Today, sand is one of the most common building materials. This is the main element of construction. Its purchase must be approached thoughtfully.
The specific gravity of sand or specific gravity is the weight that fits in a unit volume. In most cases, a volume of 1 cubic meter is used for sand. In tables and reference books, specific gravity is indicated in grams per 1 cm³, kg per m³ or in tons per m³.
The specific gravity of bulk material can vary from 1500 to 2800 kg per cubic meter.
How much does a cube of sand weigh? Its specific gravity
depends on the following factors:
- grain composition;
- fraction size;
- mineralogical composition;
- size of solid particles - impurities;
- degree of compaction;
- humidity.
Density
Sand is a bulk material. Its density depends on the size of the air layers located between the solid particles. There are several types of density:
- real;
- technological;
- bulk, is defined as the ratio of the mass of sand to the volume it occupies. This value includes all voids and pores;
- conditional or true density is the limit of the ratio of the mass of sand to the occupied volume without taking into account the air cavities present in it.
The true density always turns out to be higher than the real one, and is a conditional, theoretical value. In practice, the material has a density close to bulk.
What affects the weight of sand in one cubic meter
The weight of sand in 1 m3 is expressed as a physical quantity as a bulk material. It is measured in kilograms or tons per cubic meter. In relation to sand, this value can most often fluctuate between 1500 and 2800 kilograms per 1 m3.
This is influenced by many different factors
, among which builders and specialists highlight the following:
- degree of material;
- chemical and mineralogical composition of sand;
- grain size modulus;
- a type of
sand mixture; - sand moisture;
- the size of the fractions that make up the volume, etc.
The above factors directly affect how much a cube of sand weighs. This is due to the fact that this indicator for bulk materials may change periodically.
That is why you should always measure it at the time of purchase or shortly before, since there is a possibility that after transportation or any additional intervention there will be either more or less construction sand.
Such building material as belongs to bulk substances. Because of this, its mass will directly depend on the size of the air gaps between its various components.
Solid particles, due to their loose arrangement among themselves, allow some free spaces within their mass that do not carry any weight.
In accordance with this, the more there are, the less will be the weight of construction sand per 1m3.
Materials scientists distinguish several types of sand density, among which the most common are the following:
- real density
; - technological density;
- . This indicator is determined by the ratio of the weight of the material to the volume it occupies at the time of measurement. This value includes all voids and air gaps in the mass of sand;
- conditional or true density. This value shows the ratio of weight to volume of the material in its most compacted state. It is worth noting that sand, due to its flowability, is not as dense as possible under normal conditions. For this you should use special presses
.
In any case, the true density will always be higher than other indicators. Most often, this value turns out to be even twice as large as the others.
In practice, in the vast majority of cases, only bulk density plays a role, since it is in this state that sand is used for preparation and for construction. Thus, it is necessary to determine how much weight there is in a cube of sand, focusing only on this physical quantity
.
Sand fineness modulus
This indicator characterizes the grain composition of the material. By sifting it through special sieves, the content of gravel fractions of certain sizes in the material is determined. Depending on the size module, it is divided into:
- coarse-grained, with grain sizes greater than 2.5 mm. This may be a quarry or river type of material;
- medium-grained, with fractions from 2 to 2.5 mm;
- fine-grained, with grains from 1.5 to 2 mm.
Grain size affects flow rate
building material and its water requirement.
Based on size, it is divided into 2 groups:
- Class I, this group may include material with grain sizes from 1.5 mm;
- Class II, sand of any size.
Cost of a cube of sand
The price is determined depending on the quality characteristics and monetary costs for production purification of the material. The site contains the necessary information about the affordable cost of the material at the moment in Moscow and the Moscow region.
One of the most inexpensive materials is sand, mined in quarries, as it is loaded and delivered to construction sites directly after extraction. Pre-screened material has a higher cost, and sand processed on washing conveyors is of higher quality. This sand contains no inclusions, no debris or lumps, and the required humidity is achieved by drying after washing. River, also characterized by the absence of debris inclusions, but its surface is polished with water. This material is not suitable for a strong grip as angular edges are required. The small amount of mined sand limits the possibility of fixing a price lower than that of washed sand from the quarries. The most expensive is quartz sand, obtained artificially by crushing natural quartz.
Varieties of sand
Sand can be natural or artificial. Natural species are classified depending on their place of origin.
- River
. It is obtained from the bottom of rivers and is distinguished by its purity. Has a yellow or gray color. The grain size ranges from 0.3 to 0.5 mm. It is used in the preparation of solutions and mixtures, installation of drainages. It is the most common type. - Career
. It is mined by open-pit mining. May be brown or yellow. Contains impurities in the form of dust particles and small stones. Grain sizes can range from 0.6 to 3.2 mm. It is used when constructing trenches and as a topping for foundations and paving slabs. When washed and sifted, it can be used for plastering and finishing work, and the preparation of cement screeds. - Marine
. It is extracted from the bottom of the sea and is of high quality. It can be used in all areas, but is rarely used due to its high cost.
The artificial material is made from hard and dense rocks by crushing them. The result is a material with a homogeneous composition, containing no impurities, but having an acute angular grain shape
. Suitable for preparing high-strength concrete. The most common types are:
- Quartz
, obtained by grinding and scattering white quartz. It is used to create finishing, decorative and welding materials. - Expanded clay
, obtained by crushing expanded clay gravel and crushed stone or by firing small residual clay rocks. This sand is considered clay. It is used in the preparation of lightweight concrete, for backfilling pits, and leveling surfaces. - Slag
. Crushing the slag into small grains is carried out by sharply cooling it with water. This material has grains of various sizes, from 0.6 to 10 mm. Used when mixing concrete mixtures.
Number of tons in 1 m3 of construction sand
Drawing up estimates when performing large-scale construction and installation work requires taking into account all the components that will be used, including bulk ones. Quarry and river sand is an integral part of many cement mixtures. Knowing how much of it is in a cubic meter, you can calculate the amount required for purchase.
Types of sand
Manufacturers measure it per cubic meter, but building compositions are calculated in tons and kilograms. Therefore, it can be difficult to make ordinary calculations with cubic meter conversion in practice.
1. Weight depends on humidity, variety and origin. These factors must be taken into account in the calculation.
2. By origin it can be natural or artificial. Moreover, the second option is somewhat more stable than the first.
| View | Name | Characteristic | |
| Natural | River | It is extracted from the bottom of freshwater reservoirs by dredging; used after preliminary drying: homogeneous; fine-grained. | Low cost per cubic meter; does not require pre-treatment; necessary for mixing solutions. |
| Career | Diverse composition; It is mined in quarries using excavators. In its natural form it is suitable for filling. | Needs additional processing and grain separation; contains a large number of impurities. | |
| Silicate | It has a perfect white color. Suitable as a drainage layer. | It heavily limes the soil, inhibiting plant growth. | |
| Nautical | High-quality universal construction sand. | Has a high cost; it takes a lot of water to wash off the salt; rounded grain shape. | |
| Artificial | Quartz | Homogeneous fine-grained. | For finishing. |
| Expanded clay | Low strength properties. | In the production of lightweight concrete. | |
| Slag | It is obtained by recycling metallurgical waste. | It is very cheap and rarely seen. | |
River and quarry types are in greatest demand among developers. Their size is <0.5 mm, so they can be purchased both for mixing solutions and for forming a drainage system.
What does weight depend on?
The number of cubes per ton is interconnected with the number of impurities, dust particles, and grain size.
1. The nature of foreign inclusions has a great influence on the mass of construction sand. Clay impurities can increase it by more than 7%.
2. When calculating, the particle size modulus must be taken into account.
3. If the material has high humidity, then there will be more sand per ton of cubic meters:
- basic humidity level – up to 6-7%;
- raw – 20%.
The percentage is added during calculations to the bulk of the cube.
| Options | Indicators | ||||||
| Absolute humidity, % | 0 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 20 |
| Bulk, kg/cub.m | 1510 | 1190 | 1160 | 1230 | 1515 | 1775 | 2100 |
4. The average density is in the range of 1300-1800 kg/cub.m, but the value of 1600 is taken as an average option.
5. If the bulk density is known, then the mass can be found out by using the formula: m=V*P, where V is the cubic footage and P is the density. To do the opposite and convert tons to cubes: V=m/P.
6. Generalized indicators of how many kilograms are in one cube of sand, depending on its origin, are shown in the table.
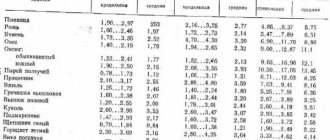
| View | Weight in 1 m3 (t) | Weight in 1 bucket (kg) | |
| River | Dry | 1,4-1,65 | ≈19,5 |
| Compacted | ≈1,59 | ≈18,8 | |
| Coarse grain | 1,47-1,63 | ≈19,3 | |
| Wet | 1,77-1,86 | ≈22,0 | |
| Building | Dry | 1,44-1,68 | 16,9-19,8 |
| Wet | 1,92-2,54 | 22,8-30,2 | |
| Normal humidity (GOST 8736-93) | 1,54-1,7 | 18,2-20,1 | |
| Molding, normal humidity (GOST) | ≈1,7 | ≈20,7 | |
| Career | Medium grain | ≈1,5 | ≈18,3 |
| Fine grain | 1,72-1,8 | 20,9-21,9 | |
| Nautical | ≈1,62 | ≈19,4 | |
| Quartz | Ordinary | 1,41-1,95 | 17,2-23,8 |
| Dry | ≈1,5 | ≈18,3 | |
| Ground | ≈1,45 | ≈17,7 | |
| Compacted | 1,6-1,7 | 19,4-20,1 | |
| gravelly | 1,7-1,9 | 20,1-23,2 | |
| Dusty | 1,61-1,75 | 16,0-21,0 | |
| Expanded clay | 0,4-1,0 | 4,9-12,2 | |
| Mountain | 1,5-1,6 | 18,3-19,4 | |
| Chamotte | ≈1,4 | ≈16,9 | |
| Basaltic | ≈1,8 | ≈21,9 | |
| Ovrazhny | ≈1,4 | ≈16,9 | |
| Natural coarse | 1,49-1,61 | 14,8-16,0 | |
| Natural medium grain | 1,53-1,64 | 18,1-19,4 | |
| Washed | 1,3-1,6 | 15,7-19,4 | |
When calculating how many tons of sand are in a cube, it is necessary to take into account shrinkage during transportation. According to average indicators, it is equal to 10-30% of the total mass.
The degree of density of any substance depends on the air layers present between the particles. Therefore, the small size leads to severe shrinkage. When compared, a cube of material mined from a quarry will be lighter than one taken from a river. The density parameter can be true or conditional, with the true indicator always being higher.
Author: Valentin Tokarev
| Related articles: | |
| What does sand fineness modulus mean? Coarse sand in construction The use of sand in construction | |
Sand classification
- monomineral
consists of grains of one mineral (quartz, mica, feldspathic, hornblende); - polymineral
contains several different minerals (quartz-mica, quartz-feldspathic, mica-quartz, etc.).
To find out how much a cube of sand weighs
, you need to use the formula:
where m is the specific gravity of sand, in kg,
V - volume, in meters cubed,
p—bulk density, in kg per cubic meter.
For 1 m³ the weight is equal to the density of the material. The seller should know what the bulk density is. Humidity averages 6−7%. In the case of wet material, its mass increases to 20%. This difference must be added to the resulting weight.
Mass of a cube of river and quarry sand
These varieties are mined from the bottom of reservoirs or quarries. They are mined using hydromechanical equipment, draglines, dredges, rope scrapers, etc. The materials are mineral chips and are in demand in private construction, arrangement of drainage systems, and landscape work. The specific application depends on the particle size: fine-grained (with a particle size of up to 1.5-2 mm) - for screeds, plaster, and coarse-grained - for the production of concrete and foundation work.
To find out how much 1 cube of sand weighs, use the same method. Fill a 15 liter bucket and weigh. For example, the weight is just over 31 kg. Substitute the data into the formula:
31 kg: 0.015 l = 2066 kg/cu. m
The result obtained indicates that this is compacted, wet quarry sand (its specific gravity reaches 2080 kg/cubic m). This building material is suitable for preparing concrete and for arranging sand cushions, since the particles inside are arranged tightly, which helps create a solid foundation.
How much does a cube of sand weigh?
Different types of material have the following approximate specific gravity
:
- river - 1500 kg per m3;
- sea - 1600 kg per m3;
- quarry - 1500 kg per m3;
- slag - 700−1200 kg per m3;
- quartz - 1400−1900 kg per m3;
- expanded clay - 400−1000 kg per m3.
For sand with different parameters, you can take the following bulk density
(kg per m3):
- for river dry - 1400−1650;
- river wet - 1770−1860;
- river compacted - 1600;
- quarry fine-grained - 1700−1800;
- dry quartz - 1500;
- ground quartz - 1450;
- compacted quartz -1600−1700;
- expanded clay grade 500−1000 - 500−1000;
- made from blast furnace, dump and granulated slag - 600−2200;
- molding normal humidity according to GOST - 1700;
- dusty (with an admixture of dust) - 1600−1750;
- mountain - 1500−1600;
- construction, normal humidity according to GOST - 1550−1700.
When purchasing material, it is necessary to correctly calculate the required quantity. To find out how much you will need, you need:
- multiply the required quantity by a factor of 1.1−1.3, since its volume changes during transportation and storage;
- find out the bulk density at the place of purchase;
- calculate specific gravity.
Don't rush into purchasing. It is beneficial to do this in the warm season and dry weather.
Sand is the material that is considered No. 1 on construction sites.
, without it it is difficult to carry out the construction of various kinds of structures. It is a granular mixture that appears due to the destruction of rocks by water.
There are a sufficient number of varieties of sand, which differ in their characteristics and have different areas of application. It is worth understanding that before starting the construction process, you need to understand how much sand is in a ton.
How to determine the mass of 1 cubic meter?
To calculate how much a cube of construction sand weighs, use the formula:
p = m: V, where m is the mass of the material, V is the volume of the filled vessel, p is the bulk density.
If you need to find out the approximate weight of material stored at your summer cottage, take a standard metal bucket. Fill it, weigh it and substitute the known parameters into the formula. For example, a 10-liter bucket of sand weighs 19.2 kg. Let's make the calculation:
19.2 kg: 0.01 l = 1920 kg/cu.m. m
The result corresponds to the bulk density of wet construction sand, which is indicated in the table above. When wet it is about 20-25% heavier than when dry. If you loosen it and dry it thoroughly, the specific gravity will become significantly less. It is not necessary to carry out complex calculations to determine the exact characteristics. When ordering bulk materials, you can request a batch certificate, which specifies the required parameters. You can also find out how much 1 m3 of construction sand weighs in a matter of minutes. If the type of bulk building material is known, use the calculator on the website!
Varieties
There are a sufficient number of varieties of sand. Each of them has found its application in everyday life and construction. Below are the most common types of sand.
Outwardly, it is a bulk material, not ore.
You can find it at the bottom of the river, which is where it is mined. What distinguishes it from others is that it is the purest of all other types of sand.
The advantage of it is that it does not contain: clay, dust, salt, pebbles, and so on.
This type of sand is extracted in two ways - equator draglines and hydromechanized methods. River sand can be easily distinguished from others by its appearance. It can be white, yellow, or with a gray tint. Sand is used in everyday life and construction.
If we talk about construction, it is used in the manufacture of reinforced concrete structures
, as well as in the manufacture of paving slabs, road slabs and so on. Characteristics: density – 1.5 kg/m3, sand humidity – 4%, specific gravity – 2.65 g/cm3;
Sand is a special bulk material that consists of small granules with a diameter of 0.05-3 mm.
It is formed as a result of the destruction of rocks that contain quartz in quarries. It may contain various types of impurities (clay materials, iron oxide, slag, and so on).
It is the impurities that give the sand a certain shade; if we talk about pure quartz sand, it is milky white. It is used in many areas: sandblasting, glass making, concrete making
and other materials.
Due to its good characteristics, such sand can be painted in any color, which helps to create decorative plaster. Characteristics: humidity less than 10%, clay content 1%;
At its core, sand is an ore-like, granular, granular material. It contains particles ranging in size from 0.7-5 mm. There are 3 main ways to obtain this type of sand: sifting, washing, open method.
Sand contains many impurities: dust, clay, small pebbles, and so on.
This type of sand is used in all foundation work and road construction work.
. Sand characteristics: fineness modulus 0.7-5 mm, impurity content 10%;
It is a non-metallic bulk material. It is easy to find, on the seabed.
Its advantage is that there are almost no impurities in its composition, but there is salt during cleaning. It is he who is considered the most in demand today.
It has a wide range of applications, ranging from banal construction to the production of various dry mixtures. But unfortunately, this type of sand is quite rare
, since it is not always possible and convenient to extract it;
Since the above types of sand are natural (except quartz), artificial sand can also be noted.
It can be created by grinding marble, limestone, and granite. In fact, it has a homogeneous composition, without impurities, and this allows for the correct calculation of its consumption.
Before choosing the right sand, you need to know all its characteristics
, and correctly calculate the volume of sand using rules and formulas. The main characteristics of sand include:
- dimensions, size indicator;
- radioactivity;
- specific gravity;
- a direct indicator of the volume of bulk mass;
- the amount of impurities in the sand;
- coefficient ;
- coefficient ;
- density.
Material characteristics in detail
The capacity of one ton depends on a number of features, one of the main ones being the ratio of body weight to the volume it occupies. The level is determined by the presence of air gaps. For example, bulk density is expressed by the ratio of specific gravity and volume occupied by the material. Moreover, not only solid particles are taken into account, but also pores and voids. True density is the maximum indicator of the ratio of specific gravity and volume minus voids and pores.
Important! The density of river sand is 1.3, quarry sand is 1.4 t/m3.
How many kilograms in a cube of sand also depends on the size of its fractions. To understand this, it is sifted through a (special) sieve. If done correctly, you can estimate the “concentration” of gravel particles of specific sizes. A “bulk” of 1.5-2 millimeters is considered small, medium 2-2.5, and coarse more than 2.5 mm. Taking this indicator into account, sand can be divided into classes. The cost of sand in the Moscow region depends on this.
Properties of sand, its forms and types
The sand itself is not homogeneous, as it consists of different grains, and based on this it can be divided into:
- coarse
sand, containing grains with a diameter of 0.5-5mm;
- medium-grained
bulk material, consists of grains 0.05-0.25mm;
- the finest
type of sand, fine-grained - 0.25-0.05mm.
Sand differs not only in color, the shape of its grains can also be different: rounded, angular, sharp, and so on. The shape depends on the transport of material by wind or water.
Speaking about its composition, it is also divided into several main types:
- sand, which consists of a single mineral.
For example, quartz sand or carbonate sand. In the literature you can find the name - oligomictic; - sand, which consists of different minerals. It could be quartz sand with impurities. In technical dictionaries you can find the name - polymictic.
its composition and classification, calculation, specific gravity factors
No construction site is ever complete without such a material as sand; in addition, it is widely used for the production of foundry molds and glass. It appears in nature through the destruction of rocks by water, weathering and the force of the atmosphere. This material may vary in composition, grain size, location and conditions of formation. In addition, you need to know how much of it is contained in one cubic meter.
Physical differences
The composition of sand includes a great variety of different minerals, rock particles, and possibly the ingress of skeletons of organisms.
Its composition can vary even within the same deposit; this is due to additional impurities, which are very diverse.
It is classified according to the following indicators.
By grain size:
- sand dust;
- fine fraction;
- large faction;
- gravel;
- crushed stone
By location and conditions of formation:
- dune;
- dune;
- river;
- nautical;
- mountain.
By composition:
- lime;
- magnetic;
- quartz;
- gold-bearing.
Sand consists of fragments of the following minerals:
- feldspars;
- quartz;
- mica;
- various impurities, such as small fragments of rocks and skeletons;
By grain size:
- coarse-grained;
- clayey;
- medium grain;
- fine-grained;
- dusty.
Sand can vary in density, the pattern is as follows: the finer the grains, the stronger their compaction occurs. This may also be influenced by other factors acting from the external environment. Setting the weight of sand to 1 m³ is not so simple; it must be calculated taking into account many rules, such as its composition, grain size, density, humidity and others.
Factors that influence specific gravity
Sand can perfectly absorb and retain moisture, and this factor can significantly increase its mass of 1 m³. It is for this reason that when measuring its weight, its moisture content must be taken into account .
In addition, you need to know that the finer the grains, the more moisture they absorb, and the weight of dry material and with high humidity can vary by more than one and a half times. The second factor affecting mass is its density . Since it is a granular material, it tends to compact and loosen depending on the impact. When loading and unloading the machine, the sand loosens, its density decreases, as well as its weight per 1 m³. During transportation of the material, it can become significantly compacted, then the weight of 1 m³ will be significantly greater, and its total volume will become smaller. The degree of compaction may depend on the composition of the material, for example, river sand is less compacted than quarry sand.
Rules for converting tons to cubic meters
To find out how many tons of sand are in a cubic meter, you need to know the following data about the material:
- Density of the material.
- Sand moisture.
- The degree of its compaction.
You can take an example of fine-grained quarry sand , usually its density is 1700 - 1800 kg/m3, and the humidity should be in the range of 6 - 7%.
1 m³ of such material will weigh about 1.7 - 1.8 tons.
You can calculate the weight that an average dump truck can transport. The volume of its body is usually 12 m³, therefore:
1700 kg * 12 m³ = 20400 kg, that is, 20.4 tons.
If the humidity of the sand reaches 20%, then its mass will increase by 4 tons, therefore, one dump truck can accommodate about 25 tons of such material.
Next, you can look at the table, which provides information on the mass of 1 m³ of this or that type of sand.
| Type of material | Number of tons in 1 m3 |
| Dry | 1,21 — 1,75 |
| River | 1,5 |
| River compacted | 1,59 |
| River coarse | 1,47 — 1,63 |
| Building | 1,68 |
| Construction dry friable | 1,44 |
| Construction dry compacted | 1,68 |
| Career | 1,5 |
| Quarry fine grain | 1,72 — 1,8 |
| Quartz regular | 1,41 — 1,95 |
| Nautical | 1,62 |
| gravelly | 1,7 — 1,9 |
| Dusty | 1,61 — 1,75 |
| Natural coarse | 1,49 — 1,61 |
| Natural medium grain | 1,53 — 1,64 |
| Normal humidity for construction work | 1,54 — 1,7 |
| Mountain | 1,5 — 1,6 |
| Chamotte | 1,4 |
| Perlite | 0,074 — 0,4 |
| Ovrazhny | 1,4 |
| Alluvial | 1,65 |
| Medium size | 1,5 — 1,7 |
| Large | 1,53 — 1,6 |
| Small | 1,7 — 1,8 |
| Washed | 1,3 — 1,6 |
| Compacted | 1,68 |
| Wet | 1,92 |
| Wet | 2,08 |
| Water-saturated | 3 — 3,2 |
| Pumice | 0,5 — 0,6 |
| Soil sand | 2,66 |
| Sand and crushed stone | 1,5 — 1,8 |
| Sand and cement | 1,1 — 1,7 |
| Clay red brick fight | 1,2 |
| Magnesite | 2 |
| Titanium alumina | 1,7 |
| Basaltic | 1,8 |
This table does not show all types of material, but the main ones that are most often used in construction and other work. The mass is also not absolutely accurate, since it constantly changes depending on density and humidity.
Exact calculation of the required quantity
It is almost impossible to accurately calculate the amount of sand for a number of reasons.
For a mathematically accurate calculation, it is necessary to conduct laboratory research and find out the exact density of the material, the degree of its compaction and humidity. The last two data are subject to constant change due to weather conditions. It is for these reasons that converting tons into cubes and vice versa is an extremely difficult task, and calculating the exact volume of the required material is almost impossible. Based on all this, approximate data for calculations are accepted, usually the humidity is considered to be 7%, and the density of sand is 1600 kg/m3. The error of specific calculations is more cost-effective than the prices for laboratory work and studies of the physical properties of the material.
To correctly calculate the volume of sand required for certain work, you should always take 1 to 3 cubic meters more. This is due to changes in the volume of the material during transportation, it is significantly compacted, and may also dissipate a little. When purchasing, a coefficient of 1.1 - 1.27 is usually used to take into account all changes in the material during transportation and storage that may arise from weather factors.
plita.guru
Why know the density of sand, why is it needed?
Almost all building materials are either artificial or natural. Speaking about the last option, it consists of grains with a size of 0.16-5 mm, and its bulk density is in the range of 1300-1500 kn/m3.
Sand of natural origin is most often used in construction and everyday life.
Whatever type of sand you choose, you need to know that it has one very good property - it absorbs moisture, removing it from other finished products, while increasing its flowability. It is logical that if the volume changes, then the bulk density itself changes, which in turn depends on how the humidity changes.
If, for example, humidity fluctuates in the range of 3-10%, then this material differs from dry material in its density. It is worth understanding that a grain of sand, which is covered with a layer of water, increases in volume, and this leads to an increase in the density of the sand.
This suggests that when calculating construction work, it is worth taking this into account (bulk density) and knowing how the density changes as humidity increases. It is the level of sand quality that depends on its density.
The density of different types of sand, such as or will vary slightly from each other.
This is a very necessary characteristic, especially when it comes to professional construction, since this property affects the strength of the object and, accordingly, its service life.
There are two types of sand density
:
- True.
This value is influenced
Some factors to consider:
- the amount of impurities in the material itself (clay, dust, debris);
- immediate humidity level. A fairly humid factor, it is this that influences the density. If the humidity increases to 10%, then the density of the sand decreases, as different lumps form in it. But in such a situation the volume increases;
- particle size
. Since sand consists of small grains, to take into account its density, you need to know the fraction of the material; - You also need to take into account the type of sand, which depends on where the sand is mined.
For more information on determining sand density, watch the video:
Classification
M=V*P, where V is the volume of material, measured in cubic meters, and P is the bulk density in kilograms per cubic meter.
It is worth noting that the weight of 1m3 of sand is the same as the density of this material. The person selling the product should have information about the bulk density of the mixture.
The average humidity of this building material is 5-10 percent.
If it is too wet, this indicator can increase the weight by a fifth. Thus, for example, the weight of 5 cubic meters of river sand, the mass of which is 1500 kg/m3, will be equal to 5 * 1500 = 7500 kilograms (that is, 7.5 tons).
Using such simple arithmetic operations, you can calculate the number of machines of a given material that will be needed to carry out certain construction tasks. This saves money and time.
During the construction of structures, these factors play a significant role and are of great importance.
For more information about how much a cube of sand weighs, watch the video:
Specific gravity, what affects it
- this is a value that shows how much weight a material takes up relative to its volume.
The calculation is carried out using a simple formula: specific gravity = mass/volume.
This value is affected by two main characteristics that you need to know and take into account:
- density. Since sand is a bulk material, it is logical that it can loosen, or, conversely, become compacted from various influences. For example, during unloading and loading, sand loosens, its density decreases, and the mass per cubic meter also decreases;
- when the car drives, the material becomes compacted (as the body shakes). The weight per 1 cubic meter increases, but at the same time the volume will become slightly smaller. For example, it can be noted that river sand is less compacted than quarry sand;
- moisture absorption and retention
. Sand itself is a material that easily absorbs moisture and retains it, and this affects the increase in mass per cubic meter.
It is advisable to know how to calculate the volume of sand in m3, so that when purchasing the material you do not make a mistake in its weight. There is a certain procedure that helps to make the correct recalculation. In order to carry out this process, you need to know the following sand parameters:
- density of the material (you can take it from the reference table, since this value is already known);
- humidity
;
- immediate compaction level.
To show the whole situation clearly, you can take a fine-grained type. The density of such material is 1700 kg/m3. Humidity of the material is 6% -7%. This means that such material will have a weight of 1.8 tons with a volume of 1 cubic meter.
Laying tiles on a warm floor is no different from the standard procedure and does not require a special approach. all about the different types and properties of tile adhesives for heated floors.
Currently, decorative plaster has become quite fashionable and widespread among the population. By clicking on, you will become familiar with the technology of its application.
Bathroom wall panels are quite durable, they are easy to install, they cope well with temperature changes, are durable, and are easy to dismantle and remove. about the features of their selection and installation.
Many people are interested in the question of how much sand is in a Kamaz truck, since transportation will be carried out by just such vehicles. Using the same example. The body size (average) is 12 cubic meters, we calculate the required weight:
1700 kg* 12 m3 = 20.4 tons. If the sand is wet, and this figure reaches 20%, then the weight of the material increases by as much as 4 tons. This shows that one dump truck can accommodate approximately 25 tons of sand.
If the construction is not very large-scale, then sand can be taken in bags. This is convenient in terms of transportation and storage. The volume of sand in a 50 kg bag is 0.038. This information is needed in order to make the solution in the correct proportion, because during construction the concepts used are m3, not kg.
One cubic meter (cube, m3) of sand is how many tons?
| Name | Weight 1 m 3, (kg) | Capacity in a 12 l bucket, (kg) |
| Construction sand of normal humidity, corresponding to GOST 8736-93 | ||
| River sand compacted | ||
| River wet (over 6–7% humidity) | ||
| Dusty quarry sand | ||
| Quarry fine grain | ||
| Sand and gravel | ||
| Cement |
If, on the contrary, we convert from tons to cubic meters, then the table will also come in handy. For example, 5 tons is how much? Answer: 5 t ː 1.7 t/m 3 = 3 m 3.
The table shows the average bulk density. The same river sand varies from 1.45 tons to 1.6 tons - this is quite a big difference. Any material has its own specifics, which are expressed in the degree of moisture, fractionation and grain shape.
Characteristics of sand that you should know when purchasing building materials:
- 1. The wetter the sand, the denser and heavier the bulk density will be. Material stored outside in winter increases its weight by up to 15% due to snow and ice.
- 2. The grain size depends on the geological and climatic characteristics of the deposit. The larger the grain of sand, the larger the bulk area and the lighter the weight. Accepted sand material size modules: fine - 1.5–2 mm; average - 2–2.5 mm; large - from 2.5 mm.
- 3. Raw materials from a reservoir are characterized by roundness, ensured by the action of water and friction. The material from the quarries is more angular, which gives better results in the adhesion of solutions. If a mechanical impact has been applied to the substance, the flakiness index increases (the presence of flat, needle-like grains of sand). High flakiness slightly reduces the strength of the finished product. For a private building that does not involve multi-story and heavy structures, this is not a fundamental factor.
- 4. Bulk density varies depending on the degree of compaction, which increases when shaking, and decreases when pouring or unloading. Having decided on the amount of bulk building material required for construction, it is recommended to multiply the weight by a compaction coefficient of 1.1–1.3.
In construction technologies, the content of impurities in the composition of natural components is of great importance. The quarry material contains dust, clay, and foreign substances (small stones, plant remains). When creating a durable foundation, impurities play a negative role, so professionals use washed construction sand. Cement or concrete mortar made from a dirty dry mixture cracks. For leveling and landscaping work, the presence of additional elements is not essential. To create plaster mixtures, clay is used as a separate component.
There is artificial sand, which is made from quartz, slag and expanded clay. Such material is rarely used for private construction, especially since natural sand is the most common rock on the planet.
If you need to know the weight for construction, then you can do without weighing. To obtain accurate values, it is advisable to purchase sand in warm and dry weather.
How much does 1 cubic meter of ASG OPGS weigh, the weight of 1 m3 of ASG OPGS. The number of kilograms in 1 cubic meter, the number of tons in 1 cubic meter, kg in 1 m3. Bulk density of ASG OPGS and specific gravity.
What do we want to learn today? How much does 1 cubic meter of ASG OPGS weigh, the weight of 1 m3 of ASG OPGS? No problem, you can find out the number of kilograms or the number of tons at once, the mass (weight of one cubic meter, weight of one cube, weight of one cubic meter, weight of 1 m3) is indicated in Table 1. If anyone is interested, you can skim the small text below and read some clarifications. How is the amount of substance, material, liquid or gas we need measured? Except for those cases when it is possible to reduce the calculation of the required quantity to the counting of goods, products, elements in pieces (piece counting), it is easiest for us to determine the required quantity based on volume and weight (mass). In everyday life, the most common unit of volume measurement for us is 1 liter. However, the number of liters suitable for household calculations is not always an applicable way to determine the volume for business activities. In addition, liters in our country have not become a generally accepted “production” and trade unit for measuring volume. One cubic meter, or in its abbreviated version - one cube, turned out to be a fairly convenient and popular unit of volume for practical use. We are accustomed to measuring almost all substances, liquids, materials and even gases in cubic meters. It's really convenient. After all, their costs, prices, rates, consumption rates, tariffs, supply contracts are almost always tied to cubic meters (cubes), and much less often to liters. No less important for practical activities is knowledge of not only the volume, but also the weight (mass) of the substance occupying this volume: in this case we are talking about how much 1 cubic meter weighs (1 cubic meter, 1 cubic meter, 1 m3). Knowing mass and volume gives us a fairly complete idea of quantity. Site visitors, when asking how much 1 cube weighs, often indicate specific units of mass in which they would like to know the answer to the question. As we noticed, most often they want to know the weight of 1 cube (1 cubic meter, 1 cubic meter, 1 m3) in kilograms (kg) or tons (t). Essentially, you need kg/m3 or t/m3. These are closely related units that define quantity. In principle, a fairly simple independent conversion of weight (mass) from tons to kilograms and vice versa is possible: from kilograms to tons. However, as practice has shown, for most site visitors a more convenient option would be to immediately find out how many kilograms 1 cubic meter (1 m3) of ASG OPGS weighs or how many tons 1 cubic meter (1 m3) of ASG OPGS weighs, without converting kilograms into tons or vice versa - quantities tons to kilograms per cubic meter (one cubic meter, one cubic meter, one m3). Therefore, in Table 1 we indicated how much 1 cubic meter (1 cubic meter, 1 cubic meter) weighs in kilograms (kg) and tons (t). Choose the table column that you need yourself. By the way, when we ask how much 1 cubic meter (1 m3) weighs, we mean the number of kilograms or the number of tons. However, from a physical point of view, we are interested in density or specific gravity. The mass of a unit volume or the amount of substance contained in a unit volume is bulk density or specific gravity. In this case, the bulk density and specific gravity of ASG is OPGS. Density and specific gravity in physics are usually measured not in kg/m3 or tons/m3, but in grams per cubic centimeter: g/cm3. Therefore, in Table 1, specific gravity and density (synonyms) are indicated in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3)
As you know, there is no smoke without fire. Likewise, the construction process cannot happen without building materials. provides non-metallic materials with a wide spectrum of action. They can be used for different purposes. In the first case, this is an independent type of building materials, which are used either for making foundations for buildings and structures or as ballast for railways and roads. In another case, bulk non-metallic materials act as a filler for concrete, mortars and other mixtures.
We offer materials with delivery throughout Perm at the following prices:
| Name | Bulk density t/m3 | Material strength | Price including VAT (18%) rub. |
| Crushed granite | |||
| Fraction 5-20 | 1,69 | ||
| Fraction 10-40 | 1,67 | ||
| Fraction 20-40 | 1,52 | ||
| Fraction 40-70 | 1,54 | ||
| Fraction 5-20 | 1,42 | ||
| Fraction 20-40 | 1,45 | ||
| Fraction 40-70 | 1,42 | ||
| Fraction 0-10 (elimination) | |||
| Fraction 20-40 | 1,26 | ||
| Fraction 40-70 | 1,45 | ||
| Other materials | |||
| PGS | |||
| Gravel 5-20 | 1,58 | ||
| Fine river sand | |||
| Medium river sand | |||
| Peat | |||
For orders over 500 tons, discounts of up to 10% are possible, and for regular customers - deferred payments!
This is interesting to know!
Bulk non-metallic materials can be distinguished by certain characteristics: by density, by grain size, by shape, by origin. Based on their density, non-metallic materials are divided into dense (density more than 2 g/cm3) - sand, crushed stone, and porous (density less than 2 g/cm3) - expanded clay, etc. Based on their origin, they can be natural, artificial, or from industrial waste. The shape of grains among bulk non-metallic materials can be different: if it is round, then it is probably gravel or natural sand. And if it’s angular, then most likely it’s crushed sand or crushed stone. engages in the sale of bulk non-metallic materials, such as construction sand, crushed stone, gravel, sand and gravel mixture (SGM).
ASG is a sand and gravel mixture. Indispensable for road construction, foundation filling and other construction purposes. Pourable density 1.6 (gravel grain content up to 25%).
PGS - poured density 1.7 (gravel grain content not less than 60%)
River sand - Can be used to prepare mortar for brick laying.
Sand - Plays a significant role in the production of various types of concrete and asphalt, and also to reduce ice on winter roads.
Gravel - Used for concrete, as well as in special cases of construction.
Gravel (fractions 20-200) - used for road construction.
Crushed gravel is used in the production of concrete.
Crushed granite - used for the production of concrete and jointing in road construction.
Is it possible to carry out an accurate calculation of sand?
Of course, it is difficult to calculate the exact volume of sand per ton, since for this you need to know the characteristics described above. But in order to know these numbers, it is necessary to conduct laboratory studies, for this you need to have exact numbers, and not those that we see in the tables (rounded).
Parameters such as humidity and compaction change depending on the weather. This is what affects the exact calculation of the volume of sand, but it is extremely difficult to do this.
To make the task easier for the builders, it was decided to take approximate figures for calculation:
- humidity – 7%;
- density – 1600 kg/m3.
Of course, there will be a small error in the calculation, but it is more cost-effective than the decision to conduct laboratory research. The volume of sand is calculated approximately.
But in order to get clearer data, it is worth taking 1-3 cubic meters more.
This is necessary to take into account the losses that occur during transportation - compaction, dissipation.
How many tons of sand in a cube (1m3): tables, online calculation
Sand is usually measured in cubic meters when sold in hardware stores. But there are calculations for various mixtures, which are based on measurements in tons or kilograms. Making a recalculation in practice turns out to be very difficult. As a result, you almost have to weigh the control volume in the form of a bucket, and then make an adjustment for cubic meters. This approach gives a large error, so it is best to find out how the density of sand depends on various factors. There are a lot of them, but everything is predictable if you have certain knowledge.
Varieties of sand
Experts in this field count several dozen varieties, but in everyday use the generalized concept of “construction sand” most often applies. For these purposes, the following types of this material are used:
- River sand . Contrary to popular myth, it is taken not from the shore, but from the very bottom of the river bed. This material is extracted by dredging and then either thrown ashore by an earthen shell or stored on barges. Next, it is dried, after which it is used for its intended purpose. This is pure sand, but does not require pre-treatment. The quality is not inferior to the next variety, but costs several times less.
- Alluvial sand . It is formed as a result of artificial washing of quarry sand with a large amount of water under pressure on sieves.
- Silicate sand . It has a dazzling white color. It can be used as a cheap drainage layer, but there is a limitation in its use - it can lime the soil, making it impossible for trees to grow on the site.
- Quarry sand . It is mined in specialized quarries using excavators and does not undergo any additional processing.
- Sea sand . It is completely unsuitable for concrete mixtures for two simple reasons. The first is that it is salted, and to wash off all the salt, you will need to spend too much water. The second is that it is ground by the surf until the grains of sand are rounded, which then negatively affects the overall strength of the concrete.
What affects the weight of one cube of sand
There are several main factors that determine the mass of sand:
- Humidity . This factor can be considered variable, but it is very relevant when measuring the weight of sand, due to the fact that most construction sand is stored in open areas. Even if he lies under a canopy, it doesn’t matter. Because sand absorbs and retains moisture very well, and this significantly increases the mass of 1m³ of sand.
- Density _ A factor such as density has a significant impact on the mass of sand, since it has the ability to compact and loosen when exposed to external factors. For example, during loading and unloading of sand, it loosens and, in turn, its density becomes less and its weight per 1 m³ also decreases. During transportation, sand, on the contrary, is compacted and the mass of 1 m³ of sand will increase and the volume will decrease.
- Presence of third-party inclusions . This can be clay, various roots, leaves, mollusk shells. It should also not be ruled out that these inclusions may be present as fragments, which also needs to be taken into account when measuring mass.
- Formative rock . Typically sand is formed from quartz and quartzite rocks. But the presence of impurities of another rock, even in an amount of 10% of the total volume, can significantly change the density and, in turn, the mass of sand.
- Fraction size . Grain sizes have an impact on the consumption of building material and its water demand.
Converting sand from cubic meters to tons
The most accurate calculation is the dependence of bulk density on humidity, because the more moistened the sand is, the more it depends on the amount of water. It fits more tightly into containers when poured.
Table of dependence of sand density on absolute humidity
| Absolute humidity (%) | 0 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 18 | 20 |
| Bulk density (kg/m3) | 1510 | 1190 | 1160 | 1230 | 1515 | 1775 | 2100 |
An abnormally low mass per cubic meter for a certain humidity is possible due to clumping and changes in the adhesive characteristics of the mixture. Low humidity levels depend on the permeability of the material. Maximum sand moisture is 20%. If there is more water, it is considered unfit for sale.
In order to convert sand from cubic meters to tons you need:
- First you need to determine the bulk density of the material. Which, as we already know, is measured in kilograms per cubic meter. We can determine the density value of sand from a physical reference book or use the above table. Ideally, the density of natural sand is 1300 kg/m3, but it can increase with increasing humidity.
- Then you can determine the mass of sand using the formula: m = V*P (V – volume (number of cubes), P – density).
- Then convert the result into tons from kilograms, dividing the resulting value by 1000.
For example, we have 15 cubic meters of wet sand (V), the density (P) of which is 1500 kg/m3. In order to determine the mass (m), we multiply the volume by the density and divide the result by 1000:
m = V*P
m = 15 m3*1500 kg/m3 = 22500 kg
22500/1000 = 22.5 tons.
As a result of the calculations, it turns out that 15 m3 of wet sand weighs 22.5 tons.
Table of mass of 1 m3 of sand of various types
| Type of sand | Number of tons in 1m³ |
| Dry | 1,21 — 1,75 |
| River | 1,5 |
| River compacted | 1,59 |
| River coarse | 1,47 — 1,63 |
| River dry | 1,4 — 1,65 |
| River wet | 1,77 — 1,86 |
| Building | 1,68 |
| Construction dry friable | 1,44 |
| Construction dry compacted | 1,68 |
| Construction wet | 1,92 |
| Construction wet compacted | 2,54 |
| Construction, normal humidity according to GOST | 1,54 — 1,7 |
| Molding, normal humidity according to GOST | 1,7 |
| Career | 1,5 |
| Quarry fine grain | 1,72 — 1,8 |
| Quartz regular | 1,41 — 1,95 |
| Quartz dry | 1,5 |
| Quartz ground | 1,45 |
| Quartz compacted | 1,6 — 1,7 |
| Nautical | 1,62 |
| gravelly | 1,7 — 1,9 |
| Dusty | 1,61 — 1,75 |
| Slag | 0,7 — 1,2 |
| Expanded clay | 0,4 — 1 |
| Pumice | 0,5 — 0,6 |
| Mountain | 1,5 — 1,6 |
| Chamotte | 1,4 |
| Perlite | 0,074 — 0,4 |
| Magnesite | 2 |
| Basaltic | 1,8 |
| Ovrazhny | 1,4 |
| Alluvial | 1,65 |
| Titanium alumina | 1,7 |
| Natural coarse | 1,49 — 1,61 |
| Natural medium grain | 1,53 — 1,64 |
| Medium size | 1,5 — 1,7 |
| Large | 1,53 — 1,6 |
| Small | 1,7 — 1,8 |
| Washed | 1,3 — 1,6 |
| Compacted | 1,68 |
| Wet | 1,92 |
| Wet | 2,08 |
| Water-saturated | 3 — 3,2 |
| Soil sand | 2,66 |
| Sand and crushed stone | 1,5 — 1,8 |
| Sand and cement | 1,1 — 1,7 |
The data presented can be considered generalized indicators. But with this knowledge, calculating the mass of sand is much better than making calculations without knowing the real values. As practice shows, it is still better to measure bulk materials in cubic meters. Sand is rarely measured by mass because it varies depending on humidity, and there are no accurate hygrometers to measure this indicator yet.
Online form for calculating sand mass
remontnichok.ru
conclusions
Sand has a wide range of uses
. The main one is the construction of various kinds of objects. But this is not the only option where such material can be used. Sand is used in the agricultural industry and in housing.
In addition, in recent years, sand has found its use in landscape decoration. Also, bulk material is used during the production of flooring and in welding production.
It doesn’t matter what type of sand you choose for your work, you should correctly calculate the volume of sand in 1 ton in order to buy the right amount of material and correctly calculate the estimate.
Today sand is an important and necessary material
, without which it is difficult to imagine construction of any scale. When buying sand, pay attention to all its characteristics and data.
How many tons are there in a cube of sand?
Construction sand is one of the main components of most mortars. It is needed for drainage pads and foundation concrete, and is used in masonry mixtures and leveling plasters. And until you finish construction, it will be required constantly.
Varieties
The classification of sand is based on its origin. Natural types include:
- River sand is the most popular in construction. The pure mass, raised from the bottom of freshwater bodies of water, is excellent for preparing solutions due to its fine grain.
- Quarry is a material that is heterogeneous in its fractional composition with a large number of impurities. In its natural form it is used only for filling. But after washing and sifting into size classes it becomes no worse than river water.
- Marine is the highest quality and in every sense universal type. But its cost is quite high and therefore, like ordinary construction sand, it is almost never used.
Artificially, the granular mass is obtained after crushing various rocks. This filler is ideal for preparing particularly strong concrete due to its high roughness.
Main types of artificial sand:
- Quartz is a universal option, but it is better to leave it for finishing work.
- Expanded clay - suitable only for lightweight concrete.
- Slag is an inexpensive type of bulk materials obtained by recycling metallurgical waste.
Unlike natural ones, all artificial types are monomineral materials and have stable characteristics.
What affects the weight of 1 cube
The average density of sand is in the range of 1500-1800 kg/m3. But this is too large a run-up to be guided by when making calculations. Therefore, first of all, you need to start from the selected type of bulk building material. If you don’t know what kind of sand it will be and how much it weighs, it is recommended to use an average of 1600 kg/m3.
The accepted specific gravity is then adjusted depending on other factors:
Silty and fine-grained fractions have not been used in construction, so this parameter can be neglected.
- The number and size of particles of foreign inclusions (usually clay).
For example, river sand can contain only 0.3-0.7% impurities, and quarry sand up to 7%. Then for the first the weight of one cube will hardly increase, but for the second it will increase to 1.75 tons.
- Moisture contents.
This indicator changes not only the weight, but sometimes also the volume of the sand mass. That is why it is better to buy it immediately, as much as you need, in the summer, even if construction is planned for a later date. For a state of normal humidity, the number of tons per cube must be increased by about 6%, that is, the net weight must be multiplied by 1.06. As a result, the river sand from our example will weigh up to 1700 kg, and the quarry sand will weigh 1855 kg.
If the material is offered wet, the tons per 1m3 will be 20% more. This time we will multiply the density indicators by 1.2. Then in one cube the weight of two types of sand will be 1920 and 2100 kg, respectively.
In quarries, construction sand has its natural density; during transportation and sale, it changes and turns into bulk. Artificially compacted material is obtained during the process of laying it on the ground, and how much of it is required depends on the degree of compaction. For construction calculations, only bulk weight is needed.
Weight calculation
If the bulk density is known, it is easy to determine the mass of any volume of sand - simply multiply the specific gravity by cubic meters. But when there is no exact data, an approximate figure can be obtained as we did above.
In cases where it is necessary to determine how many cubes are in a ton of sand, the calculation is performed in the reverse order - the mass of the batch is divided by the density. Please keep in mind that during delivery by road, bulk materials shrink. In order not to make a mistake with the cost of the order, it is better to calculate it like this:
- Determine how much sand is needed for all planned work in units of volume.
- Allow about 10-30% shrinkage during transportation.
- Based on bulk density (you can check with the seller or take the average parameter), convert the volume into tons.
Price
| View | Tons per cube | Price per ton, rubles |
| River | 1,45 – 1,5 | 950 – 1 700 |
| Career | 1,7 – 1,8 | 850 – 1 500 |
| Quartz | 1,5 | 4500 – 5 000 |
| Expanded clay | 0,5 – 1,0 | 1 900 |
| Nautical | 1,6 | 6 000 |
Similar articles
- Cost of finishing a balcony: how much does it cost to finish it yourself, video instructions, photos
In order to say how much it costs to finish a balcony, you first need to imagine its design, and also determine in advance what will be… - Paint consumption rates: video instructions for DIY installation, how to calculate how much is needed per square meter, calculator, price, photo
How to calculate paint consumption for a known surface area? In what cases can paint consumption per 1 m2 significantly exceed that specified by the manufacturer... - Plastering a garage: video instructions on how to plaster it yourself, which is better, how much it costs, price, photo
Today, no construction is complete without plastering work. Even though with the advent of drywall (many prefer...
www.ristroy.ru
How many tons are there in a cube of sand?
Construction sand is one of the main components of most mortars. It is needed for drainage pads and foundation concrete, and is used in masonry mixtures and leveling plasters. And until you finish construction, it will be required constantly.
Varieties
The classification of sand is based on its origin. Natural types include:
- River sand is the most popular in construction. The pure mass, raised from the bottom of freshwater bodies of water, is excellent for preparing solutions due to its fine grain.
- Quarry is a material that is heterogeneous in its fractional composition with a large number of impurities. In its natural form it is used only for filling. But after washing and sifting into size classes it becomes no worse than river water.
- Marine is the highest quality and in every sense universal type. But its cost is quite high and therefore, like ordinary construction sand, it is almost never used.
Artificially, the granular mass is obtained after crushing various rocks. This filler is ideal for preparing particularly strong concrete due to its high roughness.
Main types of artificial sand:
- Quartz is a universal option, but it is better to leave it for finishing work.
- Expanded clay - suitable only for lightweight concrete.
- Slag is an inexpensive type of bulk materials obtained by recycling metallurgical waste.
Unlike natural ones, all artificial types are monomineral materials and have stable characteristics.
What affects the weight of 1 cube
The average density of sand is in the range of 1500-1800 kg/m3. But this is too large a run-up to be guided by when making calculations. Therefore, first of all, you need to start from the selected type of bulk building material. If you don’t know what kind of sand it will be and how much it weighs, it is recommended to use an average of 1600 kg/m3.
The accepted specific gravity is then adjusted depending on other factors:
- Grain size and fractional composition - the finer the grains of sand, the denser they are packed.
Silty and fine-grained fractions have not been used in construction, so this parameter can be neglected.
- The number and size of particles of foreign inclusions (usually clay).
For example, river sand can contain only 0.3-0.7% impurities, and quarry sand up to 7%. Then for the first the weight of one cube will hardly increase, but for the second it will increase to 1.75 tons.
- Moisture contents.
This indicator changes not only the weight, but sometimes also the volume of the sand mass. That is why it is better to buy it immediately, as much as you need, in the summer, even if construction is planned for a later date. For a state of normal humidity, the number of tons per cube must be increased by about 6%, that is, the net weight must be multiplied by 1.06. As a result, the river sand from our example will weigh up to 1700 kg, and the quarry sand will weigh 1855 kg.
If the material is offered wet, the tons per 1m3 will be 20% more. This time we will multiply the density indicators by 1.2. Then in one cube the weight of two types of sand will be 1920 and 2100 kg, respectively.
In quarries, construction sand has its natural density; during transportation and sale, it changes and turns into bulk. Artificially compacted material is obtained during the process of laying it on the ground, and how much of it is required depends on the degree of compaction. For construction calculations, only bulk weight is needed.
Weight calculation
If the bulk density is known, it is easy to determine the mass of any volume of sand - simply multiply the specific gravity by cubic meters. But when there is no exact data, an approximate figure can be obtained as we did above.
In cases where it is necessary to determine how many cubes are in a ton of sand, the calculation is performed in the reverse order - the mass of the batch is divided by the density. Please keep in mind that during delivery by road, bulk materials shrink. In order not to make a mistake with the cost of the order, it is better to calculate it like this:
- Determine how much sand is needed for all planned work in units of volume.
- Allow about 10-30% shrinkage during transportation.
- Based on bulk density (you can check with the seller or take the average parameter), convert the volume into tons.
Price
| View | Tons per cube | Price per ton, rubles |
| River | 1,45 – 1,5 | 950 – 1 700 |
| Career | 1,7 – 1,8 | 850 – 1 500 |
| Quartz | 1,5 | 4500 – 5 000 |
| Expanded clay | 0,5 – 1,0 | 1 900 |
| Nautical | 1,6 | 6 000 |
stroitel-list.ru