what is the ground floor in an apartment building
Construction norms and rules of the Russian Federation
SNiP 31-01-2003
"Residential multi-apartment buildings"
(adopted by Decree of the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation dated June 23, 2003 N 109)
4.10 In the ground, first and second floors of a residential building (in large and largest cities * (2) on the third floor), it is allowed to place built-in and built-in and attached premises for public purposes, with the exception of objects that have a harmful effect on humans.
It is not allowed to post:
specialized stores of mosquito chemicals and other goods, the operation of which can lead to pollution of the territory and air of residential buildings; stores containing explosive substances and materials; stores selling synthetic carpets, auto parts, tires and automobile oils;
specialized fish stores; warehouses for any purpose, including wholesale (or small wholesale) trade;
all enterprises, as well as shops with operating hours after 23:00*(3); consumer service establishments that use flammable substances (except for hairdressing salons and watch repair shops with a total area of up to 300 m2); baths and saunas (except for individual saunas in apartments);
catering and leisure establishments with more than 50 seats, a total area of more than 250 m2 and with musical accompaniment;
laundries and dry cleaners (except for collection points and self-service laundries with a capacity of up to 75 kg per shift); automatic telephone exchanges with a total area of more than 100 m2; public restrooms; funeral homes; built-in and attached transformer substations;
production premises (except for premises of categories B and D for the work of disabled people and older people, including: points for delivering work to home, workshops for assembly and decorative work); dental laboratories, clinical diagnostic and bacteriological laboratories; dispensaries of all types; day hospitals of dispensaries and hospitals of private clinics; trauma centers, ambulance and emergency medical care substations; dermatovenerological, psychiatric, infectious diseases and phthisiatric medical offices; departments (rooms) of magnetic resonance imaging;
X-ray rooms, as well as rooms with medical or diagnostic equipment and installations that are sources of ionizing radiation, veterinary clinics and offices.
Stores selling synthetic carpet products may be located attached to blind areas of the walls of residential buildings with a fire resistance rating of REI 150.
4.11 In the ground and basement floors of residential buildings, it is not allowed to place premises for storage, processing and use in various installations and devices of flammable and combustible liquids and gases, explosives, combustible materials; premises for children; cinemas, conference halls and other halls with more than 50 seats, as well as medical and preventive institutions. When placing other premises on these floors, you should also take into account the restrictions established in 4.10 of this SNiP and in Appendix 4* of SNiP 2.08.02.
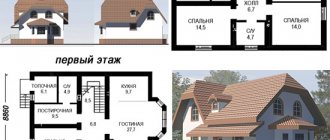
Almost every residential or administrative building has underground premises. Some of them contain water supply, heating, and sewerage communications. Others turn into additional rooms, shops, cellars, significantly expanding the usable area of the house. We are talking about basements and ground floors, the difference between which not every person understands. In the meantime, it is quite significant. Let's take a closer look at how a basement differs from a ground floor.
Architectural possibilities
The presence of a basement floor allows you to build a house with more floors. This is especially important, since in accordance with SNiP and other standards it is impossible to build a private house with a height of more than two floors with an attic. In most cases, the ground floor is not taken into account (if it falls under the definition given above), so a country homeowner can get a full-fledged three-story mansion at a lower cost.
Due to the basement, a two-story house turns into a three-story one.
The basement floor, the floor level of which is located slightly below the design ground level, is suitable for use for a variety of purposes. In particular, the homeowner can place a boiler room with a gas boiler here without violating SNiP.
In terms of area, the ground floor can be larger or smaller than the first level of the house. In the first case, the covering of the basement space becomes a usable roof on which a terrace can be placed. Naturally, it is necessary to provide not only a decorative component, but also effective insulation of underground premises.
Does the ground floor belong to the residents of the house who are the owners?
At the end of the 20th century, the number of residential buildings with a basement began to decline significantly. The practice of arranging bomb shelters in them is a thing of the past, and the introduction of central heating has made its presence felt. In addition, the construction of houses without basements can significantly reduce the cost of the underground part. Meanwhile, these premises give the building additional stability. Spacious basements often house warehouses, shops, small industries and offices, as well as car parks.
Ground floor is a room located below the ground level. It is buried in the ground and rests on the foundation of the building. Suitable for placing both utility facilities and living rooms. The area of the basement can be larger or smaller than the first level of the house. It must be equipped with special ventilation ducts that ensure air circulation and prevent the formation of condensation on the building structures. This part of the building often houses hairdressers, shops, catering establishments, parking lots, etc.
Features and technical requirements
There are few structural differences in the construction of a foundation with a basement floor from a conventional one. If the base is a concrete slab, it is placed below ground level; if the foundation is strip, its underground part above goes into the basement.
Walls and ceilings are most often made of either monolithic concrete. The characteristics of the materials depend on the characteristics of the soil and climate in the area. For dry, stable soils, hollow blocks with low mass can be used. Their advantage is low thermal conductivity: when constructing a functional basement, the energy consumption for heating will be less.
note
Even when using materials with low thermal conductivity in “dry” conditions, the base blocks must be waterproofed and insulated.
An important point of the device is to provide ventilation. Unlike residential floors, the basement does not have windows, or the glazing area is small. is ensured by creating special ones in the design and/or by installing modern climate control equipment with an air dehumidification function on the floor. This will avoid excessive humidity and, as a result, the formation of condensation on the walls.
What you can and cannot save on:
- on good soil, it is possible to make an intermittent prefabricated foundation instead of a classic monolithic one: arrange the blocks not end-to-end, but at certain intervals. At the end of installation, the areas between the slabs are covered with soil. The calculation of such a basis should be entrusted to a specialist;
- For the sake of economy, you should not violate the technology of hydro/thermal insulation protection of the room. This will lead not only to dampness, deterioration of materials and the microclimate in the house, but also to accelerated wear of load-bearing structures;
- for the same reasons, the blind area should not be neglected, and with a high groundwater level -;
- for cladding plinths, a separate group of finishing materials is used: , etc. It is undesirable to use façade materials instead of them, because their strength and wear resistance do not meet the requirements for foundations.
Comparison
First, let's talk about the design features of the premises in question. Thus, the basement is part of the foundation of the building and is often located almost entirely underground. Due to the absence of windows, a stable annual temperature is maintained in the room, making it an ideal storage for vegetables, preparations, wine, etc. The base is buried in the ground only half the height of the above-ground floors of the building. Relying on the foundation of the house, it is not part of it. The basement floors are equipped with small windows, which makes them unsuitable for arranging cellars. But such premises are used for a number of very diverse needs.
This leads to another difference between the basement and the ground floor, which lies in the purpose of the underground parts of the building. The first room is used primarily for the location of equipment and communications. It lacks heat and waterproofing, floor and wall finishing, and has a damp and cool microclimate. In this regard, it is rarely possible to use the basement for residential purposes. Whereas as a shelter it is simply ideal. In addition, a basement can only be constructed with strip or pile foundations. Groundwater poses a particular threat to it.
The ground floor is much more often used for arranging living rooms. The air temperature in it is not much lower than in the house itself. It protects the building from the penetration of excess moisture. The ideal foundation for the construction of a basement is considered to be a slab version. A room partially buried in the ground is not afraid of groundwater, but moisture from melted snow and other precipitation can enter it.
Technical buildings
According to SNiP rules, many technical rooms cannot be located in most basements of country houses. This is because often the basement does not meet the relevant requirements. The main technical room of most country houses is a gas boiler room, which can be located on the ground floor without any problems. This is due to the fact that, due to its design, the basement room, unlike the basement, in most cases will meet all SNiP requirements for the placement of boiler rooms.
An example of boiler room placement.
Also a good option for saving space on the site is to install a garage on the ground floor of the building. However, recently homeowners have begun to abandon this solution, because chemical odors from a car when it is parked under the house begin to rise into the living spaces. And this negatively affects the comfort of people staying in the house.
To solve this issue, car owners will have to equip the base with a high-quality ventilation system that could successfully remove exhaust gases and unpleasant odors immediately after they appear. It is also recommended to seal the room in accordance with SNiP standards and recommendations of specialists (not only the ceiling, but also the walls). For this, various finishing materials and insulating compounds can be used.
Table
| Basement | Ground floor |
| Often located entirely underground | Recessed into the ground only half the height of the above-ground floors |
| Is part of the foundation | Relies on the foundation |
| No windows | There are small windows |
| Damp and cool microclimate | The air temperature is not much lower than in the house itself |
| Constructed with a strip or pile foundation | The ideal foundation is considered to be a slab foundation |
| Used primarily for household needs | Often equipped as a living space |
Living spaces
If there is enough space, the basement of the building can become an additional residential floor with several rooms, as well as a sports area. When arranging residential premises on the ground floor, it is necessary to effectively isolate the space from moisture and temperature changes, and this must be done during the construction stage of the building. It is advisable to carry out all insulation work from the outside of the foundation. In this case, you can get the most effective result at low cost.
It is very good if a country house with a basement is located on a slope. In this case, you can get one wall that will be placed higher or at the same level with the ground. This circumstance allows you to organize a living room or bedroom on the ground floor with a completely glass wall, which will allow you to get an incredible design effect.
Living room.
In addition, the following will look great on the ground floor: sauna, bathhouse, hammam. It is also popular to place billiard rooms, gyms, and swimming pools. SNiP standards do not regulate the presence of certain residential premises on the ground floor, so anything can be placed here.
Placing bedrooms, offices and children's rooms in the basement is popular. The underground space is a zone sufficiently protected from the external environment, which has a beneficial effect on a person’s rest, work process and relaxation. The main thing is to take care of a comfortable indoor microclimate.
Number of storeys
This term is defined in SNiPs, in particular in SNiP 31-01-2003. From the definition available there, several important data about the number of storeys follows:
- This concept includes only above-ground floors;
- Basement and technical floors can be classified as above-ground only if their top floor is 2 m above ground level;
- Any number of floors, of any height, located below ground level is not included in the concept of number of floors;
- Interfloor space, the height of which is less than 1.8 m, is also not included in the number of storeys;
- But the attics are included.
The essence that we can take away from here is that the number of storeys implies above-ground floors, and ignores the technical ones.
Number of floors
This concept is outlined in the Town Planning Code and is used in various examinations.
The reason for the confusion and various misunderstandings is that it is not equivalent to number of floors. The consequence of a misunderstanding of this difference may be:
- rejection of project documentation upon approval;
- problems with examinations;
- difficulties in coordinating individual housing construction projects;
- difficulties when participating in government orders;
- and so on.
As you may have guessed, the key difference between the concepts is that the number of floors includes underground floors. In addition, the following are also added here:
- basement;
- basement;
- technical;
- and attic floors.
Thus, the number of floors in a building can easily be higher than its number of storeys.
The most common collisions
This confusion in terminology most often concerns individual housing construction. The fact is that an individual housing construction object is considered to be a house whose number of floors does not exceed 3. When constructing such facilities, state expertise is not required.
However, if the house has 3 above-ground floors and a technical one, in which, for example, boiler equipment and other engineering components are located, then the total number of floors in this house is already 4. If this is not taken into account in detail during the preparation and approval of project documentation, they may subsequently various troubles will arise.
Please note that almost all regulatory provisions of the Town Planning Code and other regulations are focused specifically on the number of floors, and not on the number of storeys.
Conclusion
Since the concept of the number of floors is more important in regulatory documentation, it is advisable to rely on it in your own plans. This will help avoid unnecessary misunderstandings, especially regarding individual housing construction.
What is a ground floor?
Not a base.
Answer: To be honest, I did not hold this document in my hands and there is little to discuss its usefulness. However, I will say that the “basement floor,” no matter how you hide it, is still a floor. If you are interested in the “number of floors of the building”, then the building is three-story; if you are interested in the “number of floors”, then it is fair to say that there are four. Both are existing terms. Perhaps you will be interested in SP 118.13330.2012 Appendix D (mandatory). Rules for calculating the total, useful and estimated areas, construction volume, building area and number of storeys of a public building
Appendix D (mandatory) D.1 The total area of the building is determined as the sum of the areas of all floors (including technical, attic, ground and basement). The total area of the building includes the area of mezzanines, galleries and balconies of auditoriums and other halls, verandas, external glazed loggias and galleries, as well as transitions to other buildings. The total area of the building separately indicates the area of open unheated planning elements of the building (including the area of the usable roof, open external galleries, open loggias, etc.). The area of multi-light rooms, as well as the space between flights of stairs greater than the width of the flight and openings in floors of more than 36 m2 should be included in the total area of the building within only one floor. Floor area should be measured at floor level within the interior surfaces (clean finish) of exterior walls. The floor area with sloping external walls is measured at floor level. The area of the attic floor is measured within the internal surfaces of the external walls and attic walls adjacent to the attic cavities, taking into account G.5.
D.2 The usable area of a building is defined as the sum of the areas of all premises located in it, as well as balconies and mezzanines in halls, foyers, etc., with the exception of staircases, elevator shafts, internal open stairs and ramps.
D.3 The estimated area of a building is determined as the sum of the areas of the premises included in it, with the exception of: corridors, vestibules, passages, staircases, internal open stairs and ramps; elevator shafts; premises intended for placement of engineering equipment and utility networks.
D.4 The total, useful and estimated area of the building does not include the area of the underground for ventilation of the building on permafrost soils, the attic, the technical underground (technical attic) with a height from the floor to the bottom of the protruding structures of less than 1.8 m, as well as external vestibules, external balconies, porticoes, porches, external open stairs and ramps.
D.5 The area of the premises of a building is determined by their dimensions, measured between the finished surfaces of walls and partitions at floor level (excluding baseboards). The area of the attic floor is taken into account with a reduction factor of 0.7 in the area within the height of the sloping ceiling (wall) at a slope of 30° - up to 1.5 m, at 45° - up to 1.1 m, at 60° or more - up to 0 .5 m.
D.6 The construction volume of a building is defined as the sum of the construction volume above the 0.00 mark (above-ground part) and below this mark (underground part). The construction volume of the above-ground and underground parts of the building is determined within the bounding surfaces with the inclusion of enclosing structures, skylights, domes, etc., starting from the level of the finished floor of each part of the building, without taking into account protruding architectural details and structural elements, underground channels, porticos, terraces , balconies, volume of passages and space under the building on supports (clean), as well as ventilated underground areas under buildings on permafrost soils and underground channels. D.7 The building area of a building is defined as the horizontal sectional area along the outer contour of the building along the base, including protruding parts (entrance platforms and steps, verandas, terraces, pits, basement entrances). The area under a building located on pillars, passages under the building, as well as protruding parts of the building that cantilever beyond the plane of the wall at a height of less than 4.5 m are included in the building area. Additionally, the construction area of the underground parking lot, which extends beyond the outline of the building's projection, is indicated. D.8 When determining the number of storeys of a building, all above-ground floors are included in the number of above-ground floors, including the technical floor, attic, and also the basement floor, if the top of its ceiling is at least 2 m above the average planning level of the ground. Mezzanine, occupying more than 40% of the space should be considered a floor. The underground space under the building, regardless of its height, as well as the interfloor space and technical attic with a height of less than 1.8 m are not included in the number of above-ground floors. When determining the number of floors, all floors are taken into account, including underground, basement, basement, above-ground, technical, attic and others. If the number of floors is different in different parts of the building, as well as when the building is placed on a site with a slope, when the number of floors increases due to the slope, the number of storeys is determined separately for each part of the building. When placing a building on a site with a slope, when it is impossible to determine the belonging of the floor according to Appendix B, the determination of the number of storeys should be applied for each room separately. To do this, it is necessary to take into account the layout of the given floor and room, the position of the outer wall of the room relative to the blind area and the parameters of natural light in the room. When determining the number of storeys of a building for structural or other calculations, technical floors are taken into account depending on the features of these calculations established by the relevant regulatory documents. When calculating the number of elevators, the technical attic located above the top floor is not taken into account. The technical floor, located in the middle part of the building, is taken into account only in the lift height of the elevators. D.9 The retail area of a store is defined as the sum of the areas of sales floors, premises for receiving and issuing orders, a cafeteria hall, and areas for additional services to customers.
Tags: Terms