Composite reinforcement
(eng. fibre-reinforced plastic rebar, FRP rebar) - non-metallic rods made of glass, basalt, carbon or aramid fibers, impregnated with a thermosetting or thermoplastic polymer binder and cured. Reinforcement made from glass fibers is usually called fiberglass reinforcement (FRP), those made from basalt fibers are called basalt plastic (ABP), and those made from carbon fibers are called carbon fiber reinforced plastic. To ensure adhesion to concrete, special ribs are formed on the surface of the composite reinforcement during the production process or a sand coating is applied.
What is she like?
Fiberglass reinforcement has been around since the 60s of the last century, but its use has been limited due to its high cost. Fiberglass reinforcement for the foundation was made exclusively for harsh climates, where conventional steel reinforcement quickly failed and corroded. Fiberglass reinforced bridge supports and other critical structures that were operated in harsh weather conditions.
But the chemical industry does not stand still; its constant development has led to a significant drop in prices for fiberglass. This point became decisive in the availability of fiberglass rods, which are used in modern construction for the construction of any structures.
Flexible approach to the needs of builders
The fittings can be manufactured in different sizes. Any construction length can be ordered according to the project requirements. In the photo of composite reinforcement you can see that in cross-section it is a rod with a diameter of three to twenty millimeters with corrugation, and depending on the characteristics of the construction work, the corrugation can be given a longitudinal or spiral direction. In most cases, the best adhesion to concrete is provided by a winding profile at an angle of 45 degrees to the axis of the rod.
The reinforcement rolls up without problems and has natural flexibility. It allows the operation of construction projects under severe temperature variations, typical of areas with the harshest climates. Flexural elasticity and the ability of the reinforcement to restore its original position after loading are also highly rated.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of fiberglass reinforcement in strengthening the foundation has its advantages and disadvantages.
The main advantages include:
- The material wound into coils can be easily transported using your own transport. This reduces the costs of constructing a private facility.
- The fittings are light in weight, making them easier to work with. The involvement of additional labor and special equipment is excluded. Fiberglass is more than 4 times lighter than metal.
- Corrosion resistance. The most important disadvantage of steel reinforcement is its rapid failure as a result of “eating” the alloy by rust. Fiberglass rods are not afraid of moisture and aggressive environments. It can be used for foundations with the addition of various modifiers, for example, antifreeze substances.
- Fiberglass does not retain heat well and does not conduct electricity at all. A concrete foundation does not provide thermal insulation for a building, so a layer of insulation is always laid down; in this case, fiberglass reinforcement does not play a big role. But poor electrical conductivity protects the structure from lightning strikes. It has electromagnetic transparency, which does not interfere with the passage of radio waves.
Concrete adhesion testing
In 2013, composite reinforcement with smooth winding was invented. In the same year, domestic researchers experimentally studied how such a rod works with concrete. The research results were published in the journal “Industrial and Civil Construction”, issue No. 9 of 2013. Authors of the work:
- A. V. Benin, Candidate of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor, Head. Mechanical Laboratory named after. prof. N.A. Belelyubsky (Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education "Petersburg State Transport University" (PGUPS));
- S. G. Semenov, engineer (St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University).
Sample tests were carried out in the mechanical laboratory named after. prof. N.A. Belelyubsky on an electromechanical testing machine Shimadzu AGX-300. Scientists studied how well ribbed and plain wound bars, as well as conventional periodic steel reinforcement, worked with B35 concrete. The result is reflected in the table and graph:
It has been proven that smooth winding produced by Alien Technologies (TU 2296-001-30604955-2012) is superior in adhesion strength to all types of reinforcement - both fiberglass and metal.
And a little more about the features of the material
- Price. The gain here is not significant. Fiberglass is almost 30% higher in cost than steel, but due to the fact that thin reinforcement can be used, the costs are comparable.
- Tensile strength. The material in question is 2-3 times superior to steel in this indicator.
- Seamless. There is no need to cut the rod, because there are 100 or 150 meters in one bay. Metal reinforcement is cut to be delivered to the site, and then welded into a single structure, and all the seams are weak points in the foundation. Fiberglass reinforcement is knitted without a single seam.
- Fiberglass material can be purchased in quantities as needed. It all goes away, leaving no scraps.
- To install fiberglass reinforcement for the foundation, a welding machine and similar tools are not required.
- Concrete is obtained without cracks as a result of equal values of the coefficient of thermal expansion of the materials.
Characteristics
Basic properties of composite reinforcement according to table No. 4 GOST 31938-2012:
| Index | ASK | ABK | AUK | AAK | ACC |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 800 | 800 | 1400 | 1400 | 1000 |
| Tensile modulus of elasticity, GPa | 50 | 50 | 130 | 70 | 100 |
| Ultimate compressive strength, MPa | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 |
| Ultimate strength at transverse cut, MPa | 150 | 150 | 350 | 190 | 190 |
To evaluate the main advantages of composites for concrete frames, consider the characteristics of non-metallic reinforcement in the table relative to table rods of similar strength:
| Characteristics | Fiberglass composite ASK | Steel A-III (according to GOST 5781-82*) |
| Density, kg/m3 | 1900 | 7850 |
| Relative extension, % | 2,2 | 14-25 |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 800 | 355-365 |
| Modulus of elasticity, MPa | 5 000 | 200 000 |
| Diameter, mm | 4…40 | 6…80 |
| Thermal conductivity, W/mK | 0,48 | 45 |
| Length of rods, m | 6…12 | |
Composite polymer reinforcement in comparison with steel in equal strength replacement:
| Steel A-III | Fiberglass | ||||
| Diameter, mm | Weight of 1 meter, kg | Meters per ton | Diameter, mm | Weight of 1 meter, kg | Meters per ton |
| 6 | 0,222 | 4504 | 4 | 0,02 | 50000 |
| 8 | 0,395 | 2531 | 6 | 0,04 | 25000 |
| 10 | 0,617 | 1620 | 8 | 0,08 | 12500 |
| 12 | 0,888 | 1126 | 8 | 0,08 | 12500 |
| 14 | 1,21 | 826 | 10 | 0,14 | 7142 |
| 16 | 1,58 | 633 | 12 | 0,2 | 5000 |
| 18 | 2 | 500 | 14 | 0,26 | 3846 |
| 20 | 2,47 | 405 | 16 | 0,32 | 3125 |
This is worth paying attention to
There are many advantages of fiberglass reinforcement in strengthening the foundation. Let's see what shortcomings this material has. The main disadvantage of this material is its low fracture strength.
It is several times lower than the same indicator for metal reinforcement. Since it has little flexibility, the fiberglass rod cannot absorb the tensile force. This will act on concrete, so it must be used in concrete that has already been subjected to maximum tension. Fiberglass rod can be used to a limited extent, because it must already be in a stretched form.
This reinforcement is not recommended for use in mass construction.
Composite reinforcement. Is glass stronger than metal?
In the history of mankind, technologies for the production of building materials have never stood still, moving forward at different rates, responding to the needs of a growing population. The priority has always been the speed of production and installation of products, durability, as well as reducing their cost by using cheaper resources. The invention and use of composite reinforcement was no exception. When in the distant sixties of the twentieth century the first samples of this unique building material arrived at construction sites, few believed that a replacement had come for the then seemingly unshakable traditional steel reinforcement. But as time has shown, their doubts were not confirmed. Composite reinforcement has occupied a worthy niche and is widely used today throughout the world. The main component of this reinforcement is glass roving, which is a white strand consisting of untwisted fiberglass strands. These threads are interconnected with a polymer based on epoxy resin.
For ease of delivery, the reinforcement is rolled into a coil, the length of which may depend on the wishes of the customer. Composite reinforcement is resistant to deformation and is quite flexible, which allows it to straighten out like a spring when unwinding the coil and take its original form in a short time. Composite reinforcement has an undoubted advantage over its metal counterpart. Composite reinforcement is not subject to corrosion, electrical conductivity and metal fatigue; its weight is approximately 5 times less, which, given its compact size, does not create unnecessary hassle during transportation and loading and unloading operations. In tensile tests, it outperformed many classes of steel reinforcement. Among other advantages of this fittings, one should highlight its acid resistance and protection from the effects of sea water, the almost complete absence of thermal conductivity, and radio transparency. Composite reinforcement does not lose its properties at ultra-low or ultra-high temperatures (their range ranges from -70 to +90 degrees Celsius), as well as under the influence of electromagnetic fields. Structures built with its help last an average of 70 years, which is twice as long as when using steel reinforcement.
Composite reinforcement is used everywhere in the construction of various structures. Due to its wear-resistant qualities and protection from caustic liquids, it is preferred in the construction of offshore and onshore structures, and in some components of chemical infrastructure, in order to reduce the likelihood of leakage of harmful substances. Over the years, it has increasingly found its use in restoration and repair work, in road and railway construction, in the construction of bridges, houses, sewerage and water supply units. Over time, this list only lengthens, as composite reinforcement finds more and more new areas of application.
Nowadays, the production technology of composite reinforcement is so high that it has made it possible not only to significantly reduce the cost of its production, but also to surpass the cheapness of its metal counterpart. Therefore, many customers who have already appreciated the advantages of this material leave only positive reviews, which undoubtedly leads to an even greater increase in the use of this particular type of reinforcement in various areas of industrial and civil construction.
What experts say
To understand how good or bad fiberglass reinforcement is for a foundation, expert reviews and even serious studies do not provide specific recommendations for its use. Therefore, this material can be used at your own risk.
You can simply study the possibilities of fiberglass in a specific situation, if, for example, it was used in the construction of a strip foundation. Then the opinion of experts really reflects practical results and analyzes of causes.
If there are no specifics, then these reviews can be called advertising or anti-advertising. The use of fiberglass is permitted if high demands are placed on corrosion, dielectric and thermal conductivity properties.
How is fiberglass used in construction?
Fiberglass reinforcement has proven itself well in industrial construction, but in low-rise construction it is gradually gaining popularity. Using the technical characteristics of the reinforcement, you can clearly indicate where to use fiberglass and where to use a metal rod.
Fiberglass reinforcement is successfully used to strengthen the banks of rivers and reservoirs, and on sections of roads exposed to aggressive environments.
In the construction of private houses, fiberglass reinforcement is done in the following structures:
- Enclosing structures made of concrete. Not applicable for load-bearing walls and ceilings.
- In the foundations.
- For laying walls made of aerated concrete and foam concrete.
True, the use of aerated concrete for laying walls requires the use of reinforcement with a thickness of 6 mm.
In addition, in the corners of the wall it is necessary to reinforce with a metal rod, so combined reinforcement is obtained.
Links[ | ]
- GOST 31938-2012 [2] Composite polymer reinforcement for reinforcing concrete structures. General technical conditions
- GOST 5781-82 Hot-rolled steel for reinforcement of reinforced concrete structures. Specifications
To improve this article it is desirable:
Please, after fixing the problem, remove it from the list of parameters. After eliminating all the shortcomings, this template can be deleted by any participant. |
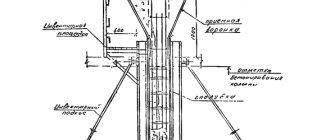
Foundation reinforcement with fiberglass
If we take into account that the foundation of fiberglass reinforcement is made in a low-rise building, then a rod with a diameter of up to 8 mm is used.
The procedure for reinforcing a foundation with fiberglass consists of several steps, where the following sequence is distinguished:
- A calculation is made of the required quantity and diameter of the rod.
- The formwork is being constructed. If it is used more than once, it should be covered with parchment to protect it from the harmful effects of moisture and cement.
- Placement of level marks, along which concrete is then poured into the formwork.
- The base is being prepared - a cushion of broken brick or a mixture of sand and gravel, on which the reinforcing mesh will lie. It must be laid at a distance of 5 mm from the sides of the foundation.
- Laying fiberglass reinforcement. If several layers are used, then the first one is placed on the pillow, and all subsequent layers are placed on the vertical posts of the reinforcement.
- Reinforcement connection. In the presented question, how to knit fiberglass reinforcement remains the key point? In strip and pile foundations, a plastic screed connection is used, which provides a flexible connection. In monolithic types, soldering is used using a blowtorch.
- Attaching vertical rods, longitudinal and transverse, which are the same size as the lower reinforcement mesh.
- The final stage is pouring the foundation with concrete.
Features of the material
The new reinforcement material has some features:
- Lightweight compared to other materials. Therefore, it is easy to transport, no need to rent a truck.
- Does not have a cold bridge.
- Provides a certain tensile strength.
- Lays in layers without limitation. Can be cut with mounting scissors.
- Concrete does not form cracks even at low temperatures.
The material is easy to connect and cut. This does not require a lot of time and additional machinery or labor. Due to the fact that fiberglass does not react to various additives in concrete, it is convenient to use during winter construction.
Let's sum it up
It is important to remember that fiberglass reinforcement is a fairly new material in domestic construction. It has not been sufficiently studied and has not been tested by time. If you decide to use it in personal construction, you take responsibility for its properties upon yourself.
In general, the material perfectly demonstrates its positive properties in small-scale construction - outbuildings, bathhouses, garages and other structures on the site. It is not advisable to use it in large-scale construction - it is better to wait for tests to be carried out using modern methods.
Manufacturing technologies[ | ]
Needletrusion method[ | ]
NIIZhB has developed a new method for the die-free production of composite reinforcement with periodic profiles - the needletrusion method.
With this production method, a rod consisting of fibrous threads impregnated with a polymer binder is first divided into separate parts, passed through separate channels, and then reconnected with simultaneous spiral braiding and the tension of a winding bundle embedded in a bundle of fibers. The authors have received patents for the technology of production of fittings.
Reinforcement manufactured by the needletrusion method has high anchoring properties in a concrete environment, reliable fastening of the spiral winding on the power rod, as well as high physical and mechanical properties.
Method "Planetrusion"[ | ]
Technology for manufacturing non-metallic reinforcement using the die-less broaching method.
Method "Pulltrusion"[ | ]
The technology of forming and curing rod fibers impregnated with a polymer binder by drawing them through a system of dies with a gradually decreasing cross-section.[2]