Due to the fact that monolithic low-rise construction is becoming more widespread, the issue of constructing formwork for the floor (floors) is becoming very relevant. Formwork for floors can vary in many ways and have different designs.
Floor formwork on telescopic racks
Below we will explain in sufficient detail what kind of horizontal formwork for floors there are, what are their differences and design features, and how to install the formwork for floors.
Floor formwork: types of structures
Experts recommend that if the ceiling height exceeds 3.5 meters, it is better to use the services of companies that rent out such devices. Or, when funds allow, buy factory-produced inventory formwork.
There are several types of horizontal formwork for buildings. In fact, these products are horizontally laid out panels on fairly powerful supports.
Floor formwork on telescopic racks
- Frame formwork on wedge scaffolding or cup scaffolding;
- Formwork on volumetric racks - used for small areas, characterized by low cost and simplicity;
- On telescopic stands with variable length - one of the most convenient options, telescopic stands will allow you to achieve an ideal horizontal position.
Floor formwork on volumetric racks
To create horizontal formwork elements of the first two types, conventional scaffolding of the specified type is used. These types of formwork are also called “volumetric”, since in them horizontally standing and vertically lying elements are connected into a single system. Thus, ceilings up to 5 meters high are built.
Disadvantages of using a metal shield mold
Despite its light weight and ease of assembly, the aluminum panel mold is not used very often because it is a soft metal and is easily subject to deformation. Also, aluminum formwork is difficult to repair (expensive argon welding is required). Steel formwork is much stronger, its service life is much longer, and therefore the rent for steel formwork is lower. To protect against corrosion damage, paint is used on metal formwork, so you need to be gentle during the installation and pouring process.
To install metal formwork, a flat surface is required, so a tightly compacted cushion of sand or lean mortar is installed under the base. When pouring the sub-wall, you need to make sure that the solution does not get on the metal panels, since once it hardens it is difficult to clean off.
Metal formwork with reinforcement
Wooden floor formwork - components
Wooden floor formwork
Wooden formwork is the most affordable and common type. The advantages of wood include the following:
- To create horizontal formwork, it is not necessary to buy expensive lumber from softwood; soft hardwoods are quite suitable:
- rafter systems can be used;
- To reduce the cost, previously used materials and products are suitable.
Elements for horizontal slab formwork are listed below.
- Racks. This structural element can be made from large cross-section timber.
- Beams that are designed to distribute the existing longitudinal pressure onto the load-bearing posts.
- Braces designed to distribute the existing load between vertical beams.
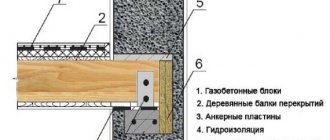
- Shields for holding concrete. The main material for this element is plywood. Plywood floor formwork is not the only option. In fact, any sheet materials that are resistant to moisture, such as profiled metal decking and slate, will do. Laminated plywood would be a good option. In addition to the fact that it is not at all afraid of water, this material is convenient in that it makes subsequent dismantling of the structure easier, since concrete sticks less to this type of plywood.
Wooden posts will need underlays for secure alignment. Thin boards (up to 50 millimeters thick) can be used as deck material. Then it will not be possible to achieve an ideal ceiling surface, which practically does not require rough finishing.
Design characteristics
To create metal formwork, sheets 1-2 mm thick are used. Despite the high cost, the use of this material has its advantages. These include:
- foundation installation of any configuration;
- additional waterproofing;
- versatility;
- creating a completely smooth surface;
- ideal for monolithic and strip foundations (due to reinforcement welded to the formwork);
- simplicity of cladding (with a significant elevation of the base of the house above the ground);
- maximum rigidity;
- resistance to loads without deformation or bending;
- ease of installation work.
Steel formwork has the following technical characteristics:
- shield height - 0.6-3 m;
- their width is 0.25-1.2 m;
- frame turnover is up to 300 cycles, deck turnover is up to 80 cycles;
- deflection - no more than 1/400 of the span;
- concrete pressure - 75-80 kPa.
The frame of the panels is a closed circuit, for the manufacture of which 2 types of profiles are used: rectangular (for stiffeners) and edge (located along the perimeter of the panels). To create the deck, plywood is used, which is up to 2 cm thick.
Floor formwork: instructions for installation and dismantling of wooden structures
Installation of horizontal beams and posts
Before you begin installing the floor formwork, you need to make the necessary calculations. For this purpose, a special computer program “Installation of horizontal formwork” is used. Without an accurate calculation, installing horizontal formwork makes no sense; all the work will go down the drain, since uniform distribution of pressure on the supports will not be achieved.
The following should be taken into account (for construction thicknesses up to 200 millimeters):
- The longitudinal pitch for the racks is 2 meters;
- Rows spaced 25 centimeters apart;
- The pepper beams are laid strictly perpendicularly, the laying step is 62.5 centimeters, adhering to the rule that at least 25 centimeters must remain from the wall to the counter.
How to install floor formwork?
Installation of telescopic stands
Installation begins after the construction of floor columns and concrete beams, which will bear the main load, if any according to the building plan. If the floor in the room does not meet the requirements (not level enough), it is necessary to lay a base of boards, taking into account that each board will have at least one support.
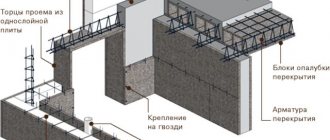
- The first row of racks is formed, to which the upper longitudinal beam is nailed.
- This beam is attached to the wall.
- Strengthen the bases of the racks by laying, if necessary, a board 50 millimeters thick. The racks are plumb in this case.
- After this, the next row is constructed in a similar way.
- At the end of the row installation procedure, the transverse beams are nailed or laid without fastenings, maintaining a distance of 60 cm. The use of spacers without rigid fastenings when installing the longitudinal beams will greatly facilitate the disassembly of the structure in the subsequent period.
- After aligning the structure to make sure the cross beams are horizontal, braces are installed—“diagonal” bars between the posts.
- The next step is to lay moisture-resistant plywood. The sheets must be cut in such a way that the seams fall exactly on the longitudinal bars. Sheets of plywood are also laid without fastening.
- The last stage is the creation of side shields.
Installation of volume racks
Upon completion of assembly, it is necessary to carefully check the strength and rigidity of the structure, the bottom of the deck, all fasteners, and eliminate any cracks found to prevent leakage of concrete mortar.
The installation of the floor slab formwork is completed, you can begin to knit the reinforcement cage. To protect the concrete floor from freezing, bricks are first laid around the perimeter.
You can start dismantling the formwork in a week; in the summer, you can start dismantling it in three or four days; you can read about this in more detail. At the same time, construction work can be continued only after 3 weeks. They begin dismantling the structure from the walls, since they themselves are a support; dismantling the central part can begin on the second day.
Monolithic formwork
An important difference becomes clear from its name. Fixed formwork is not removed after pouring concrete and hardening and remains an important part of the structure. As a material for such a solution, various insulating materials are used, reliable enough to withstand concrete pressure at the time of pouring and with low thermal conductivity, which makes up for the monolithic concrete structure, which quite easily transmits heat and cold. In the end, the result is a wall with several layers, in which concrete is responsible for strength and structural strength, and thermal insulation material retains heat and does not allow cold penetration into the structure. This option also guarantees better protection of concrete from external factors, such as humidity.
In addition, various ready-made panels of cladding material are used, which create formwork for the walls. They also remain part of the structure and provide the proper appearance of the result.
To create permanent formwork with your own hands in a private building, interest is expressed specifically in the option of using blocks of materials for insulation.
Nowadays, various materials are widely used for construction, but initially everything is included in the designs of one-story houses.
What is monolithic formwork made from?
Ready-made blocks of expanded polystyrene or wood concrete are used as material for permanent formwork.
Wood concrete is a material made by mixing wood chips with cement mortar and forming them into specialized empty blocks.
Similarly, you can very quickly build the walls of a house or utility room. As a result, walls appear that are already insulated. Similar variations of wall construction are significantly cheaper than brick masonry and take up little space, thereby guaranteeing more space inside. Moreover, such a structure also weighs less and the foundation can be made based on a lower load.
You need to understand: Polystyrene foam is an excellent insulating material, but it still emits substances that are harmful during operation. Thus, a limitation is imposed, according to which there is no need to construct polystyrene foam formwork for residential premises. Wood concrete blocks will cope better with this task.
Becoming a permanent system
The process of forming walls and formwork for pouring concrete using permanent systems is very simple. To do this, blocks of polystyrene foam or wood concrete are laid in the form of the required wall. The blocks are connected to each other using specialized locks provided on them. In most cases, the process is similar to dry laying a brick wall, only without the necessary dressing, in other words, the blocks are placed in perfect rows, one above the other.
For compacting concrete and high-quality pouring, the blocks are laid in a pair of rows, reinforced and filled with concrete, which is compacted and compacted. Then they start laying the next few rows, and so on.
Reinforcement is placed in special grooves and directly into the vacuums of the blocks, which will add auxiliary rigidity to the entire structure and eliminate the destruction and cracking of concrete. Then all that remains is to pour the concrete.
Monolithic formwork is used to construct walls for buildings with a small number of storeys or to create walls as part of frame structures. As a foundation material, this option is only suitable for small resulting loads.
How to install a front door with your own hands
How to choose the right metal tiles
How to choose the right hood for the kitchen
How to choose the right jacuzzi
How to choose the right roof windows?
« To the article section