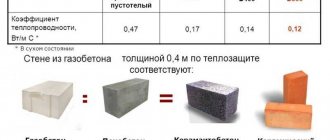
Foam concrete products
Thermal conductivity is one of the main characteristics of foam concrete, because it is responsible for the material’s ability to retain heat. This criterion is often decisive regarding the scope of application of the material and the assessment of its performance qualities.
In this review we will analyze what the thermal conductivity of foam concrete is, what it depends on and what its values are.
What is foam concrete
Let's, first, briefly get acquainted with the material itself and understand its basic properties, because the thermal conductivity coefficient of foam concrete is inextricably linked with many values of other characteristics.
Foam concrete is a porous material that is a representative of cellular concrete. It consists of a mixture of sand, water, cement and a foaming agent, which causes swelling of the solution - and, as a result, the formation of cells.
The porous structure largely determines the main set of properties, which we will now consider.
Structure of a foam concrete block, photo
Material characteristics:
Density | The density of foam concrete ranges from 300 to 1200 kg/m3. Depending on its meaning, there is even a classification, which we will pay attention to a little later. After all, the thermal conductivity coefficient and the average density indicator are inextricably linked. This range of material, in terms of density, allows it to be used in various fields, from thermal insulation to the construction of load-bearing structures. |
Strength | Strength grades are dictated by GOST and are priced depending on the above properties. The minimum value for non-autoclaved foam concrete is B0.5, and the maximum (for autoclaved) is B12.5. The higher the average density, the higher the strength grade. |
Frost resistance | Frost resistance is responsible for the ability of a material to withstand a certain number of freezing and thawing cycles. In accordance with the requirement of technical documentation, the minimum value must be at least 25 cycles, which applies exclusively to material intended for the construction of external structures. But, for example, for thermal insulation products and partition walls, the brand has not been established at all. The maximum value can reach 150 cycles. |
Environmental friendliness | We have already talked about the composition of foam concrete and were able to verify its environmental friendliness, since the materials contained are not harmful. |
Heat resistance | Foam concrete can be exposed to high temperatures for a certain period of time, but this period of time does not exceed 2 hours. The material is not flammable. |
Moisture absorption | Hygroscopicity is inherent in the material. However, in comparison with other representatives of lightweight concrete, it is somewhat reduced due to the fact that its pore structure is closed. The figure is about 10-15%. |
Shrinkage | Shrinkage is also typical for foam concrete. And this is one of the main disadvantages. |
It is also worth saying that foam concrete has a fairly broad classification. The material is divided into types depending on: the type of silica component, the type of binder, the hardening method, and the density index.
Foam concrete is produced, as it becomes obvious, not only in liquid form, but also in the form of various products that have different characteristics and have different areas of application. These are panels, blocks, slabs, lintels and much more.
Thermal conductivity
The second most important characteristic of a building material is its ability to conduct heat. At the same time, the thermal conductivity of foam concrete is inversely proportional to its strength characteristics.
Air is the most effective natural thermal insulation material. The presence of a large number of air-filled pores in the structure of the foam concrete block made it possible to reduce its thermal conductivity to the level of 0.08 W/m°C, which is an order of magnitude lower than that of concrete or brick.
The key factor when choosing a material is thermal conductivity
For the average user, this digital indicator doesn’t mean much, so here are the comparative characteristics of foam concrete, ceramic bricks and cinder blocks: to get a wall with a thermal conductivity of about 0.18 W/m°C, you need a layer of D700 foam concrete 300 mm thick. For cinder blocks, the wall thickness will be 1080 mm, for red brick – 1400 mm.
What is thermal conductivity, and what are its values for foam concrete?
Now let's move directly to the main topic of our article. So, the thermal conductivity of foam concrete blocks and foam concrete in general: what does this property affect?
The concept of thermal conductivity, its dependence on other characteristics
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to maintain temperature. That is, a building constructed from a certain structural material can cool and heat up quickly or slowly. This is exactly what the heat retention indicator influences.
Foam concrete can boast quite competitive values; products in a dry state are characterized by values from 0.08 to 0.37 W*mS. Under operating conditions, the value will increase slightly, but this applies not only to foam concrete, but also to any other material.
As already mentioned, the ability to retain heat depends on the density characteristics of the material. Let's take a closer look.
- The thermal conductivity coefficient of foam concrete blocks intended for thermal insulation is about 0.08-0.10 W*mS. Such products are called thermal insulation. Their density brand is D300, D400.
Application of monolithic low-density thermal insulation foam concrete
- If we talk about structural and thermal insulating foam concrete, its thermal conductivity is slightly higher, and is about 0.11-0.18 W*mC, and the density grade varies from D500 to D900.
Structural and thermal insulation blocks
- If you use structural foam concrete blocks, the thermal conductivity of which will be up to 0.35 W * mS, know that, in contrast to the weak ability to retain heat, such products are characterized by increased strength values. And their density reaches 1200 kg/m3.
Structural product
In addition to thermal conductivity, with increasing density, the frost resistance of products also increases - and, as a rule, their durability.
Comparative analysis of the thermal conductivity of foam concrete and other materials
Now it’s time to compare the thermal conductivity of foam concrete products with its indicators for other popular materials for construction.
Foam concrete blocks: thermal conductivity of products and comparison of its values with other materials:
| Material (product) | Average density indicator (grade D) | Thermal conductivity coefficient of a material in a dry state, W*mS |
Aerated concrete | 300-1200 | 0,09-0,38 |
Expanded clay concrete | 400-2000 | 0,14-0,48 |
Foam concrete | 300-1200 | 0,08-0,35 |
Polystyrene concrete | 150-600 | 0,04-0,16 |
Wood concrete (sawdust concrete) | 300-850 | 0,07-0,3 |
Tree | 450-550 | 0,14 |
Ceramic brick | 1400-2100 | 0.4 (slit) - 0.8 (solid) |
Silicate brick | 1500-1900 | 0,5-0,7 |
As you can see, the direct relationship between density and thermal conductivity applies not only to foam concrete, but also to any other material. If a product excels in density, it will be significantly inferior in its ability to retain heat.
The leader in this ability is undoubtedly polystyrene concrete, but its structural capabilities are severely limited in the form of not so high strength indicators.
Structural and thermal insulation block
It's worth starting with a structural block. It is distinguished by the fact that its density is the highest among all types, and the number of pores is minimal. Because of this, the thermal conductivity of this type of foam block is the highest and is in the range of 0.29-0.38 W/m K. Most often, this material is used only for the construction of foundations and load-bearing structures of buildings. But you need to understand that due to the high heat conductivity coefficient, additional thermal insulation materials will be required. Today, such foam concrete is available in grades from D900 to D1200.
As for the thermal conductivity of a heat-insulating foam block, it is, of course, the best. The numerical indicator of this characteristic is 0.09-0.12 W/m·K. However, it follows from this that the structure contains the largest number of cells, that is, pores. Because of this, the strength is worse than that of the other two types. It is not allowed to build a house from such foam blocks. It can only be used as a thermal insulation material for a finished structure. The building materials of this group are marked from D300 to D500.
Methods for increasing the ability to retain heat, calculations of the minimum wall thickness
The two indicators discussed above can be influenced. If we talk specifically about products, their density and thermal conductivity are established during the production process, which we will discuss below. But first, let's try to calculate what thickness a wall built from foam concrete should have while maintaining high heat retention characteristics.
We calculate the thickness of the foam block wall taking into account the region
To calculate the optimal wall thickness, you need to know the so-called heat transfer resistance index. It is specified in SNiP and is individual for each individual region. The average value is 3.4, which is what we will rely on.
The instructions are as follows:
- Let's assume that we will use a block with a density of D500 with a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.17 W*mC for masonry.
- 3.4*0.17=0.578 m. This is exactly how many meters the thickness of the wall should be.
- Since insulation is usually carried out, you should subtract the value of its thermal conductivity of the material used for it, and multiply the values again.
- Let us assume that the thermal conductivity of the insulation is 0.02 W*mS.
- 0.17-0.02=0.15. 0.15*0.34=0.51 m. This means that when planning insulation, the thickness of the walls may not exceed 50 cm. If the insulation is made more intense, then the value can be reduced to laying one block 400 mm wide.
Heat transfer resistance coefficients by region
Methods for changing the thermal conductivity coefficient of a future material at the stage of the production cycle
All indicators of the future material are determined at the production stage:
- The first stage will be drawing up a recipe, or, more precisely, selecting a composition. At the start of production, the nominal composition is determined, which is preceded by the preparation of a special assignment, which contains all the requirements for future performance.
- After development, the mixture is mixed and a kind of test is performed, upon completion of which, if the result is positive, the composition is transferred to production. If the results do not correspond to the planned ones, then an adjustment is made.
- All these actions are carried out, of course, during the manufacture of the material in a factory.
- When making products with your own hands, all proportions of raw materials are measured manually, guided only by recommendations, since there is no exact recipe for making a foam concrete mixture.
- That is why, with independent production, it is not always possible to obtain the necessary indicators of thermal conductivity and density.
Options for foam concrete compositions
Note! When making foam concrete at home, you can significantly reduce your construction budget, and the price of blocks will definitely decrease. The only disadvantage is the high labor costs, time consumption and the high probability of products not meeting GOST requirements.
What exactly influences the change in indicators?
- Type of silica component;
- The ratio of cement in the composition: the more of it, the higher the density and thermal conductivity;
- Specialized additives;
- Material hardening method. With the autoclave method, as a rule, blocks are obtained with a much better combination of the indicators we are discussing, but it is not available for home production.
The video in this article will demonstrate the basic methods of producing foam concrete.
Options for insulating structures built from foam concrete
But it is quite possible to increase the heat-retaining ability of a wall by insulating the structure. There can be a lot of options, and we will briefly look at the most popular insulation materials used by developers.
The most common materials for insulating foam concrete walls:
Basalt (mineral) wool | This type of cotton wool has a number of advantages, the main ones of which are as follows:
Minuses:
|
Styrofoam | No less common among consumers. It also has a number of advantages and disadvantages. Low price, high installation speed, low weight and moisture resistance are significant advantages. The disadvantages include the fact that the material does not breathe at all, and if it catches fire, the foam can release harmful substances. |
Spraying with polyurethane foam | Overall, this is a very good option. However, when applying it you cannot do without specialized equipment. Moreover, this method of insulation is quite expensive. If we talk about thermal insulation, then it is at a high level. |
Application of warm plasters | The most expensive option. Such specialized mixtures are expensive. The advantages are high performance characteristics, moisture resistance and non-flammability. Difficulties may arise during application. The fact is that the composition sets extremely quickly, which requires high speed when carrying out work. In a word, you can’t do without certain skills. |
Briefly about well masonry
Separately, I would like to say about the method of insulating structures using the well masonry method. It is used exclusively when facing a building with brick.
- In this case, the brickwork is carried out in parallel with the main one, and the gap is filled with loose insulation.
- Expanded clay is most often used, but other materials can also be used, such as polystyrene granules, penoizol, vermiculite, sawdust, crushed stone, slag and others.
- Those materials that are not susceptible to biological effects are used as dry backfill. But, for example, sawdust or other organic materials are used together with binders in the form of lightweight concrete with filler.
As a result, the thermal insulation capacity of the wall increases significantly. One of the disadvantages is that the work process is quite labor-intensive and requires certain skills.
Brief description of well masonry
Reviews and characteristics of foam block
As for the characteristics of this material, the following average indicators can be given. The density of the material is from 600 to 1000 kg/m3, thermal conductivity is in the range of 0.14-0.22 W/m·K, strength is 15-25 kgf/cm2, water absorption is from 10 to 16% of the mass of the block, frost resistance is determined in cycles and on average starts from 35 cycles. For the middle climate, the acceptable thickness of a foam block wall with these characteristics is 0.6 m.
As for the reviews, many highlighted the following advantages: significant savings in the construction of the foundation, the shape of the blocks is large, which makes it possible to reduce the amount of material needed and reduce the time needed to construct walls.
One of the disadvantages is that such material is quite fragile and it will not be possible to attach heavy hanging structures to such walls.