How to use the calculator
In the first field of the calculator for calculating blocks per house, you need to select the type of block (its size and density). The initial data for calculating aerated concrete or expanded clay concrete blocks are also the building parameters determined from the project:
- Perimeter of load-bearing and internal walls.
- The height of the walls.
- The number of window and door openings, the sizes of each.
- Wall thickness.
- The thickness of the mortar layer of masonry.
Using simple calculations, the area of all walls is determined (their width is multiplied by the height). Then the area of door and window openings is subtracted from it.
The final figure will be the area of the masonry, and to determine its volume, the resulting value must be multiplied by the thickness of the walls. If you need to calculate the number of blocks in pieces for a purchase, the formula is used:
K = V class. : V bl. , PC.,
where V class. – masonry volume, m³,
V bl. – volume of one block, m³.
Cost-effective houses made from aerated concrete blocks are constructed from materials of different sizes. For walls, the most popular material is sized 300 mm x 200 mm x 600 mm (width, height, length); for partitions, blocks 100 x 200 x 600 (mm) are most often used.
In the first case, V bl. = 0.3 x 0.2 x 0.6 = 0.036 m³, the volume of the block for the construction of partitions will be 0.1 x 0.2 x 0.6 = 0.012 m³. Thus, for a cubic meter of an external wall made of aerated concrete blocks, 28 pieces will be required. blocks (1 m³: 0.036 m³ = 27.8 pcs., take 28 pcs.). To lay a cubic meter of partitions you will need 84 pieces. aerated concrete blocks (1 m³: 0.012 = 83.3 pcs., take 84 pcs.).
The final operation of determining the consumption of blocks using a calculator is to press the “Calculate” button.
Initial data
To independently calculate the cost of building a house from aerated concrete blocks, you need to have a set of initial data. Let's consider the main ones:
- The total length of all walls along the foundation is the perimeter of the building.
- The height of the building is necessary to calculate the area of the wall surface. Also, knowing the height of the walls and the size of an individual element, you can determine the row of masonry;
- The total area of the wall masonry is determined by the product of the perimeter and the height of the building minus the total area of all window and door openings. By the way, this value will correspond to the area of the required insulation;
- The thickness of the walls - the installation method and the initial choice of the size of the elements depend on it. This parameter is also affected by the thickness of the adhesive (mortar) seam. But based on the permissibly small thickness of the glue layer (3-4 mm). This parameter does not significantly affect the final size of the building;
- The number of elements is a calculated value determined by the initial parameters of the building.
- The total mass of gas silicate and the total volume are necessary to determine the optimal method of delivering materials to the site. When determining the load on the foundation, the mass of the adhesive mortar and masonry mesh is added to the total mass of the “bricks”.
When determining the number of elements for internal partitions separately, you have to count using a similar algorithm. In this case, the thickness of partition walls is usually determined by the height of a separate element, which is laid on the side edge, that is, half of the block.
***
Important! If the gables of your house are also planned to be built from aerated concrete blocks, you will also have to calculate their area.
***
Masonry mesh - it reinforces the masonry, enhancing the mechanical strength of the entire building. Usually each row of masonry is reinforced.
Area as a criterion for calculating the need for wall blocks
In our example, two types of blocks were mentioned - for external and internal walls - differing only in width, which does not affect the area of the walls. In this case, it is easier to calculate the required amount of building material per wall area.
Initial data:
1. House length – 18 m;
2. Width -10.5 m;
3. Ceiling height – 2.8 m. The design height of the building, equal to 3 m, provides for raising the wall by 14 rows:
3 m: 0.215 m = 13.95 (assuming 14 rows), where:
0.215 m – block height taking into account the thickness of the mortar. That. the height of the building would be 2.8 m (0.2 x 14) without taking into account the solution.
4. Doorways measuring 1.3 x 2.1 – 3 pcs. – in the external walls and 5 doors (1.25 x 2.1) – in the internal walls.
5. The length of the internal walls is 38 m.
6. Number of windows – 7 pcs. (size 1.4 x 1.85).
Calculation method for expanded clay blocks
As an example, a one-story house with gables and an interior partition. Let this house be square in shape with each wall 10 meters long and 2.8 meters high. The house has two windows 1.6x1.4 meters and an entrance door 1x2 meters.
Calculation for the perimeter of the building
The thickness of the external walls is 19 cm (half a block). The outside of this house is lined with facade brick. Therefore, the length of each expanded clay wall will be 30 cm less than on the building plan. These 30 cm will be taken up by insulation and facing bricks - 15 cm from each of the two ends of the wall.
- We find the total perimeter of the expanded clay walls: (10 – 0.15*2)*4=38.8 m.
- Let’s say the length of one expanded clay block together with the seam is 40 cm. How many blocks are needed for one row of walls: 38.8/0.4 = 97 pieces.
- The height of the selected block is 20 cm. Find the number of rows: 2.8/0.2=14 rows.
- We find the total number of blocks for the perimeter: 97*14= 358 pieces.
- How many blocks does one window take? Length 1.6/0.4=4 pieces. Height 1.4/0.2=7 pieces. Two windows: 4*7*2=56 blocks.
- Next, the calculation is performed for the front door. Length: 1/0.4=2.5 pieces. Height 2.0/0.2 = 10 pieces. The door takes up 2.5*10=25 blocks.
- We subtract the volume of voids of doors and windows: 1358-56-25 = 1277 blocks are required for laying external walls.
Calculation for internal walls
Now you need to calculate the number of expanded clay blocks for the wall inside the house. The calculation is carried out in the same sequence. In our example, the length of the internal wall is 9.2 meters, the thickness is 0.4 meters (1 block). There is a door in the wall with dimensions of 1x2 m.
- Number of expanded clay blocks along the length of the wall: 38.8/0.2 = 46. In this case, we divide the length of the wall by the width of the block instead of the length, since the blocks will be laid crosswise.
- The number of rows is 14, since the height of the inner wall is equal to the height of the outer ones. In total, 14 * 46 = 644 expanded clay blocks are needed to lay the wall.
- The volume of the door is calculated differently than for external walls. It is necessary to take into account the direction of laying the blocks. Length 1/0.2 = 5 pieces. Height 2.0/0.2 = 10 pieces. The door takes up 5*10 = 50 blocks (instead of 56 for the outer door).
- We find the total number of blocks: 644–50 = 596 pieces.
Calculation of material for gables
In the example, the height of the gable is 2 meters, and the length is also 9.7 meters. Calculations are performed according to geometric formulas, according to which the total area of the gables is equal to the area of one wall of 9.7 × 2 meters.
- We calculate the number of blocks for two gables: (9.7/0.4)*(2.0/0.2)= 242.5 blocks.
- Laying begins with a full row. The perimeter of the walls is 97 blocks, and two full rows are 48.5 pieces. Total required: 242.5 + 48.5 = 291 pieces.
- Since the blocks are sawn when laying the gables, you should buy them with a small margin. Let's round the resulting value to 300 pieces. This amount takes into account the masonry of both gables.
Calculation of the required quantity
Cost calculation example diagram.
Whatever building blocks are used to build a house: aerated concrete or foam concrete, expanded clay concrete or ceramic, the method for calculating the number of blocks required for construction is the same. You need to calculate:
- V – cubic capacity of masonry taking into account technological openings.
- V is the volume of one building block.
- N = V / V – estimated number of building blocks.
It is very important that the volume of the masonry (V) and the individual block (V) are in the same units. In order to eliminate possible errors, it is better to measure them in cubic meters. For this purpose, all linear dimensions should be converted into meters, and areas - into square meters.
Read on to find out more!
House on a personal plot: choice of material
What to do with a crack in the wall of the house
How to cover a house with siding yourself
Chalet style house
How to properly insulate a frame house?
How to build a house without a construction crew
- 2.66
Rating: 2.7 out of 5 Votes: 191
- 6
Reply
5 years ago
Bazna Alina
5 years ago
Quote
In addition to calculating the quantity, you need to take into account the quality of the foam block, since the strength also depends on the quality. It is better to take organic protein, it is stronger and environmentally friendly in comparison with synthetic ones, which have a 4th degree of danger.
farich
5 years ago
Quote
I myself am a design engineer by profession. Therefore, this topic is very interesting to me. Now I know how to calculate the amount of foam block for the construction of buildings. I never thought that so much foam block was needed to build even a small building.
Irina
5 years ago
Quote
A really large amount of foam block is required, at least it’s not expensive. And I absolutely agree about the quality; not every brand of foam blocks even meets the mandatory requirements.
Lada
5 years ago
Quote
We built the cottage from shell rock, so the material consumption had to be determined. But they took a little more than was necessary, just in case. We have enough left to build a barn as well. It’s worse if there’s not enough stone, but you can always use an extra one.
Vitaly
5 years ago
Quote
To calculate the required number of blocks, you can use a specialized calculator, which includes such indicators as the type of block, the desired thickness of the walls and mortar in the masonry, the total length of the walls, the height at the corners, the masonry grid, the average price per unit, and takes into account door and window openings . Quite a convenient thing for initial calculations.
Instructions for the calculator
Here the explanation of the columns “Input data” and “Result” will be presented.
Initial data
Type 1
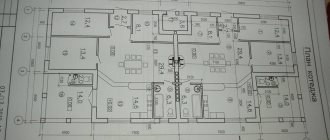
The total length of the walls (L) is the length of one wall or walls if you want to count all the walls of a floor at the same time with the same thickness. For example, in the figure L=L1+L2+L3+L4+L5+L6.
Wall height (H) - the height of the wall(s) for which you want to calculate the number of blocks. For example, floor height.
The area of openings (S) is the sum of the areas of all openings of the wall (walls) that you currently want to calculate.
Block length (A) is the longest dimension.
Block width (B) - wall thickness.
Block height (F) - H=F1+F2+...+Fn, taking into account the layer of binding adhesive.
Price for 1 m3 and for 1 piece - You indicate the price depending on which quantitative unit you are going to calculate the cost of the blocks (you can also specify 2 prices at the same time).
The number of blocks in a package is indicated if you are going to purchase blocks packaged in several pieces.
Packaging price is the price for one package with blocks.
Glue consumption per 1 m3 of blocks is most often indicated on the manufacturer's packaging. For example, for laying 1 m3 of foam blocks, the glue consumption can be 25-40 kg of dry mixture. It also depends on the thickness of the glue layer.
Weight and price of packaging - how much one package of glue weighs and costs.
Reserve % - reserve for battle or other unforeseen situations.
Type 2
Number of walls - usually there are two such walls (if the walls are no different, for example, they have the same size and window opening), they can be calculated simultaneously by putting the number 2 in the column.
Type 3
Lengths L1 and L2 and Heights H1 and H2 are the dimensions of the pediment.
Cinder block calculator: where to find it and how big is the error?
Accurate calculation is an important condition before starting any business, especially construction. However, it is better to make such calculations yourself or use proven calculators. Of the online calculators, I like this one better. This online cinder block calculator calculates the total area of the masonry, the number of blocks required for the construction of the structure, the total weight of the blocks, their total volume, the number of blocks in a cube, the total cost of the blocks (if you indicate the cost per unit), the amount of mortar for the entire masonry, the approximate weight of the mortar , number of rows of blocks, approximate weight of finished walls, load on the foundation from the walls. This calculator can also take into account gables and windows/doors.
and yet, I advise you to double-check the information they provide, you never know. But it’s best to do the calculations by hand. If you need to calculate such things often, then the best solution would be to write a simple program for yourself; anyone can handle this task. You can write a program with an interface in a matter of minutes in C# or Java, or any other language you like. If you don’t want to program, you can create a formula in Excel, which can also be done in one go.
Now, as for the calculations. We do it manually like this:
Knowing the dimensions of the cinder block (the sizes of cinder blocks may vary, so be careful; the figure below shows the main types of cinder block with a standard size, but it can be ordinary - 390*190*188mm; three-quarter - 290*190*188mm; half - 190*190* 188mm; cloisonne - 590(390)*90*188mm; ventilation or chimney - 390*390*188mm) we calculate its lateral area - multiply the height and length.
Now, knowing the lateral area of one block, we can easily calculate how many blocks are needed to build a wall of 1 square meter: divide one by the area of one block. The resulting value will be slightly larger than the actual value, because we did not take into account the thickness of the mortar joint. However, this is not critical. So, if the height of the cinder block is 188 mm and the length is 390 mm, then the side area is 0.073 square meters. This means that we will need 1/0.073 = 13.64 blocks to build a wall of 1 square meter. If we take the thickness of the seam to be 8-10 mm, then we will need not 13.64 blocks, but exactly 13. As we can see, with small volumes the error is quite small.
Now it remains to calculate how many door and window openings we will have and subtract their area from the area of the walls.
As you can see, there is nothing complicated and such data can be easily entered into a program or Excel.
How to use the online cinder block calculator?
Working with the calculator is extremely simple: you just need to enter four parameters into the appropriate form - the size of the block (from the drop-down menu), the length and height of the walls, as well as the total area of the openings.
The length of the walls is obtained by ordinary folding. For example, for a box 7 by 8 meters - 7+7+8+8=30. The height of the wall is chosen based on personal preferences (the higher, the more comfortable, and the lower, the cheaper). Usually they focus on a height of 2.7 meters.
The sizes of windows and doors are converted into meters and multiplied. For example, for a doorway the area will be 2.0 × 0.8 = 1.6 m2. Having determined the areas of all openings, we add them up and enter them into the form on the website.
Next, click on the “Calculate” button, after which the calculator will display the finished result - the total area of the walls excluding openings, as well as the required number of cinder blocks and their total volume. You can also evaluate the difficulties of transporting and storing building materials.
The calculator makes an estimate of the number of blocks per wall. In reality, you will most likely need to buy more. Firstly, in accordance with GOST, the dimensions of a cinder block can vary within 7.5% of the declared ones (unscrupulous manufacturers underestimate them slightly). Secondly, you need to take into account the margin for a likely fight, because it is inevitable both during transportation and during stowage.