Brick and foam block
When preparing to build a house, every developer is faced with the pressing problem of choosing materials. Often the choice of products intended primarily for the construction of walls becomes especially difficult.
Many indicators of the future structure depend on the quality and characteristics of the product, the main ones being: practicality, durability, performance. In this article we will make a choice between wall materials.
Brick or foam block, which is better? Let's consider the main properties, purpose, and analyze the data by comparison.
Brick Review
Brick is an extremely durable material, which is due to its special composition and set of properties. In addition, it has many more worthy indicators, with which we will begin.
Main characteristics, material composition
The most popular products are fired bricks, so we will mainly consider them. The material is made exclusively from natural materials, the main of which is fine clay.
Average composition of ceramic bricks
Brick production can be done through two main methods: Plastic method and pressing (semi-dry). The latter method is more modern and popular. The future set of properties and qualities of the material depends on the above factor.
Let us briefly consider the averaged general characteristics of ceramic bricks:
- Frost resistance . It depends, first of all, on the brand of the product, the type and, accordingly, its purpose. The indicator can reach 200 freezing and thawing cycles.
- Thermal conductivity of products is not the strongest side of brick. Due to the high density, its value is slightly increased.
- Strength and density . But in this regard, brick is ahead of many materials intended for the construction of walls. Especially when you compare it with cellular concrete.
- The environmental friendliness of brick is questionable . The indicator is 10. It depends largely on the location of the clay sources.
Some characteristics of brick
Types of bricks and scope of application
Now let's figure out what types of bricks there are, and how they differ from each other.
Depending on its purpose, bricks can be:
- Private. It is used in the construction of building walls inside and outside. It is divided, in turn, into hollow and solid.
Ordinary brick
- Facing. It has improved external characteristics. Special requirements apply to the front part.
Such products do not require further finishing and serve as cladding material. The variety of colors has made this type of product especially popular.
Facing brick
Depending on the structure, brick is divided into:
- Hollow;
Hollow brick
- Full-bodied.
Solid brick
The first option is distinguished, as the name suggests, by the presence of voids. It has a lower density and a lower thermal conductivity coefficient. It is used in the construction of partitions and cladding of buildings.
Using Hollow Brick
Solid brick is denser and more durable. But, at the same time, its ability to retain heat is reduced. It is used when laying load-bearing walls and partitions.
Solid brick laying
Another classification is based on easily dividing bricks into sizes. In accordance with this, the following products can be distinguished:
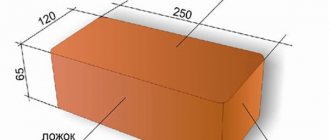
- Single. Their marking is 1NF. The standard size is 250*65*120.
- One and a half. Their marking is 1.4 NF. They are distinguished by their greater height, equal to 8.8 cm.
- Double, marked 2.1 NF. Their height is 13.8 cm.
- Euro bricks. They differ from the previous ones not only in height, but also in width, which are 6.5 and 8.5 cm, respectively.
Single brick dimensions
One and a half brick
Double brick
Euro brick, photo
Products of different types differ from each other depending on the grade of strength. Let's consider the possible options:
- M 50. This brand is the least durable. Such products can be used in the construction of structures that are not subject to significant load. These could be, for example, fence posts or partitions between rooms.
- M75, M100. More durable products have this brand. You can use them to lay out almost any wall, with the exception of a load-bearing one.
- But M125 brand bricks can be used in the construction of load-bearing walls and partitions. This strength is quite enough for this.
- M150, M175, M200. Such products can be used to build a base, load-bearing walls and even the supporting part of foundations.
Brick brands
As already mentioned, many quality indicators depend on the type of brick. Let's look at how they will change using the table.
Table 1. Characteristics of different types of bricks:
| Type of brick | Frost resistance | Thermal conductivity | Density | Compressive strength | Porosity |
| Hollow | 15-50 | 0,3-0,5 | 1000-1450 | 75-150 | 6-8 |
| Full-bodied | 15-50 | 0,6-0,7 | 1600-1900 | 75-300 | 8 |
| Super efficient | 15-50 | 0,24-0,26 | 1100-1150 | 75-300 | 6-10 |
| Facing | 35-75 | 0,25-0,26 | 1300-1400 | 75-250 | 6-14 |
| Clinker | 50-100 | 1,16 | 1900-2100 | 450-1000 | 5 |
It would be fair to pay attention to bricks containing other raw materials. These are silicate and hyperpressed bricks.
The latter is made from a mixture of cement, limestone and dye. It is used in the construction of small architectural structures, fencing, and wall cladding.
Hyperpressed brick
Sand-lime brick is made from a mixture of quartz sand and slaked lime. It is characterized by density and a fairly high thermal conductivity coefficient. Its color can be white or grayish. There are products that are tinted.
Sand-lime brick
Strengths and weaknesses of products
Like any building material, brick has its advantages and disadvantages, and in order to compare materials: brick and foam block, it is necessary to analyze all possible strengths and weaknesses of the products.
The advantages boil down to the following:
- Brick is a durable material, buildings made from it have high performance characteristics.
Brick house
- On the modern market, brick is presented in a wide range of colors, textures and shades, so each developer will be able to choose the appropriate option for himself.
Brick assortment
- Good sound insulation performance can make staying in a future room as comfortable as possible, protecting those in it from extraneous noise.
Soundproofing brick walls
- According to the manufacturers, the material is completely environmentally friendly and safe for the environment.
- In general, the thermal conductivity indicator can be considered a plus if you compare it with the strength and density of the material.
There are also disadvantages:
- The prices for some types of bricks are simply fantastic.
- Products are prone to efflorescence, which can really ruin the appearance of the building.
- Defective products are not uncommon. When purchasing, you should carefully consider the products.
- The brick crumbles, and quite easily. This is especially noticeable during transportation and installation.
- If the laying technology is violated, or low-quality materials are used, the brick may simply crumble.
- The main disadvantage is the hygroscopicity of the material. It is able to absorb moisture.
Efflorescence on brick
Poor quality brick
Shedding of brickwork
These disadvantages can be partially offset by following certain rules, which boil down to the following:
- Materials for masonry and finishing must be of high quality and specialized;
- Masonry work must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of technical documentation.
- Transportation should be done with caution.
- Be sure to check whether the supplier has a certificate for the product.
Example of a certificate for a brick
Advantages and disadvantages of brick
One of the advantages of brick is that it can be used to decorate walls, fences, fireplaces and much more.
Let's start with the most famous and common material - brick. According to some experts, it remains one of the most popular building materials due to tradition rather than due to its unique qualities. However, the advantages of brick include strength, good sound insulation, and environmental safety. Brick walls are durable, and floors made of reinforced concrete slabs allow you to create large-area interiors. Due to its size, brick is suitable for masonry using decorative elements. The same applies to walls with complex configurations.
Brick is one of the heaviest building materials, requiring special equipment for transportation.
This material has no less disadvantages than advantages. Firstly, brick absorbs moisture well (this is more true for sand-lime brick), which can lead to dampness. Secondly, this is a fairly heavy material that requires special equipment for transportation. And due to the weight of the brick, a certain shrinkage of the foundation of the house is inevitable in the first years after construction. Thirdly, the small size of the brick causes increased labor costs in terms of increasing the number of masonry operations, especially when compared with aerated concrete blocks. This is true both for bricks of standard dimensions and for large-format porous ceramic blocks. Fourthly, brick is one of the most expensive building materials, and if you include the cost of insulation, the price of such masonry will be 1.5-2 times higher than masonry made from aerated concrete blocks.
What is foam concrete
Foam concrete is a type of cellular concrete, which is characterized by the presence of a special porous structure. This result can be achieved by introducing a foaming agent into the solution, which provokes swelling of the mixture (see Let's look at how foam blocks are made).
It is thanks to this structure and partly its composition that foam concrete has properties and qualities that are different from other materials. Since we have to find out what is better than foam blocks or bricks, we will consider them, and also analyze the existing types and types of material and products made from it.
Foam concrete structure
Main characteristics
Let's use the table. Table 2. Indicators of technical and operational properties of foam concrete:
| Indicator name | Meaning and Description |
| Density | The density of foam concrete varies from 300 to 1200. The most popular material is the density D 500-600. This value is quite enough for the construction of the walls of a private house on three floors. |
| Strength | The strength of foam concrete is B1.5 – B12.5. It directly depends on the density of the products. |
| Frost resistance | Frost resistance can reach up to 100 freezing and thawing cycles. The minimum value established by GOST is 15. Frost resistance of products not intended for external walls is not standardized. |
| Thermal conductivity of foam block | The thermal conductivity coefficient is in the range from 0.08 to 0.32. These indicators are typical for products in a dry state. With operating humidity, the numerical value will increase. |
| Water absorption | Foam concrete is hygroscopic. It is able to absorb moisture. However, if we compare it with another type of cellular concrete - aerated concrete, then foam concrete wins in this indicator (see Moisture-resistant foam block: material characteristics). Aerated concrete absorbs moisture in an amount of 25%, and foam concrete - 10-16%. This is largely due to the closed pore structure of the latter. |
| Fire resistance | The material does not burn and does not interact with fire. Moreover, foam concrete can be exposed to high temperatures for several hours. |
| Environmental friendliness | Foam concrete does not contain harmful or toxic substances. |
| Shrinkage | Foam concrete is characterized by shrinkage. Cracks and deformations are common. |
| Recommended wall thickness. | The minimum recommended wall thickness is 0.5 meters. Note! It is worth considering that this indicator depends on many factors, such as: the climatic characteristics of the region, the thickness of the joint during laying, the number of cold bridges, and the intensity of insulation. |
Properties of foam concrete
Classification
In accordance with GOST, foam block has several classifications, each of which is based on a specific factor or quality of the material.
Let's take a closer look using the table. Table 3. Classification of foam blocks:
| Depending on the density of the material, foam concrete can be | Thermal insulation | The least durable material, the density varies between D300-D400. Has the lowest thermal conductivity coefficient. Used as a thermal insulation material. |
| Structural and thermal insulation | More durable foam block. Numerical density values range from 500 to 900. Products made from such foam concrete are the most common. They are used mainly in the construction of partitions and walls. | |
| Structural | The most dense. Its indicator is D1000-D1200. Can withstand significant loads. It is used in the construction of buildings and structures up to 3-4 floors high.
| |
| Depending on the type of hardening of foam concrete products, it can be: | Autoclaved | It is also called synthetic hardening foam concrete. It differs in that at the last stage of production, it is processed in special equipment - an autoclave. It is there under the influence of high pressure and temperature. |
| Non-autoclave | Or hydration-hardening foam concrete. Products made from it reach technical maturity naturally. Sometimes they are slightly heated in specialized ovens. The temperature in them does not exceed 1 degree, and the pressure is below atmospheric. | |
| Depending on the type of binder, foam concrete can be | On cement binder | It contains more than 50% cement of a grade not lower than 400. |
| On limestone | Contains lime in an amount of at least 50%. | |
| On Ash | This foam concrete contains highly basic ash. | |
| On the slag | The composition includes slag in an amount of more than 50%. | |
| On mixed | Contains cement, lime, slag and gypsum may be added. | |
| According to the silica component, the material can be manufactured | On sand, most often quartz | The type of silica component has a direct impact on quality indicators, especially with regard to the ratio of thermal conductivity and density. |
| On the ashes | ||
| On other secondary industrial products | ||
| Depending on the geometric deviations of products made from foam concrete, they are divided into | First category blocks | Permissible deviations are 1.5 in size, up to 2 mm diagonally. |
| Blocks of the second category | Up to 2 mm – in size, up to 3 mm – diagonally, broken corners and chips – up to 5 mm. | |
| Blocks of the third category | Deviations in size should not exceed 5 mm, diagonally - 7 mm, chips at the corners - 10 mm. | |
| Foam blocks are distinguished according to their purpose | Wall | Designed for the construction of walls |
| Septal | Used in the construction of partitions | |
| Highly specialized U-shaped | Such products can play the role of stationary formwork. They are also used in the construction of lintels, reinforcement belts, and in the construction of roof structures. |
Wall foam concrete block
Foam block partition
U-shaped foam block
It is also worth noting that the range of foam concrete products includes blocks with a facing side (see Decorative foam block: let’s look at it in detail), which do not require subsequent external finishing.
Foam concrete with lining
Advantages and disadvantages
When choosing which is better: brick or foam block, you need to consider in detail the strengths and weaknesses of both materials. And, since we are now talking about foam concrete, we will start with its pros and cons.
The advantages include:
- Large sizes of foam concrete products, which will significantly speed up the construction process.
- A low thermal conductivity coefficient will allow you to save a little on wall insulation and heating of the building in the future.
- Good density of the material, allowing the construction of buildings several floors high.
- Variety of sizes and large selection of manufacturers.
- High frost resistance. Reaching 100 cycles.
- Environmental friendliness and fire resistance of the material.
- The low weight of the products will reduce the load on the foundation.
- The variability of interior and exterior decoration is also a significant plus. The main thing is to comply with the technical requirements.
- Low price for material. Foam concrete is in the first position in this regard.
- Easy to manufacture and do-it-yourself. This will not require large expenses; it will be enough to have a minimum set of equipment and raw materials. And the instructions will help with this.
- Another advantage is the percentage of water absorption. As already mentioned, due to the closed pore structure, this ability is somewhat reduced.
- Foam concrete is easy to use. Products made from it are easy to cut, grind, and saw. In this case, a specialized tool is not required. You can get by with a hacksaw or saw.
- Good product geometry will reduce cold bridges due to the small thickness of the seam.
- The earthquake resistance of buildings constructed from this material is a significant plus.
Pros of foam concrete
The main disadvantages are as follows:
- Poor fixation of hardware. To fasten the elements, it is necessary to purchase specialized hardware designed for cellular concrete. If you want to secure particularly heavy objects in the form of heating radiators, you will have to plan the fastening points in advance at the project level.
- Not the best adhesion to finishing materials. This may lead to additional costs associated with the purchase of specialized plaster mixtures, primers, and reinforcing mesh. If the technology is not followed, cracks may appear on the walls.
- Shrinkage also leads to cracks. It can reach 0.5-0.6 mm/m2.
- The prevalence of handicraft production increases the chances of purchasing low-quality products.
- Fragility of products. Foam concrete is afraid of mechanical influences. Its use and transportation require careful and careful handling.
Cracks on the foam block
Dowel for foam concrete
Poor quality foam concrete blocks are visible to the naked eye
Aerated concrete wall
The advantages of aerated concrete blocks are vapor permeability and heat capacity, strength and durability, lightness, environmental friendliness and ease of use.
We have already mentioned aerated concrete blocks in comparison with brick, and this is no coincidence. Many compare the characteristics and cost of these materials, trying to figure out which one is better and more profitable. Noting the advantages of this material, they usually name vapor permeability and heat capacity, strength and durability, lightness, environmental friendliness and ease of use. First of all, it should be noted that, despite all their strength characteristics, aerated concrete blocks are easy to process; they can be drilled, cut and planed with conventional tools. You can easily drive nails into them and screw in self-tapping screws.
But this does not mean that aerated concrete is an ideal material, as some manufacturers are trying to present it to customers. He also has shortcomings. Firstly, aerated concrete blocks are still inferior to red (ceramic) brick in terms of strength indicators. For example, brick can withstand a compression load that is almost 10 times higher than that of aerated concrete. That is why aerated concrete blocks, unlike brick, are not used in the construction of high-rise buildings, but they are very popular in the construction of cottages and other private houses. Secondly, brick has greater frost resistance and thermal conductivity than aerated concrete. Thirdly, despite manufacturers’ assurances of long-term durability, in practice there is a lot of evidence that microcracks appear in aerated concrete blocks over time. Aerated concrete also requires special fasteners. Nails and screws really fit into this material easily, like they do into wood, but they don’t always stay in it well. And if something heavy is suspended on this mount, it may fall off along with a piece of the block.
A wall made of aerated concrete blocks can be erected quite quickly, and building a house from this material does not require any special skills. The first row of blocks should be laid on a cement-sand mortar, and the laying should begin from the highest corner of the house being built. Glue for aerated concrete should be poured into horizontal joints, and also used when laying additional blocks.
Tools for laying aerated concrete: special trowels for applying mortar, a square for cutting at right angles, drill attachments, a hand wall chaser, a rubber hammer, a drill attachment for holes, a coarse grater with metal teeth, a grater with coarse sandpaper, a saw with carbide teeth.
After the row is completely laid, you need to remove the unevenness by wiping it with a grater. As for the additional blocks, they are easily cut with a hand saw. Experts recommend reinforcing the first row of masonry and then every fourth row. In addition, the wall above the window and door openings and the entire belt under the interfloor ceilings are reinforced. Grooves are cut into the masonry into which the solution is poured. The reinforcement must be completely immersed in the solution; the remaining solution is simply removed. To build a house from aerated concrete blocks we will need:
- band saw or hand saw;
- corner;
- drill with special attachments;
- manual wall chaser;
- rubber hammer and sanding board;
- special fasteners and masonry adhesive for aerated concrete.
Comparison of main indicators and properties of materials
Since we have considered the properties, qualities and scope of application of both materials, it’s time to move directly to the comparison. So, what is better: brick or foam blocks?
Let's use the table. Table 4. Brick or foam blocks, which is better? Comparing materials:
| Name of characteristic, indicator | What is better foam block or brick? |
| Coefficient of thermal conductivity | If we talk about this indicator, then the foam block definitely wins, and by a large margin. According to the recommendations of the manufacturers, while maintaining the same indicators, the thickness of a wall made of foam block should be at least 50 cm, and that of brick – 120 cm. Agree, the difference is noticeable. |
| Frost resistance | The frost resistance of both materials is quite high. However, still, high-quality and expensive brick will surpass foam block in this indicator. |
| Density and strength | Brick is stronger and denser. It can withstand significantly higher loads. |
| Durability | And yet, in this case, the palm should be given to the brick. According to the statements of the developers, and from the experience of many years, it becomes obvious that the foam block is not so durable. And brick buildings, as time shows, last for 150-200 years. |
| Shrinkage | Both materials are subject to shrinkage. |
| Moisture absorption | Both foam block and brick are characterized by hygroscopicity. For foam blocks this figure is 10-16%, and for bricks it is about 16. In general, they are at approximately the same level. |
| Variability of finishes | Both materials can be finished in almost any material. |
| Which is cheaper: foam block or brick | Of course, brick is much more expensive, which for many future home owners is sometimes a decisive argument. Below we will clearly look at what is cheaper - brick or foam block. |
| Difficulty of processing | Foam block is easy to process. But brick, in fact, does not need this. Its assortment includes products of various shapes and sizes. |
| Speed of construction and complexity of installation | Brick is much more difficult to deal with. Laying it requires skill. This is especially true for the cladding of buildings. The speed of construction also increases significantly - also due to its small size. 1 block can replace laying up to 14-15 bricks. |
| Architectural possibilities, product range | As already mentioned, brick comes in a variety of shapes and sizes, providing a wide range of architectural possibilities. The structure can be made in various styles. The same cannot be said about the foam block. |
Comparison of brick, foam concrete and other building materials
Cutting foam block
Architectural possibilities of brick
Brick building with decorative masonry on the facade
Exterior view of a foam block house requiring finishing
Foam block house with finishing
Additionally, it is worth noting that the load on the base of the building when laying bricks will be much higher, since its weight is not small. Now, let's calculate the estimated difference in price.
So: brick or foam block - which is cheaper:
- First, let's calculate how much material we will need to build a building measuring 14*16 meters. To make the calculation easier, we will not take into account partitions.
- We calculate the perimeter of the building and the area of the walls, taking into account that they will be 3 meters high. 14*2+16*2=60 60*3=180m2 – this is the area of all the walls.
- We will use blocks of size 625*400*300. Block area – 0.625*0.4=0.25 m2. Next, 180/0.25=720 is the number of blocks we will need.
- Convert to m3. Block volume=0.625*0.4*0.3=0.075 m3.
- 1/0,075=13,3
- 720/13.3=54.13. Let's round up, that is, 55 m3.
- The cost of a cube of blocks is on average 3,500 rubles. 55*3500=192500.
Let's assume that we need the same amount of bricks. A cube of products costs about 4,600 rubles. We will use ordinary bricks.
55*4600=253,000. That is, when purchasing the same amount of material, we will overpay 60,500 rubles for bricks. Therefore, when considering a comparison: foam blocks or bricks, which is better, it is in this aspect that the former will be the motivator.
- Since we are considering a comparison of foam block with ceramic products, let's take a look at another alternative to foam block, which is warm or porous brick.
- In this comparison, it is impossible to say unequivocally which material is better.
- Both one and the other have a low thermal conductivity coefficient, they have large dimensions, which increases the speed of construction.
- However, a warm ceramic block is much stronger and more durable. The latter also wins in water absorption.
- It is inferior to foam block in ease of processing and price.
Ceramic block
Use of both materials in construction
A fairly popular option for using both materials is: constructing walls from foam concrete and lining them with ceramic bricks.
There may be several options:
- The brick can be laid close to the aerated concrete wall. With this option, some important technical conditions should be taken into account. The interior decoration of the walls must be done correctly technically, and in this regard be combined with the exterior.
The inside of the room can be finished using tiles, cement-based plaster and other materials that can ensure tightness. If this condition is not met, then the developer can expect quite unpleasant consequences, which boil down to the following: the moisture that has accumulated inside the building will look for a way out.
And, since it is not there, it, in the form of condensation, will accumulate between the layer of brick and foam concrete. As a result, the destruction of foam concrete and a decrease in its performance qualities will begin.
- Another option is to lay ceramic bricks with a gap in relation to the foam concrete wall in the absence of ventilation. This option is not very popular and is more suitable for unheated rooms. Condensation, due to the lack of ventilation, will flow down and accumulate in the layer of materials.
A positive point is the increase in thermal insulation properties.
- The most optimal method of combining materials is brick cladding with a gap and a ventilation device. The distance should be about 3-5 cm, and if you plan to attach insulation, then its thickness is also taken into account.
Brick lining of foam block, diagram
Close brick cladding
Foam concrete and brick, combining materials during construction
The video in this article will tell you in more detail how best to combine these materials.