Conditions for assembling foundation formwork and its functions
Formwork controls the shape of concrete, levels it and isolates it from the ground.
Construction formwork for a strip foundation must be strong and have stable dimensions. The texture of the future base and the number of cracks on the surface depend on the quality of the internal plane. Assembly accuracy is an important condition during installation.
The formwork performs the following functions:
- controls the shape of the concrete mass before hardening;
- evens out the texture of the foundation surface;
- isolates the base from the ground.
The installation and use of formwork is regulated by State Standard No. 52085 - 2003 “Formwork. General technical conditions", which began to be applied by decree of the State Construction Committee of Russia dated May 22, 2003 No. 43.
Formwork installation
Formwork installation
The formwork is assembled from separate parts, the forming base being panels made of wood, metal, and other materials. The interior is cleared of debris and leveled to minimize the finishing process.
Attention is paid to the strength of the connection of the fastening elements to each other, because The concrete mass is heavy and can compromise the integrity of the structure. The foundation of the house is formed correctly if the shell does not allow water to pass through. The height of the auxiliary structure is 15–20 cm higher than the foundation level. The panels are reinforced with wooden posts, which are driven into the ground and placed at intervals of 0.7–1.0 meters.
Drawing and diagram
Concreting the foundation includes choosing the type of formwork and making schematic markings in the plan for its precise installation. Great importance is attached to laying the foundation, the process is controlled by specialists, and installation begins with design design.
Drawings of the molding system are developed taking into account:
- size and material of shields;
- fastening devices.
Formwork assembly diagrams are part of the project for the production of PPR work, which also includes plans for the placement of tape elements, time-bound organizational charts, and process maps. The marking drawing contains a strategy for the arrangement of elements with reference to the central axes of the building by numbers.
Types of formwork for strip foundations
The choice of formwork design depends on the shape and design parameters of the strip foundation, soil characteristics, characteristics of the material used and environmental factors. The following types of formwork can be used for strip foundations:
- Removable formwork, the design of which provides for the possibility of disassembling it into its component elements after the concrete has hardened.
- Permanent formwork, the elements of which are an integral part of the strip foundation and may have additional functions of thermal insulation, waterproofing, decorative and protective purposes. A set of modular elements reduces installation time and does not need to be removed after the concrete has hardened.
If the soil does not crumble and has sufficient hardness and viscosity, then concrete casting directly into the strip foundation trench is allowed, which can reduce material consumption.
Selection of formwork material
The limiting structure is selected taking into account the type of foundation, its massiveness, length, and type of concrete. The material must be available and have an acceptable cost.
Specialized types are used:
- wood;
- metal;
- reinforced concrete;
- expanded polystyrene.
Small foundations are poured using improvised means that do not require spending money. For example, old boards, dismantled door panels, furniture parts, and pieces of slate are used. Formwork from such items is difficult to perform and is not always popular, because... it is difficult to select the appropriate parts and sizes.
Metal
Metal formwork
The metal form is a suitable option for monolithic and strip bases. The reinforcing posts are welded to the steel panels, resulting in a reliable collapsible structure, the blocks of which are secured with bolts. Galvanized or galvanized metal is also used. The coating on the steel surface protects the material from corrosion, so such shields can be turned over multiple times and are easy to clean and remove.
Aluminum sheets are lightweight and convenient in construction, but have a high cost. The material differs from steel in lower strength and increased fluidity, so it quickly loses its shape. Aluminum panels are almost never repaired, so their use is limited.
Reinforced concrete
Reinforced concrete formwork is rarely used
Such formwork is unconventional and is rarely installed due to the complexity of installation and high cost. To make the formwork correctly, ready-made reinforced concrete slabs are taken. The advantages include the fact that the powerful shell is not removed and allows you to reduce the transverse size of the foundation body.
Another option for a reinforced concrete shell is when a reinforced layer is concreted on top of permanent slabs of foam or other plastic material. A mesh of metal rods encloses the insert on both sides and is connected with wire pallets. Concrete is applied using the spray method using special installations.
Expanded polystyrene
Expanded polystyrene formwork
A shell made of this material stably retains its technical properties during operation over a long period of operation of the building. The formwork has high strength and protects concrete from freezing and moisture in harsh climates.
Plates made of expanded polystyrene brand PSB-S with a density of 25 - 35, a thickness of 40 - 100 mm must be placed in the design position in accordance with the step-by-step instructions. The slabs are connected by monolithic partitions. The overlying blocks are engaged with the lower elements due to special locks, and concrete is laid in the internal space.
Tree
Wooden structure
Boards or boundary sheets made of chipboard, OSB impregnated from moisture are used. Plywood formwork for the foundation is assembled using ties and wooden supports, which are connected with nails or screws. The blocks must be placed in rows so that there are no voids between them, and restrictive plates must be installed at the end using a similar principle.
The top of the structure is tied with reinforcement so that the concrete does not fall apart at the edges. A frame made of reinforcement or a mesh of metal rods is installed inside. Heat-resistant foam inserts are used to coordinate thermal resistance. Concrete is poured into the resulting space, and after hardening, the panels are removed.
Dock for stairs in Penza, Makhachkala
One of the new developments in the field of cast-in-place formwork is the doka technology, which implies high quality of the final result at a minimum of costs. It is a system of plastic cylinders, frames or columns, which are used in the construction of small-sized objects and large industrial enterprises. What is doka for stairs? At their core, these are piles that support the shape of the future flight of stairs, which, depending on the required structure, can be attached at different points of the future staircase. Moreover, such a system is easy to install and dismantle due to special fastenings on the connecting elements.
Types of formwork for foundations
Removable formwork can be rented
According to its purpose, the shell can be vertical, for example, formwork for a columnar foundation, or horizontal. The vertical structure moves upward as it is filled with concrete, as when pouring a pile foundation.
The frame system consists of panels on a metal frame and supports, connected with nails, bolts, and self-tapping screws. The design is rigid and can be used many times. The beam system includes formwork panels, beams, crossbars, scaffolding, where the elements are connected by welding. This design is used for the construction of walls, but is not used for concreting foundations.
Removable
The replaced systems differ only in material, because... the design is always made similar and contains decks, a connecting belt, supports and braces. In construction, modular or inventory versions of shields are used, which are manufactured at the factory. Such formwork is quickly installed and removed and is characterized by high accuracy of geometric dimensions.
In private housing construction, the turnover of the structure does not play a role, so wood is more often used, for example, the formwork of a strip foundation is made from boards. Once removed, the material will no longer be used.
Inventory formwork can be rented if such a decision is economically justified.
Fixed
Fixed formwork becomes part of the foundation
The structure consists of easily assembled formwork parts, which, after the concrete hardens, become the category of working elements and perform the specified functions. The shell protects the foundation from soil liquid, and the base can withstand freezing and thawing without destruction.
Factory modules are used, which are assembled using grooves and tenons in the appropriate places. External supports are not used, because internal tabs hold the structure and provide load resistance. More often, non-removable options are made from materials that conserve heat and do not allow moisture to pass through easily, but metal, fiber-reinforced concrete, porcelain stoneware or plastic are also used.
Collapsible
Collapsible formwork
The system is intended to be disassembled after use and moved to the next plot. You can construct such formwork for the foundation with your own hands, purchase a reusable one on the market, or rent it. The formwork consists of panels and a load-bearing frame. Supports and braces support the panels in working position so that the concrete does not spread during the hardening process.
The collapsible version differs in the way the elements are fastened. The panels are connected with bolts, which are removed if necessary, and the stationary formwork is secured with nails or by welding the frame, which makes it impossible to remove it without destruction.
Small shield
Small panel formwork
The design is used on small objects so as not to use cranes for installation. Panels weighing less than 50 kg are placed in the design position manually during the construction of private houses, where a large volume of concrete work on pouring the foundation is not provided.
Small-panel formwork contains elements of standard sizes and is connected using the impact lock method and using tie screws. The advantage of the device is its repeated use and long service life. The labor of workers is saved, the installation technology is clear and simple, each element has grooves and mounting holes for fitting parts.
sliding
Sliding formwork
This type of shell can be adjusted in height and is used in the construction of buildings with monolithic concrete walls and columns. Rigid panels of the chosen design are mounted at a certain height, and concrete mixture is supplied inside. After hardening, the shell is disassembled and rearranged higher to accept a new portion.
For rearrangement, jacks, hoists, and lifts are used.
The use of sliding formwork is effective in buildings with a constant wall perimeter in plan and for structures with a minimum number of window and door openings, for example, the walls of elevators, water towers, and lighthouses.
Assembly and installation rules
Making formwork for a strip foundation is not difficult. But there are nuances that indicate which design will be used. The word “what” means for the base or for the entire foundation. Despite the apparent similarity of the two designs, the second is much more complex in terms of assembly, in terms of fastening, and in terms of preparing the trench. Therefore, we will consider both options separately.
For plinth
First of all, you need to decide on the amount of material needed. To do this, you need to know the total length of the foundation structure and the height of the base part. The length of a board with a width of more than 150 mm is 6 m. Therefore, it is necessary to make several mathematical calculations.
- Divide the height of the base by 150 mm, we get the number of boards located in the vertical plane.
- We divide the total length of the foundation by 6 m, we get the amount of material according to the horizontal arrangement. We multiply the resulting value by “2”, because the strip foundation is fenced on both sides.
- Now all that remains is to multiply both values together, you will get the required amount of material for assembling the strip foundation formwork.
There are two assembly options: assemble the boards and then install them in place, or install the boards on supports (stakes) driven into the ground, adjusting them to the size of the sections of the foundation structure. The simplest option is a panel one. To do this, you need to assemble the boards into small panels, the width of which should be equal to or greater than the height of the base. For example, if the height of the base part is 50 cm, then to assemble the shield you need to take either 4 boards 150 mm wide, or 3 x 200 mm, or 2 x 250 mm.
Before installing the strip foundation formwork with your own hands, the boards are knocked together with bars with a cross-section of 50 x 50 mm, which are installed in increments of 1 m. Fastening is carried out with self-tapping screws 100 mm long. Now the formwork for the strip foundation is being installed.
- Two shields are installed on both sides of the dug trench.
- It is necessary to align the formwork vertically, for which a plumb line is used.
- They are fastened together by crossbars. These are boards or bars, cut to a length equal to the width of the foundation, plus two thicknesses of the formwork boards. Installation step - 1 m. Fastening with self-tapping screws 70 - 100 mm long.
- The structure is being strengthened. To do this, at a distance of 1 m from the installed shields, wooden stakes made of bars with a cross-section of 50 x 50 mm are driven into the ground. Their ends are simply sharpened with a knife, and they are driven in with a heavy hammer. Installation step - 2 m.
- Cross members from the same bars are laid on the ground between the formwork panels for the strip foundation and the hammered stakes. The crossbars are attached to the boards and stakes with self-tapping screws 100 mm long. It is recommended to screw at least three screws into each connection.
- The braces are installed. These are elements that are installed at a slope and connect the stakes and the upper edge of the shields.
The photo below shows the formwork of a strip foundation, or rather its basement part.
Let us add that not all formwork designs for strip foundations use crossbars on the ground. If the width of the tape is not very large, no more than 50 cm, then you can do without them.
Foundation
This is a more complex option, because in addition to the fact that you have to build a full-fledged structure, you will also have to prepare a trench so that it is easy to work with. To do this, you will have to dig the lower plane of the trench (bottom) to match the width of the foundation, plus two thicknesses of the shields, and the upper plane is twice as wide as the bottom.
For example, if the width of the foundation is 50 cm, the thickness of the boards is 5 cm, the thickness of the bars holding the boards together is 5 cm. It turns out that the width of each panel is 10 cm. And since there are two of them, their total width is 20 cm. B In the end, it turns out that the width of the bottom of the trench should be 70 cm. The upper part should be 140 cm. Both planes are connected by bevels, so in cross-section the trench should be in the form of a trapezoid.
The installation of formwork for a strip foundation of this type is also more complicated in the sense that thrust elements will have to be installed inside the trench that will hold the panels in a stationary position. Therefore, experienced builders widen the base of the trench more.
The steps for installing formwork under the foundation are almost the same:
- Shields are installed in the trench. They are set vertically with a plumb line.
- Crossbars are mounted along the upper edges of the panels in 1 m increments.
- Stakes are driven in every 2 m at a distance of 1 m from the edge of the trench.
- The lower cross members are not installed because there is no solid foundation for them. The soil is selected for expanding the trench.
- The upper braces are installed in such a way that their lower ends are located above the ground.
- Additional braces are attached to them, the lower ends of which rest against the panels at the level of the ground surface.
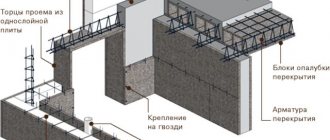
- Pay attention to the bottom photo . It shows that in addition to the crossbars, the shields are held in place by steel studs, which, after pouring the concrete solution, remain in the body of the foundation. Sometimes the studs are inserted into tubes, which remain in the concrete, and the fasteners themselves are pulled out and used further.
- But the most difficult thing is the braces inside the trench. Typically, such formwork is installed on loose soils, so it is important for the braces to prepare stops in the form of plates that will create a rigid surface. The ends of the jib will rest on it. To do this, you can use boards 4-5 mm thick and half a meter long. They are laid longitudinally on the slopes and one end of the brace rests against them. The other end supports the lower part of the shield.
Installing formwork for a strip foundation is not a simple process. It must be approached responsibly, because the concrete solution creates enormous pressure on the panels. After all, there are 2.5 tons in one cubic meter of concrete mass.
Features of formwork calculations
Standard calculations boil down to determining the number of boards or sheets of chipboard and comparing their cost. To do this, the area of the side wall of the strip foundation is divided by the area of the element. For example, the side surface of the base is 7 m² (length - 10 m, height - 0.7 m). The board has an area of 0.9 m² (length 6 m, width 0.15 m). The number of boards is 7 / 0.9 = 8 boards (7.77).
Typically, in a private house, 40 - 50 pieces of boards are taken per 1 m³ of concrete mixture. To do this, the volume of the entire foundation is calculated. It is equal to the perimeter multiplied by the height and width of each free-standing or rotating section, then the volumes are added.
Preparatory stage and do-it-yourself production technology
At the preparatory stage, the plant soil is cut off
The initial stage includes the acquisition of materials and preparation of tools. Before you install the formwork yourself, you need to level the construction area.
The operation includes:
- cutting of plant soil;
- trench digging;
- cleaning the bottom of the pit to the design mark.
The ditch for the strip base or the holes for the pillars are selected so that there is a margin of 10 - 15 cm on the sides for installing shields along with spacers. Vertical fences for flat screens are installed after installing a backfill of sand and crushed stone at the bottom of the trench.
Do-it-yourself foundation formwork installation
All horizontal and vertical parts of the structure are leveled or a construction level is used.
Step-by-step sequence of actions:
- installation of vertical racks;
- mounting and fastening of panels;
- installation of stops and connection of the upper edges.
The panels are hung on vertical bars so that there are no gaps larger than 5 mm between them, through which moisture will leak out of the concrete. Stops and braces are placed to strengthen the formwork; boards or bars are used.
The encircling frame is placed in two tiers, at the bottom (height 10 cm) it absorbs the initial load from the concrete, and at the top (40 cm) it will simultaneously protect the panels from spreading to the sides. The inner surface of the formwork is covered with polyethylene to prevent leaks and moisture absorption into the wood.