- Advocacy
- Centrifugation
- Filtration
- Action by magnet
- Evaporation. Crystallization
- Distillation (distillation)
To obtain pure substances, various methods of separating mixtures are used.
| Methods for separating mixtures | |
| heterogeneous (heterogeneous) | homogeneous (homogeneous) |
| — Settlement — Filtration — Magnetic action — Centrifugation | — Evaporation. Crystallization. — Distillation (distillation) |
Processes for separating mixtures are based on the different physical properties of the components that form the mixture.
Preparing a solution for pouring the foundation - the ratio of sand and cement
The choice of concrete proportions used for the foundation is influenced by many factors: soil parameters, expected loads, type of foundation.
The basis of cement mortar is cement, sand, crushed stone or gravel and water; its properties directly depend on the quality and uniformity of mixing of the components. Changing the regulated ratios is unacceptable; the slightest errors lead to a decrease in the strength of the foundation and, as a consequence, the risk of destruction of the load-bearing structures of the building. Choosing a concrete grade
The main criteria include the geological conditions of the site (relief, level and partial pressure of groundwater on foundation elements, climate, freezing depth), type of foundation, presence or absence of a basement, height of the building and other weight loads. The limiting factor is the work budget; using high-quality types of concrete for the construction of light buildings on summer cottages is not economically feasible. The recommended minimum is:
- M400 – for houses over 3 floors.
- M200-M250 – for frame and panel buildings.
- M250-M300 – for buildings made of wooden beams.
- M300 - for low-rise buildings made of expanded clay, gas silicate or cellular blocks.
- M350-M300 - when building with brick or pouring load-bearing walls made of monolithic concrete.
The specified gradations are relevant when constructing one- or two-story houses; when adding another floor, it is advisable to choose a higher grade. The same applies to ready-made purchased solutions, especially if purchased from an unverified manufacturer. In general, the minimum permissible strength when concreting the foundations of residential buildings on slightly heaving soils is M200; when building on less stable soils, it increases.
Concrete composition
It is easy to change the characteristics of concrete by varying the ratio of the mixture components:
- cement,
- sand,
- crushed stone,
- water.
If necessary, add plasticizers and powders. They are used for the construction of small structures in private construction using M400 cement. The composition of the classic mixture is: one part cement, two sand and four crushed stone. These proportions approximately correspond to concrete grade M250. This indicator is sufficient for structures that have to withstand significant loads.
The ratio and consumption of ingredients when using different grades of concrete are shown in the table.
Proportions of concrete mixtures
Basic proportions
When preparing solutions, the working measure is the mass or volume fraction of the binder; the most common and convenient ratios include 1:3:5 (cement, sand, gravel, respectively). The regulated proportions, depending on the required strength of concrete, are:
| Final brand of solution | Mass fraction, kg | ||
| Cement M400 | Sand | Crushed stone or gravel | |
| M100 | 1 | 4,6 | 7 |
| M150 | 3,5 | 5,7 | |
| M200 | 2,8 | 4,8 | |
| M250 | 2,1 | 3,9 | |
| M300 | 1,9 | 3,7 | |
| M350 | 1,2 | 2,7 | |
| M400 | 1,1 | 2,5 | |
The strength of concrete is primarily affected by the ratio of sand and cement, but in addition to strict control over the proportion of dry components, the amount of water introduced is monitored. When using Portland cement, the W/C proportions are:
| Binder grade | Concrete strength grade | ||||
| 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 400 | |
| M300 | 0,65 | 0,55 | 0,50 | 0,40 | |
| M400 | 0,75 | 0,63 | 0,56 | 0,50 | 0,40 |
| M500 | 0,85 | 0,71 | 0,64 | 0,60 | 0,46 |
| M600 | 0,95 | 0,75 | 0,68 | 0,63 | 0,50 |
When building a foundation on dry soils, it is allowed to add lime or clay to the cement mortar; these components increase its plasticity. The recommended proportions when using Portland cement M400 are:
| The resulting brand of solution | Share of cement | Lime percentage | Sand fraction |
| M100 | 1 | 0,4 | 4,5 |
| M150 | 0,2 | 3 | |
| M200 | 0,1 | 2,5 |
In private construction, it is inconvenient to separately determine the mass of all poured ingredients; a bucket is usually used as a measuring tool. In this case, all fillers are pre-weighed in a dry state. The W/C ratio largely depends on the moisture content of the sand; experienced developers add no more than 80% of the recommended proportion of water during mixing and then, if necessary (the consistency is not sufficiently plastic), pour it in portions. Fiber, PAD and other plasticizers are added to concrete at the very end along with the liquid; their share usually does not exceed 75 g per 1 m3.
Component Requirements
To prepare cement mortar for pouring the foundation, the following is used:
- Fresh Portland cement, ideally the release date does not exceed 2 months before the start of concreting. The recommended brand is M400 or M500.
- River sand with particle sizes ranging from 1.2-3.5 mm with admixtures of silt or clay not exceeding 5%. It is recommended to check its cleanliness (fill with water and monitor the change in color and sediment), sift, and, if necessary, rinse and dry.
- Pure crushed stone or gravel with fraction sizes from 1 to 8 cm, with flakiness within 20%. When preparing concrete for the foundation, hard rock screenings are used; limestone is not suitable due to its low strength.
- Water: tap water, free of impurities and foreign particles.
- Additives: antifreeze, plasticizing, reinforcing fiber. The introduction of such impurities is carried out in strict compliance with proportions.
It is important to understand the principle: coarse filler is introduced into the solution not only to replace the more expensive binder, it is precisely this that imparts the necessary rigidity. The minimum compressive strength of gravel or granite screenings is 800 kgf/cm2; in its absence, concrete simply will not withstand the weight load. A mixture for a foundation without crushed stone is prepared only when constructing it from individual blocks or slabs, and sometimes for quickly pouring pile supports.
The recommended proportions of cement and sand for masonry mortars are 1:3 or 1:2. The first ratio is considered universal, the second is chosen when constructing foundations on unstable soils. In practice, this means that for one bucket of cement with a grade not lower than M400 (M500 for increased loads), take 2 or 3 sifted quartz sand and no more than 0.8 parts of water. A properly prepared mixture has a consistency similar to toothpaste; to increase workability, 75-100 g of plasticizers (liquid soap or other PADs) are added per 1 m3.
How to make cement mortar for the foundation?
The process begins with the preparation of components and a concrete mixer; the presence of the latter is mandatory when mixing concrete for underground structures. The amount of building materials is calculated in advance according to the volume of the foundation and is purchased with a small margin. It is extremely important to fill the solution on the same day; when preparing the solution yourself, all components are washed and dried in advance. Next, they are poured into buckets into a concrete mixer in the following sequence: part of the water → sand and cement → dry additives and fiber (if necessary) → coarse filler → the remaining liquid in small portions. After adding the new ingredient, the drum is turned on for 2-3 minutes, and no more than 15 minutes later the finished solution is unloaded.
There is a time-tested method for selecting the correct proportions, chosen in the absence of data on the size of crushed stone. In this case, the bucket is filled with coarse filler, shaken several times and completely covered with water. The resulting volume of water corresponds to the required proportion of sand in the solution. After that, sand is poured into the bucket and filled with water again to determine the proportion of cement. But some consider this approach to be complex and outdated; a more correct method is the standard method of recalculating the mass fraction into the volume fraction and pouring the components into a concrete mixer.
Selection of crushed stone
If you use limestone, you can get concrete up to grade M-350; it is characterized by low resistance to frost. When using crushed stone or gravel, you can get concrete up to grade M-450; they are characterized by high strength and frost resistance, so they are usually used in private construction. To produce high quality concrete mix (from M-450), granite is used. As a rule, such concrete is used in road construction, as it has high resistance to compression. Sometimes you can see cracks or potholes on city roads - this indicates that the builders made a low-quality solution. This fact can be affected by both the incorrect amount of water and the additional component.
Cement proportions for foundation
Almost all low-rise and most high-rise buildings in Russia stand on strip or block foundations made of heavy concrete. This is not surprising, given that heavy concrete, due to its plasticity, high load-bearing capacity and affordable cost, is the preferred material for constructing foundations for low-rise and high-rise buildings.
The building structure - the foundation, is its basis, taking on the weight of: walls, roofing, facade cladding, interior decoration, floor slabs and other structures and elements of a private house, cottage, villa or small country house. Therefore, saving on materials for its construction is unacceptable!
The proportions of cement for the foundation, as well as the proportions of other components of concrete for pouring it, must correspond to the accepted brand of concrete. And the accepted grade of concrete must correspond to the load on the structure being built.
Brands of cement mortars for the foundations of low-rise buildings
The brand of mortar for pouring the foundation is indicated in the specification or in the margins of the working drawings of the house or outbuilding project. Using this information and the capabilities of the Internet, you can quickly and completely free determine the proportion of cement and sand for the foundation in kilograms or liters for a particular brand of mortar. All that remains is to calculate the required volume of cement, sand and other components depending on the volume of pouring, purchase them, mix and pour the foundation.
Unfortunately, very often developers build country houses and private houses without a design. Accordingly, the question immediately arises: What are the proportions of cement for the foundation so that the structure can stand for a long time and withstand harmful factors? In this case, you should adhere to the following recommendations, based on the practical experience of many generations of private builders:
- Heavy concrete M150. Suitable for constructing a foundation for small-sized one-story buildings with walls made of cinder block, shell rock or aerated concrete. The specified grade of concrete can be used for pouring the foundation for garages and outbuildings.
- Heavy concrete M200. A universal brand of concrete suitable for the construction of foundations for 90% of low-rise buildings (one- or two-story buildings with light floors).
- Heavy concrete M300. This is a very durable concrete material with high load-bearing capacity. Used for the construction of foundations for large private houses up to 5 floors high.
Having decided on the brand of concrete, you can move on to considering a practical question: What proportions of cement and sand for the foundation should be used to prepare the selected brand of concrete?
Ethyl alcohol ethanol
This is what is used in winemaking, and according to the method of production and degree of purification, it is divided into several varieties. Their chemical formula and properties are the same; they differ in the method of preparation and the percentage of impurities. We will not talk about alcohol, which is synthesized using the hydration of ethylene - due to the toxic additives it contains, it is unsuitable for making homemade vodka.
This is true for any industrial alcohol, even prepared from mash. The mash is made from pulp production waste and contains many harmful substances. In addition, fusel oils, which are contained to one degree or another in fermentation alcohol, are not characteristic of strong drinks familiar to consumers, therefore, even with a high degree of purification, it cannot be used to make vodka.
Important! Do not use denatured alcohol to make homemade vodka, and feel free to ignore the stories of “experienced” people about cleaning it with the help of a camshaft flower and a fish udder!
Not suitable for homemade vodka and distilled spirits. Not because the quality is low. More often than not, it's just the opposite. It is used to prepare skate, moonshine, grappa, chacha, vodka, rum and other drinks based on distilled alcohol. For vodka and bitters - only rectified. According to GOST, there are the following grades of drinking rectified 96% alcohol in terms of purification level and impurity content:
- "Alpha" is the purest alcohol;
- "Lux";
- "Extra";
- "Basis";
- Highest purification;
There is also a first grade - it is not used for alcoholic beverages.
You can also use medical alcohol to make homemade vodka, but its production does not follow such strict standards - after all, it is intended more for external use, and is used internally only in pharmaceutical doses, so you can get both crystal clear “Spiritus vini” and Not good.
There are also special home distillation columns that allow you to obtain rectified alcohol at home. Its standard strength is 96%, to be absolutely precise - 95.57%, at this concentration it forms an azeotropic (inseparable at normal pressure) mixture with water. Absolute alcohol (100%) is obtained by vacuum rectification.
Proportions of cement and sand for pouring the foundation
To prepare concrete, as a rule, two grades of Portland cement are used: TsEM I 32.5N PTs and TsEM I 42.5N PTs. The characteristics of these brands of “binder” correspond to the old brands of Portland cement M400 and M500.
In this case, the solution for the foundation can be prepared on the basis of other types of cement (pozzolanic, slag Portland cement, etc.), however, at this point in time, “binders” CEM I 32.5N PC and CEM I 42.5N PC can be purchased in wide retail sales.
We will use it for practical calculations. For the convenience of users, taking into account the requirements of the current regulatory document GOST 26633-2012 “Heavy and fine-grained concrete”, we present two tables:
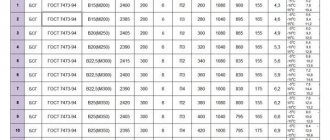
Proportions for a foundation made of M400 cement
Concrete grade
190
| Proportions of components: C:P:SH:V, kg | Consumption of components per 1 m3 of solution, kg | |||
| Cement M400 | Sand | Crushed stone | Water | |
| M150 | 1:3,5:5,2:0,9 | 215 | 735 | 1140 |
| M200 | 1:3:4,5:0,7 | 255 | 715 | 1125 |
| M300 | 1:2:3,3:0,6 | 338 | 670 | 1105 |
Proportions for a foundation made of cement M500
Concrete grade
190
| Proportions of components: C:P:SH:V, kg | Consumption of components per 1 m3 of solution, kg | |||
| Cement M500 | Sand | Crushed stone | Water | |
| M150 | 1:4:6:1 | 190 | 755 | 1140 |
| M200 | 1:3,3:5:0,8 | 225 | 738 | 1125 |
| M300 | 1:2,5:3,5:0,7 | 290 | 705 | 1105 |
Analyzing the data given in the tables, we can draw the following conclusion: with an increase in the “grade” of concrete, the consumption of the most expensive component (cement) increases. Therefore, the choice of concrete grade for pouring the foundation should be approached responsibly - calculate the mass of structures and the bearing capacity of the foundation.
Otherwise, there may be a significant increase in the cost of construction or the risk of destruction of the building. Moreover, each individual calculation will be different for each specific option. The magnitude of the bearing capacity of a particular foundation depends on the area of its outer surface and the grade of concrete.
When considering the question: how to make cement mortar and take into account the proportions for the foundation, it is necessary to dwell on the cost of this work. The fact is that the foundation can be poured in two ways.
The first way is to purchase the required amount of ready-made concrete at the factory. The second way is to prepare concrete according to the above proportions yourself. For the information of private developers, we present prices for 1 m3 of ready-made concrete M200 and concrete prepared by hand using M400 cement.
Calculation example
The average price of 1 m3 of ready-made concrete M200 purchased at a concrete plant with delivery on the day of order will be on average: 3,600 rubles including value added tax.
The cost of M200 concrete prepared by hand consists of the cost of the main components:
- Cement: 255 kgx5.4 (price of 1 kg of cement packaged in a bag, rub.) = 1377 rub.
- Sand: 715 kg x 0.2 (price of 1 kg of sand, rub.) = 143 rub.
- Crushed granite: 1125x1.65 (price of 1 kg of crushed stone, rub.) = 1865 rub.
- Total: 1377+143+1865=3385 rub. for 1 m3 of concrete.
The cost calculation does not include: the cost of water, the cost of renting or purchasing a concrete mixer, the cost of tools and the cost of “own” labor costs.
As follows from the calculation, if it is possible to purchase ready-made concrete at a factory, it is best to use the services of the factory and receive a guarantee of the grade of the material and its continuous delivery until the end of the foundation pouring process.
How to dilute cement with sand for a foundation
Mixing sand with cement
Concrete is the most popular material used in modern construction. It consists of several components: binder, water and filler (sand, crushed stone). The binding component is cement. The grade of concrete depends on its quality.
First, let's get acquainted with several general rules on how to dilute cement for a foundation and how to use materials correctly:
- to obtain a high grade of concrete, it is necessary not only to choose a high grade of cement, but also to increase its consumption and consumption
- You can’t do without tools: containers, shovels, concrete mixers (if large volumes)
- You need to add water to the finished dry batch gradually. As a rule, in practice, a smaller volume of liquid is poured than expected
- if the mixing is carried out in hot and dry weather, special additives are introduced into the solutions - clays, lime. Stone wall materials, blocks and panels in contact with the mortar are moistened with water
- the water must be clean. If it is not taken from a drinking water source, testing for impurities is required
- purchased materials must have a passport with the results of laboratory tests conducted by the enterprise
- You cannot add additional water or other components to an already set solution.
- at a temperature of +18 - +22 ° C, concrete will harden and acquire all its strength properties within 28 days
- The formwork can be removed only when the structure reaches 70% of its strength characteristics. Minimum period – after 1 week (in summer at an ambient temperature of 20 °C)
Evaporation. Crystallization
Evaporation is a method of separating liquid mixtures by evaporating one of the components. The rate of evaporation can be controlled by temperature, pressure and evaporation surface area.
Example.
To separate table salt dissolved in water from the solution, the latter is evaporated:
The water evaporates, and table salt remains in the porcelain cup. Sometimes evaporation is used, i.e. partial evaporation of water. As a result, a more concentrated solution is formed, upon cooling of which the dissolved substance is released in the form of crystals. This process is called crystallization .
Choice of cement and proportions
The proportional ratios for concrete mortar depend on the type of future construction. How strong should it be, how wear-resistant and fire-resistant?
Having decided on the type of building and selecting the required brand of concrete for it, you need to choose a brand of cement.
| Required grade of concrete (according to the project) | Cement grades, under natural hardening conditions |
| recommended/acceptable | |
| M100 | 300 |
| M150 | 300/400 |
| M200 | 400/300, 500 |
| M250 | 400/300, 500 |
| M300 | 400/ 500 |
| M350 | 400/ 500 |
| M400 | 500/ 550, 600 |
| M450 | 550/ 500, 600 |
| M500 | 600/ 550, 600 |
| M600 | 600/ 550 |
The table shows a pattern that to obtain concrete M150, M200, M250, you need a binder with an indicator twice as high as the data (for 150 - 300, for 200 - 400).
The most common brands of binders for construction are M400 and M500.
If mixing is carried out manually, the main preparation proportions for each brand of concrete are:
when choosing the M400 cement brand -
- for M100 (or concrete class B7.5) - for 1 kg of dry cement there are 4.5 kg of sand and approximately 7 kg of crushed stone
- for M200 (B15) – per kilogram of binder – 2.7 kg of sand and 4.7 kg of crushed stone
- for class B22.5 (M300) - to 1 kg - 1.9 (parts of sand) and 3.7 (crushed stones)
- for M400 (B30) - for 1 kg of binder there is a little more than 1 kg of sand and 2.5 kg of filler
when choosing brand M 500 -
Selecting a cement brand
With this brand of cement M500, the bag weighs 235 kg. You need to obtain the concrete grade M300. This means 235 kg - 1. Sand required 1:2.2. We multiply 235 by 2.2, we get 517 kg. Crushed stone is needed 1:3.7 - with a similar calculation we get 869.5 kg. Water consumption depends on the moisture state of the sand, but the approximate proportion is 1: 0.5 (117.5 l).
If there are no tables: The approximate ratio of all dry components can be taken - 1: 3: 4. This means that 1 is cement, 3 is sand, 4 is crushed stone. But still, when constructing load-bearing elements and foundations, it is worth using calculated coefficients.
In the preparation of more durable concrete grades, cement consumption is increased. Attention is also paid to sand criteria. It is recommended to use river sand as a filler: it contains less clay and other impurities. But such sands have worse adhesion to the solution, since the surface of river sand grains is smooth. Gully sand, on the contrary, adheres well to the components, but requires preliminary washing.
Components
To obtain high-quality concrete, it is necessary to select the correct proportions of components and carefully comply with all technical requirements.
The concrete strip foundation completely hardens in a month
- Cement is the main binder. Portland cement with 78–80% calcium silicates in its composition is considered ideal for concrete. Their increased content ensures better adhesion of the solution. The frost resistance indicators of the same mixtures are also higher, which is especially important for construction in the climatic conditions of our country. Cement grade M500 is suitable for construction. It must be stored only in rooms specially prepared for this purpose.
- Sand is used as a fine aggregate in concrete mixtures. In rare cases, when crushed stone or gravel can be compacted very tightly, you can do without it. It is recommended to add sand of a fraction of 2–5 mm to the solution, without foreign impurities, lumps and debris. River sand, which does not contain dirt and clay, meets these requirements. You can also use an artificial one, after checking the radiation background.
- Gravel and crushed stone provide the strength of concrete. For example, pebbles are not able to form adhesion to the solution; it quickly collapses. The best stones are those obtained by artificial crushing, that is, crushed stone (with an uneven surface). Most often, fractions from 8 mm to 40 mm are used. There should be no impurities, dirt or even dust in it. If you prepare the solution yourself, then mix several types of crushed stone of different shapes. In industrial conditions, where machines are involved in compaction, batches with the lowest flakiness are used.
- Water is necessary to dissolve the cement. There are not such strict requirements for it: it is enough to use simple clean water, without undissolved particles, alkali and other foreign elements.
In Russia, the most popular plasticizer for concrete is liquid soap.
Their main purpose of adding additives to concrete mortar is to improve its characteristics. Most often used:
- • slaked lime, which facilitates the process of surface leveling;
- • plasticizers that increase fluidity;
- • reinforcing substances, in particular polypropylene fibers, which make it stronger;
- • other auxiliary components.
The process of preparing the solution
- Calculation of proportions in kilograms or liters
- Dry ingredients are mixed. It is customary to pour them in layers:
Procedure for preparing the solution
- after ½ crushed stone (sifted)
- then the whole part of the cement
- adding crushed stone and sand.
If you have a concrete mixer, this dry mixture is mixed for 10 minutes. Manually takes longer.
- Water is gradually poured in in small parts. The solution should be viscous, but not too viscous. Usually a ratio of 1: 0.5 (amount of binder/water) is used. All this is constantly thoroughly mixed. The finished solution should look like thick sour cream.
If you can draw something on the surface of the mixture, and the drawing will not blur, but will only soften slightly, the solution is ready.
Important! The batch should be made in such a volume that it can be used within an hour. Concrete hardens over time, and when it is moved to a new place, it loses some of its future strength.
Compaction of the concrete solution in the formwork should be carried out every 10-15 cm of the layer. As a rule, the final layer is compacted until the cement “military” - tiny air bubbles on the surface - comes out. This will prevent cracks from forming.
Advocacy
Settling is the separation of a heterogeneous liquid mixture into components by stratifying it over time under the influence of gravity.
By settling, you can separate a mixture of water-insoluble substances that have different densities.
Example.
A mixture of iron and wood filings can be separated by pouring it into a vessel with water (1), shaking it and letting it sit. Iron filings will sink to the bottom of the vessel, and wood filings will float on the surface of the water (2), and they, along with the water, can be poured into another vessel (3):
The separation of mixtures of liquids that are poorly soluble in each other is based on the same principle.
Example.
Mixtures of gasoline with water, oil with water, and vegetable oil with water quickly separate, so they can be separated using a separating funnel:
Sedimentation can also be used to separate substances that precipitate in water at different rates.
Example.
A mixture of clay and sand can be separated by pouring it into a vessel with water (1), shaking it and letting it settle. Sand settles to the bottom much faster than clay (2):
This method is used to separate sand from clay in ceramic production (production of pottery, red bricks, etc.).
What kind of cement is used for foundations?
For such important buildings as the foundation, a cement grade higher than M350 is used in construction. The most important thing is to pay attention to the weight, production date and shelf life of the cement for the foundation.
Worth remembering! Every six months of storage costs this material a quarter of the adhesive force in solution.
The material should be stored in a dry place; it is better to pack it on top of the factory shell with a polyvinyl chloride bag, so as not to end up with stone instead of cement at the start of construction.
How to dilute cement with sand?
In the construction industry, concrete mixtures and cement mortars are used to solve various problems. Their main component is Portland cement, which acts as a binder. The concentration of cement in concrete or cement mortar determines the strength characteristics of the foundation, masonry, as well as the quality of finishing measures. It is important to understand how to dilute cement in order to ensure the required performance properties of the finished composition. Let us dwell on the technology of performing the work, the optimal ratios of cement and other ingredients.
How to dilute cement with sand
Beginner developers who do not have practical experience in carrying out construction activities encounter problems when trying to dilute cement. The composition turns out to be too thick or, conversely, very fluid. And after hardening, it cracks and does not gain the required strength. Despite the apparent simplicity of the task, not everyone knows how to dilute M500 cement, as well as other brands of Portland cement. Let's start with the basics.
How to properly dilute cement with sand when preparing a cement-sand mortar? Builders often use the following methods for diluting Portland cement:
- The first method involves pouring water into a mixing container, followed by adding sand and cement. The ingredients of the sand-cement mixture are thoroughly mixed with the addition, if necessary, of a small amount of water;
- the second method is based on a different principle. First, the bulk components of the mixture - Portland cement and sand - are poured into the container. Then they are mixed evenly. The prepared cement-sand mixture is diluted with water to a plastic state.
Not everyone knows how to dilute cement during the preparation of cement mortar or concrete.
Regardless of the preparation technology, the ingredients are pre-sifted to remove foreign inclusions and large particles. Compliance with the ratios of the introduced ingredients and the quality of the fillers affect the performance properties of the finished composition. The main requirements of the preparation technology are maintaining proportions, uniform mixing and a plastic consistency of the solution, especially if additives were used. It is important to distribute them evenly throughout the entire volume of the solution.
It is important to be able to dilute cement when preparing concrete mortar. In addition to the standard set of ingredients, sand, cement and water, it includes crushed stone filler or gravel. The filler increases the strength characteristics of concrete and its rigidity. The binder is diluted manually or using a concrete mixer.
The technology for preparing the concrete mixture involves following the sequence of operations:
- Weighing ingredients according to recipe.
- Mixing sifted sand with Portland cement.
- Adding mid-fraction crushed stone to the mixture.
- Pour into water and stir the mixture until smooth.
When independently preparing concrete mortar or cement mixture for construction work, it is important to understand how to dilute the mortar.
Filtration
Filtration is the separation of a liquid heterogeneous mixture into components by passing the mixture through a porous surface. The porous surface can be a paper funnel, gauze folded in several layers, or any other porous material that can retain one or more components of the mixture.
Filtration can be used to separate a heterogeneous mixture consisting of water-soluble and water-insoluble substances.
Example.
To separate a mixture of table salt and sand, you can pour it into a vessel with water, shake it, and then pass this mixture through filter paper. The sand remains on the filter paper, and a clear solution of table salt passes through the filter:
If necessary, dissolved table salt can be separated from water by evaporation.
Necessary tools and materials to dilute cement
Prepare the necessary tools and materials before starting work.
To independently prepare cement mortar or concrete mixture, you will need the following equipment and tools:
- concrete mixer or container of appropriate size;
- bayonet or scoop shovel, as well as buckets;
- electric drill equipped with a mixing attachment.
The choice of equipment and tools used is determined by the volume of concrete or cement mortar produced:
- with an increased batch volume, it is advisable to use an industrial concrete mixer;
- It’s easy to prepare a small amount of solution in an old bathtub, tub, or just on the site.
To get a cement solution, prepare:
- fine sand, cleared of foreign inclusions;
- Portland cement marked according to the recipe;
- additives that determine the properties of the finished composition;
- water added to the required mixture consistency.
If a concrete composition is being prepared, then the list of materials additionally includes crushed stone, gravel or other building materials that increase the strength of concrete after hardening.
Cement along with sand must be sifted through a sieve in advance, and then mixed thoroughly
How to dilute cement mortar - brand of Portland cement and working mixture
An important factor influencing the quality of construction work is the correspondence of the markings of the binder used with the brand of the prepared mortar. Compliance with standard ratios guarantees the strength of brick walls and the reliability of the foundation. Having information about the labeling of the building materials used, and following the dilution rules, it is easy to determine how to dilute M500 cement and other brands of binders from reference tables.
In the construction industry, special standards are applied to guarantee the strength properties of the finished composition:
- when laying brick walls marked M100, cement mortar of the same grade is used;
- the stability of building walls constructed from M300 grade brick is ensured by the use of a cement mixture marked M150;
- carrying out measures for the interior and exterior decoration of building walls requires the use of a solution marked M50–M100;
- To make the concrete screed and foundation, a more durable mixture of grade M200 is used.
Remember that the marking of the finished cement mortar depends on the brand of Portland cement used in the mixture.
Distillation (distillation)
Distillation (distillation) is a method of separating liquid homogeneous mixtures by evaporating the liquid, followed by cooling and condensation of its vapors. This method is based on the difference in boiling points of the components of the mixture.
Example.
When heating a liquid homogeneous mixture, the substance with the lowest boiling point boils first. The resulting vapors condense when cooled in another vessel. When this substance no longer remains in the mixture, the temperature will begin to rise, and over time another liquid component will boil:
In this way, for example, distilled water is obtained.
| New on the site | | | [email protected] |
| 2018 − 2020 | © | izamorfix.ru |
How to mix cement with sand - proportions
Trying to increase the strength of the mortar, some inexperienced developers independently increase the ratio of M500 cement. Let's look at how to dilute in a proportion that guarantees the quality of the mixture using specific examples.
When preparing concrete, cement, blocks, as well as mortar for plaster and screed at home, maintain the following proportion:
- By mixing Portland cement, fine sand, gravel filler or crushed stone with the addition of water in a ratio of 1:2:4, we obtain concrete grade M350. Water is added in an amount of no more than 50% by weight of Portland cement;
- the composition for the brick screed is prepared from cement grade M300 or M400, mixed with sand in a ratio of 1:3 or 1:4 with the addition of water. Adding slaked lime in a volume of 20% by weight of cement will give the solution increased plasticity;
- plastering of external and internal surfaces is done with a cement mortar consisting of fine sand and Portland cement mixed in a 3:1 ratio. Water is added in portions until a plastic solution is obtained;
- the M150 mixture for screed is prepared according to the classical proportions, which involves mixing fine sand and M350 cement in a 3:1 ratio. The introduction of granulated expanded clay into cement mortar increases its thermal insulation properties.
When preparing the working solution yourself, remember that as the grade of cement used increases, the amount of sand introduced increases. If you have no experience, purchase the working solution from trusted suppliers. When performing low-responsibility work, minor changes to the recipe can be made without prior approval.
To dilute the main bulk substance, you can use a manual method or a mechanized one.
To get 1 m3 (volume weight 2300–2500 kg/m3) of concrete:
- grade M200 will require 280 kg of M500 cement, 740 kg of sand, 1250 kg of crushed stone or gravel;
- grade M300: 380 kg of cement M500, 630 kg of sand, 1250 kg of gravel or crushed stone;
- for the foundation: 300 kg of M500 cement, 600 kg of sand, 1200 kg of crushed stone or gravel (weight ratio 1:2:4);
- for the fence take cement M500 - 236 kg, sand - 710 kg, good quality crushed stone - 1420 kg (weight ratio 1:3:6), ratio 1:4:4 for crushed stone fraction 19–20, ratio 1:2.5: 3.5 if a very strong fence is required.
How to properly dilute cement - introducing additives
To improve the performance characteristics of the solution, various additives are introduced into it:
- crushed stone or gravel, increasing strength properties;
- liquid soap that improves the plasticity of the mixture;
- plasticizers that have a positive effect on frost resistance;
- additives that shorten the hardening time.
When adding special additives to the solution, follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and proven recipe.
Cement powder must be diluted according to certain proportions
Centrifugation
Centrifugation is the separation of heterogeneous liquid mixtures by rotation.
Example.
If the components of a heterogeneous liquid mixture are very small, such mixtures are separated by centrifugation. Such mixtures are placed in test tubes and rotated at high speed in special devices - centrifuges.
Before centrifugation, the particles of the mixture are distributed evenly throughout the volume of the test tube. After centrifugation, lighter particles float to the top, and heavier particles settle to the bottom of the tube.
Centrifugation is used, for example, to separate cream from milk.
Cement hardening
After applying and leveling the cement mortar, for normal hydration processes of the binder, observe the following conditions:
- periodically moisten the formed surface;
- avoid sudden heating of the array under direct exposure to sunlight;
- protect fresh solution from the negative influence of drafts.
Failure to comply with the requirements causes:
- accelerated drying of the outer layer at elevated temperatures with further chipping;
- the formation of deep cracks, significantly reducing the strength characteristics of the hardened massif;
- uneven hardening of the cement composition with the occurrence of internal stresses.
After completing the work, rinse and clean the tools. Thermal insulation of the surface of the poured base will reduce the duration of the hardening process in winter. The strength characteristics of the screed allow people to move on the surface 3–4 days after pouring. Operational strength is gained over the course of a month.