ASG concrete is used in many areas of construction. It is applicable in road construction, drainage construction, embankments for road pavement.
This option is often chosen by builders when constructing suburban buildings. Their choice is determined by the composition of such concrete, suitable for constructing a solid foundation for the planned building.
But in order to properly prepare such material, you need to understand what raw materials it is made from and in what ratio the components must be mixed.
Composition of ASG
Sand and gravel mixture is a natural material. It is mined in quarries, or from the bottom of rivers and seas.
Based on the content of PGS components, two types are distinguished:
- Natural origin - the amount of gravel containing 10-20%, sand 80-90%;
- Enriched by artificial method - gravel 15-75%, sand 25-85%.
Certain types of ASG belonging to the first group are suitable for the production of concrete, but enriched mixtures are superior to them. In the manufacturing sector, they have a reputation as a filler that is close to ideal, due to the absence of foreign components in the form of dust and clay particles.
Types of sand and gravel mixtures
Sand-gravel mixtures (SGM), in general, according to the content of the main filler (gravel) and origin, are divided into:
- Natural mixtures - gravel content from 10 to 20 percent;
- Artificially enriched ASG – gravel content from 15 to 75 percent;
- Mountain-ravine ASG. There are rock inclusions with acute-angled irregularly shaped elements;
- Lake-river PGS. It is distinguished by grains that have smooth, water-treated shapes, small inclusions of clay and shells;
- Marine ASG. It is characterized by a homogeneous composition, round rock inclusions and a low content of harmful impurities.
Concrete for general construction purposes is prepared from an enriched river or sea sand-gravel mixture, and mountain-gully ASG, due to its heterogeneous structure, is used primarily for backfilling pits, cushions for asphalt concrete road surfaces, as a drainage layer and for other auxiliary work.
There are 5 groups of enriched ASG, which differ in gravel content, expressed as a percentage. In this case, the grain sizes should not exceed 10, 20, 40 or 60 millimeters. In some cases, a maximum grain size of 150 millimeters is allowed.
Which mixture is suitable for preparing concrete?
If we take the percentage of gravel particles in the composition as a basis, then there are five groups of enriched ASG.
The most suitable for construction is the fifth group (contains no more than 25-35% sand). The best option is when the mixture includes stones of different sizes - large, medium and small. Then a high level of strength is achieved during the hardening period, good indicators of the concrete mixture’s thickening, and there is a saving in cement consumption.
Determining the specific type of ASG used depends on the project and type of structures:
- Simple concrete work - gravel size maximum 80 mm;
- Production of reinforced concrete structures (not factory type) - gravel with a particle diameter of no more than 30 mm;
- Making foundations - 30-45% sand with a size of 5 mm and 55-70% gravel with a diameter of 5-70 mm.
The ratio of cement and ASG in concrete
Concrete is a universal building material used for the construction of a wide variety of structures. The main components of concrete are cement, water and filler; some types of concrete may contain special chemical additives that improve certain characteristics of the original material.
Sand, crushed stone, screenings, brick scrap and ASG are used as fillers for preparing concrete. ASG, or sand and gravel mixture, is one of the most common fillers for concrete.
Types of PGS
There are different types of sand-gravel mixture depending on the size of the sand and gravel fractions, purity, and the absence of various silt-clay and limestone impurities.
The main components of concrete and their ASG are:
- cement,
- the mixture itself
- and water.
To obtain high-quality concrete, you must strictly adhere to the preparation technology, use only good quality ingredients, and also follow the proportions of the recipe; a special calculator will help you with this.
Proportions in the batch
The proportions of concrete from a sand-gravel mixture can be different, it all depends on the type and quality of the latter. The ratio of cement and ASG in concrete is usually taken in the proportion 1:3 or 1:4 (one part of cement and three or four parts of ASG).
Well, in general, the percentage of cement and ASG in the solution depends on what quality of concrete you want to get, what brand of cement you will use, and on the composition of the ASG itself, as well as on the size of the fractions of its components. Typically, the above ratio is taken to prepare concrete from a fine-grained mixture.
Use of concrete
And a lot depends on what purposes you will use this concrete for later. For example, if you need concrete for pouring a foundation, then the ratio of cement to ASG should be 1:8 (eight parts of ASG for one part of cement).
Typically, it is not necessary to add sand or gravel or crushed stone separately to concrete made from ASG. But, again, focus on the composition of your mixture. Where you buy it, you should be told the percentage of sand and gravel in it. If gravel predominates, then sand can be added to the solution. There are mixtures in which sand predominates, if this is yours, then you don’t need to add anything.
dom-fundament.ru
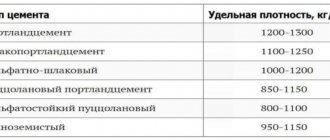
Which cement to choose
In the production of concrete, which is based on ASG, it is necessary to use Portland cement of grades no lower than M300, with an additive content of no more than 20%.
It is possible to use the M500 or M600 brands. Brand M400 is not suitable in this case due to its rapid setting properties. Its use is not recommended.
The correct ratio of components in concrete is the key to obtaining a high-quality building material
One of the most popular materials in construction work is concrete. It does not burn, is not destroyed by mold and fungi, has a long service life, and over time it only becomes stronger. This article will focus on the correct proportions of ingredients when making it.
The photo shows the proportions of the main brands for construction
General information
Its main components are natural substances:
- cement – specially burnt and finely ground lime;
- sand, preferably river or sea sand. Its price is quite affordable;
- crushed stone of various fractions;
- pure water.
If you think about it, there are few construction sites where concrete is not used. And most likely this can only occur in one case - where it is impossible to cook it.
Ingredient proportions
During construction work, you can most often observe a cement-sand mixture, where the ratio of cement and sand is used for concrete. The brand of the finished material also depends on the portions of the last component.
For construction work - preferably M400-500
Let's take a closer look:
| M50 | The instructions recommend mixing M200 cement with sand in a ratio of 1:3. If M400 is used, the proportion will be 1:4. |
| M100 | In this case the proportion is:
|
| M75 | Proportion of cement and sand:
|
Tip: crushed stone can also be added to such solutions.
Below are solutions where crushed stone is not used:
| M10 | M200 and sand in a ratio of 1:6. |
| M25 | at M200 – 1:4. at M400 – 1:6. |
River or sea sand is considered the best
The main filler is crushed stone, sometimes gravel, the volume of which in 1 m3 of the finished composition can reach up to 80%. Cement-sand mortar allows you to fill the voids between its particles, eliminating their movement.
Builders strive to ensure that the finished composition contains as much crushed stone as possible so that the filling solution experiences as little stress as possible. Its pebbles allow it to be distributed evenly throughout the entire volume.
PGS and OPGS
This is the name of a sand-gravel mixture, where the main components are sand and gravel. I usually get it from the river or sea bottom.
ASG for construction work
Tip: the quality of the mixture and its bonding characteristics largely depend on the place of its extraction.
ASG is the main component of concrete and reinforced concrete structures, including:
- house foundations;
- road surfaces.
It is divided into several types based on:
- proportions of sand and gravel;
- gravel fractions;
- strength;
- the presence of clay and silt particles;
- frost resistance.
There is also OPGS, where the first letter means “enriched”. In this case, the amount of gravel in it is artificially increased.
OPGS - enriched mixture with artificial addition of gravel
For example:
- in an enriched mixture its percentage is about 25-75%;
- in the usual - about 10-20%.
The main ingredients of such mixtures are:
- cement;
- water;
- PGS or OPGS.
Advice: to obtain high-quality material, it is necessary to maintain the correct ratio of cement and ASG in concrete.
When using OPGS you must:
- cement – 1 part;
- mixtures – 4 parts;
- water – 0.5 parts.
In this case, the ratio of concrete, cement, sand, gravel takes into account not the volume of materials, but their weight. Sometimes it is recommended to add sand to this solution, however, this issue is controversial. You should definitely take into account its percentage in the OPGS itself.
When manufacturing from ASG it is also necessary to take into account:
- final grade of concrete;
- the brand of cement used;
- proportion of sand and gravel in the mixture.
Although the last parameter is usually indicated at the time of purchase, if it is not there, you can determine the ratio yourself. For example, sifting a certain volume through a metal mesh with your own hands.
A high-quality composition requires the correct proportions
Usually sand is not added to such a mixture, since there is enough of it as is. On the contrary, crushed stone is added to some types of ASG.
The most optimal and verified ratio of concrete for the foundation will be as follows:
- cement – 1 part;
- ASG – 8 parts.
What is taken as a basis - volume or weight?
It is impossible to obtain high-quality concrete without strictly observing:
- technology for its preparation;
- composition recommendations;
- ratios of the components used.
Other factors are also taken into account, including fractions of crushed stone and sand, their humidity and density.
Proportions in most cases are taken either by weight or volume. In this case, the basis is the mass (volume) of cement, which is taken as a unit, other materials are correlated with such a “standard”.
The amount of water is also expressed in parts of its weight, so when 10 kg of the base substance is used in the mixture, and you need, for example, 5 liters of water, the water-cement ratio of the concrete mixture is calculated as follows:
W/C = 5: 10 = 0.5.
The strength of concrete will increase as a result of the interaction of these two components, but this occurs best under warm, moist conditions. Remember, if it starts to dry out or freeze before a certain time, the interaction may stop completely, which will deteriorate the final properties of the material.
The amount of water is an important component
Favorable conditions in the initial period of laying the field for a period of 15-28 days can be created independently:
- water in hot weather;
- cover with plastic wrap;
- apply bitumen emulsion.
In this case, the material acquires up to 80% of the required strength after 7–14 days.
Conclusion
When producing high-quality concrete, the proportion between its ingredients plays a decisive role. Depending on the required strength, you can vary them, saving on the final scope of work (see also the article “Ratio of brand and class of concrete + main purpose of the compositions”).
The video in this article will help you find additional information on this topic.
masterabetona.ru
Component proportions
The ratio of dry Portland cement and OPGS for preparing concrete mass:
| Concrete grade | Cement/OPGS in liters | |
| Portland cement M400 | Portland cement M500 | |
| M100 | 1:10,2 | 1:12,4 |
| M150 | 1:8,2 | 1:9,8 |
| M200 | 1:6,7 | 1:8,1 |
| M250 | 1:5,3 | 1:6,3 |
| M300 | 1:4,9 | 1:5,9 |
| M400 | 1:3,5 | 1:4,2 |
| M500 | 1:3,2 | 1:3,7 |
Classification of concrete grades according to the purpose of the building foundation:
- Foundations of light outbuildings not higher than one floor - M150;
- Slab foundations in the form of strips for houses no higher than one floor - M200;
- Foundations made of monolith or slabs - M250;
- Monolithic foundations for houses with a height of 2 or more floors - M300;
- Heavy-duty foundations with short setting times - M400.
Practical recommendations
You can determine the proportions for mixing concrete without weighing or complex calculations. The method is based on meeting the conditions under which durable concrete is obtained. The cementitious emulsion should fill all the free space between the solid fractions of the mixture.
To do this, take a measuring container and a 10 liter bucket. The enriched sand and gravel mixture is poured into a bucket and filled with water, measuring the volume with a measuring cup. When the water rises to the surface of the mixture, record the measured volume of water. This will be the volume of cement that needs to be added to the OPGS.
If it was possible to pour 2 liters of water into a bucket with filler, then to obtain concrete, mix a bucket of OPGS and 2-liter measures of cement. The cement-mixture proportion will be 1/5. Water is added to the dry mixture in portions until a plastic mass is formed.
But to continue construction, you don’t have to wait that long. In warm weather, after three days the concrete gains 70% strength, which is enough to build walls.
In cold weather, you should wait a week, after which you can continue construction.
Small volumes of concrete are prepared mechanically or manually for strip foundations of garages, outbuildings, dachas, and one-story buildings. The average mixing volume of a concrete mixer is 125–300 liters, and for the foundation of a house with a basement, up to 20 m 3 of concrete may be needed.
It is technologically unacceptable to pour concrete in layers over several days, so it is better to order ready-made concrete, which will be transported in a mixer directly to the construction site.
The sand-gravel mixture is on a par with other types of basic fillers (crushed stone, gravel, construction waste, slag) intended for the production of heavy concrete.
The fundamental difference is that for the production of Gost concrete, Gost fillers and Gost sand are used, and for the production of heavy concrete approximately corresponding to GOST, a mixture of coarse and fine aggregates is used in the form of a sand-gravel mixture “PGS”.
At the same time, concrete made from ASG has its own individual advantages - it is an accessible and relatively inexpensive material that performs its functions, all other things being equal.
Requirements for the solution
It’s a completely different matter when strict requirements are imposed on the base of the floor: static and dynamic loads, wear resistance, etc. The customer can also include in the contract a footnote to the requirements of SP 29.13330.2011 (previously SNiP 2.03.13-88).
In most cases, the screed is made on the basis of cement-sand mixtures (CPS). This is the most universal method. For floors made on the basis of cement mortar, fairly high operational requirements are met at minimal production costs. How to make a mortar for floor screed based on sand and cement, observing building regulations, will be discussed here. In the case of home preparation, the above rules can be followed approximately.
Examples of preparing concrete mortar for screed.
To construct a cement screed, it is necessary to use cement of a grade that would exceed the given grade of concrete by 2-3 times (for Portland cement - 2 times; for other cements - 3 times). For example, for concrete of a grade of 160 kgf/cm2, it is necessary to use cement of a grade of at least 400 kgf/cm2.
An excess of cement in concrete can lead to excess consumption of concrete, and a deficiency will reduce its density, water permeability, and frost resistance, which will lead to rusting of the laid reinforcement. If you decide to prepare a large volume of concrete mass, then keep in mind that the mixture will noticeably decrease in volume. From 1 cu. m of dry mixture is obtained from 0.59 to 0.71 cubic meters. m of concrete mass. Therefore, to prepare 1 cu. m of concrete mass, it is necessary to take much more dry materials.
- One concrete composition requires 0.445 cubic meters. m. sand, 0.870 – gravel, 0.193 cubic meters. m. cement (250 kg), 178 l. water;
- For another - 0.395 cc. m. sand. 0.880 – gravel, 0.198 cu. m. cement (260 kg), 185 liters of water.
- For the third - 0.445 cubic meters. m. sand. 0.880 – gravel, 0.204 cu. m. cement (265 kg), 189 liters of water.
"People's" technology
Approximate ratio of cement and sand for the most common grades of cement.
Many people don’t really think about what kind of solution is needed to screed the floor. ...And the poured floor fulfills its functions. For this:
- Mix the mixture in any way (concrete mixer, drill with a mixer attachment, manually in a bath, etc.). Take approximately 1 to 3 parts of any sand (construction sand, screenings or ordinary river sand), add 1 part cement (the most common is M-400 or strength class B30). Mix dry first.
The sooner you use the solution, the better.
However, such an approximate technology does not guarantee the strength of the floor, the absence of cracking, etc. With a large amount of cement, the mortar is stronger, but it dries faster and is more difficult to level, and the final quality deteriorates. By increasing the amount of sand, the setting time increases, but the final strength decreases. Thus, by varying “by eye” you can make a significant mistake. It is better to follow the recommendations given by experts. But this is a “folk” technology without special requirements.
The correct ratio of cement, sand, crushed stone and water for preparing concrete
Concrete has found application in various fields of construction. Its main components are: sand, water, cement and gravel. To obtain a high-quality mixture, they must be used in a certain ratio. A serious deviation from the norm will lead to the formation of a low-quality solution that cannot be used for the construction of foundations or other building elements.
The ratio of components in cement-sand mortar
To prepare a concrete mixture, you cannot use only cement and water. Concrete obtained from them does not have good strength and frost resistance. A building erected using a “low-quality” mixture will shrink.
Sand is an important component of concrete. It needs to be clean. The presence of fine gravel, clay and other impurities is allowed, but not more than 5% of its mass.
Fine grain material is not suitable for making concrete. It is acceptable to use sand with particle sizes of 2-3 mm.
How much sand is present in different grades of concrete?
The type of material depends on the amount of sand in the mixture.
- M50 - when using M200 cement, the ratio of sand and cement is 1:3, when using M400 - 1:4;
- M100 - when using material M200 the ratio is 1:2, when using M400 - 1:3;
- M75 - when using material M200 the ratio is 1:1.25, when using M400 - 1:1.35.
Solutions that do not contain crushed stone will require additional addition of sand. Thus, when producing M10 concrete using M200 material, the ratio will be 1:6, in the M25 concrete grade it will be 1:4.
In some cases, the ratio of components in the concrete solution can be increased or decreased. To increase strength it is necessary to increase the amount of cement in its composition. If you increase the amount of M300 cement by 10%, you will get a solution whose characteristics are similar to a mixture using M400 cement.
When using sand that is too fine, it is recommended to reduce its amount by 10%, otherwise the flexural and compressive strength of the material will be low.
Sand and crushed stone are mixed gradually with the addition of a small amount of water. It is recommended to prepare the concrete mixture in small portions so that it does not have time to “set.”
Proportions of sand, cement and crushed stone
The use of crushed stone can reduce the cost of concrete and increase its strength. In order for the finished solution to provide high adhesion, it is necessary to use aggregate with small fractions and a corrugated surface.
The standard ratio of cement, sand and crushed stone is 1:3:2. This means that there should be less crushed stone than sand, but more than the main component - cement.
There should not be a lot of water in the solution, otherwise it will negatively affect the strength of the material. Ideally, its amount should be up to 25% of the total mass. To prepare a high-quality mixture, use only clean water without impurities, preferably filtered.
If wet sand and crushed stone are used as materials, the amount of water can be reduced; when using dry components, it can be increased.
Ratio of cement and ASG (OPGS)
ASG is a sand and gravel mixture consisting of 2 components. It is the location of sand and gravel extraction (sea or river bottom) that influences the quality of the mixture. Gravel should not contain clay, which reduces the performance characteristics of concrete. The size of pebbles for PGS should be from 1 to 8 cm.
ASG is used for the construction of foundations and road surfaces. The main difference between PGS and OPGS is the artificial increase in the amount of gravel in the enriched mixture. Thus, its amount in PGS is up to 25%, in OPGS - 25-28%.
To obtain a high-quality concrete mixture, it is necessary to maintain the proportion of cement, water and ASG in it. To make high-quality concrete you will need 1 part of the base material, 4 parts of ASG and 0.5 parts of water. The weight of the components is taken into account as a part, not the volume. There is no need to add sand to this solution, since it is already present in the ASG.
The above ratio is not a standard. In each case, it is necessary to take into account the purpose of the concrete mixture, the quality of crushed stone and sand, as well as the use of plasticizers and other materials.
What should you take as a basis - volume or weight?
The measurement is based on the mass of one unit of cement. The remaining components are also taken by weight. The amount of water is determined by part of the weight. For example: to produce a mixture, 12 kg of base material and 6 kg of water are taken, then the water-cement ratio is calculated as follows: 6/12 = 0.5 liters of water.
The mass fraction of sand and cement in a concrete mixture depends on the following factors: cement brand, amount of water and fractions of bulk components. When constructing critical structures, concrete grade M400 and higher is used. To obtain it, you need cement, sand and crushed stone in a ratio of 1:1.2:2.7, provided that cement 400 is used.
tehno-beton.ru