GOST 26633 2012 heavy and fine-grained concrete. Application area
- Making curb stones.
- Pouring foundations for high-rise buildings.
- Pillow for road surfaces.
- Manufacturing of reinforced concrete products.
- Hydraulic structures.
The main feature of heavy concrete GOST 26633 2012 is its high density, which is achieved by mixing a large amount of high-quality cement with fine and coarse filler in an optimal ratio.
Heavy concrete GOST 74732010 technical characteristics
According to GOST requirements, this type of concrete must meet the following technical indicators:
- Medium density.
- Workability.
- Temperature.
- Delamination.
- Porosity.
- Volume of entrained air.
- Stability of properties over time.
Areas of functional application of the material
- Production of load-bearing walls of structures.
- Manufacturing of reinforced concrete products.
- Construction of monolithic structures.
GOST 26633 91 heavy and fine-grained concrete
This type of concrete is suitable for individual construction. Durable, but relatively thin material due to the inclusion of small filler fractions. It does not contain large crushed stone and gravel. Suitable mixture for finishing work.
Specifications
- Water resistance - W6-W12.
- Frost resistance - F500.
- Shrinkage – 0.15 mm per 1 m.
- Tensile strength – Bt10-Bt40.
It is these requirements that heavy concrete GOST 26633 91 must meet. Carefully study the parameters when choosing materials for construction.
produces strictly in accordance with GOST and independently sells concrete mixtures since 2002. We work with large enterprises and private buyers. Thanks to our own production and direct cooperation with the client, we are able to offer products at a low price. This does not in any way affect the highest quality of our mixtures.
» Guests
| Document Number | Name | Download link |
| GOST 4.211-80 | System of product quality indicators. Construction. Non-metallic building materials and porous concrete fillers. Nomenclature of indicators. | Download |
| GOST 4.212-80 | System of product quality indicators. Construction. Concrete. Nomenclature of indicators. | Download |
| GOST 5578-94 | Crushed stone and sand from ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy slags for concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 5742-76 | Heat-insulating products made from cellular concrete. | Download |
| GOST 6133-99 | Concrete wall stones. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 6665-91 | Concrete and reinforced concrete side stones. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 6927-74 | Concrete facade slabs. Technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST 7473—2010 | Concrete mixtures. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 8020-90 | Concrete and reinforced concrete structures for sewer, water and gas pipeline wells. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 8717.0-84 | Reinforced concrete and concrete steps. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 8717.1-84 | Reinforced concrete and concrete steps. Design and dimensions. | Download |
| GOST 8736—2014 | Sand for construction work. Specifications | Download |
| GOST 8829-94 | Factory-made reinforced concrete and concrete building products. Load test methods. Rules for assessing strength, stiffness and crack resistance. | Download |
| GOST 10060-2012 | Concrete. Methods for determining frost resistance. | Download |
| GOST 10180-2012 | Concrete. Methods for determining strength using control samples. | Download |
| GOST 10181-2014 | Concrete mixtures. Test methods. | Download |
| GOST 11024-2012 | External concrete and reinforced concrete wall panels for residential and public buildings. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 11118-2009 | Autoclaved cellular concrete panels for external walls of buildings. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 12504-80 | Internal concrete and reinforced concrete wall panels for residential and public buildings. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 12730.0-78 | Concrete. General requirements for methods for determining density, humidity, water absorption, porosity and water resistance. | Download |
| GOST 12730.1-78 | Concrete. Methods for determining density. | Download |
| GOST 12730.2-78 | Concrete. Method for determining humidity. | Download |
| GOST 12730.3-78 | Concrete. Method for determining water absorption. | Download |
| GOST 12730.4-78 | Concrete. Methods for determining porosity indicators. | Download |
| GOST 12730.5-84 | Concrete. Methods for determining water resistance. | Download |
| GOST 12852.0-77 | Cellular concrete. General requirements for test methods. | Download |
| GOST 12852.5-77 | Cellular concrete. Method for determining the coefficient of vapor permeability. | Download |
| GOST 12852.6-77 | Cellular concrete. Method for determining sorption humidity. | Download |
| GOST 13015-2012 | Concrete and reinforced concrete products for construction. General technical requirements. Rules for acceptance, labeling, transportation and storage. | Download |
| GOST 13087-81 | Concrete. Methods for determining abrasion. | Download |
| GOST 13531-74 | Concrete pavers for precast concrete plants. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 13578-68 | Panels made of lightweight concrete on porous aggregates for external walls of industrial buildings. Technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST 13579-78 | Concrete blocks for basement walls. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 14794-79 | Concrete current-limiting reactors. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 17608-91 | Concrete paving slabs. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 17623-87 | Concrete. Radioisotope method for determining average density. | Download |
| GOST 17624-2012 | Concrete. Ultrasonic method for determining strength. | Download |
| GOST 17625-83 | Reinforced concrete structures and products. Radiation method for determining the thickness of the protective layer of concrete, the size and location of reinforcement. | Download |
| GOST 18105-2010 | Concrete. Rules for monitoring and assessing strength. | Download |
| GOST 19010-82 | Concrete and reinforced concrete wall blocks for buildings. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 19570-74 | Panels made of autoclaved cellular concrete for internal load-bearing walls, partitions and ceilings of residential and public buildings. Technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST 20054-82 | Non-pressure concrete pipes. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 20910-90 | Heat-resistant concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 21520-89 | Small cellular concrete wall blocks. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 21807-76 | Portable bunkers (tubs) with a capacity of up to 2 cubic meters. for concrete mixture. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 22000-86 | Concrete and reinforced concrete pipes. Types and basic parameters. | Download |
| GOST 22685-89 | Molds for making control samples of concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 22690-88 | Concrete. Determination of strength by mechanical methods of non-destructive testing. | Download |
| GOST 22783-77 | Concrete. Method for accelerated determination of compressive strength. | Download |
| GOST 22904-93 | Reinforced concrete structures. Magnetic method for determining the thickness of the protective layer of concrete and the location of reinforcement. | Download |
| GOST 23009-78 | Prefabricated concrete and reinforced concrete structures and products. Symbols (brands). | Download |
| GOST 23037-99 | Unmolded refractories. Fillers for concrete products, masses, mixtures, coatings and mortars. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 23732-2011 | Water for concrete and mortars. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 24211-2008 | Additives for concrete and mortars. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 24316-80 | Concrete. Method for determining heat generation during hardening. | Download |
| GOST 24452-80 | Concrete. Methods for determining prismatic strength, elastic modulus and Poisson's ratio. | Download |
| GOST 24544-81 | Concrete. Methods for determining shrinkage and creep deformations. | Download |
| GOST 24545-81 | Concrete. Endurance test methods. | Download |
| GOST 24830-81 | Fireproof concrete products. Ultrasonic quality control method. | Download |
| GOST 25137-82 | Non-metallic construction materials, crushed stone and dense sand from industrial waste, porous aggregates for concrete. Classification. | Download |
| GOST 25192-2012 | Concrete. Classification and general technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST 25214-82 | Silicate concrete is dense. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 25246-82 | Concrete is chemically resistant. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 25485-89 | Cellular concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 25592-91 | Ash and slag mixtures from thermal power plants for concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 25818-91 | Fly ash from thermal power plants for concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 25820-2014 | Concrete is lightweight. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 25881-83 | Concrete is chemically resistant. Test methods. | Download |
| GOST 25932-83 | Radioisotope portable moisture meters-density meters for concrete and soil. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 26134-84 | Concrete. Ultrasonic method for determining frost resistance. | Download |
| GOST 26633-2012 | Concrete is heavy and fine-grained. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 26644-85 | Crushed stone and sand from thermal power plant slag for concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 27005-2014 | Concrete is light and cellular. Medium density control rules. | Download |
| GOST 27006-86 | Concrete. Rules for selecting the composition. | Download |
| GOST 27338-93 | Mechanized concrete mixing plants. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 27677-88 | Corrosion protection in construction. Concrete. General requirements for testing. | Download |
| GOST 28570-90 | Concrete. Methods for determining strength using samples taken from structures. | Download |
| GOST 28574-2014 | Corrosion protection in construction. Concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Test methods for adhesion of protective coatings. | Download |
| GOST 28575-2014 | Corrosion protection in construction. Concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Testing the vapor permeability of protective coatings. | Download |
| GOST 29167-91 | Concrete. Methods for determining crack resistance characteristics (fracture toughness) under static loading. | Download |
| GOST 30459-2008 | Additives for concrete and mortars. Definition and evaluation of effectiveness. | Download |
| GOST 31359-2007 | Autoclaved cellular concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 31360-2007 | Non-reinforced wall products made of autoclaved cellular concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 31383-2008 | Protection of concrete and reinforced concrete structures from corrosion. Test methods. | Download |
| GOST 31384-2008 | Protection of concrete and reinforced concrete structures from corrosion. General technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST 31914-2012 | High-strength, heavy and fine-grained concrete for monolithic structures. Rules for quality control and assessment. | Download |
| GOST 31938-2012 | Composite polymer reinforcement for reinforcing concrete structures. General technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 32016-2012 | Materials and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures. General requirements. | Download |
| GOST 32017-2012 | Materials and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures. Requirements for concrete protection systems during repairs. | Download |
| GOST 32486-2013 | Composite polymer reinforcement for reinforcing concrete structures. Methods for determining durability characteristics. | Download |
| GOST 32487-2013 | Composite polymer reinforcement for reinforcing concrete structures. Methods for determining characteristics of resistance to aggressive environments. | Download |
| GOST 32492-2013 | Composite polymer reinforcement for reinforcing concrete structures. Methods for determining physical and mechanical characteristics. | Download |
| GOST 32495-2013 | Crushed stone, sand and sand-crushed stone mixtures from crushed concrete and reinforced concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 32496-2013 | Porous aggregates for lightweight concrete. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 32803-2014 | Concrete is prestressing. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST 32943-2014 | Materials and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures. Requirements for adhesive joints of structural reinforcement elements. | Download |
| GOST EN 12001-2012 | Machines for transporting, applying and distributing concrete and mortar mixtures. Safety requirements. | Download |
| GOST IEC 60745-2-12-2013 | Manual electric machines. Safety and test methods. Part 2-12. Additional requirements for vibrators for compacting concrete mixtures. | Download |
| GOST ISO 18652-2014 | Construction machinery and equipment. External vibrators for concrete. | Download |
| GOST ISO 21573-1-2013 | Construction machinery and equipment. Concrete pumps. Part 1. Terminology and technical conditions for delivery. | Download |
| GOST ISO 21573-2-2013 | Construction machinery and equipment. Concrete pumps. Part 2. Test methods. | Download |
| GOST ISO 21592-2013 | Construction machinery and equipment. Machines for shotcrete concrete mix. Terminology and technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST ISO 4635—2013 | Molded rubber seals used between concrete slabs of highways. Technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST R 51824-2001 | Non-returnable protective containers for radioactive waste made of concrete-based structural materials. General technical requirements. | Download |
| GOST R 52541-2006 | Fireproof concrete. Preparation of samples for testing. | Download |
| GOST R 52804-2007 | Protection of concrete and reinforced concrete structures from corrosion. Test methods. | Download |
| GOST R 54854-2011 | Lightweight concretes based on organic aggregates of plant origin. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST R 55260.1.3-2012 | Hydroelectric power stations. Part 1-3. Hydroelectric power station structures. Concrete and reinforced concrete structures. Safety requirements. | Download |
| GOST R 56178-2014 | Organo-mineral modifiers type MB for concrete, mortars and dry mixes. Technical conditions. | Download |
| GOST R IEC 60745-2-12-2011 | Manual electric machines. Safety and test methods. Part 2-12. Particular requirements for vibrators for concrete compaction. | Download |
tehno-beton.ru
Advantages
- Own certified laboratory. Each batch of manufactured products undergoes quality control.
- Automated weighing complex. Loading is carried out under strict control, accuracy is maintained down to the kilogram.
- Qualified company managers. You can count on receiving complete information about GOST for heavy concrete and technical production conditions.
- A fleet of special equipment for delivery. The machines are equipped with a GPS control system. You receive the goods quickly without delays or downtime.
- Ease of ordering. You can buy concrete by calling, emailing or visiting the factory in person.
Concrete according to GOST
Concrete is the most common building material. There are many types of concrete, which are used depending on specific conditions and requirements. When preparing a concrete mixture, there are rules for selecting the composition of concrete, which are regulated by the requirements of GOST 27006-86. The selection of workers is carried out in several stages.
1. Selecting a material for concrete with certain characteristics.
2. Calculation of the starting composition and proportion of concrete.
3. Additional calculation of the composition to obtain concrete with certain characteristics.
4. Preparation of concrete, sampling, testing of samples.
5. Determination of the nominal composition of the concrete mixture.
Concrete components according to GOST
Any concrete is a mixture of water, cement and filler. The main requirements for the components are that they should not contain foreign inclusions or impurities. Only fresh water should be used.
To prepare the mixture, there is a special concrete table, from which you can familiarize yourself with the composition of certain grades of concrete.
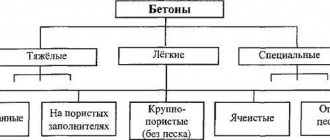
Heavy concrete GOST 26633 2012
Heavy concrete GOST 26633 2012 is used for the construction of special-purpose facilities: nuclear power plants, bunkers, bridges, hydraulic structures. This is a type of especially strong, dense concrete that can withstand heavy loads and does not collapse under the influence of the environment.
GOST 26633 2012 - heavy and fine-grained concrete
GOST 26633 2012 heavy and fine-grained concrete, concrete mixtures BSG heavy concrete, technical conditions
Strength of concrete GOST
The standards have been developed over decades. Currently, they are being supplemented and edited, albeit slightly. Strength refers to the load that a mixture can withstand without breaking. There is a certain GOST for the strength of concrete, where the strength is determined in laboratories.
Load is measured in MPa. There are two ways to indicate strength: grade and compressive class of concrete. The stamp encodes the pressure in kilograms per square centimeter of plane. That is, if the M-200 brand is indicated, then this means the following.
The structure does not collapse if it is acted upon with a force of 200 kg/sq.cm. Other brands - accordingly. By destruction we mean a violation of integrity. This does not always mean an array bursting in two. Any crack, missing parts, chips and other visual damage indicate destruction .
The concrete class encrypts the load already in Megapascals. This is a requirement of international standards. B25 concrete means that the maximum non-destructive load is 25 MPa.