In some cases, due to the characteristics of the soil and surface topography of the site, the construction of a full-fledged recessed strip foundation is not possible.
It also happens that only depth is required, without a foundation of large mass, since the structure itself does not create such a large load, but the features of its design require a more reliable foundation than a shallow strip foundation.
This is exactly what houses and other buildings made of aerated concrete or sibit are, therefore, when erecting buildings from this material, a lightweight version of a strip foundation is used, that is, combined with piles.
Other options for combining piles with any other type of foundation are not suitable because, although sibit is considered a lightweight material, the load is quite noticeable, and only a concrete mass in the form of a strip can cope with it.
Types of foundations for a house made of aerated concrete
Before starting construction, you need to know that to create a basement or basement floor, you will need to make a deep strip foundation. If the area where the house should be located has large differences in height - more than 1.5 m, then it is necessary to erect a pile-screw grillage.
Let's take a closer look at the possible foundation options.
Slab foundation
If the house is to be built on “difficult” land, where groundwater is close to the surface, you should opt for a monolithic slab. They are divided into 2 varieties: with and without stiffeners.
A slab without stiffeners is suitable only for small buildings. You cannot build a house or cottage on it. For an aerated concrete house, you will need to make a shallow foundation with a slab with stiffeners. The fittings will provide the following properties:
- good load-bearing capacity;
- resistance to soil freezing;
- resistance to ground movements and stability.
A monolithic foundation with stiffening ribs makes it possible to build 2-3 storey houses from aerated concrete. The slabs can also be used for sandy soil where there is no heaving.
The disadvantages of such a foundation include:
- the inability to make a basement in the house, since the slab will lie under the entire foundation of the building;
- the cost of such a foundation will be high due to the large volume of mortar and reinforcement.
Strip foundation
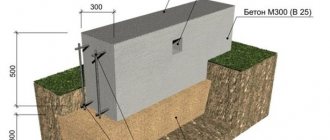
This is the most popular type of foundation not only for aerated concrete houses. It can be used for 2-3 storey buildings. To create such a base, high-quality concrete and 120 mm reinforcement are used.
It is not recommended to make a foundation from aerated blocks, since they have a low density and are not able to provide sufficient rigidity. The material will absorb moisture from groundwater and quickly become unusable.
If you want to make a block foundation, FBS blocks (solid foundation block) are perfect for this. These are large rectangular blocks weighing 300 kg. Their advantage is that they are installed very quickly (using special equipment). The disadvantage of FBS is the presence of technical seams between the blocks. They are best suited for the construction of a basement or basement.
The main parameters when creating a strip foundation are: the width of the trench, its depth and diameter.
For a shallow foundation, the depth is 50 - 70 cm. If you plan to make a basement in the house, then you will need to make a buried foundation of 1.5 m.
It is also necessary to take into account the depth of soil freezing. The width of the trench can be determined using calculations. It depends on the weight of the entire structure.
Most often, the width of the strip foundation trench for an aerated concrete house is 40 - 50 cm.
Pile and column foundation
These types of foundations are characterized by high construction speed and material savings. In addition, piles and pillars make it possible to conduct construction on difficult soils. Piles and pillars are installed pointwise along the entire perimeter of the future house. To install the pillars, you will need pre-prepared recesses.
A grillage is installed on top of them, connecting all the pillars or piles into a single platform. The weight of the future building is evenly distributed over all supports.
What advantages does this type of base have?
- you can work at any time of the year;
- reduction and uniform distribution of weight and settlement of the house;
- The closed contour of the grillage increases the stability of the entire structure.
Foundation of a house on stilts
As a foundation for an aerated concrete house, you can use a grillage on stilts.
The technology for constructing such a foundation is similar to a columnar one, but there are significant differences.
The piles used for this type of foundation have a smaller diameter but a longer length.
Piles can be bored or screw metal. These two types are most often used in the construction of country houses. A pile-grillage foundation, like any other, has its pros and cons.
Let's start with the disadvantages:
- when drilling holes (wells) to a depth of more than 3 m, part of the soil may crumble during lifting, so over time the level during settlement on each pile will be different and there is a risk of cracks forming;
- the foundation area will be smaller due to the relatively small diameter of the piles;
- piles are unstable during horizontal ground movements.
- the laying depth may be below the soil freezing level, even in the northern regions;
- suitable for areas with difficult soils and even for above-water structures;
- a pile-grillage foundation in a shallow location can be done with your own hands or with helpers;
- ideal for areas with large differences in heights;
- erected relatively quickly, with minor contamination of the site.
Metal piles are equipped with blades that are welded at the bottom.
This makes it easier to screw into the ground, and in addition they serve as an anchor and increase the support area of the piles.
After installation, it is better to fill the internal space of the pile with concrete.
This will protect the metal from corrosion and slightly strengthen the structure. When screwing in piles, it is imperative to control the verticality with a level or plumb line; deviations are not allowed.
You can also make a pile foundation from asbestos pipes reinforced with steel reinforcement in several rods.
The free space is filled with concrete.
For uneven areas or when the soil is deeply frozen, it is better to install a bored pile-grillage foundation.
Holes are drilled manually or with a drilling machine. The formwork can be made from thin-walled steel pipes so that it protrudes 30 - 50 cm above the ground.
A reinforcement frame is placed inside and filled with concrete. It is better to make the distance between the piles within 1.5-2 m, but not more than 2.5 m. The required number of piles should be calculated based on the total weight of the structure plus the load during operation (partitions, floor, roof).
The pile heads are tied with a grillage, creating a single, monolithic structure that can protect the fragile aerated concrete block from any type of deformation.
I hope that the information presented answered your questions and helped with choosing the type of foundation. If yes, then share this information with your friends and acquaintances on social networks. Don't forget to subscribe to blog updates.
Requirements for the foundation for an aerated concrete house
The dimensions of the future foundation, its depth and height, are calculated according to the individual characteristics of the house. The design of the foundation should be entrusted to a specialist, since the durability of the entire house will depend on it.
The reinforcement and height of the foundation from the base must be carried out in such a way as to cope with possible soil movements. When creating a foundation for a house, you need to be guided by such factors as:
- maximum static load (walls, roof, partitions);
- temporary load (furniture, communications);
- relief of the site.
In addition, you need to know the geological features of the site. How deep does the groundwater go, what bearing capacity does it have, etc. The foundation must be equipped with vertical and horizontal waterproofing and insulation.
Under no circumstances should you skimp on materials for the foundation. Use concrete m200. Reinforcement should be made from special rods connected to each other with clamps.
Features of foundation calculations
When calculating the foundation, a large number of parameters are taken into account. So, for example, not only the material from which you will build a house matters, but also insulation and insulation materials. The greatest importance is played by the total weight of the house with cladding and communications.
Calculation of the foundation for a one-story house
When building a one-story house, all figures given in the project are taken according to the minimum limit. So, for example, if a shallow foundation should have a depth of 50 - 60 cm, you should choose a depth of 50 cm. The sand cushion is also taken into account here. Trenches dug to a depth of 50 cm will be filled as follows:
- sand pillow - 20 cm;
- formwork is installed on the sides;
- a frame of rods connected to each other with clamps, 30 cm apart, is placed in the formwork;
- the gap between the formwork and the reinforcement should be 5 cm;
- concrete solution is poured.
When pouring concrete, it is advisable to have a concrete vibrator on site. With its help, you can remove excess air from the solution and make it more uniform and dense.
Calculation of the foundation for a two-story house
When working with the foundation of a two-story house, you should take the maximum parameters specified in the project. Here's how to fill a trench, 60 cm deep:
- sand cushion 30 cm;
- formwork;
- frame made of reinforcement 12 - 14 mm, secured with clamps, in increments of 20 cm;
- concrete solution.
When creating a columnar or pile foundation for a 2-story house, the dimensions of the supports will differ. They should have a larger cross-section than for a 1-story house. Their size is determined during calculations and indicated in the project.
When installing a monolithic slab, a thickness of 40 cm is suitable for a 1-story house, and 50 cm for a 2-story house.
How to calculate
When performing design measures, it is necessary to calculate the piles and grillage.
Pile calculation
When calculating a pile, it is necessary to determine the following characteristics:
- pile pitch;
- length of the pile to the edge of the grillage;
- section.
As a rule, the cross-sectional dimensions are determined in advance, but the remaining criteria are selected based on the available data. As a result of the calculation, you can obtain a value that will indicate the distance between the piles and their length. But how to replace the foundation under a wooden house with your own hands is described in great detail in this article.
The video shows the causes of accidents with such a foundation:
To determine the load on each m2 of the foundation, it is necessary to divide the entire weight of the building by the total length of the grillage. In this case, both external and internal walls must be taken into account.
To determine the bearing capacity of one base element, use the following formula:
P = (0.7 x R x S) + (u x 0.8 x fin x li), where:
- P is the load that one pile can withstand without destruction;
- R—soil strength;
- S—sectional area of the lower part of the pile;
- u is the perimeter of the foundation element;
- fin is the soil resistance along the lateral sides of the base element;
- li is the thickness of the earthen layer that is in contact with the side surface of the pile;
- 0.7 and 0.8 are coefficients.
Grillage calculation
To determine the dimensions of the grillage, you must use the following formula: B = M / (L x R), where:
- B is the minimum distance for belt support;
- M is the weight of the house without taking into account the mass of the piles;
- L - strapping length;
- R is the strength of the soil at the surface of the earth.
The video shows the calculation of the grillage:
How to fill
To build a pile-grillage foundation, you must adhere to the following plan:
- Mark the area. Here it is necessary to maintain maximum accuracy. Place the piles at a distance of 1.5 m from each other.
- Now you can proceed to the installation of piles. This process is simple but requires care. It is very important to maintain the immersion depth and vertical position of the elements.
- Most often, piles are installed to a depth of 1.5 - 2 m. All elements should rise 20-25 cm above the ground. This is necessary to form a grillage.
- Upon completion of the installation of the piles, it is necessary to complete the next stage - this is the arrangement of the grillage. Before making the formwork for it, it is necessary to apply waterproofing mastic over the piles.
- For a strong and reliable installation of the formwork, it is necessary to install pegs along the outer and inner perimeter. Their height should be slightly higher than the height of the formwork. A distance of 1.5-2 m must be maintained between the pegs. The bottom of the formwork and the side parts should be made from edged boards. It is fixed using self-tapping screws.
- After this, lay a waterproofing layer on the board. Perform reinforcement and fill the grillage with concrete. When it dries, remove the formwork. But how to make a columnar foundation for a frame house with your own hands, and what you should pay attention to, is indicated in this article.
The video shows how to pour a pile-grillage foundation:
Recommendations
When calculating the foundation, you must contact a professional architect who can correctly calculate all the necessary parameters of the future foundation. Another important point is compliance with all construction standards during work. If you are planning to make the foundation with your own hands, make sure that you have sufficient qualifications and experience, and do not overestimate your strength. In the end, it’s your work and your money, and the durability of the built house will depend on how well the work is done.
Choosing a foundation for a house made of aerated concrete - which is better?
Aerated concrete has excellent properties, which make it an ideal building material for the construction of walls of private houses. However, it also has some disadvantages - fragility and susceptibility to shifts - so it is important to seriously consider the question of which foundation is best to choose for a house made of aerated concrete.
At the stage of designing the foundation of a house, the following parameters need to be taken into account:
- weight of the future building;
- fragility of aerated concrete blocks;
- type of soil on the site;
- terrain;
- groundwater level;
- freezing depth.
It is most reliable to entrust the research and design stage to specialists, but, if desired and have some skills, you can actually do this work yourself.
Pile foundation
Most often, houses made of aerated concrete on sites with close groundwater are installed on bored or screw piles, connecting them together with a monolithic grillage. They differ from columnar structures:
- dimensions - the diameter is smaller and the length is longer;
- material of manufacture;
- installation method.
Pile foundations are laid deeper than the maximum soil freezing level recorded in the construction region.
Features of foundations on screw piles
In areas with difficult soils (heaving, weak-bearing, subsidence), it is recommended to build a house made of aerated concrete on screw piles. They are installed even in frozen conditions and during the installation of above-water structures.
On the metal piles on the lower side there are welded blades or coils that make it easier to screw the pipe into the ground and increase their supporting area. The screw blades, in this case, act as an anchor fixed in a strong soil layer.
Technological holes are provided in the upper part of the pipes and heads can be located, or installed later. If the foundation is slightly deepened (up to 2m), the piles can be screwed in independently with the help of 2-3 assistants using additional devices. At greater depths, special construction equipment is required.
After installation, the pile cavity is filled with concrete mortar. In addition to strengthening the structure, it protects the inner surface of metal pipes from the effects of corrosion processes.
For screw piles, when determining the dimensions of their depth, the following should be taken into account:
- blade length;
- soil freezing level;
- the depth of a strong load-bearing soil layer.
It should be noted that screw piles must penetrate at least 300 mm into the dense supporting soil layer. When screwing them in, vertical deviations should be controlled using geodetic instruments, a building level, or a simple plumb line. Do not forget that even a slight distortion can lead to the removal of screw pipes and their re-installation, but in a different place.
The advantage of screw piles is:
- speed of construction;
- high load-bearing capacity;
- relative cleanliness of the construction site;
- the optimal solution for differences in landscape heights.
Features of the foundation on bored piles
In addition to erecting a low-rise building from aerated concrete on screw piles, there is the option of installing buildings on bored piles. They are widely used on uneven areas, as well as when the soil freezes to a significant depth.
Wells for the foundation of a private building are usually drilled manually using a construction drill. Its length-adjustable rod allows you to make recesses of up to 5 meters, and in some cases even more. A modern tool has the ability to make expansions in the lower part of each of the wells to make it possible to make support pads.
Formwork is made from roofing felt with a diameter corresponding to the size of the pile, and a length 20-30 cm greater than the depth of the well. The “pipe” is inserted into the drilled recess and a simple-shaped reinforcement frame is placed inside, the size of which is chosen taking into account the height of the future grillage.
Bored piles without reinforcement are not allowed to be installed on heaving or horizontally moving soils. They can only withstand axial loads, since they cannot withstand bending, stretching or lateral forces.
At the final stage, concrete solution is poured into the well, compacting the mixture with vibrators. After the final hardening of the concrete, they begin to install a monolithic foundation piping, on which aerated concrete blocks will subsequently be laid.
The ground parts, or heads, of separately installed piles are tied with a solid rigid frame of a reinforced concrete grillage. This creates a single, unified foundation structure. The main function of the grillage is to uniformly distribute permanent and temporary loads, as well as to ensure the possibility of erecting walls.
What type of foundation is suitable for building a house from aerated concrete?
Considering the tendency of blocks to split during shifts, it is best to choose the most rigid type of foundation that will remain motionless in any circumstances, or will “float” entirely, without exposing the walls to the risk of deformation. In this case, the base does not have to be too massive, because the load on it will be small.
Most often, the following types of foundations are built for houses made of aerated concrete:
- Slab;
- Pile;
- Grillage;
- Tape (solid or prefabricated from FBS).
Choosing the type of foundation depending on the type of soil
Slab
This foundation is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab. A slab foundation is best suited for a house made of aerated concrete blocks, since it evenly distributes the load from soil movement during seasonal heaving or as a result of its uneven shrinkage. The possibility of distortion and destruction of walls is excluded.
A slab foundation is a shallow foundation; the thickness of a monolithic foundation slab usually starts from 0.2 m. But even with this modest thickness it has a high load-bearing capacity.
The foundation is laid in such a way that the entire house along with the formwork is placed on it. For strength, the slab is fastened with two or more layers of reinforcing mesh (depending on the thickness of the slab). Due to the fact that the base area is very large, the specific load on the soil is minimal.
Seasonal ground movements do not affect a house that stands on a monolithic slab - it moves synchronously with the ground.
The foundation slab is suitable for any type of soil, even heterogeneous and highly heaving ones, on which no other foundation can be placed. However, this is one of the most expensive options and you need to be prepared for it.
Suitable for one-story or two-story houses made of aerated concrete blocks. Setting up a basement is almost impossible.
Pile
Building on pile foundations is suitable for areas with a high risk of flooding or when other types of foundations are not suitable for this type of soil (due to soil instability) and a deep foundation of the building is required.
Finished piles are installed in pre-drilled holes of the required depth, or filled with mortar on site (self-leveling piles). Driven piles are also used, which are screwed or driven into the ground using special equipment.
The advantage of a pile foundation is that there is no need to dig a pit for it - this significantly reduces the cost of excavation work.
A pile foundation for a house made of aerated concrete will be a suitable option in an area with wet soil (due to the shallow passage of groundwater), as well as in the presence of a terrain slope. Using piles of different heights, you can achieve a perfectly level house.
However, if soil movements in the horizontal plane are predicted at the site, a pile foundation will not be suitable, since it is not capable of providing the necessary stability and reliability. The piles will tilt and the house will sag unevenly.
Grillage
This is a type of pile foundation in which vertical supports are connected into a single system using a monolithic grillage. It can be installed at three levels:
- above ground level (in wet soil or in a periodically flooded area);
- flush with the ground (on stable rock or rock);
- buried in the ground (in areas with a minimum level of soil freezing and deep groundwater).
For a house made of aerated concrete blocks, a grillage foundation built at ground level is best suited, as it most evenly distributes the load on each support pile.
Tape
The most common type of foundation in the Russian Federation. The building support is a reinforced concrete strip with a width equal to or greater than the wall. It is laid along the perimeter of the future house and under its external and internal load-bearing walls. The gaps are filled with crushed stone or other bulk materials.
Since aerated concrete has a small specific gravity, when constructing buildings from such blocks, a shallow strip foundation is made (with a laying depth of 50 cm). A shallow strip foundation is the most budget option. It is suitable for stable soil that is not prone to seasonal swelling and with low groundwater levels.
If the building design provides for a garage under the house, a ground floor or a basement, it is necessary to make a deeper strip foundation. Its depth will be equal to the required height of the basement.
Strip foundations can be of two types:
- Monolithic. Most often used under aerated concrete. It is a solid strip of reinforced concrete. Its advantage is uniform rigidity, which is especially important for preventing deformation of the walls of a block house when the base settles.
- Prefabricated from FBS (foundation wall blocks). The advantage of FBS over a monolithic foundation is its ease of installation, however, prefabricated foundations do not have the rigidity necessary for buildings made of aerated concrete. In view of this, prefabricated foundations are not recommended for use, and when used, it is necessary to place a monolithic reinforced belt on top of the FBS blocks.
If it is impossible to make a monolithic belt, it is necessary to reinforce block dressings of FBS blocks.
The principle of choosing the type of base
Selecting a foundation for a house is a responsible and difficult task. Its type and method of construction depend on many factors:
- soil characteristics;
- groundwater flow level;
- degree of soil freezing;
- house designs;
- what material will be used for the walls.
It makes the most sense to start by examining the soil on the site, in cases where you do not have a site passport with detailed information about it. If you have decided on the materials for the walls and it will be aerated concrete, then it’s time to decide on the type of foundation.
Despite the fact that aerated concrete blocks are light in weight, the base for walls made of such material must be strong so that unpleasant surprises do not happen later, namely cracking of the blocks.
Choosing is always a difficult matter, so you need to explore all possible options. Let's do just that.
So, the foundation for an aerated concrete house can be:
- tape;
- columnar;
- pile-grillage;
- monolithic reinforced concrete.
Any of the above options is possible for an aerated concrete structure. To choose the right one for your home, you need to get acquainted with their features. I wrote about the shallow shallow foundation in a separate article. Let's talk about columnar and pile-grillage.
Useful tips
- You should never skimp on materials for the foundation of your home. If funds are limited, it is better to build a house with a smaller area, but with a solid foundation, than a large house, but at the same time it will burst at the seams due to an improperly constructed foundation.
- Before starting work, it’s worth checking everything again so that it doesn’t turn out that you could have made an inexpensive pile foundation, but installed a monolithic slab.
- If seasonal fluctuations in groundwater levels are not taken into account during construction, this can lead to flooding of the basement or ground floor.
- Aerated concrete is a hygroscopic material. In conditions of high humidity, it loses its heat-insulating properties, and due to prolonged exposure to water it can begin to deteriorate. Therefore, when building a house from aerated concrete, it is necessary to make a base with several layers of waterproofing. This does not replace the thorough waterproofing of the foundation.
In addition to the above, we recommend watching a useful video on foundation construction and aerated concrete laying:
A correctly selected and constructed foundation for a house made of aerated concrete blocks will create a reliable foundation for the future building.
Construction stages
Piles are placed at angles, at intersections of load-bearing walls, in places of heavy load and along the perimeter of the building with an interval of up to 2.5 meters.
Stages of constructing a pile screw foundation:
- design and structural calculations;
- geological assessment of the construction site;
- carrying out static and dynamic tests at the construction site;
- marking the site and transferring the plan to the area;
- installation and screwing of piles;
- checking the horizontal level of the pile heads and cutting off the ends of the piles;
- installation of formwork and pouring of grillage or monolithic slab;
- quality control at the deepening stage and after completion of work.
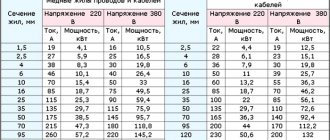
When building a house from aerated concrete on stilts, the weight of the building and the quality of the land under the future structure are taken into account. There are elements on sale with different characteristics in terms of load, cross-section, and material. For aerated concrete walls, piles with a diameter of 89 mm or more, produced by casting, are used. Sometimes welded elements are accepted for work, but after preliminary calculations.
The calculation of the number of screw piles is carried out by technical specialists, because Collecting house loads requires precision and specific knowledge. The weight of the floors is distributed to the walls, and they transfer the load to the foundation. The force from the roof also acts. Wind and snow loads are taken taking into account the coefficients given in the SNiP tables. The numbers show the influence of the roof windage, its slope, the height of the ridge and its location relative to the wind rose on the amount of transmitted voltage.
Choosing the optimal foundation for an aerated concrete house
Korovin Sergey Dmitrievich
Master of Architecture, graduated from Samara State University of Architecture and Civil Engineering. 11 years of experience in design and construction.
When deciding which foundation is best for a house made of aerated concrete, several factors must be taken into account. First of all, the design features are influenced by the properties of the wall material. Foundations for houses built from aerated concrete must take into account some of the distinctive characteristics of this material.
Reviews
- Oleg, 34 years old: “I used a pile-grillage foundation when I was building a dacha. The fact is that this is the most suitable option for the site, since there is close groundwater. I consulted with experts and they offered me such a design. Of course, it also has its downsides. The most important thing for me is that all the calculations were carried out by professionals, since I was not able to cope with this work on my own. But I carried out the process of building the foundation myself. The dacha was built 3 years ago, but so far I haven’t noticed any flaws.”
- Kirill, 39 years old: “I also used a pile-grillage foundation to build a house made of aerated concrete. But to be honest, I'm not particularly happy with it. The fact is that it cannot be placed in an area where there is sand. But no one told me about this, and I made a mistake. As a result, after 4 years the foundation began to shrink. In addition, building such a structure is a costly affair, so you need to carefully weigh everything and consult with specialists in order to avoid the situation that arose with me.”
- Andrey, 56 years old: “I’ve been working as a builder for a very long time, but only a few years ago my team and I started using a pile-grillage foundation. Of course, building it is not so problematic, but there are a number of criteria that must be taken into account when choosing it. I would like to note that it is advisable to use a foundation for low-rise buildings and on a site with stable soil.”
The pile-grillage foundation is only gaining momentum in popularity today. It has its drawbacks, but they can be eliminated if you use high-quality materials, perform accurate calculations and examine the soil.
We also recommend that you read in more detail about the pros and cons of a slab foundation.
Features of aerated concrete blocks
Here we will consider those characteristics that have a direct impact on the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete. Before choosing a type, you need to consider the following features.
Aerated blocks are piece material. Even with the right choice of masonry mortar and compliance with the technology for performing the work, they are poorly connected with each other. This factor results in the fact that the walls of the building are extremely sensitive to various deformations of the base.
If the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete subsides or, conversely, rises from the ground, cracks may appear on the walls of the building. In most cases the cracks will be inclined. The opening width and length depend on the scale of displacement of the supporting part of the building. To prevent damage, it is necessary to provide reliable supports that will resist various types of displacement. The design must connect the wall from individual blocks into a single system.
The task of the foundation is to prevent such phenomena
The foundation for aerated concrete needs a less powerful foundation than for a brick house. This is caused by the lower density of the material, and, accordingly, the mass. For comparison, the density of aerated blocks ranges from 350 to 700 kg/m3, while a brick wall will have a density of 1800 kg/m3. Blocks with a minimum density cannot be used as structural elements; the material of load-bearing walls weighs from 500 to 700 kg per cubic meter.
Despite the advantages of blocks compared to brick, it is worth remembering that the material is inferior to wood. The building will also be heavier than a frame house. When selecting foundations for houses made of lightweight aerated concrete, it is necessary to take this feature into account.
Description
The pile-grillage foundation is a type of pile-strip structure. Its peculiarity is that there is a special frame on the surface, which can consist of beams or slabs. It connects all the foundation piles to each other. Thanks to such a frame, it is possible to give the building durability.
A distinctive feature of this design from the tape one is that the tape used to connect the piles is located in an elevated position above the ground.
Thus, she has no contact with him. They began to use such a foundation in construction only recently, but it has already become in great demand.
The video shows the features of a pile-grillage foundation:
Advantages and disadvantages
To understand the question of whether it is worth using a pile-grillage foundation for the construction of your house, you need to study and weigh its advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages include:
- If we draw an analogy with a strip or pile-screw foundation, then the type of structure in question is cheaper . There is no need to use drilling rigs, as you can get by with a motorized drill. There is no need to dig a trench under the tape. This type of foundation is ideal for self-building a house. The low cost of the design is due to the fact that cast-in-place piles are used, and their pouring occurs separately from the grillage. So you can mix concrete yourself.
- It is impossible to erect strip structures on soft soil, but pile-grillage structures are ideal for such terrain.
- The construction of such a foundation requires 3-4 days.
- Since the grillage is tied, all the piles are concentrated into a reliable chain . During shrinkage, such a scheme will allow the base not to collapse and sit evenly on the ground like a grillage without distortions. Thus, before pouring concrete under the grillage, it is necessary to cover the soil with a waterproofing agent. But the video from the article will help you understand what the depth of the foundation should be for a house made of foam blocks.
The video shows the positive aspects of such a foundation:
The pile-grillage foundation has its disadvantages. These include:
- When building a house on such a foundation, it is impossible to create a basement or plinth.
- On unstable ground, the grillage may sag. But if you perform the correct calculation, such problems can be avoided.
With a monolithic slab
If a site located in a lowland or with clay soil is allocated for the construction of a house, then the level of freezing will go beyond 120-130 cm. In this case, it is worth using a pile foundation. But for non-rigid walls made of foam concrete or aerated concrete, the foundation will have to be tied with too thick and powerful reinforced concrete grillage. Laying a monolithic slab will cost more, but using a pile structure with a monolithic slab is the most suitable option. But how to properly pour a foundation slab for a house, and how to do it correctly, is described in great detail in this article.
Its advantages include:
- Even when installing a monolithic grillage in a reinforced version, the cash costs will be 2 times less than the cost of casting a full-fledged slab base or strip structure.
- The transverse stiffness in relation to bending loads is slightly inferior to the slab foundation in the center and exceeds it in the edge zone, where a large number of piles are concentrated.
- Thanks to the reinforced base part and deepened supports, pile structures with a monolithic grillage will last a long time on any terrain. But it is only necessary that the piles be buried to the level of dense rocks, below the freezing area. But how you can make a foundation for a house from timber, and how to choose it correctly, is described in great detail in this article.
The video shows a pile-grillage foundation with a monolithic slab:
What kind of houses is it suitable for?
You can use a pile-grillage foundation even when building a house made of aerated concrete. This design is quite profitable and reliable. It can also be used in the construction of a light wooden house, when the construction of a strip base underneath is impossible or not too reliable.
For those who want to understand exactly how to pour a foundation for a greenhouse, and how to do it correctly, you should follow the link.
This article will help you understand what the depth of the foundation for a fence with brick pillars should be.
But this article will help you understand how to pour the foundation for a fence:
Here's what the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete looks like, and how it can be made. The information from the article will help you understand.
What types of foundations are used?
All foundations, depending on operating conditions, can be divided into four large groups:
- columnar;
- pile;
- tape;
- slab.
Variants of bases used
The first and second in private construction (taking into account the most popular sections) have a relatively low load-bearing capacity. Such elements only work under compressive loads. It is especially advantageous to make them from concrete, since this material has good compressive strength. Also recently, metal screw piles have become widespread.
The strip foundation absorbs mainly compressive loads. When installed on soft soils, slight bending effects may also occur. If a monolithic foundation is made in accordance with the technology, they do not cause problems.
The use of a slab foundation is different in that this structure works on bending and pushing. Concrete does not resist such influences well. To prevent damage, a mixture of sufficiently high grades is chosen for filling, and reinforcement is prescribed with special care. Before installing the slab, it is recommended to calculate its strength and rigidity. Only a professional designer or constructor can perform such work.
Columnar foundation
For a small one-story country house, a columnar monolithic foundation is suitable.
This is a series of pillars located at corners, in the center of long spans, and also at the junction of walls. The distance between pillars should not exceed 2.5 m.
Pillars are used with a round or rectangular cross-section. If necessary, they can have an extension (shoe) at the base. Depending on the type of section, formwork is selected (wooden panels, plastic pipes or asbestos-cement pipes of suitable diameter).
If the soil is dense and stable, the simplest option is roofing felt rolled into a pipe. The reinforcement frame is placed inside the formwork, positioned in such a way that it is 20-25 cm higher than the pipes (for connection with the grillage).
A monolithic grillage is poured on top of the pillars. The dimensions of the grillage are determined depending on the structure, but its width should not be less than that of the wall, and its height above ground level should not be less than half a meter. This will isolate the blocks from moisture.
It is better to entrust the calculation of dimensions and number of pillars to qualified specialists. Such a foundation cannot be used on soils with horizontal movements and for buildings with basements or basements.
How to choose a foundation type
Before choosing which type of support is best for a house made of aerated concrete, you need to consider the following points:
- geological conditions of the construction site, foundation strength, soil water saturation, groundwater level;
- the mass of the building (when comparing buildings made of the same material, this characteristic is strongly influenced by the number of floors);
- economic opportunities.
Influence of soil characteristics
Moisture in the soil and soil type affect the elevation of the supporting part. Soils on the site can be one of the following types:
- coarse clastic;
- coarse sand;
- medium sand;
- clay;
- loam;
- sandy loam;
- fine or dusty sand;
- bulk soil.
The last two positions have very low strength indicators. It is not recommended to build on such foundations (the only exception may be pile foundations). The best option would be to replace the material with sand of medium or coarse fraction.
The best soils for construction will be coarse and sandy (medium and coarse) . Such foundations have high strength and are not prone to frost heaving (one of the main enemies of foundations for houses made of aerated concrete).
Refractory clays and loams also have good strength characteristics. But all clayey soils (clay, loam, sandy loam) can lead to uneven elevation of the building in winter. This phenomenon occurs due to frost heaving. In this case, the outer walls of the building rise more than the inner ones. Cracks appear on the walls made of aerated blocks. When building on such foundations, it is necessary to take timely measures to prevent frost heaving.
When building on heaving soils, it is necessary to choose those types of foundations that are buried below the freezing point of the soil. The value is determined according to regulatory documents. On average, this value is within 1–2 m.
Soil freezing depth
The foundation for a house made of aerated concrete (its base) must be at least 50 cm above the groundwater level. Depending on the location of the moisture, you can use a buried structure (going 1.5 m or more into the ground) or a shallow one (the depth in this case is taken to be approximately 70-100 cm). Also, when choosing the depth of foundations, it is necessary to take into account the need to construct a basement.
Structural features of the building and load on the foundation
To choose which foundation is best for a block house, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the table below. The dimensions and thickness of the supporting part are determined by calculation.
| Soils at the construction site | For a one-story block house | For a two-story block house |
| Coarse soils, medium and coarse sands | To save money in this case, columnar bases or strip bases with a shallow depth are used | Pillars are used for such buildings. In this case, the strip foundation for a house made of aerated concrete should have a T-shaped section (increased thickness at the bottom). It is better not to use a rectangular type of section due to low load-bearing capacity |
| Clays, loams and sandy loams (most often they are water-saturated) | You can use a pile foundation made of screw supports. They are perfect even in moisture-saturated soil. A reliable monolithic grillage is made along the pile heads, which will connect the individual supports into one system. A slab foundation would also be an excellent option (due to the low load, the thickness of the foundation used is relatively small, approximately 200mm) | The foundation for a house made of aerated concrete in this case is assigned to the strip or slab type. In this case, the tape must be laid below freezing or have reliable insulation. To protect the building from moisture, a drainage system, waterproofing and perimeter blind area are designed. The tape can be made of monolith or FBS blocks. The monolithic option is preferable, since the FBS are weakly connected to each other. You will still have to make a reinforced concrete belt along their edges. The thickness of the foundation is determined depending on the thickness of the walls. If a basement is not planned, a shallow slab is used. This approach will reduce construction costs |
| Areas with high groundwater levels (swampy areas) | As a supporting part, you can use a tape made of monolith or FBS. In this case, it is necessary to maintain a distance of 50 cm between the base of the foundation and the water level. If the moisture rises very high, a slab or screw piles are used as a foundation | Screw piles have a fairly low load-bearing capacity. When building a two-story house in a swamp, it is recommended to use a slab foundation as a foundation. |
Advantages of a screw foundation
The best option is to build aerated concrete walls on a pile foundation. This way, the vertical fences of the house will gain stability and will not collapse from shifts.
Screw racks in the form of supports have positive qualities:
- stands with blades are easily and quickly screwed in; installation of one element takes about 20–30 minutes;
- installation of piles does not depend on the topography of the construction site; support rods are placed on slopes where there would be an overuse of concrete for a monolithic foundation;
- can be installed in wet and landslide-prone soils if the end of the pile rests on solid soil.
Thanks to the screw attachments, traction with the ground is increased and buoyancy forces are not triggered. The penetration point is below the freezing depth. The installation of screw piles can be carried out at any time of the year.
Foundation for a house made of aerated concrete
A foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is necessary. One of the reasons for the popularity of aerated concrete for building houses is the ability to build a structure on different types of foundations. The most reliable foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is considered to be a reinforced monolithic slab. This foundation evenly distributes the loads from the building and soil, and minimizes the risk of deformation of the building. But this type of foundation is also the most expensive, so more often the foundation for a house made of aerated concrete is built with columnar and strip foundations, as well as their variants, for example, a columnar foundation can be reinforced with a reinforced concrete grillage.
We understand the features of a pile-grillage foundation for aerated concrete
Groundwater causes deformation and destruction of the foundation of a foam block house. Initially, these waters loosen the soil, which gradually leads to the foundation sagging, and then, in winter, the soil saturated with water freezes, bulges and, ultimately, deforms the foundation of the house.
And to solve this problem, protecting the building from the destructive effect of soil waters, they use a pile foundation for a house made of aerated concrete or foam blocks (drive-in round reinforced concrete piles are used) or a pile-grillage type of foundation for a house made of aerated concrete or foam blocks.
Pouring the grillage of a pile-grillage foundation
However, using piles in a foundation with your own hands requires technical knowledge about it, as well as knowledge of some of the nuances and features of the pile-grillage type of foundation in general.
Monolithic slab for aerated concrete house
Type of "floating" foundation. Installing a slab under the entire area of the structure is a solution for construction on heaving soils. Moving simultaneously with the foundation soils, the slab does not transfer uneven loads to the building, and due to the large area of the slab, the load on it from the base is minimal.
The slab is not buried to the freezing depth; its height is about 400 mm, and 100 mm is immersed in the ground. Drainage around the perimeter must be performed. In some cases, reservoir drainage is done under the slab, this depends on the nature of the movement of groundwater in the area (pressure or infiltration). In addition, a two-layer waterproofing is made from rolled materials under the slab. Recently, profiled geomembranes have become increasingly popular.
The thickness and composition of the cushion under the slab depends on the properties of the specific soil, but concrete preparation must be done, 100 mm thick, from lean concrete or mortar. Waterproofing is laid on the concrete base, then the assembly of the spatial reinforcement frame begins. The slab formwork is rigidly fixed with tie bolts, struts and leveling beams. The volume of concrete poured is large, and the dynamic loads on the formwork and frame will be significant. The inside of the formwork is lined with thick polyethylene film or roofing felt to prevent the laitance from leaking out.
The reinforcement frame is assembled using the knitting method, and it is necessary to ensure the safety of the waterproofing. The protective layer of the lower tier of the reinforcement is provided with plastic clamps - “chairs”. After assembling the lower mesh, the upper mesh is assembled, then the meshes are combined into a spatial frame. All reinforcement must be cleared of snow, ice, dirt, oil and loose rust before pouring concrete. After securing the frame in the formwork, they begin pouring concrete. The slab structure must be poured in one step; the formation of cold seams must not be allowed. Concrete is laid in layers of 150-200 mm with compaction using a vibrator, as well as any devices that allow you to expel air from the mixture - shovels, reinforcing bars. When bayoneting and vibrating the mixture, you must not touch the reinforcement cage, so as not to move it from the design position and not to disturb the protective layer of the reinforcement. From the outside, the formwork can be tapped with a hammer.
After pouring the concrete, conditions must be created for normal hardening. You should not walk on freshly laid concrete. To prevent the surface from drying out, the concrete is covered with plastic film. In hot weather, water. The first day of hardening is very important for the future strength of the structure.
Stripping is done after the concrete has gained strength. There is no need to rush to remove the formwork, as it protects the concrete from drying out and temperature changes. The curing time of concrete in the formwork depends on temperature, air humidity and weather conditions.
After stripping, the slab is backfilled with local soil or a sand-gravel mixture.
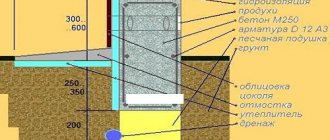
Shallow strip foundation (MZLF) for a house made of aerated concrete
Shallow strip foundations are used on slightly heaving and non-heaving soils (sand or sandy loam, with inclusions of pebbles and gravel).
The tape is buried to 0.5 -0.7 freezing depth, with the obligatory arrangement of a cushion of sand and crushed stone, or gravel, 40-50 cm high. The cushion is made in layers of 10 cm, with each layer thoroughly compacted. The pillow serves as a drainage base and reduces the load from frost heaving of the soil.
Waterproofing is laid under the tape, then the formwork is placed and the reinforced frame is assembled in it. The tape runs under all the load-bearing walls of the house and differs from other foundations in that it must be a closed solid frame; its calculation and operation are based on this. At corners, intersections and junctions, the reinforced frame of the tape is reinforced with additional bent elements - clamps, hooks or tabs, according to the design. Reinforcement and pouring of concrete is carried out using standard technology. The tape must be poured without interruptions in concreting.
If the soil on the site allows you to build a MZLF for a lightweight house made of aerated concrete blocks, then in the warm season this will be a low-cost and quick option. If you have to pour MZLF at subzero temperatures, then the concrete will have to be heated. A small volume of tape concrete with a large surface area will not heat up from hydration, and it will be necessary to insulate the formwork and use heat guns.
Aerated concrete is a very hygroscopic material, so the height of the plinth under the first row of blocks is often raised from the ground surface by no less than 50 cm. Cut-off from capillary moisture, or horizontal waterproofing, is required under aerated blocks, in a reinforced version.
It makes sense to arrange MZLF if the house does not need a basement or ground floor. Otherwise, you cannot do without a buried tape.
Columnar foundation for a house made of aerated concrete blocks
This option is economical, but it can only be used if the terrain is level, without changes in the susceptibility of the soil to landslides and horizontal shifts.
Consists of support pillars. It is made of monolithic concrete, in a prefabricated version, it is possible to construct it from brick. The cross-section of monolithic pillars depends on the type of formwork used; sometimes asbestos-cement or PVC pipes are used for this purpose. Provided the soil is dense, hard and stable, it is possible to pour concrete without formwork; in this case, the walls of the well or pit are lined with waterproofing roll material so that water does not escape from the concrete. This is a successful, but rather rare version of a columnar foundation.
The support columns are connected at the top with a grillage made of monolithic reinforced concrete. All dimensions, the number of supports and the spacing between them, the density of reinforcement are determined by calculation, the initial data for which will be the architecture of the future house, its dimensions in plan, number of storeys, weight. Data on the groundwater level and the nature of the soils at the site’s base are also required. Of course, this applies to all types of foundations. With any option, you need to make a calculation or rely on a standard design, because a solid foundation is the basis for the life and safety of a house and its residents.