How is an approximate calculation of power consumption made?
First of all, the implementation of such mathematical operations is required to ensure the safety of the premises.
Any cable or wire is the main means for transmitting and distributing current to electrical devices. Almost every day, an electrician needs to connect an electric kitchen stove somewhere, fix an outlet, or install a new lamp. In a word, the need to calculate the wire cross-section is due to ensuring a constant flow of electricity and avoiding various unpleasant situations, which include some damage to the electrical wiring itself.
If you connect the device via a cable and the cross-section of the selected wires is small, unable to ensure the normal functioning of the device in the required volumes, then the cable itself will overheat, which, in turn, leads to slow destruction of the insulation. As a consequence of a possible short circuit. As a result of a decrease in the reliability and service life of the electrical wiring in the room, the operation of the electrical wiring in the room will sharply drop or, moreover, disappear, that is, burn out.
The most common everyday situation today is an attempt to save on the cost of wires, which inevitably leads to short circuits or fires.
It is for this reason that before carrying out the electrical wiring of the cable, it is necessary to determine the cross-section of the wires used throughout the apartment:
- the number of household appliances that will be in the apartment;
- total power and consumed load of devices, taking into account a small margin;
- carry out mathematical calculations;
- determine the type and cross-section of the required wires.
In order to find out how to determine the wire cross-section by power, you need to perform a number of sequential actions:
- We make a complete list of electrical appliances used in a given room.
- Determine the total power consumption of all equipment located in the room. To do this, take a sheet on which the entire list of devices is marked and mark its power consumption next to each one. This value can be determined by taking readings from the label on each device or by studying the package insert from the equipment.
- Let's sum up all the obtained values.
- We determine which devices will be in continuous operation, how many units in periodic operation and the number of rarely used ones. Such measures are necessary to calculate a more accurate cross-section of all wires.
- We sum up the power of constantly operating devices and periodically switching ones. We determine the approximate operating time of the wiring with such a load (if the operating coefficient is 70%, then in further calculations it is necessary to take the value 0.7).
- We calculate the cable cross-section based on power. To do this, we divide the total power of energy consumed by the network operating coefficient and obtain the required value of wire power. Using a special table of wires, we determine the cross-section of the cores.
Which foundation is cheaper: monolithic or FBS?
The quality and degree of reliability of the foundation is most clearly demonstrated by the popularity it has gained among builders.
The recognized and undisputed leader among all options is the strip base, which demonstrates an optimal set of performance qualities and cost-effectiveness.
Alternative types of support structures are designed for specific conditions and are used only in situations where the tape cannot perform its functions.
In order to determine the advantage or disadvantage of one or another type of foundation, it is necessary to analyze their qualities and features.
Let's consider the parameters of the tape in comparison with another type of base - a monolithic slab.
What is a strip foundation
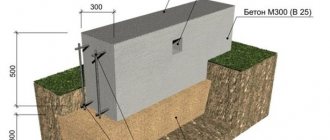
A strip foundation is a support for external and internal load-bearing walls, made in the form of a thickened strip immersed in the ground. It takes on the weight of the building and evenly redistributes it, transferring the load to the soil layers.
All parameters of the tape - thickness, height, immersion depth - directly depend on the load-bearing properties of the soil, the composition of the layers and the groundwater level (GWL).
The main factors affecting the soil on the belt are:
- Composition, homogeneity of structure.
- Deposition level and presence of layers of soil water.
Both factors interact with each other. The most problematic type of soil is clay. It does not allow water to pass through, but is capable of accumulating it in the pores, creating in winter the danger of heaving - expansion of frozen water, causing a change in level.
Heaving loads are uneven and act on different points of the foundation, deforming it. In addition, such forces are not constant and can occur alternately in different areas of the supporting structure.
The solution to the problem is to immerse the tape to a depth below the winter freezing level. Under such conditions, heaving loads do not occur from below, but the developed lateral surface of the tape experiences significant forces in the horizontal plane.
To reduce these loads, a shallow type of strip foundation is used, which is immersed relatively shallowly - 0.5-1.5 m.
Horizontal lateral loads are reduced, and forces from below are collectively compensated:
- The weight of the building.
- No freezing of the soil under a heated house.
- A layer of sand backfill that performs drainage functions and takes on heaving loads.
The design of the tape is quite simple and understandable; there are no special difficulties in creating it, which reduces the risk of illiterate construction and reduces the risk of destruction.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the tape are:
- High load-bearing capacity.
- Durability, reliability.
- Resistance to external loads.
- Simplicity, cost-effectiveness of construction.
- Several design options are available to best suit existing conditions.
- Possibility of arranging a basement or cellar.
The disadvantages include:
- The need for a thorough examination of the hydrogeological conditions of the site, the composition of the soil layers, and other features.
- Quite a large volume of excavation work, for which it is often necessary to involve construction equipment.
- The mass of the tape is quite high and concentrated on one line, which contributes to soil subsidence during unscrupulous construction.
Kinds
Tape bases differ in several ways.
According to the depth of placement, there are types:
- Unrecessed . Almost the entire tape is located on the daytime surface. It is built in conditions where immersion in the ground is impractical or impossible - on dry dense soils, rock slabs, etc. In practice, it is rare, since appropriate conditions in northern latitudes are almost impossible.
- Shallow . Used on dry, non-heaving (or slightly heaving) soils. It is used for the construction of relatively small buildings, low-rise residential private houses.
- Recessed . A full-fledged type of tape is intended for large and massive buildings. It has the greatest load-bearing capacity and strength, but requires a lot of labor and consumption of building materials.
By tape design:
- Monolithic . It is a continuous strip of reinforced concrete. It has maximum strength and load-bearing capacity, and is highly resistant to heaving loads. The disadvantage is that the concrete needs to be cured to gain technological strength, which takes a month.
- Prefabricated . The strip is built from special foundation blocks (FBS), brick, stone, etc. This option is only suitable for non-heaving soils with no deforming effects. The most durable tape is made from FBS; as the size of the fragments decreases, the resistance to the deforming influences of the soil decreases. Beneficial in appropriate conditions due to the high speed of construction.
- Combined . An example of such a foundation is the pile-tape type. A combination of two types of support is formed when the piles provide contact with dense and stable layers of soil, and the tape accepts and redistributes the load from the walls of the building. Used in difficult conditions, in heaving, loose or marshy areas. Construction requires the use of special equipment.
There are also various design options for the sole, the supporting element of the foundation, used in certain conditions.
What conditions is it suitable for?
Strip bases are designed to function in a variety of conditions, but they perform best on dense, dry and stable soils with low groundwater level.
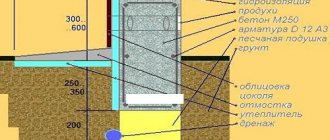
With an increase in problematic positions due to the hydrogeological conditions of the site, the load-bearing capacity decreases and the need arises for additional measures - increasing the backfill layer, installing a durable base (concrete footing), drainage. On heaving soils, strip foundations are used to a limited extent, only if design capabilities are available.
The base tolerates low temperature conditions well, but requires taking certain measures to isolate it from groundwater or condensate (waterproofing, insulation).
What is a monolithic slab
A monolithic foundation is a solid reinforced concrete slab on which a house is built. It does not create a significant load on the ground, since due to the large area the specific pressure is relatively low.
The concrete pad, together with the house, moves freely on the surface of the soil as it moves; the rigidity of the slab is quite enough to ensure a level and reliable foundation for the building.
During construction, a small pit is dug - in most cases, the top layer of soil is simply removed. Then a layer of sand backfill is created, it is leveled and compacted, and a layer of geotextile is laid.
Insulation (mainly specialized polystyrene foam) is placed on top, formwork and reinforcement frame are installed. After this, concrete is poured and the slab is kept until it reaches technological strength.
As a result, a strong, insulated base is formed, ready to accept the loads from the building and resistant to soil influences.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of a monolithic base include:
- Possibility to build houses on weak-bearing, heaving or water-logged soils.
- The high load-bearing capacity of the slab allows the construction of fairly large and heavy buildings.
- With proper reinforcement, the slab is able to withstand all impacts that can arise and disappear suddenly. All ground movements are perceived quite easily; the slab “floats” on the soil surface like a raft.
- The design of the slab is simple, which allows you to avoid serious mistakes during construction.
- The creation of a slab immediately forms the floor of the 1st floor, which greatly simplifies further work.
Proponents of this technology claim that a monolithic foundation has no disadvantages.
This is not entirely true:
- The slab does not allow for a basement.
- There is practically no possibility of repairing the base.
- The consumption of building materials and the volume of excavation work are very high.
- The cost of such a foundation is very high, which is one of the main limiting factors.
The disadvantages are not too fundamental, since the conditions in which a monolithic slab is used are most often not suitable for alternative options.
Varieties
There are several types of slab base:
- Prefabricated slab. It consists of ready-made reinforced concrete slabs laid on a prepared site.
- Monolithic slab, which is poured directly on the site.
According to the type of construction they distinguish:
- Solid slab . Used for relatively light and small buildings.
- Ribbed plate . The sole of such a base has stiffening ribs that firmly anchor the supporting structure in the ground, preventing it from moving horizontally. In addition, the presence of ribs contributes to a more even distribution of loads from the weight of the building.
- Box . A type of slab in which the ground floor floor is a separate floor and the surface of the slab forms the basement.
Source: https://betfundament.com/kakoy-fundament-deshevle-monolitnyy-ili-iz-fbs/
Calculation of cable cross-section by power: table with important characteristics
The optimal cross-sectional area of the cable allows the maximum amount of current to flow without heating up. When carrying out an electrical wiring project, it is important to find the correct value for the wire diameter that would suit the specific power consumption conditions. To perform the calculations, you need to determine the total current. In this case, you need to find out the power of all equipment that is connected to the cable.
This table will help you choose the optimal parameters
Before work, the wire cross-section and load are calculated. The table will help you find these values. For a standard 220 volt network, the approximate current value is calculated as follows: I(current) = (P1 P2 .... Pn)/220, Pn – power. For example, the optimal current for an aluminum wire is 8 A/mm, and for a copper wire is 10 A/mm.
The table shows how to carry out calculations, knowing the technical characteristics
Load calculation
Even having determined the desired value, you can make certain adjustments for the load. After all, it’s not often that all devices work simultaneously on the network. To make the data more accurate, it is necessary to multiply the cross-sectional value by Kc (correction factor). If all equipment is turned on at the same time, then this coefficient does not apply.
To perform calculations correctly, use the table for calculating cable cross-section by power. It should be taken into account that there are two types of this parameter: reactive and active.
This is how the calculation is carried out taking into account the load
An alternating current flows in electrical networks, the indicator of which can change. Active power is needed to calculate the average. Electric heaters and incandescent lamps have active power. If there are electric motors and transformers in the network, then some deviations may occur. At the same time, reactive power is generated. In calculations, the reactive load indicator is reflected as a coefficient (cosph).
Features of current consumption
Calculation by length
Calculations of parameters along the length are necessary when constructing production lines, when the cable is subjected to heavy loads. For calculations, use a table of cable cross-sections for power and current. When current moves along highways, power losses appear, which depend on the resistance appearing in the circuit.
According to technical parameters, the largest voltage drop should not be more than five percent.
The use of the table helps to find out the value of the cable cross-section along the length
Arguments for choosing a monolithic strip foundation
There are times when there is no point in making a choice: a structure made of FBS or a monolith. There are conditions under which it is necessary to construct a monolithic concrete foundation in the form of a continuous strip:
- If the site has heaving soil foundations.
- There is a risk of increased seismicity in the construction area.
- Significant loads on the foundation, as a result of which the structure will be subject to bending moments.
Considering all these factors, we can conclude that the savings should be reasonable. The main thing for the foundation is strength, stability and reliability of the entire structure and ensuring the integrity of the entire structure.
It is difficult to say unequivocally which type of load-bearing base will be cheaper: monolith or FBS. To make an accurate comparison, it is recommended to link construction to the individual conditions of the site, the nature of the terrain and soil types.
The durability of the building directly depends on the characteristics of the foundation - the underground foundation must successfully withstand operational loads and impacts from the soil. Therefore, at the stage of designing a house, it is important to choose the right type and technology for making the foundation.
What factors influence the heating of wires?
- Cross-sectional area of the core. To give a more accessible idea to the common man, it should be noted that the larger the cross-sectional area of the selected wire in size, the greater the current it can safely conduct. The cross-section of the wires used can be determined in 2 ways: by brand, measured with a caliper.
- Production material. Please note that copper wires have lower resistance. From which it follows that heating will be slower than with aluminum.
- Wiring option. A single wire can always carry a higher current than a wire laid together with others.
- Execution of the gasket. The cross-section of wires laid in a pipe will always heat up faster than in open wiring, since it provides good cooling.
- Isolation. The quality and material of the insulation directly influence the temperature range that the cross-section of the selected wires can pass.
Pile foundations
The material consumption of a pile foundation for a house is really minimal, if you consider the consumption of concrete for pouring the supports. However, the price also includes the price of piles (the total amount depends on their number, depth, design, wall thickness - these parameters are determined by engineering calculations).
The situation with the assessment of labor costs when creating a house support is also ambiguous. The work of installing and pouring piles is really done quickly, which reduces the amount of payment. However, to screw the piles, it is necessary to use special equipment, the rental of which will also require expenses. The literature describes the possibility of screwing it yourself, but this option is acceptable for light buildings and enclosing structures; for a residential building it is better to prefer a machine installation, which will ensure the accuracy of the geometric position and the possibility of deep immersion of piles.
A pile foundation is suitable for a timber, log or frame house. The possibility of their use for houses made of bricks and heavy blocks should be assessed by a specialist.
Thermal calculation using correction factors
For several lines in one cable channel, the tabulated values of the maximum current should be multiplied by the appropriate coefficient:
- 0.68 - for the number of conductors from 2 to 5 pcs.
- 0.63 - for conductors from 7 to 9 pcs.
- 0.6 - for conductors from 10 to 12 pcs.
The coefficient refers specifically to the wires (cores), and not to the number of passing lines. When calculating the number of laid wires, the neutral working wire or grounding wire is not taken into account. According to PUE and GOST 16442-80, they do not affect the heating of wires during the passage of normal currents.
Summarizing the above, it turns out that in order to correctly and accurately select the wire cross-section, you need to know:
- The sum of all maximum powers of electrical appliances.
- Network characteristics: number of phases and voltage.
- Characteristics of cable material.
- Tabular data and coefficients.
At the same time, power is not the main indicator for an individual cable line or the entire internal power supply system. When selecting a cross-section, be sure to calculate the maximum load current, and then check it with the rated current of the home circuit breaker.
In practice, a table is used to carry out calculations. Calculation of the cable cross-section for power is carried out taking into account the shown dependence of the current and power parameters on the cross-section. There are special standards for the construction of electrical installations, where you can view information on the required measurements. The table shows common values.
You can find out the exact indicator using various parameters
- calculate the current strength indicator;
- round to the highest using the table;
- select the closest standard parameter.
The role of power consumed by devices when choosing a wire cross-section
So, the known power of each electrical appliance in the house, the known number of lighting fixtures and lighting points allow us to calculate the total power consumed. This is not an exact sum, since most values for the powers of various devices are averages. Therefore, you should immediately add 5% of its value to this figure.
Average power readings for common electrical appliances
| Consumer | Power, W |
| TV | 300 |
| Printer | 500 |
| Computer | 500 |
| Hair dryer | 1200 |
| Iron | 1700 |
| Electric kettle | 1200 |
| Toaster | 800 |
| Heater | 1500 |
| Microwave | 1400 |
| Oven | 2000 |
| Fridge | 600 |
| Washing machine | 2500 |
| Electric stove | 2000 |
| Lighting | 2000 |
| Instantaneous water heater | 5000 |
| Boiler | 1500 |
| Drill | 800 |
| Hammer | 1200 |
| Welding machine | 2300 |
| Lawnmower | 1500 |
| Water pump | 1000 |
And many believe that this is enough to select almost standard copper cable options:
- cross section 0.5 mm2 for wires for lighting spotlights;
- cross section 1.5 mm2 for lighting wires for chandeliers;
- cross-section 2.5 mm2 for all sockets.
At the level of household use of electricity, such a scheme looks quite acceptable. Until the refrigerator and electric kettle decided to turn on in the kitchen at the same time, while you were watching TV there. The same unpleasant surprise overtakes you when you plug in a coffee maker, washing machine and microwave into one outlet.
The power of electrical appliances is of course a useful and very important characteristic, and most importantly it is informative. It can be used to judge both the electricity consumption and the quality of operation of the device. But when choosing the cross-section of the electrical wiring, power plays the role of an intermediary.
General table for selecting cable cross-section by power
| Conductor cross-section, mm | Voltage, 220 V | Voltage 380 V | ||
| current, A | power, kWt | current, A | power, kWt | |
| 1,5 | 19 | 4,1 | 16 | 10,5 |
| 2,5 | 27 | 5,9 | 25 | 16,5 |
| 4 | 38 | 8,3 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 6 | 46 | 10,1 | 40 | 26,4 |
| 10 | 70 | 15,4 | 50 | 33,0 |
| 16 | 85 | 18,7 | 75 | 49,5 |
Cable size selection table for open wiring
| S | Copper conductors | Aluminum conductors | ||||
| mm2 | Current | Power kW | Current | Power kW | ||
| A | 220 V | 380 V | A | 220 V | 380 V | |
| 0,5 | 11 | 2,4 | — | — | — | — |
| 0,75 | 15 | 3,3 | — | — | — | — |
| 1 | 17 | 3,7 | 6,4 | — | — | — |
| 1,5 | 23 | 5 | 8,7 | — | — | — |
| 2 | 26 | 5,7 | 9,8 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 |
| 2,5 | 30 | 6,6 | 11 | 24 | 5,2 | 9,1 |
| 4 | 41 | 9 | 15 | 32 | 7 | 12 |
| 5 | 50 | 11 | 19 | 39 | 8,5 | 14 |
| 10 | 80 | 17 | 30 | 60 | 13 | 22 |
| 16 | 100 | 22 | 38 | 75 | 16 | 28 |
| 25 | 140 | 30 | 53 | 105 | 23 | 39 |
| 35 | 170 | 37 | 64 | 130 | 28 | 49 |
When using hidden wiring, it is necessary to choose a wire with a cross-section that is 25-30% larger, since the risk of fire increases due to its rapid heating. If several current-carrying lines pass through the channel, then the cross-section can be increased by 40%.
Table for selecting cable cross-section for closed electrical wiring (in a cable duct, pipe)
| S | Copper conductors | Aluminum conductors | ||||
| mm2 | Current | Power kW | Current | Power kW | ||
| A | 220 V | 380 V | A | 220 V | 380 V | |
| 0,5 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 0,75 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 1 | 14 | 3 | 5,3 | — | — | — |
| 1,5 | 15 | 3,3 | 5,7 | — | — | — |
| 2 | 19 | 4,1 | 7,2 | 14 | 3 | 5,3 |
| 2,5 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 | 16 | 3,5 | 6 |
| 4 | 27 | 5,9 | 10 | 21 | 4,6 | 7,9 |
| 5 | 34 | 7,4 | 12 | 26 | 5,7 | 9,8 |
| 10 | 50 | 11 | 19 | 38 | 8,3 | 14 |
| 16 | 80 | 17 | 30 | 55 | 12 | 20 |
| 25 | 100 | 22 | 38 | 65 | 14 | 24 |
| 35 | 135 | 29 | 51 | 75 | 16 | 28 |
All such tables contain power indicators, but the current indicator is more important. The total power is quite easy to calculate, which is why it is designated as the “reference criterion”. But the maximum value of the current consumed by the load is a more important indicator, and it is on this basis that the wire cross-section must be selected correctly.
| Core cross-section mm2 | For cable with aluminum conductors | |||
| Voltage 220 V | Voltage 380 V | |||
| Current A | Power, kWt | Current A | Power, kWt | |
| 2,5 | 20 | 4,4 | 19 | 12,5 |
| 4 | 28 | 6,1 | 23 | 15,1 |
| 6 | 36 | 7,9 | 30 | 19,8 |
| 10 | 50 | 11 | 39 | 25,7 |
| 16 | 60 | 13,2 | 55 | 36,3 |
| 25 | 85 | 18,7 | 70 | 46,2 |
| 35 | 100 | 22 | 85 | 56,1 |
| 50 | 135 | 29,7 | 110 | 72,6 |
| 70 | 165 | 36,3 | 140 | 92,4 |
| 95 | 200 | 44,0 | 170 | 112,2 |
| 120 | 230 | 50,6 | 200 | 132,0 |
To determine an accurate calculation of the cable cross-section for power in the network, it is necessary to use data on the current consumption of devices from an average calculation. However, it should be taken into account that the data on the devices are often given as average values. Therefore, 5% of the full value should be immediately added to this figure.
Some electricians believe that for conducting lighting wires for spotlights, a cable cross-section of 0.5 mm² is sufficient, for chandeliers - 1.5 mm², sockets - 2.5 mm².
Only a careless specialist would argue that the implementation of such an electrical circuit and the cross-section of the purchased wires look quite acceptable for use for domestic purposes. However, what should you do if, for example, in the kitchen you turn on the refrigerator, electric kettle, TV and microwave at the same time?
The same unpleasant situation will happen to you if you plug in a coffee maker, washing machine and multicooker into the same outlet at the same time.
Block or strip foundation: which is better and cheaper?
The longevity and strength of the superstructure depends on choosing the right type of foundation and materials for its construction. Nowadays, two technologies are used to construct the most commonly used strip foundations: pouring a reinforced belt or laying foundation blocks (FBS).
Developers are naturally interested in the question of which technology is better in a particular situation in terms of strength criteria. The financial factor is also important, because building a foundation is a costly undertaking.
What type of building foundation is better, monolithic or block, and which will be cheaper, you will find out by reading the article.
Recessed and shallow strip foundation, features
A tape deepened by 3-4 meters is poured or laid out with FBS when it is planned to arrange a basement floor or a technical basement
The tape, deepened by 3-4 meters, is poured or laid out with FBS when it is planned to arrange the basement floor or technical basement. This is the most voluminous type of foundation in terms of labor costs and material resources.
In addition to the possibility of constructing a basement, a buried foundation has another advantage - such a foundation is much more stable when compared with a shallow foundation. Considering this factor and significant material investments in the construction of an underground structure, it is logical to use a technology that turns out to be cheaper.
A shallow strip foundation is constructed only where soil characteristics allow.
This type of foundation structure will not be an effective support for construction on heaving, sandy soils, or with significant swampiness of the site.
Even if it is possible to fill a shallow-depth tape, special attention is paid not to the cheapness of the material, but to the strength characteristics of the structure being created.
Strength of monolith and block construction
Any monolith is stronger than a structure assembled from fragments
Any monolith is stronger than a structure assembled from fragments. The same applies to foundations. Each block individually also represents a reinforced concrete monolith, but in general the structure laid with FBS is not a single whole.
This must be taken into account when choosing the type of foundation. A block foundation can be especially unstable when there are horizontal movements of the soil, which displace the blocks, compromising the integrity of the foundation structure.
If the surface soil layers are unstable or on highly inclined areas (hills), a poured monolithic foundation looks much more preferable.
It is also better to fill a reinforced monolith for a shallow strip base. Typically, surface soil is most susceptible to displacement and seasonal deformation, so structural strength is very important here. Shallow foundations are also constructed from blocks, but only on stable soils and horizontal areas for relatively small buildings.
It is more expedient to use FBS for laying buried foundations. Such structures are much more stable than surface tapes and better resist ground movements. The use of ready-made concrete blocks greatly speeds up the construction of the bulk underground part of the building and makes it cheaper, which is why many developers prefer FBS masonry to pouring a concrete monolith.
Monolithic foundation and FBS foundation, cost comparison
From the beginning of the construction of the formwork to the complete maturation of the concrete, 1-1.5 months pass, which is much longer than the laying of FBS
If we consider both technologies from the point of view of constructing a buried foundation, the initial work and associated costs will be approximately the same (preparing the construction site, digging a pit). Further, the process of constructing the underground part of the building differs radically in terms of labor intensity, costs and time required to carry out the complex of work.
This is what building a foundation structure with blocks looks like:
- planning and filling of the base;
- FBS masonry.
It will take 2-3 days to build the foundation for an average house, involving 2-3 workers and a crane. In addition to the foundation blocks, 3-4 tons of sand and a ton of cement will be needed for masonry.
Filling is much more difficult. These are the technological processes involved in the formation of a concrete monolith:
- placing formwork;
- waterproofing device;
- knitting of the reinforcing structure;
- step-by-step filling of the formwork cavity;
- removal of formwork.
All work steps are labor-intensive and time-consuming. From the beginning of the construction of the formwork to the complete maturation of the concrete, 1-1.5 months pass, which is much longer than the laying of FBS.
The materials you will need are several self-propelled concrete mixers, 6-10 cubic meters of timber, 2-4 tons of reinforcement, and this is not counting the “little things” (nails, binding wire, plastic film).
Foundation blocks and hiring a crane will also cost a lot, but with careful calculations, laying the blocks ends up being cheaper. Another important factor is the time saved, which takes an order of magnitude less to lay blocks.
Formula for calculating power by current and voltage
If you already have some cables available, you should use a caliper to find out the required value. In this case, the cross section is measured and the area is calculated. Since the cable has a round shape, the calculation is made for the area of the circle and looks like this: S(area)= π(3.14)R(radius)2. You can correctly determine, using the table, the cross-section of a copper wire by power.
Standard formulas for determining current strength
Cable options for different applications
What are some examples?
A specific diagram will allow you to make the right choice of cable cross-section for your apartment. First of all, plan the places where the light sources and outlets will be placed. You should also find out which equipment will be connected to each group. This will allow you to draw up a plan for connecting all elements, as well as calculate the length of the wiring. Don't forget to add 2 cm at the joints of the wires.
Determination of wire cross-section taking into account different types of load
Using the obtained values, the current value is calculated using formulas and the cross section is determined from the table. For example, you need to find out the wire cross-section for a household appliance whose power is 2400 W. We calculate: I = 2400/220 = 10.91 A. After rounding, 11 A remains.
Cabling diagrams
To determine the exact cross-sectional area, different coefficients are used. These values are especially relevant for a 380 V network. To increase the safety margin, it is worth adding another 5 A to the obtained indicator.
Three-wire wiring diagram
It is worth considering that three-core wires are used for apartments. Using the tables, you can select the closest current value and the corresponding wire cross-section. You can see what wire cross-section is needed for 3 kW, as well as for other values.
Wires of different types have their own calculation subtleties. Three-phase current is used where equipment of significant power is needed. For example, this is used for production purposes.
To identify the necessary parameters in production, it is important to accurately calculate all coefficients, as well as take into account power losses due to voltage fluctuations. When performing electrical installation work at home, you do not need to carry out complex calculations.
You should be aware of the differences between aluminum and copper wire. The copper version has a higher price, but at the same time surpasses its analogue in technical characteristics. Aluminum products can crumble on bends, and also oxidize and have a lower thermal conductivity. For safety reasons, only copper products are used in residential buildings.
Basic cable materials
Since alternating current moves through three channels, a three-core cable is used for installation work. When installing acoustic devices, cables with a minimum resistance value are used. This will help improve signal quality and eliminate possible interference. To connect such structures, wires are used, the size of which is 2 * 15 or 2 * 25.
Some average values will help you choose the optimal cross-sectional indicator for everyday use. For sockets it is worth purchasing a 2.5 mm2 cable, and for lighting design - 1.5 mm2. Equipment with higher power requires a cross-section size of 4-6 mm2.
Wire connection options
A special table will help if you have any doubts during the calculations. To determine accurate indicators, you need to take into account all the factors that influence the current in the circuit. These are the length of individual sections, installation method, type of insulation and permissible overheating value. All data helps to increase productivity on a production scale and use electrical energy more efficiently.
What is cheaper? FBS blocks or monolith
Strip foundation of a residential building made of FBS blocks
When calculating the cost of construction work, the cost of erecting foundations is a quarter of all costs of constructing a building.
Each individual developer would not mind saving significant money on this part of the construction work, while maintaining a balance between price and quality, and in the case of foundations, also strength and reliability.
For a technical and economic comparison, we can consider the cost of constructing popular types of foundation structures: monolithic concrete and prefabricated from FBS blocks.
Monolithic and prefabricated foundations: comparative characteristics
Block design diagram
To make a comparison and draw a conclusion - which foundation is cheaper: monolithic or prefabricated from FSB blocks, you need to understand their structure and installation.
Monolithic concrete and prefabricated load-bearing structures can have two types of designs: strip and column.
There are many differences in the construction of these types of foundation structures:
Monolithic made of concrete Prefabricated from FBS blocks
| Preparatory stage: excavation work | Required to be completed in full | Required to be completed in full |
| Financial costs for purchasing or renting removable formwork | Required in full | Not needed |
| Labor costs for installation and dismantling of formwork | Required, but can be reduced when using permanent formwork structures | Not needed |
| Time and season of work | Significant, including the period of strengthening of the concrete mixture and the warm season | Minimum |
Block structures are recommended for use in deep foundations.
Ready-made FBS significantly speeds up the laying of the underground part of the house, and therefore prefabricated foundations are cheaper than other types.
Prefabricated block foundation strip made of FBS blocks
Comparison of monolithic and block foundations
In the comparison table you can see the main differences in the design and installation of foundations:
- The volume of excavation work for the installation of both types of load-bearing structures is approximately the same, with a slight advantage for a monolithic structure, which will require a little more space during reinforcement and installation of the formwork system.
- The price of precast reinforced concrete and ready-mixed concrete for a monolithic concrete mass is almost the same.
- Foundation blocks are laid on a layer of cement-sand mortar using a truck crane.
- Monolithic tape requires significantly more costs for the purchase of materials for formwork and reinforcement, the manufacture of reinforcement cages and their installation, the production of concrete (for small volumes) or purchase with delivery by a concrete truck - a mixer of ready-mixed concrete and laying the concrete mixture into the tape structure. Here we also need to add labor costs for compacting the concrete mixture by vibration and caring for the concrete for 3 to 7 days until it gains 70% strength.
- The cost of replacing a truck crane for unloading and installing a prefabricated block structure is about 12,000 rubles. The installation of FBS can be completed in a few days by a team of workers - installers in the amount of 3 people. If we carry out the simplest calculations, we can draw the following conclusions that the total cost of renting a truck crane, wages for installers and the purchase of cement mortar will be two or three times cheaper than performing similar work during the construction of a monolithic load-bearing structure.
Combined combined method of foundation construction
Based on the listed conditions for the work and economic feasibility, we can make an unambiguous conclusion that a strip foundation made of FBS blocks will be better in all respects than a monolithic one.
Savings when installing a block structure
There are several additional opportunities to reduce the cost of constructing block structures. For example:
- When installing, use used blocks in good condition, the price of which will be several times lower than new ones.
- The possibility of constructing a block foundation in winter, when large seasonal discounts are offered for installation work.
- When constructing a prefabricated foundation, a combination of both FBS blocks and small-sized stones (cinder block or brick).
Such simple measures can significantly reduce the cost of constructing a prefabricated load-bearing foundation for a house.
Features of choice
Scheme for constructing a strip foundation on a site with a steep slope
Despite the comparative price indicators, one cannot be so clear about the choice: FBS or monolith. There are times when it is better to opt for a more expensive foundation design and at the same time ensure maximum reliability and strength of the entire structure.
It is known that any monolithic structure will be stronger than a prefabricated one made from individual fragments. This truth applies perfectly to foundation arrays. The reinforced concrete block itself is a single monolith, but a structure assembled from individual foundation blocks will not be completely intact and monolithic. This must be taken into account when choosing the type of supporting base.
If the building site has a soil foundation with possible horizontal displacement, the prefabricated foundation may end up in an extremely unstable position, which can lead to loss of integrity of the foundation mass.
If the soils on the site have unstable surface layers or the site is located on steep terrain or hills, it is better to give preference to a monolithic concrete foundation.
Construction of strip foundations on difficult terrain:
Criteria for choosing the type of foundation
Type of shallow strip foundation
The desire to save money when constructing load-bearing elements of the foundation is not always the main criterion for choosing a particular structure. There are basic situations for the construction of load-bearing structures:
- When constructing one-story brick, slag concrete, stone buildings or multi-story buildings with foam concrete walls, it is allowed to construct buried foundations from FBS blocks. More massive houses and structures are recommended to be installed on a monolithic solid foundation.
- If the foundation has a shallow structure, it is better to make it from monolithic concrete using a reinforcing metal frame. FBS blocks can be used in stable, strong soils.
- The combined technology of creating a foundation with a combination of laying FBS blocks and pouring a reinforcing monolithic concrete belt, which will simultaneously serve as the base of the building, has proven itself well.
You can make a foundation strip using any of the following methods. It is necessary to carefully weigh all the nuances of constructing foundation structures in each specific situation.
Arguments for choosing a monolithic strip foundation
There are times when there is no point in making a choice: a structure made of FBS or a monolith. There are conditions under which it is necessary to construct a monolithic concrete foundation in the form of a continuous strip:
- If the site has heaving soil foundations.
- There is a risk of increased seismicity in the construction area.
- Significant loads on the foundation, as a result of which the structure will be subject to bending moments.
Considering all these factors, we can conclude that the savings should be reasonable. The main thing for the foundation is strength, stability and reliability of the entire structure and ensuring the integrity of the entire structure.
It is difficult to say unequivocally which type of load-bearing base will be cheaper: monolith or FBS. To make an accurate comparison, it is recommended to link construction to the individual conditions of the site, the nature of the terrain and soil types.
Source: https://KakFundament.ru/ustrojstvo/kakoj-fundament-deshevle-monolitnyj-ili-iz-fbs
Correct selection of cable conductor cross-section
Determination of maximum current
From the total power (P) it is easy to obtain the value for the total current: I = P/220 or more precisely from the formula
for a single-phase circuit: P = U * I * cos(φ);
U= 220 or 380 V;
Safety factor or power factor: cos(φ) = 1 is taken as the value for household appliances. But the recommended exact value for calculating current supply lines to powerful electrical devices is cos(φ) = 1.3.
To accurately determine the maximum power, you should know the current consumption and the type of phase (single- or three-phase network).
For a single-phase network, the total power will be equal to P = 220*I*1.3, where I is the total current consumed.
For a three-phase network, the calculation is carried out slightly differently: P = √3*380* I*1.3.
However, it must be taken into account that the cross-section of the wires used must meet the following criteria:
- length of the current-carrying line;
- method of implementing electrical wiring;
- general characteristics of the machine.
The correctly selected cross-section of the wires used is the most important criterion for the implementation and installation of reliable wiring in the room. Everyone knows that only a stingy person pays twice, and not only for the cable, but for the entire repair in general.
The material of the conductors determines the technical and economic indicators of the cable line.
Select Copper (Cu) Aluminum (Al)
The load power for a cable is defined as the sum of the power consumption of all electrical appliances connected to this cable.
Enter load power: kW
Enter voltage: V
Power supply system: SelectSingle-phaseThree-phase
Power factor cosφ determines the ratio of active energy to total energy. For powerful consumers, the value is indicated in the device passport. For household consumers, cosφ is taken equal to 1.
The laying method determines the heat dissipation conditions and affects the maximum permissible load on the cable.
SelectOpen wiringHidden wiring
For direct current, all wires are considered loaded, for single-phase alternating current - phase and neutral, for three-phase alternating current - only phase ones.
Select Two wires in separate insulation Three wires in separate insulation Four wires in separate insulation Two wires in general insulation Three wires in general insulation
Minimum cable cross-section: 0
A cable with a calculated cross-section will not overheat at a given load. To make the final selection of the cable cross-section, it is necessary to check the voltage drop on the current-carrying conductors of the cable line.
Block foundation. Advantages and disadvantages
A block foundation has its pros and cons. The positive characteristics that a block foundation for a house has include the following:
- Solidity, as well as strength and excellent reinforcement of the structure are ensured due to increased density and are responsible for the length of its service life.
- The ability to withstand fairly large long-term loads without causing any deformation of the structure.
- It is resistant to the formation and proliferation of fungi or mold, so it can withstand dampness and is not subject to destruction as a result of corrosion when exposed to various aggressive chemicals.
- Block foundation blocks are characterized by good frost resistance - they are suitable for construction under conditions of temperature changes in the range from -70 to +50 °C.
- In the manufacture of reinforced concrete, special chemical additives are used, which ensure a noticeable improvement in the anti-corrosion properties of the material.
- Reduced moisture permeability.
- Quite a high level of environmental friendliness, which is expressed in the excellent resistance of the structure to rotting and intense corrosive destruction.
- There is a wide variety of block sizes. In addition, they can be cut, so you can easily adjust them to the required parameters for each specific case. As a rule, such blocks are made in the form of rectangular parallelepipeds in compliance with all GOST standards and do not deviate from generally accepted dimensions.
- The improved fire resistance of the blocks allows them to be used in the construction of foundations for a wide variety of buildings with residential or civil purposes.
- The process of its construction is much simpler and takes a short period of time - just a few days are enough.
- A cost-effective option due to the low cost of this material.
- Installation work can be carried out in almost any weather conditions in different areas.
- Excellent for use in areas with highly acidic soils.
- The construction does not require the involvement of highly qualified specialists; you can build a block foundation with your own hands.