is monolithic reinforced concrete. To build it, you will need to carry out large excavation works, which will be difficult to do manually, since it is necessary to dig a pit the size of the entire building footprint and a depth below the freezing level of the soil.
This type of foundation ensures uniform distribution of the load from the entire building onto the foundation. Even if the soils change their load-bearing properties, the house will sink evenly over the entire surface and this will not lead to a violation of the overall integrity of the building.
A buried foundation can be made in such a way that there is a basement under the entire house, and if you increase the depth of the foundation, then you can build a basement, including a garage. But any increase in construction volumes leads to an increase in the total cost of the house, so it is necessary to weigh all the pros and cons of construction.
You can also save on installing a buried foundation. If the depth of the foundation is more than 1 meter and the width of the pit is large, you can use rubble and clay concrete mortar. Rubble are stones of various sizes and origins. Clay concrete mortar is a mixture of soil or clay with cement.
If there is a quarry near the construction of the house, then this advantage must be used. To prepare a clay concrete mixture, you will need to sift the clay through a sieve (mesh size 3-5 mm) and mix it with cement in a dry state. For 1 m3 of solution you will need 150 kg of cement.
After complete mixing, water is added - 270-320 l. The rubble is placed in the formwork and filled with mortar, followed by compaction. The foundation will gain strength in 28 days, but this does not mean that further construction should be suspended for this period. The solution will harden within a day and within a week the foundation will gain 70% of its strength.
When constructing a rubble foundation, it is necessary to lay it in layers, i.e. one layer no more than 200 mm. Each layer is laid on a thick solution or poured with a liquid mixture layer by layer. Also, to increase strength, you can build a trapezoidal buried foundation, i.e. In cross-section, the foundation has a descending trapezoidal shape.
After removing the formwork, all holes and cracks must be sealed with mortar. After complete drying, it is necessary to perform vertical waterproofing of the foundation and subsequent surface cladding.
When building any type of foundation, you must clearly understand that its load-bearing capacity must be sufficient to uniformly transfer the load to the foundation. Therefore, take the construction of the foundation very seriously, since a bad foundation will ruin your life in any, even the most sophisticated, house.
Options for non-buried strip foundations
Let's take a closer look at how you can build such a foundation.
Prefabricated shallow foundation
It is mounted from FBS. The pillow for the base is prepared using conventional technology, having planned and marked the area.
The blocks are installed tightly, leveled, and the horizontal position of the tape is checked using a level. Block stones are rigidly fastened together using cement mortar. If they have metal embedded elements, you can use welding.
Non-buried columnar foundation
This type of foundation is recommended for the construction of bathhouses, panel-type houses, and outbuildings on slightly heaving soil. Supporting elements are placed at the corners of the structure and under the edges of the proposed door blocks, along the lines in increments of two meters.
Short supports are made from:
- foundation blocks;
- wall blocks;
- monolithic structures;
- wall brick material.
Monolithic non-buried base
I arrange it for light structures erected on highly heaving and low-subsidence soils. To prevent the monolith from “floating” during changes in weather conditions, it must be flexible in bending. This can be achieved through reinforced reinforcement and appropriate thickness of the entire structure.
Where can you find strip foundations?
It is used in the construction of houses of all types and heights. A monolithic foundation is one of the few structures that can support the mass of concrete and brick load-bearing walls, but it must be laid well below the freezing depth of the soil.
It is also used in dense and heaving soils with high humidity or the presence of underground groundwater. For long-term service and to prevent water from penetrating into structures, in particular into the basement, drainage is also used.
Making it yourself is not difficult, but you need to know and understand the technology and rules for constructing a drainage system, especially when building on heaving soils.
Strip foundations must be used when building houses on slopes, where there is lateral soil pressure and possible displacement of loose rocks.
The most effective way to neutralize the side effects of soil exposure is to use monolithic concrete structures, rigidly connected to each other by reinforcement and concrete mortar.
Such a foundation is the optimal and, perhaps, the only correct solution for the construction of heavy stone and concrete houses on soft soils. This is the only type of foundation that is used in the construction of basements and ground floors located below the ground surface.
There are two key types of strip foundations:
- Unburdened foundation. It is used in the construction of private houses with a height of several floors.
- Recessed foundation with a depth of up to 1.5 meters. This design is indispensable for the construction of large and massive buildings, as well as high-rise structures.
Varieties of strip foundations, including sand cushion.
Strip foundations are almost always used on sandy and clayey heaving soils that are subject to seasonal movements. If it is used on soils saturated with water, then the maximum permissible height of the building should not exceed several floors, and the structure should be of a frame type with rigid connections of all load-bearing blocks.
Stage-by-stage execution of work
Now let's look at step-by-step instructions for constructing a non-buried strip foundation with your own hands.
Preparation
Professional surveys in individual construction are rarely carried out, since few people want to pay extra money for this set of works.
Most often I use a visual method to assess the condition of the soil. As confirmed by statistical data, a linear meter of a low-rise building undergoes load effects of 4 - 12 or 15 - 20 tons (depending on the number of floors). For this reason, at the moment of swelling, these loads do not balance each other, and deformation begins to occur.
Calculated data for deformation due to heaving are used only for MZLF and NZLF. Uneven displacements of the strip base are permissible, but they should not exceed the limit values depending on the entire structure. As a rule, these are indicators of the rigidity of walls and foundations, which are used for calculations; in the case of NZFL, a standard calculation formula is used, which requires certain data:
- calculated indicator of soil resistance - it is taken from a special reference book or from building codes according to visual inspection indicators, which is carried out independently;
- total load - this includes the weight of the structure, loads from snow and winds, furniture, people;
- groundwater depth - affects the water content of the soil at the construction site;
- soil freezing is determined in special tables for the desired region.
To determine the composition of the soil, you need to roll a ball. Clay rolls to a minimum diameter; sandy loam is more difficult to do this. The loam breaks apart from time to time right in your hands.
To determine the width of the foundation strip, the units of measurement of all necessary indicators are brought to a single form. After this, the prefabricated load is divided by the calculated soil resistance, the length of the entire foundation base.
It is not recommended to make a foundation narrower than 0.25 m, because the supporting plane of the masonry and other building materials used for wall finishing is reduced.
If necessary, certain measures are taken to combat soil heaving:
- dry the soil under the base - if there is no moisture, then even clay soil will not create heaving;
- retain geothermal heat - the ground will not freeze if the blind area is insulated to a width of 0.6 m;
- The soil is replaced, a topsoil layer 0.4 - 0.6 m thick is removed, and ASG, crushed stone, and sand are poured in its place.
Drainage is rarely provided near the NZFL; storm drains are installed within the perimeter of the blind area.
When marking, you should integrate the structure into a place where its operation will be as comfortable as possible. For example, there may be power lines, septic tanks, and wells in the immediate vicinity. It is necessary to provide for their distance from the foundation by at least three to four meters. The foundation is located at a distance of five meters from roadways and fences.
Marking is carried out in several stages:
- I plan the street wall (main facade) parallel to the road;
- lateral - placed at right angles to the existing axis. The right angle triangle method is used for construction;
- diagonals are checked, the length of which must coincide up to one centimeter.
The corner sections will be created automatically; three cords are pulled under each side of the foundation. The side ones are for setting up the formwork, the axis is for controlling the geometry of the object.
Taking into account the design and technology of floor arrangement, the top fertile soil layer is removed over the entire base area or only from the foundation trench.
Filling the pillow
Design specialists recommend various inert materials for installing a cushion under the foundation. In individual construction, they prefer to pour sand and crushed stone in layers of twenty centimeters, carefully compacting each of them.
Experienced builders advise taking into account certain factors when making the underlying foundation:
- When exposed to moisture, sand turns into a shapeless mass and quickly loses its calculated resistance to load;
- crushed stone, even completely immersed in water, is able to retain not only its shape, but also differ in drainage properties;
- The waterproofing roll material is easily joined over the sand layer, the integrity of which is guaranteed to be maintained for the entire operational period;
- To ensure that the crushed stone with its sharp edges does not damage the waterproofing, you will have to fill in the footing, the thickness of the bark should be three to five centimeters.
Formwork
For pouring a shallow strip foundation on heaving soils, the formwork is made quite simply. To do this, it is suggested to use any of the popular methods:
- modules made of polystyrene material, insulating the side edges;
- boards made of edged boards, the thickness of which must be at least 30 mm;
- sheets of multilayer plywood, from which you can subsequently make a continuous sheathing for the roof;
- OSB boards.
Reinforcement
Let's figure out how to prepare the frame base. The bottom of the foundation trench is covered with polyethylene material, after which reinforcing elements can be installed to give stability to the entire object.
Reinforcement forms the required stiffness indicator and is a connecting element created from reinforcing bars.
To give strength to the corner sections, they are reinforced with connecting corners. The reinforcing bars are connected with wire, the diameter of which is 1 mm. Sometimes it is allowed to use welding, but it is best to make connections with wire. To simplify the work, you can use a hook to tie together reinforcing bars, or prepare it like a screwdriver with a sharp, curved tip.
As soon as all the meshes of the reinforcement frame are connected, they are connected into a box of the required dimensions, transferred to the formwork structure and connected to each other.
Concreting
To pour a reliable monolithic tape, it is necessary to use concrete whose class is at least B17.5. The concrete mass is poured in portions in layers, with a thickness of no more than two tens of centimeters. After pouring the next layer, tamping is performed to remove air bubbles and allow the solution to settle evenly.
As soon as the work is completed, the foundation strip is covered with plastic film and the usual care is provided for it.
Hardening of the base lasts up to four weeks. After this, the formwork structure can be removed.
Having filled the tape, it is not left unloaded during the winter season. The active impact of heaving will begin on the foundation; the bulging soil can lift the structure above the ground and break it. The optimal load on the foundation before winter is up to thirty percent of the expected weight of the entire object.
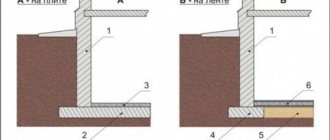
Waterproofing
A non-buried foundation base is most often represented by a lattice structure, the section of beams of which has a limit of 0.6 by 0.6 m. This greatly facilitates measures to protect concrete structures that have contact with the soil from moisture. In such cases, popular technologies are used:
- carry out volumetric waterproofing with compounds that differ in penetrating properties in order to change the molecular structure of the concrete base, giving it moisture-repellent properties throughout its entire depth;
- use adhesive waterproofing materials that have a polymer or fiberglass base with a bitumen layer;
- Coating waterproofing compounds are used in the form of bitumen or epoxy mastics.
The use of Penetron allows you to create a high-quality and almost eternal waterproofing layer, the operational period of which lasts until the foundation is completely destroyed.
It is best to paste with roll materials after applying primers.
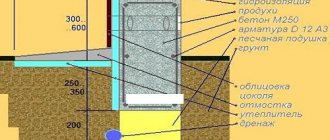
Insulation
It is recommended to carry out such work using inexpensive penoplex or extruded polystyrene foam. These materials have a high heat retention rate and are resistant to water and rodents. The insulation is fixed to the foundation after the waterproofing has been applied. At the same time, the basement part is insulated and a blind area is arranged.
What material should I use for a strip foundation?
What and how to make a deep, reliable strip foundation with your own hands quickly and efficiently? The most reliable foundation for small buildings is a foundation made of rubble concrete (large stones). They weigh about 30 kg and are considered a cheap building material. However, on sandy soils this foundation will crack.
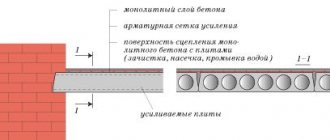
A universal option includes a recessed strip foundation made of FSB blocks. On this basis it is possible to erect a building of any size.
The most popular and cheapest option is a reinforced concrete foundation. It is durable, cheap and allows you to build houses of complex configurations. It will require proper reinforcement and proper selection of concrete mixture.
Features of use on heaving soils
Here are the basic requirements:
- if the heaving is intense, pour a monolithic strip or install a prefabricated foundation, rigidly pinching the beams of the structure;
- when making calculations, it is necessary to take into account the rigidity of the walls, due to which the deformation of the tape is reduced;
- the pillow is made of crushed stone, ASG or coarse sand;
- if a prefabricated belt is installed, the blocks are laid on a reinforced concrete base, the thickness of which is 10 - 20 cm, and are fixed on top with a reinforced belt 0.2 - 0.4 m high.
If the soil is medium heaving, it is allowed to lay blocks in two rows, placing reinforcing bars inside. If the masonry is done with brick or foam concrete, the requirements become more stringent:
- for highly heaving soil, the reinforced belt is installed along the mauerlau, interfloor ceiling, above windows and doors;
- on medium heaving soil, blocks are placed between the reinforced belt and the footing to enhance fixation.
A non-buried foundation on heaving soil has the following form:
- trench depth from 0.4 to 0.6 m;
- a layer of geotextile on which a sand-crushed stone cushion is poured, compacted with a vibrating plate;
- installation of formwork and reinforcement base;
- pouring concrete mortar.
Stripping can be carried out when the poured foundation reaches fifty percent strength.
Pillow for strip foundation
On heaving soils, measures are necessary to reduce the level of heaving deformations to an acceptable level. Pillows made from non-heaving soil, due to their elastic properties, can significantly reduce the normal heaving forces pushing out the foundation.
When constructing pillows, you can use coarse and medium-grained sand, boiler slag, fine crushed stone, expanded clay gravel, gravel-pebble or sand-gravel mixture and other non-freezing materials. The preferred option is a mixture of 40% gravel and 60% sand.
The thickness of the cushion is determined by the characteristics of the soil and is 10-50 cm. On non-heaving soils, a leveling bedding is placed under the foundation.
To limit the effect of soil freezing, it is recommended to install thermal protection under the blind area.
Developer reviews
Numerous reviews confirm that a shallow strip foundation is the best option for individual construction.
Many people like this solution because of the small volume of work, the possibility of carrying out construction on their own, and the economical use of money.
Developers who built exactly this option recommend tape dimensions of 40 by 40 cm and reinforcement of three greasy rods for a small object in order to increase the rigidity of the base. In this case, the peppered rods should be installed in increments of 0.5 m.
Experts recommend strictly maintaining the composition of the components and proportions for preparing the concrete mixture so that the base turns out to be reliable. At the same time, they advise not to take breaks in work, to pour concrete in layers, but at once, carefully compacting each of them.
As useful tips - study the soil characteristics on your site, correctly draw up a work plan, follow the technology of reinforcement, pouring and installing a waterproofing layer. If you have even the slightest doubt about your own capabilities, seek help from experienced professionals.
Moisture protection
To protect the soil at the base of the foundation, as well as the walls of the structure under construction, from the effects of water, waterproofing measures should be carried out during the construction process.
A surface drainage system is installed around the house, including a blind area and trays. They are necessary to drain rain and flood waters away from the house. The concrete blind area should be reinforced with road mesh.
At the junction of the walls and the foundation, a waterproofing layer is installed, for which bitumen mastic, roofing felt, glass insulation, roofing felt and other materials can be used.
A strip foundation mounted on the ground surface has good strength characteristics. And at the same time, requiring relatively low costs, it can significantly reduce the cost of building a house.