What type of foundation should I choose for a private house?
Laying the foundation is the most important process in any construction, be it a skyscraper or a private house. Each owner must choose the type of construction for his future home, regardless of whether he will carry out the construction himself or whether professional workers will do it. In the second case, you will receive recommendations from the experts, but it won’t hurt to figure out for yourself what types of house foundations are used today. In this article we will analyze each design in detail, and also find out in what cases it is used.
What type of foundation should you ultimately choose?
The foundation is the foundation of the house being built, on which the entire load will rest. It is the quality of the laid foundation that determines the service life of the building. So before deciding which types of foundations are best to use in a particular case, it is necessary to take into account many factors. After all, each type of foundation has certain qualities that determine the advisability of using a certain type of foundation during construction.
Read about the following stages of construction:
Which is better to choose a foundation for the soil and type of house
Water supply for a private home
Well for water supply of a private house
Watch also the video about which foundation to choose
Read about the previous stages of construction:
How to choose the right plot of land for building a house?
Layout of land for building a house
Types of foundation.
Types of foundations for a private house.
The diagram shows the main types of structures for a private house.
For structures made of wood, foam blocks or concrete, the following types of foundation are used:
It is impossible to single out the best or worst option, since the design of each type of foundation for private houses is different. Accordingly, the construction costs will also be different.
Advice: to choose a suitable foundation, you need to take into account the climate, base material and soil characteristics. In any case, consultation with professional builders will not be superfluous.
Now let’s look at each type for a wooden and concrete private house, as well as structures made of foam blocks.
Types of foundations for a house by material
There are four groups:
- Wooden. Nowadays they are practically not used due to the availability of more reliable and durable analogues.
- Rubble. Consisting of large stones, this option was widely used in the past. Now it may be relevant only for private construction if there is a sufficient amount of material used.
- Concrete and reinforced concrete. A modern replacement for rubble structures.
- Metal. The main representative of metal foundations are screw piles. This option is actively used in the construction of light houses.
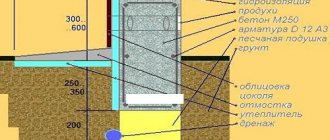
Strip foundation.
Types of foundations for a private cottage.
Detailed diagram of strip foundations.
The structure consists of concrete strips buried in the ground, which take the load from all load-bearing elements of the building: columns and walls. Foundation slabs are used as support for concrete strips, serving as distribution pads. For a private wooden house, this is the simplest option, because you do not need to prepare the soil. The forces from the load-bearing elements are transferred to a large area of land.
Strip foundations can be divided into four types:
- intermittent - there are separate pieces of tape under the walls;
- rigid - equipped with an additional reinforcement belt, this type is used in large structures;
- monolithic - standard version, looking like a continuous tape;
- flexible - there is transverse-longitudinal reinforcement throughout the entire structure.
Device.
In practice, formwork is installed in the ground, reinforced with a reinforcement belt. Next, the concrete mixture is poured into it. This type for a wooden or concrete house is quite simple, but requires a lot of time due to lengthy preparatory work.
- the easiest way to make a foundation for a private house.
- the work can be done on your own.
- requires a lot of resources;
- long hardening time.
Types of foundations for a private cottage in Siberia.
The photo shows the completed strip foundation, which also includes a porch with steps.
This option is suitable for different designs.
Pile foundation.
This type, as one might guess from the name, is made from individual elements or pre-prepared groups. The piles are connected at the top by a grillage - usually for private houses a beam or a solid slab of reinforced concrete is used. Foundations made of piles for concrete, wooden dwellings, as well as for structures made of foam blocks, are used quite often. If large loads need to be transferred to the ground, and its characteristics are not enough for this, then a pile foundation is used. It is also advisable to use this type of construction for a wooden structure.
Types of foundations for a private house in Siberia.
The diagram shows a foundation on screw piles. As you can see, this design requires a minimal amount of materials.
Pile foundations can be divided into six types:
- driven - a standard option in which piles are driven into the ground;
- cluster - used under difficult construction conditions, several piles are installed in different places of the foundation;
- driven - used in large-scale buildings, piles are poured into special wells;
- solid - the piles are located as close to each other as possible, this type is also called a “pile field”;
- screw - metal piles are screwed into the ground;
- single - the method is used under comfortable conditions, piles are mounted only at the corners of the foundation.
If the house will stand on soft soil, then piles are an excellent solution for wooden and concrete structures, as well as for structures made of foam blocks. The piles will penetrate through weak soil and “rest” on solid ground. Piles for a private house are made from wood, concrete, metal, and also from combinations of these materials.
Types of foundations for a garage in a private cottage.
Sometimes a pile-strip foundation is chosen for a private house, which is shown in this diagram.
Screw and driven piles are sold as ready-made elements for construction, so they can be immediately screwed or driven into the ground. As for cast-in-place piles, they must be made at the site where the private house is being built. Installation is followed by leveling, then using a grillage the piles are connected into a solid structure. An important point: the width of the future wall of a wooden or concrete house should be equal to the width of the grillage.
- piles can be installed regardless of the type of terrain;
- Fairly easy installation.
- Suitable only for small buildings.
Columnar foundation.
The design is similar to the pile version, only here the foundation is a pillar that is immersed in a special well. Also, the pole can be loaded without prior preparation. If pile and strip structures are connected using a grillage, then the pillars are attached to each other with reinforced concrete beams.
Do-it-yourself bathhouse foundation.
Pile columnar foundation.
This type is used for private wooden houses, as well as for buildings made of other light materials whose weight does not exceed 1000 kg/m3. If you are planning construction with your own hands, then it is best to make pillars for the foundation from brick or rubble concrete. When pouring a pillar, it is necessary to perform reinforcement every 35-45 centimeters. As an alternative, you can buy ready-made elements.
Tip: you can use a columnar foundation if the structure will stand on ground that is not subject to temperature deformation.
- fairly cheap base;
- you can do it yourself.
- not suitable for large houses.
Slab foundation.
The design is as follows: a recessed reinforced concrete slab is laid on the ground. The thickness of the main element can range from 30 to 100 centimeters. Reinforcement is a mandatory requirement for this type of structure. The slab foundation uses reinforcement with a diameter of 12 to 25 millimeters. The design is usually used on soft soils (embankments, quicksand, sand, etc.).
In private construction of a house made of concrete or foam blocks, a tiled foundation is rarely chosen, since complex calculations are required here. The main disadvantage of this design is the lack of a basement, because a solid slab cannot be disturbed. Usually this type is chosen in the most difficult situations. There is only one requirement for a solid slab - a level foundation. In other cases, pile or strip foundations are used.
Types of foundations for a private house.
This is what a finished slab foundation looks like for a dwelling made of foam blocks or concrete, as well as for a wooden private house.
Among other types, a monolithic slab has the highest load-bearing capacity and strength for houses made of wood, foam blocks or other materials. As for the disadvantages, there is only one - increased costs for materials. Either way, the design pays off in durability.
- has increased strength;
- Suitable for soft soils.
- high cost;
- requires a flat surface.
Compare all the designs, study their pros and cons, find out what kind of soil the future house made of concrete, foam blocks or wood will stand on. When you have this information, you will be able to build a reliable and comfortable home.
Pros and cons of strip foundations
Comparison of advantages and disadvantages. Some of them are subjective, and some are mutually exclusive under certain conditions.
Advantages:
- simplicity of the device . The technology for pouring a strip foundation is so simple that it is often done by hand, without involving specialists or hiring expensive equipment;
- reliability . Along with a slab foundation, it is the strongest and most reliable foundation for any home. A strip foundation can not only withstand significant loads, but also effectively redistribute them along the base;
- possibility of organizing an underground space . The arrangement of the basement allows you to use it as a place for storing workpieces, installing equipment (heating or cleaning), placing utility rooms (laundry room, pantry for storing seasonal tools or things, gym, etc.). If a basement is not planned, the soil under the floor remains in place, which significantly reduces the amount of excavation work;
- minimum restrictions on use . On almost any type of soil, a strip foundation of one type or another can be used for any building;
- relatively low cost . If we compare the cost of slab and strip foundations, the latter will cost less. Due to the absence of the need to use equipment (as when pouring piles) and available materials (concrete, brick, reinforcement), it also allows you to reduce costs;
- long service life . This indicator depends on many factors, which will be analyzed below.
Flaws:
- impossibility of use on soft soils.
- concrete reinforcement also entails an increase in costs, both financial and time;
- the need to use special equipment. To make a block strip foundation, a crane is required, and increasing the speed of pouring a monolithic foundation is possible through the use of a concrete mixer. But in general, pouring a foundation with your own hands is within the power of anyone;
- labor intensity of the work. If we exclude the use of machinery, then digging a trench, constructing formwork, tying reinforcement and pouring takes a fairly long period of time. Of course, it can be reduced through additional resources in the form of equipment and hired workers, but in this case the cost of the strip foundation will increase. Although under the indicated conditions, it can be made in a week and poured in a day;
- a significant amount of excavation work and the need to remove excavated soil;
- the presence of formwork when pouring a monolithic strip foundation increases the cost and timing of the work;
- the significant weight and dimensions of the structure affect the size of the construction budget. The price of a strip foundation can be about 30% of the cost structure for the construction of the entire house;
- the need to take into account a significant number of different factors that determine the dimensions and configuration of the foundation, as well as material consumption.
With proper calculation and strict adherence to construction technology, most shortcomings can be easily eliminated.
Basic types of foundations.
The following types of foundations can be used as the foundation for a residential building: • strip foundation:
a continuous sheet of reinforced concrete (for small buildings it can be made of brick) in the form of a closed contour, laid under all load-bearing walls;
• slab
(“floating”): is a monolithic reinforced concrete slab;
• columnar:
a system of massive concrete, brick, wooden pillars or supports with masonry, located at some distance from each other, with or without a grillage (frame connecting the pillars to each other);
Monolithic columnar foundation for a private house.
Pouring a columnar foundation.
• pile:
supports made of pipes connected by a grillage or without it; unlike the columnar one, it is not installed in holes, but is screwed or driven directly into dense soil.
Differences in depth
Pre-design calculations for the foundation are carried out in order to find out the bearing capacity of the soil and correctly select the parameters of the tape.
The degree of influence of soil heaving forces on the integrity of the structure depends on the depth of laying the foundation. Therefore, engineers examine the type of soil, find the degree of heaving, the freezing point and the groundwater level.
The found values allow you to select the height of the underground part of the base. In this regard, strip foundations are distinguished by laying depth:
- Non-recessed type . It is characterized by the fact that the tape lies on the surface of the soil, and its height starts from the zero level of the site. This type of foundation is used extremely rarely for residential buildings. Can be used for the construction of light buildings. At the same time, it is recommended to use the technology for a monolithic foundation, since when soil masses move, the risk of destruction of the block structure is quite high.
- A shallow foundation is characterized by the fact that its construction work is carried out above the freezing point. As a rule, the height of the underground part of such a foundation does not exceed 0.5-0.6 m. The technology provides for high-quality insulation of both the foundation walls and the blind area in order to reduce the destructive effects of soil heaving forces. If a geological analysis of the site showed that groundwater flows at a depth of less than 1 m, then this type of foundation will not provide the structure with the necessary stability.
- Deeply buried belts are lowered below the freezing point of the soil so that the sand cushion rests on solid rock with sufficient load-bearing capacity to support the weight of the structure. Construction is carried out using measures to waterproof the base. In the case of close groundwater, a drainage system is installed.
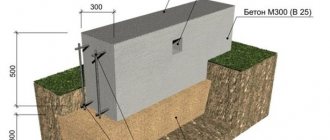
Strip foundation.
Despite the fact that the construction of such a foundation requires a large amount of work and a considerable amount of concrete, due to their high strength, such foundations are most often used in construction. They are used both in the construction of stone or brick, and wooden and cinder block single- and multi-story buildings. To construct such a foundation, formwork with a reinforcing belt is prepared, into which the concrete mixture is poured. If there is weak soil, you can make a wider base (stepped foundation) or make it in the shape of a trapezoid
. where its wider part will serve as the sole.
Types of strip foundations for a private house.
Rectangular, stepped and trapezoidal strip foundations.
According to the method of construction, such foundations are divided into:
• monolithic:
a reinforcement frame is installed in the prepared formwork, then the formwork is filled with sand-concrete or rubble concrete mixture; Brick can also be used for their arrangement, however, the service life of such foundations is much lower;
• prefabricated:
assembled from ready-made concrete blocks, fastened together with cement mortar using reinforcement; but the strength of such a structure will be lower than that of monolithic ones, since at the joints the waterproofing will be significantly reduced, which will lead to its premature destruction, especially in swampy areas.
Types of foundations for a private house advantages.
Prefabricated strip foundation.
Based on their depth, strip foundations are divided into:
• shallow
. used for light buildings on slightly heaving soils (soils that are not very susceptible to frost heaving), laid to a depth of 50-70 cm;
Types of foundations for a garage in a private house.
Shallow strip foundation.
• deep-seated:
a rigid concrete frame is installed at a considerable depth (20-30 cm lower than the freezing level of the soil); used for buildings of significant weight.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Deeply buried strip foundation.
Important!
To avoid damage by groundwater,
a layer of waterproofing
.
In areas with low temperatures in winter, such a base can be additionally insulated
.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Waterproofing and insulation of the foundation.
When planning a basement, the walls of such a foundation also serve as the walls of the basement
.
As a rule, a sand and gravel cushion
. acting as drainage and serving as protection from groundwater. It is also capable of compensating for deformations. The absence of such a cushion is allowed only when constructing small buildings.
Advice
.
It is possible to reduce material costs in the construction of lightweight buildings by laying intermittent strip foundations
. They can be made from ready-made concrete blocks or poured directly on the construction site.
Design of a prefabricated intermittent foundation for a private house.
Intermittent strip foundation.
Strip foundation, advantages and disadvantages
Strip foundations are most often laid under houses. They can be monolithic or prefabricated. To create a monolithic foundation, a trench is dug along the border of the future house, formwork and a reinforcing belt are installed in it, and mortar is poured.
Prefabricated foundations are made from blocks that are installed in the trench using lifting equipment. The blocks are fastened together with wire and mortar.
Depending on the type of foundation, there are shallow and fully buried foundations. The first option is installed where surveys have shown groundwater close to the surface. Such a foundation is poured for the construction of a wooden or brick house on one floor. The second option is suitable for buildings with two floors and thick walls.
The entire volume of mortar for a monolithic strip base is poured once, sometimes in two steps, but then a seam remains between the levels. Moisture can get into it, which will damage the base.
Advantages
The advantages of a strip foundation include:
- Reliability of the structure even on difficult soils (for fully buried ones).
- Creation of structures of any geometry (for monolithic ones).
- Low price.
- Possibility to organize a basement or ground floor (for fully recessed ones).
- Saving on materials (for shallow ones).
Flaws
For shallow ones:
- Low rigidity levels.
- There is a high probability of cracks forming if the house is made of brick or stone.
- The need to organize a high-quality drainage system and a voluminous sand cushion.
For fully recessed ones:
- High consumption of solution.
- A large amount of work to excavate the pit.
- The need for thermal and waterproofing of the base.
For a prefabricated house: the lines of the future house can only be made straight.
Slab foundation.
One of the most expensive designs. It can be either solid from monolithic concrete or in the form of a lattice slab made of crossed reinforced concrete beams with sealing of joints. Its minimum thickness is 20 cm (excluding stiffeners). Maximum thickness – 30 cm.
Method of arranging foundation formwork for a private house.
Lattice slab foundation.
Since such a foundation is not buried deep into the ground and is not subject to deformation during freezing and thawing of the soil, it is used mainly in difficult areas with mobile, loose (subsidence) or heaving soil
during the construction of small buildings (baths, garages, etc.).
If thoroughly insulated, such structures can also be used as a finished subfloor. The use of ready-made prefabricated slabs
is permissible only in the case of the construction of small buildings, since due to the heterogeneity of such a structure, its strength is reduced.
The slab foundation consists of several layers:
• geotextiles; • cushions made of sand and crushed stone; • insulation; • reinforcing belt; • the concrete slab itself; • waterproofing layer.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Slab foundation cut.
Materials
The types of materials used in the construction of foundations are very numerous - everything depends not only on the weight of the future structure and the specifics of the soil, but also on the chosen type of foundation and prices for various building materials in a particular region. At the beginning of the article, wood, brick and concrete were mentioned as the main materials, but not only them can be used, especially if the weight of the future building is not so significant.
A strip foundation for a light building can be built from relatively light materials - the same foam blocks or cinder blocks. If the soil under the construction site is quite reliable, and the building itself is planned to be small and built from the same lightweight materials or expanded clay concrete blocks, it is likely that such a foundation will be sufficient.
The use of metal is possible in almost all types of foundations. The combined reinforced concrete option can consist of both pillars and strip, and the latter can be integral, poured on site, or assembled on site from separate blocks produced by the factory method. Reinforcing metal mesh can even be used in combination with conventional brickwork. A pure metal foundation for light buildings can even be made from pipes alone, using some of them as pillars or piles, and the other welded on top in the form of a grillage or base for it.
This material is valued for its availability and the ability to be easily processed even at home, because theoretically, a columnar or pile-type foundation can be assembled even from old railroad sleepers. Another thing is that such pillars or piles will have to be additionally protected, and although it is usually recommended to use special impregnations against insects, rodents or moisture, even roofing material that could have remained after roofing work in the main house will help solve the latter problem. Sheets of roofing material must be tightly wrapped around that part of the piles that goes deep into the ground. However, it should be remembered that roofing felt only protects from moisture, but not from complete flooding.
We advise you to study - Leveling the floor under the laminate depending on the base and the nature of the irregularities
Columnar foundation.
This is one of the low-cost and least labor-intensive ways to build a foundation for houses with light wooden or frame walls. Can be used for the construction of buildings on heaving soils
under conditions of laying the foundation just below the soil freezing depth.
In small buildings, it is possible to use shallow
(half the standard depth) or
non-buried
(40-50 cm) columnar structures.
Such structures are installed every 3-6 m, as well as in the corners of the building and at the junction or intersection of load-bearing walls on a sand “cushion”. Can be either monolithic
and be erected directly at the construction site, or
prefabricated
(manufactured in factories).
Types of foundations for a private house.
Monolithic reinforced concrete columnar foundation.
The cross-section of the pillars depends on the material of manufacture. Thus, when using concrete, their minimum cross-section is 400 mm, in stone structures - 600 mm, and when laying bricks - 380 mm.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Brick columnar foundation.
Types of piles include prefabricated structures of the so-called “ glass type”
" having two or more sections. In this case, the first link is driven half the length of the pile. The second part is inserted into a tubular glass. However, such structures are used only for the construction of industrial facilities and are not used in private construction.
The main disadvantages of columnar foundations include:
• impossibility of use on moving soils due to the tendency to tip over; This drawback can be partially eliminated by installing a grillage, using anchor foundation blocks or foundations with an expanded base;
Pouring a grillage for a private house.
Arrangement of a grillage for a columnar foundation.
Anchor columnar foundation for a private house.
• restrictions during construction on weak-bearing subsidence, water-saturated or peat soils; • complexity of the arrangement of basement premises (basements, underground garages, etc.).
Types and types of strip foundation
Due to the fact that the strip type foundation is the most popular, various modifications have appeared that make it possible to obtain the required foundation reliability while saving time, money, materials or other resources.
In particular, strip foundations can be classified according to the following criteria:
By device method
There are three varieties:
Monolithic
In this case, the foundation will be a closed loop. Suitable for houses of any configuration and weight. A monolithic strip foundation is considered the most reliable type and allows you to guarantee the stability of any structure.
Another feature of the monolithic structure is that there is no need to waterproof it. Additional strength to the foundation is given by reinforcement (a connected reinforcement cage laid in the thickness of concrete).
Because a monolith is a solid wall, it is often used as a wall when planning a basement. A significant advantage of a monolithic strip foundation is the relative simplicity of its pouring and the absence of the need to use expensive equipment. However, its disadvantage is the complexity of the work and the long period of installation.
Based on the design features of this type of foundation, pouring should be timed to coincide with the warm and dry season. Thus, the seasonality factor should be taken into account. In order for the base to be durable, it must dry gradually and naturally.
Made
Block, panel, block foundation - all these are names for the same type of foundation. To speed up the construction process and eliminate the influence of weather on the strength of the foundation, some users prefer to use concrete blocks instead of pouring a monolithic foundation.
The blocks fit tightly together, which eliminates the need for cement mortar. However, experts advise using a solution. This approach simplifies design, eliminates errors during pouring, and reduces the waiting period. But its arrangement often requires the use of special equipment (depending on the size and weight of the block).
Also, a prefabricated foundation requires mandatory waterproofing. In addition, it is not able to level out soil heaving, since individual blocks can be displaced by directed pressure. In addition, the use of blocks does not allow reinforcing (strengthening) the base.
Prefabricated monolithic
As the name suggests, this type of strip foundation combines the features of the two previous options. Thus, the installation process will consist of laying blocks and combining them with panel formwork, into which concrete will be poured.
By depth
There are three varieties:
Non-buried
A distinctive feature is the absence of a recessed (underground) part. The base of the foundation (lower mark) is located at the zero level, i.e. directly on the ground, or with a slight depression of 5-10 cm. The principle of the device is focused on removing the top layer of soil and replacing it with a sand and gravel cushion.
As a rule, NZLF (non-buried strip foundation) is installed under small country houses with seasonal residence, for gazebos, verandas, bathhouses and other outbuildings.
Shallow
Some types of soil do not pose a threat to the structure, which means there is no need to lay a strip foundation to a significant depth. Therefore, on hard soils it is permissible to place the base of the foundation above the freezing depth. Often this variety is used for the construction of small wooden and frame houses, outbuildings, bathhouses, gazebos, etc.
In some cases, a shallow strip foundation (MSLF) is supplemented with supporting “legs” - piles, which are placed at key points of the perimeter (in the corners, at the intersection of load-bearing walls, under columns, etc.). The lowest point of the piles is located below the depth of soil freezing, which allows, on the one hand, to obtain a reliable foundation for the structure, and on the other, to reduce material consumption, without losing the reliability and bearing capacity of the foundation. This type of foundation is called pile-strip.
Recessed
In this case, the depth of the foundation (its base) is located at a level below the soil freezing level. In addition, mobile soil also does not allow for a shallow foundation, but requires deep burial.
Deep laying eliminates the risk of the building moving simultaneously with soil movement, and also makes it possible to make the foundation more resistant to the forces created by soil movement. In general, this type of foundation is more reliable than a shallow foundation, but its use is characterized by significant consumption of building material, accordingly, costs increase and the labor intensity of the work increases.
By type of filler used
There are five varieties:
- sandy _ Can serve as a basis only for light buildings (sheds, summer kitchens, small country houses);
- brick _ It is an analogue of a prefabricated strip foundation, only instead of concrete blocks, brick is used as a lighter material. This avoids the use of special equipment;
- concrete strip foundation. The most common option. Concrete is preferred due to the possibility of pouring directly at the construction site, as well as the ability to reinforce the base;
- rubble _ It can be considered an analogue of prefabricated monolithic, since in this case the rubble stone is laid on cement mortar. Thus, quarry, very conditionally, acts as a filler;
- soil-cement . It is advisable to use when constructing a light non-residential building on solid soil.
Note. When building a foundation, it is important to prevent the appearance of voids, because their presence reduces the strength of the base.
Pile foundation.
A similar foundation is used for the construction of buildings on water-saturated, swampy or loose soils and soils subject to severe winter heaving, when it is necessary to deepen the foundation to a very great depth.
Types of foundation piles include:
• driven piles:
reinforced concrete rods with a square cross-section and a pointed end; they are immersed into the ground using special installations using the impact method;
Types of foundations for a private house.
Driven reinforced concrete piles.
• pipe concrete:
a hollow steel pipe equipped with a cone-shaped tip;
after installation, concrete solution is poured into the pipe; driving is carried out using special pneumatic machines; rarely used in private construction; Types of foundations for a private house.
Pouring pipe concrete piles.
• bored:
a reinforcement frame is first inserted into a prepared small well, and then cement mortar is poured into the prepared hole;
Drilling and reinforcing the foundation for a private house.
Preparing holes and pouring bored piles.
• screw:
They are hollow metal rods, at one end of which there are blades, with which they are “screwed” into the ground manually or using special equipment.
Choosing the appropriate type of foundation for a private house.
Foundations for houses can be very different. They are made from various materials and using various technologies. The choice is made separately for each specific case. It is impossible to clearly say which foundation is better. Even when building identical houses in different places, the type of support and the costs for it can vary dramatically.
- bearing capacity of soils on the site;
- soil moisture and groundwater level;
- terrain;
- the need for a basement;
- number of storeys of the building and the mass of its structures.
All these factors need to be taken into account simultaneously. It is difficult for a non-professional to accurately select what kind of foundation is needed for construction. If possible, it is better to contact an experienced designer. At the same time, he needs to provide information about the soils on the site and the design features of the structure.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Extracting a pit is the easiest and cheapest way to find out the type of soil and the depth of groundwater.
Before choosing the type of foundation, geological studies must be carried out. To build a house in the private sector, you don’t have to order an expensive procedure. It will be enough to roughly determine the type of soil and its depth. This work can be done in two ways:
Choosing a foundation for a frame house
To determine which type of support is best for frames, consider the main principles:
- Construction on loose soil requires the installation of a rigid space underneath.
- The service life of the structure must coincide with the service life of the foundation.
- You cannot make a basement if groundwater is close to the surface.
What factors influence the choice:
- number of storeys of the building;
- building parameters;
- freezing depth.
Frame houses do not require a powerful foundation.
Structures of this type are lightweight and do not put much pressure on the soil. Remember, foundation costs are no more than 15% of the total estimate.
For frame buildings, you can choose any type of foundation, as well as for a veranda to a house. Under favorable conditions, it will be enough to install pillars in the corners of the building and under the internal walls.
Types of foundations.
To answer the question of what types of foundations there are, we need to consider several classifications. For the construction of a building, types of foundations are distinguished by design and manufacturing method, as well as by material.
The choice of foundation, depending on the material, is proposed to be made from three options:
The first option is currently practically not used. Wooden piles were widely used in the past to construct buildings in marshy areas. But the disadvantage of wood is its high susceptibility to rotting and low strength. In modern conditions, it is not worth considering these types of foundations for a private house.
Another option for construction is metal. It has a limited range of applications. Only a certain type of foundation for wooden houses and frame buildings is made from it - pile-screw.
Pile foundation for a private house.
A pile-screw foundation is suitable for light wooden houses.
Reinforced concrete types of foundations for houses are the most widespread. This is due to the fact that concrete performs very well when working under compression. These are the loads that occur in the underground part of the building. There are exceptions, but in this case metal fittings are included in the work. Due to the combined action of concrete and reinforcement, reinforced concrete varieties are highly reliable and durable.
When using a reinforced concrete option, the question almost always arises: which foundation to choose, prefabricated or monolithic?
Prefabricated technology involves the use of ready-made factory-made elements. These types of concrete foundations can be built quickly; there is no need to wait for the material to harden. But these options are more intended for mass construction. They allow work to be carried out on an industrial scale in a short time, but require special heavy-duty and lifting equipment. It will be difficult and expensive to make such a foundation for a house yourself.
Types of foundations for a private house.
To install a prefabricated foundation, a crane is required.
An excellent option for private construction would be monolithic types of foundations and their various variations. Manufacturing requires virtually no special equipment. If desired, all work can be done manually. But still, to improve the quality of work and reduce the time it takes to complete it, it is recommended to order ready-made concrete at the plant and have it delivered using special mixers. In addition to the mixer, it is worth ordering a concrete pump. This technique allows you to quickly and effortlessly distribute the mixture into the formwork.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Monolithic foundation is one of the most popular solutions in private housing construction.
The disadvantage of monolithic technology for manufacturing foundations will be an increase in construction time. A stone made using this type gains strength on average within 4 weeks. During this time, it is prohibited to build walls on the supporting part.
In addition to differences in material and technology, it is worth highlighting the classification according to design features. Before choosing a foundation, you need to consider four main types. There are also several modifications within each group.
The following types are used for the construction of buildings:
Strip foundation.
If you answer the question, what kind of foundation is needed for a building with a basement? then the answer will be unequivocal - tape. This is the best and practically the only option. You can also use a slab base for these purposes, but tape will have to be used in this case as well.
What are strip foundations made of? It can be made from monolithic or prefabricated reinforced concrete. The device assumes the presence of three types of tapes depending on the depth of installation:
- Recessed. These types of house foundations are used when a basement is needed, as well as for the construction of massive buildings. The laying depth is determined depending on the height of the basement and the depth of soil freezing. The last characteristic is found separately for each region. During self-construction, you can use special maps and tables to find the mark.
- Shallow. This tape is buried approximately 70-100 mm into the ground. They are used for massive buildings without a basement on fairly good soils. It is also relevant when the groundwater level is located at a distance of more than 1.5 m from the surface. When supporting above the freezing mark, enhanced waterproofing and insulation must be provided. Read more about shallow tapes.
- Not buried. Used only for small buildings on solid, non-heaving foundations. Does not have high load-bearing capacity.
Non-recessed type.
You will also have to choose a strip foundation based on the type of section. It can be rectangular or T-shaped. The second option assumes the presence of a widening at the bottom in the form of a pillow and has higher stability and load-bearing capacity. It is used for buildings made of brick or concrete. When producing tape using prefabricated technology, special FL foundation pads are used to ensure widening; their production is carried out in a factory environment.
Slab foundation.
A slab is a good option for unstable soils. Just like the tape, this type can be recessed, shallow and non-recessed. The first option is used quite rarely due to its high cost.
Monolithic slab foundation diagram for a private house.
If we compare foundations, the slab has the greatest load-bearing capacity with approximately the same labor costs. In terms of load-bearing capacity on weak or marshy soils, only some types of piles can be compared. But they will cost much more and require a lot of effort and special equipment.
Most often, when constructing private houses, a non-buried slab is used. You can also consider an insulated Swedish stove. It will be an excellent solution for heaving soils in the northern regions.
Even a non-professional can make a slab. In private construction, the thickness of the structure is usually 200-300 mm. Such a foundation can support a two-story brick house. Reinforcement is performed with meshes in two rows. If the slab thickness is 150mm or less, then one row of reinforcement must be laid. Advice: it is recommended to use concrete grades B20-B25 for pouring. This is due to the fact that the slab foundation, in addition to compressive loads, perceives bending forces, which concrete does not handle very well. To avoid the appearance of cracks, you need to take care of high-quality reinforcement and durable concrete.
The plate is used in the following cases:
- construction of a brick or concrete house without a basement on swampy or unstable soils;
- construction of buildings at a high groundwater level (at a distance of at least 50 cm from the ground surface).
Slab foundations are also used in the construction of small building forms, which must stand on separate foundations to prevent uneven shrinkage. These forms include:
Pile foundation.
Piles are the only reasonable option when building on soils with groundwater levels higher than 50 cm from the surface of the earth. They also allow you to build a house on an unstable foundation and with strong differences in elevation on the site without significant effort.
In this case, it is not possible to provide a basement. The base is covered with finishing materials, leaving ventilation gaps and openings for free air movement under the house.
A grillage is installed along the edge of the piles. It can be made of wood, reinforced concrete or metal. The choice of material is made depending on the material of the walls and the piles themselves. For example, when building a wooden house, it is reasonable to use wood frames, and when constructing reinforced concrete piles, it is wise to use concrete.
Piles are classified according to material, manufacturing method and driving method. I can make it from metal or reinforced concrete, either in a factory or on a construction site. There are four most common types of piles:
- Driven from reinforced concrete. Not common in the private sector. Initially intended for use in mass construction and require special expensive equipment.
Types of foundations for a private house.
Driven piles are installed with a special pile driving machine.
- Bored. They are made of reinforced concrete directly on site using monolithic technology. They are not recommended for use at high water levels in the ground, since they require water reduction during construction work. This is a costly undertaking. Read more about bored foundations.
Comparison of screw piles and bored pile foundations. Bored piles are often combined with a monolithic grillage. - Screw. They are made of metal. Such elements are a pipe with a screw welded at the end. Due to this screw, the pile itself digs a hole during installation, which avoids the need to excavate the soil. Screw piles do not have high load-bearing capacity. They are used mainly in private construction as supports for frame or wooden houses. Can be used for one-story buildings made of lightweight concrete. The most common element diameter is 108 mm. Read more about installing a pile-screw foundation.
Types of foundations for a private house. There are many ways to tie screw piles. - TISE. Piles of this type are made in much the same way as bored piles. But this option has a significant difference - widening at the bottom. It is made using a special drill, which at a certain mark can throw off the knives that perform the widening. The solution is perfect for working on heaving soils, since the design prevents the house from being pulled out of the ground.
Construction of pile foundations for a private house.
Due to the larger cross-section, the TISE foundation has a greater load-bearing capacity.
Columnar foundation.
This option has the lowest load-bearing capacity of all presented. The approval does not affect special glass-type pillars, which are used as a base for columns in the construction of public and industrial facilities.
Construction of a columnar foundation for a private house.
A columnar foundation is very simple to manufacture, but has a low load-bearing capacity.
Most often, poles are used in the construction of small outbuildings on solid soils. In this case, they are made shallow or shallow. They can be made from ready-made elements (bricks, blocks) or from a monolith. Read more about columnar foundations.
Before choosing a foundation for a house, you need to carefully study all the necessary information. An irresponsible attitude can lead to cost overruns, building distortions during operation, or other troubles.
Recommendation: A good large review article, from it you can learn about the different types of foundations for building a private house. The abundance of information can lead you astray and you will choose the wrong type of foundation for your home. As a result, you will lose a lot of money and time. Be extremely careful in your choice.
Types of foundations by type of construction
Each type of foundation used in construction has its own installation technology and conditions of use that must be taken into account when choosing. To build a private house, it is enough to consider four types:
- tape;
- slab;
- columnar;
- pile
Types of foundations
Tape
The most common type of foundation. Visually it looks like a tape (hence the name), which is mounted on a gravel-sand cushion under external and internal load-bearing walls. In addition to prefabricated and monolithic, the classification of strip foundations includes shallow and recessed varieties.
Strip foundation
A shallow tape is installed above the freezing point of the soil at a distance of no more than 70 cm from the ground level. They are used when it is necessary to build a frame or low-rise house on solid or deeply frozen soil.
The buried version is laid below the freezing point to a depth of 2 m. It is resistant to soil movement and heaving. Such a foundation is made for brick, stone, and concrete buildings. The recessed type is not recommended for low-rise wooden houses, since the weight of the structure is not enough to give the foundation stability when the soil moves.
In order to save money for light buildings, the strip foundation is made in the form of a broken line. Separate sections are laid only under load-bearing elements (for example, columns). To increase the support area on weak soils, the cross-section of the tape is made in the form of an inverted T or trapezoidal shape. The lower wide part is called the sole, and the vertical part is called the wall.
To install a strip foundation use:
- Reinforced concrete. The most durable material. The material is affordable, but it takes a lot of time to prepare and pour.
- Rubble concrete. Cheaper than the first option, but inferior in strength. Broken brick or stone is used as filler.
- Brick. In essence, this is ordinary masonry buried in the soil, which can support the weight of a five-story building.
- Foundation blocks. They install quickly, but the price is steep.
Advantages of the tape:
- high load-bearing capacity;
- resistance to seismic soil vibrations;
- construction of a basement or ground floor is available;
- installation of a monolithic foundation of any configuration;
- small amount of excavation work;