For monolithic construction of large structures, the latest material has recently been used - plastic formwork. It is universal in the hands of experienced craftsmen and is a real construction set. For the manufacture of columns, walls, ceilings or foundations, removable, permanent or sliding plastic formwork is used.
Plastic reusable formwork
For reinforcement, fiberglass reinforcement can be used. The formwork tie is made of metal, but it can also be made of plastic. If you are planning single work, then a good solution would be to rent plastic formwork.
Advantages of plastic formwork
Plastic formwork has a number of significant advantages compared to its traditional counterparts:
- minimal use of lubricant during construction. Since concrete does not interact with plastic, removing the mold from columns or floors occurs without problems;
- light weight. Plastic formwork, especially if it is used for foundation construction, is lighter in weight compared to its metal counterparts;
- wear resistance. This design is not subject to decomposition, as well as rotting processes; plastic can last a very long time than plywood;
- quality of finished products. The smooth surface of the boards ultimately ensures a smooth concrete surface, which is important in the manufacture of columns;
- quite low price. There is no need to use consumables such as beams, boards, plywood;
- installation speed. The characteristic universal design allows the mold to be easily mounted and then removed. The removable design has special rotary handles, thanks to which module elements can be placed in different directions.
Types of plastic formwork
Plastic formwork can vary in the way it is used for construction:
- plastic formwork made from small panels for walls and monolithic foundations is used mainly for the construction of administrative and residential buildings. It has a wide range of uses - creating columns, crossbars, ceilings, walls of buildings and other reinforced concrete structures;
- for rectangular columns. The shield is formed from 16 elements. Allows you to form columns up to 6 meters high, and the width of the structure will be from 0.3 to 0.6 meters;
- for round columns. This technology makes it possible to avoid the use of metal structures during the construction of a building. Type – pipe up to 6 meters long with no restrictions on diameter;
- for floors. It is a modular, reusable design. Using this type of construction, it is possible to create crossbars and ceilings, as well as reinforced concrete structures of varying degrees of lightness. It is installed using telescopic formwork stands.
The flexible radius model is used in cases where it is necessary to achieve complex curved shapes. It is very common in the construction of swimming pools, paving, and landscape design. All of the listed types can be combined with other formwork elements, including massive panels made of material such as plywood.
Execution of coverage
After the formwork has been assembled, you can begin to make a concrete covering around the house. In this case, adhere to the following sequence of actions:
- First, a sand cushion 10 cm high is made. The sand layer is leveled, moistened with water and compacted.
- After this, a layer of crushed stone 10-15 cm high is made. It is also carefully compacted. At the same time, you should not forget about the necessary slope of the blind area from the walls of the building, so already at the stage of making the crushed stone cushion, you can take care of creating a slope.
- A reinforcing mesh is laid on top of the crushed stone.
- Now you can start pouring the concrete solution. You can use a factory mixture or prepare the composition yourself.
Important: in order for the coating to have sufficiently high strength and not crack over time, concrete must be poured at a time, without long breaks in work.
- The solution being poured must be thick enough so that it can be laid in a thicker layer against the walls of the house, thereby creating the necessary slope. Correct filling is checked using a level. The surface is leveled according to the rule.
- During the hardening process in the first days, the concrete surface is wetted with water and covered with plastic film.
- After removing the formwork and removing the boards that are laid along the walls of the house, the resulting temperature gap is filled with polyurethane sealant.
The construction of a foundation is a labor-intensive and expensive process; in individual construction, the only way to save money is to carry out all the work (or its individual stages) on your own. In particular, this applies to the installation of formwork when pouring strip-type foundations; with the right approach and studying the video instructions, even a non-specialist can install, secure and remove it. The material of the panels and supports can be any: plastic, metal, moisture-resistant plywood, boards. Wood is used most often for reasons of economy, ease of assembly and adjustment to the required dimensions.
At the preparatory stage, the foundation is marked and its perimeter is calculated. The formwork is placed on flat and compacted layers of drainage cushion made of sand and crushed stone. The panels and supports are assembled in advance; the gap between digging the trench and their installation should be minimal, otherwise the walls will begin to crumble and rain moisture will accumulate at the bottom. It is easy to calculate the required number of boards or plywood for formwork under a strip foundation; you just need to know its area. Up to 90% of supporting structures in private construction are made of wood; their thickness depends on the mass of concrete being poured and the purpose of the building. The minimum for timber is 50x50 mm, plywood - 10 (subject to its support), boards - from 22.
Removable and permanent formwork
According to the nature of dismantling, it can be divided into 2 categories: removable formwork, or what is called permanent formwork. A permanent structure means pouring a concrete mixture into a formwork that, upon completion of construction, will become “part” of the building.
That is why it is most effective to use the qualities of permanent formwork when building walls or a monolithic foundation.
The first appearance of permanent formwork dates back to the 60s in Austria and since then its popularity has been increasing.
It is made mainly from expanded polystyrene - a cheap and very light material that is capable of permeating air, but at the same time has excellent thermal insulation properties.
Expanded polystyrene is excellent for making permanent formwork for foundations and other reinforced concrete structures. It is able to withstand aggressive chemical environments, the harmful effects of moisture and is safe for human health. And its cellular structure allows it to withstand significant pressure from concrete masses, which is typical for a foundation.
Necessary materials
- unedged or edged board;
- panel formwork can be made of particle boards (chipboards);
- Moisture-resistant plywood or oriented strand board (OSB) are also suitable for these purposes;
- some types of formwork that can withstand heavy loads are made of steel and aluminum alloys;
- permanent formwork is made of expanded polystyrene reinforced with fiber additives.
To form the blind area, unedged boards or plywood sawn in strips are suitable. Since poured concrete can slightly expand the formwork structures, bars with a cross-section of 30x30 are used as supports and a supporting frame, from which a durable structure is made.
Important: to make a protective coating around the house, removable formwork is usually used, which is dismantled after the concrete has hardened.
It is equally important to correctly determine the material for making the blind area. The covering can be made from compacted crushed stone, but in this case it is necessary to arrange a good drainage from the roof so that the flowing precipitation does not erode the fragile crushed stone covering.
A little better and more durable than coverings made of crushed stone will be a blind area made of cement mortar laid on top of compacted crushed stone. This option provides better protection for the foundation of the house from destruction by melt and sediment waters. And it is this option for arranging the blind area that involves the implementation of formwork.
A more expensive and high-quality option for constructing a blind area is laying monolithic concrete slabs or reinforced slab products. But such materials cannot be used on heaving and clayey soils, as well as at high groundwater levels, since the structure can quickly deform.
If you are making a concrete blind area, you will need the following tools and materials for the job:
- crushed stone, sand and cement;
- polyurethane sealant for isolating expansion joints between the coating and the house;
- reinforcing mesh;
- nails, screws;
- roofing felt or plastic film;
- edged (unedged) boards or strips of plywood according to the height of the coating being poured;
- level, rule;
- spatula, bayonet shovel;
- container for mixing concrete.
Construction technology step by step
Let's look at the standard instructions for building formwork with your own hands step by step (you will find more recommendations in):
1. Drawing up a foundation diagram, selection and calculation of material.
2. Knocking down shields. The boards are sawn into pieces of the same size, attached to the timber with nails or self-tapping screws, with the heads facing inward. Deviations in level are inevitable (there are none except when using plywood), but it is important that they do not exceed 2-3 cm. Gaps and cracks are unacceptable: large ones are clogged with thin slats, small ones with tow. This stage is easy to carry out yourself; the help of another person is required only with limited lines.
3. Lowering and fastening the formwork panels together. The method of fixation depends on the type: removable ones are twisted from the outside, non-removable ones (made of polystyrene foam, fiberboard or other DSP) - whichever is more convenient. Corners require special attention.
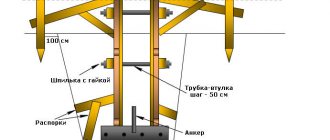
4. Installation of spacers (wooden blocks or pieces of plastic pipes in reusable formwork between panels with a length equal to the width of the strip foundation) and securing the structure from the outside with supports sawed at an angle of 45 °, the second end of which is buried in the ground.
5. Checking strength and deviations from markings. Final fixation, adding sand to the lower section. Line marking the border of the upper edge of the base.
6. Flooring inside the waterproofing film. This step is optional, but it is recommended to carry it out if there are gaps between the boards and for the convenience of removing the formwork. When working with panels made of plywood, plastic or metal, the inner surface should be lubricated with oil.
7. Pouring and spreading concrete inside the foundation formwork: layer by layer, but without significant breaks, compacting every 20 cm and leveling the top edge with a trowel. With correctly selected boards and reliable fixation, the structure does not bend under the weight of the solution and remains motionless when air is forced out. It is this condition that allows you to obtain a stable foundation.
8. Dismantling of formwork - depending on the brand and time of concrete hardening, but not earlier than 3 days. Private developers remove it after 70% hardening - that is, after 2 weeks. The main sign that such an operation is permissible is the appearance of a gap between the concrete base and the formwork. You should not carry out the work yourself, especially when removing large supports.
After this, they proceed to the next stage of constructing a strip foundation with their own hands: waterproofing, if necessary, insulation, backfilling with soil. A slightly different (simpler) step-by-step scheme of actions is observed when installing and operating permanent types of formwork, recommended for construction in areas with heavily frozen soils in winter. Structures with walls made of expanded polystyrene or DSP reduce the load on the foundation and give it stability. They are easy to assemble yourself, but unlike ordinary wooden ones, they remain in the ground (points 8 and 9 of the instructions given are skipped).
If the height of the strip foundation exceeds 2 m, it is recommended that the formwork panels be made from solid materials rather than knocked down from boards. In this case, square structures are considered the most durable; when installing too long ones, the requirements for the number and reliability of stops and internal struts increase. When laying a deep foundation, due to increasing costs, it is worth considering the option of renting formwork.
Contacting specialists (at a minimum, consultation) is required when conducting construction on loose soils. In addition to increasing the number of supports (with a standard step of 0.9-1 m), it is recommended to combine materials, for example, covering formwork boards from the inside with plywood. The opinion of professionals is also important when organizing vertical and lateral supports when the tape rises significantly above the zero mark; in some cases, the latter variety is even screwed to the walls. The standard maximum is 15 cm above the ground level; if it is exceeded, the formwork for the future foundation is supported from all sides.
When choosing internal waterproofing, two factors are taken into account: budget and the size of the filler fractions in the concrete. It is not recommended to use roofing material for these purposes; it is inferior in flexibility to polyethylene (especially in winter). Most often, the choice is made between thick film and moisture-resistant plywood; the second option is optimal when working with heavy coarse concrete.
Reviews
Igor, 45 years old, Ilovaisk : I work as an installer on high-rise buildings. I often install plastic formwork. It’s better not to mess with wooden ones - their prices are jacked up, but the quality of the material is not suitable. The same applies to plywood and polystyrene foam structures, which after one use lose their original properties.
Maxim, 30 years old, Tyumen: Plastic formwork is not a cheap pleasure. However, this material is simply not replaceable in construction - the turnover rate is high (if the construction work is large-scale), the structure is light in weight. People who want to save money often buy used formwork. You shouldn’t neglect it; you can safely buy it, since plastic equipment is reusable.
Anton, 44 years old, Krasnoarmeysk: Due to the fact that the equipment is a constructor, you need to carefully approach the assembly process. Each plastic formwork is accompanied by instructions from the manufacturer, which must be studied before construction and during assembly of parts. In a day I build about a meter of structure. The main advantage of the design is that the plastic formwork is easily washed off after separating the blocks from the dried concrete.
Ivan, 50 years old, Chelyabinsk: Plastic formwork is produced in Russia. The quality of the construction is in no way inferior to that of European importers.
Formwork is an important element in the construction of the foundation for any building. Not only the strength of the foundation, but also the comfort inside the house, as well as the durability of the structure, depend on the quality of the formwork. At the same time, different formwork options differ in many characteristics and therefore it is important to choose the right type of structure.
How to make a structure from boards
Forum members advise how to make formwork panels. To assemble horizontal panels, it is recommended to use an edged board measuring 100x25 mm and 150x30 mm, and for vertical panels, take a 100x50 mm beam, resting it against the panel with its edge
.
The vertical installation step is transverse (beam 50x100 mm) - from 70 to 100 cm. To make the formwork more rigid, two 50x100 mm beams are installed horizontally on each side, top and bottom.
With a well-thought-out design and competent execution, the strength of boards of these standard sizes is sufficient to withstand the pressure of large volumes of concrete mixture on the walls of the structure.
When choosing boards for this design, you must immediately consider the option of their further use. Because formwork for the foundation will require more than one cube; it is irrational to use boards only once. In order for the boards to remain “industrial wood” after dismantling, it is necessary to protect them from direct contact with concrete.
How to attach the film
Before concreting, the inside of the structure is lined with a durable polyethylene film for formwork, which must be secured with a stapler. Construction is best done using self-tapping screws. In this case, it can be easily disassembled, minimizing damage to the formwork boards.
Dmitrievich-50 member of FORUMHOUSE
After dismantling the formwork, I put a 30x120 mm board on the sheathing. Before this, I cleaned the surface of the boards from staples. The main thing is to disassemble everything carefully.
UKSUS70 FORUMHOUSE member
A house starts with a foundation. It’s not difficult to do it with your own hands, say experts and give their advice on step-by-step installation of formwork - a key element of the future foundation of the house. The article, as well as photos and videos, will help you understand the recommendations.
Installation features
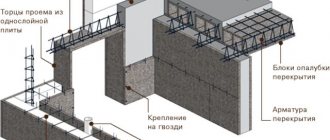
Do-it-yourself formwork for monolithic slabs is carried out according to a single algorithm. The difference in the construction of various structures comes down to the choice of other elements from the kit.
- Surface preparation. It is important to create an even coating by removing debris, moisture, tree roots, etc.
- Inspecting the cleanliness of the plastic. Ideal evenness improves the characteristics of plastic formwork, otherwise it will be difficult to dismantle, and the structure will have less strength.
- Strength of fixation of shields. Plastic plywood for formwork must be firmly fixed to each other; any weak point will provoke shrinkage during the concreting process and curvature of the wall. After installing the plastic, repairs to the mixture will not be necessary if you check the reliability of the fixation at least 2 times.
- Pouring concrete. It is recommended to use a sliding surface, for which the shields are treated with lubricant. After the installation of the plastic formwork is completed, concrete is poured into it.
There is a limitation - it is impossible to fill a container with a thickness of more than 1 m with concrete at one time, the work is carried out in stages. If a removable form is used, it can be dismantled after 1-7 days. It is better to clean the shields with water before the debris hardens.
Rules for uneven terrain
The above instructions assume laying a standard strip foundation; when working on a slope, the process becomes more complicated. In this case, the base is made stepped, at the lowest point the formwork is made higher, at the top the tape should rise above the ground. The bottom is required to be level under any conditions; by analogy, layers of sand and coarser filler are gradually filled in and compacted; it is recommended to fill in a layer of lean concrete.
This type of foundation on a slope will be appropriate when building a house made of heavy bricks (but with differences of more than 1 m, costs unreasonably increase; the height of the strip at the lowest point is not allowed to exceed four times its width); for light buildings, the pile-grillage type is considered a good alternative. The formwork for pouring a hanging grillage is distinguished by the presence of a bottom and additional supports (the weight of the concrete is directed towards it and not towards the ground).
Error Propagation
Technological violations when installing formwork for strip foundations include:
- Using uncut or different-sized boards. The correctness of the cement hydration process depends on the evenness of the inner surface and the absence of cracks. Serious deviations or gaps lead to leakage of the solution and hardening of the tape with uneven walls (more susceptible to the effects of groundwater later).
- Installation of formwork for the foundation from overdried wood (for similar reasons). In this case, preference is given to raw boards.
- Errors when choosing thickness and width. It is wrong to use plywood without support from the deck, or to knock down too thin boards.
- Removal of formwork ahead of time, rough dismantling (tearing off with force).
- Installing formwork on an uneven base.
- Lack of internal struts at the beginning of concreting. There is an important rule: all wooden elements are removed as the formwork is filled with concrete. Only reinforcing ties made of tin can be left inside the tape.
Ignoring the rules is fraught with bending of structures and excessive consumption of concrete, leakage, the formation of uneven walls and difficulties in further finishing the strip foundation. The involvement of specialists is required if concreting is necessary in winter, work is carried out on difficult soils, or installation time is limited.
Incorrectly assembled formwork from boards can be strengthened - just cover it from the inside with moisture-resistant plywood. If it is desired to reuse supporting and panel structures, the removed panels are washed, leveled and dried.
Not a single construction site is complete without concreting, and where there is concrete mortar, there is formwork. The design used in manufacturing deserves special attention. After all, the quality of the foundation for the house largely depends on its reliability.
Pouring formwork can cause the following problems:
- expansion during concreting;
- partial destruction;
- local leaks of concrete mixture.
To avoid this and find out what to make a structure from reliably and cheaply and what the requirements are, take advantage of the practical experience of experts at the FORUMHOUSE website.
Formwork for monolithic slab
Formwork for monolithic slab
Foundations from reinforced monolithic slabs are made for bathhouses built on waterlogged soils or soils with very low load-bearing characteristics. In most cases, the dimensions of the bathhouse do not exceed 4x4 meters. It is quite difficult to pour a large monolithic slab on your own; it is unlikely that you will be able to achieve its ideal horizontal performance.
Step 1. Level the ground surface as much as possible, pour and compact a sand cushion at least 20 centimeters thick.
Compacting a sand cushion with a vibrating plate
Step 2. Prepare the lumber, you will need edged boards and slats. The height of the formwork depends on the thickness of the monolithic foundation; in most cases it is no more than ten centimeters. This means that it is quite enough to have boards 20 cm wide and 20÷30 mm thick.
Step 3. Drive pegs into the corners of the future monolithic slab and pull the rope. Place boards under the rope and secure them with pegs. Drive the pegs firmly into the ground. Place the formwork in the letter “P”, this will make it much more convenient to feed and level the concrete, and you won’t have to step over the formwork every time. When concreting, do not forget about reinforcement.
Step 4. When approximately one meter remains until the end of the concrete slab, install the last board, level it, secure its position and continue pouring concrete.
Formwork for monolithic slab
Video - Box slab foundation
Video - Marking and installation of formwork for a monolithic slab
Video - Formwork and reinforcement strapping of a monolithic slab
Now we can consider several issues regarding the use of additional materials for the manufacture of formwork.