A reliable foundation is the basis of any home and determines its service life. Just a few years ago, traditional strip foundations dominated (especially among private individuals). However, today people are increasingly deciding to use a monolithic foundation slab. So which is better - a strip foundation or a monolithic slab? Before making your final choice, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the main disadvantages and advantages of both of these solutions. The economic aspect is also of considerable importance.
Slab foundation or traditional strip foundation
A foundation is a structural element that transfers all the loads of a building or equipment to the ground (a foundation for a machine); it can be made of concrete, reinforced concrete, brick or stone, or less often of wood (lightweight buildings). Under the influence of transmitted loads, soil deformation occurs, which, in turn, causes the building to settle. In this regard, the correct decision on the selection of the foundation should ensure:
- minimal and uniform subsidence of the structure and its stability;
- the correct foundation depth (must be on soil with sufficient bearing capacity and below the freezing depth);
- ease of execution;
- protecting the structure from dampness.
Foundation - the basis of a building
Home construction
Most houses are still built on traditional strip foundations (monolithic, prefabricated, shallow and recessed). Meanwhile, it is worth thinking about its alternative, that is, a monolithic slab.
The question of whether to use “tape” under the house being built or use the less popular “slab” confuses many investors. Unfortunately, there is no clear answer that dispels any doubts. It all depends on weather conditions, soil, architectural/structural type of the building being constructed, financial costs acceptable at this stage of construction and many other factors. In addition, as is usually the case in construction, both solutions have both their advantages and disadvantages.
The traditional foundation, poured into a trench and formwork, is known to everyone who, at least from stories, has encountered construction. The foundation slab is a solution still unfamiliar, less popular and seemingly expensive, and therefore accessible only to a few. For the same reasons, it is used mainly when soil conditions are unfavorable and there is concern that settlement of the foundation could lead to damage to the structure of the house.
In Scandinavian countries, the foundation slab is widely used, and in practice, the cost of placing a house on it is no higher than constructing a building on traditional foundations.
Two-level foundation slab
Foundation slab - quickly and without deep trenches
The foundation slab is widely used, particularly in Scandinavia and Japan. These are places with very difficult soil/seismic conditions in which implementing a strip foundation would be too risky and time-consuming. The foundation slab has a large load-bearing capacity and ensures uniform settlement of the building to the ground. Which gives increased stability to the entire house.
The use of a foundation slab can be recommended for people who are interested in a fast pace of construction. When using a monolithic slab, there is no need to build deep trenches. True, just as in the case of a strip base, you need to remove the top layer of soil, that is, humus and, possibly, remove other weak layers, but there is not so much of this work. In the case where there is sandy soil under the humus layer, concrete can, in principle, be laid immediately. In a situation where clay or silt is found under a layer of organic soil, a layer of sand, gravel or crushed stone is laid, the so-called drainage. This layer should be 15 cm.
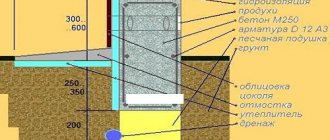
After the base has been placed under the slab, the reinforcement is laid out on it and concreting is carried out using concrete of at least class C 20/25 (B25). Reinforcement should be applied both at the bottom of the slab and at the top. In addition to the above actions, the slab also requires waterproofing and insulation. The thermal insulation layer must be at least 10-15 cm. Place it under or on the slab.
When insulation is laid under concrete, polystyrene must have the appropriate density. In such a situation, it is worth taking extruded polystyrene foam instead of polystyrene foam, since it has greater compression resistance. However, when thermal insulation is placed on top of the slab, polystyrene no longer has to be of such a high class, and then polystyrene foam can be used. If waterproof concrete is used for concreting the slab, there is no need to provide moisture-resistant insulation.
The standards require that the foundation of a building be built at least 50 cm below ground level, and only in the case where there is sand under the humus layer. Meanwhile, houses that have been built recently have a slab foundation only 30 cm below ground level, and this is considered sufficient.
The work on making the slab is going quite smoothly. There is no need for any technological interruptions (as in the case of traditional “tape”). Thanks to this, the job can be completed in just a few days. After a week or two has passed from the moment the slab is poured, you can begin working on the walls. Usually one week is enough for the concrete to “set” enough to begin building walls. In addition, when the slab foundation is made with built-in communications and a heating system, above-ground work also proceeds faster. Running heating pipes located in the slab can significantly speed up the drying of plaster or other materials located on the walls and floors of the building.
In the case of a traditional foundation, work must be carried out taking into account the necessary technological breaks, which takes more time.
Strip foundation
Strip foundation is still popular
Despite the many advantages of slab foundations, the traditional "strip" is still more popular. Such foundations are provided by the overwhelming number of ready-made designs of houses and cottages available on the market. By the way, strip foundations are often designed to be overly massive and strong. Of course, no one disputes the fact that the building should be designed in such a way that all loads are transferred through the foundation to the ground, but sometimes designers get carried away.
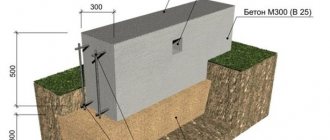
The foundation has the task of bearing not only the weight of the building itself and its equipment, but also the influence of all kinds of external forces. However, you can still find projects for small houses in which the “ribbons” are 40–50 cm high, 80–100 cm wide and must be installed to a depth of 120 cm below ground level. In many cases, this is a gross exaggeration and a completely unnecessary hit to the investor's pocket. In the case of small houses and favorable groundwater conditions, a “ribbon” 30 cm high, 40–50 cm wide, which is recessed to a depth of 50 cm below ground level, is sufficient.
Making the base for a house is carried out over several constant stages. Marking is carried out in accordance with the plan/sketch of the future structure. Before pouring a strip foundation, you need to prepare an appropriate foundation pit. It can be dug by hand or with heavy equipment. The first solution is cheaper, the second will cost more, but will bring significant time savings. After the excavator works, it will be necessary to further improve the trenches in the corners and level the bottom layer of soil.
Then waterproofing is installed, it protects the foundation from capillary rise of groundwater. The easiest way to do this is to lay a layer of waterproofing film. It is installed on the bottom and sides of the trench. To ensure complete protection, the film must be rolled over the trench. When laying the film, it is necessary to ensure complete tightness.
Waterproofing foundation walls
After completing the excavation work and laying the film, it’s time for reinforcement work. The characteristics of the reinforcement must be provided for in the construction project. It indicates the thickness of the reinforcing bars, as well as the characteristics of all connections. Making a foundation for a house, simplified, consists of reinforcement from four main rods and connecting rods. The main rods have a diameter of about 12 mm. In turn, the connecting ones are 6 mm.
The trench/formwork is then filled with concrete. It is best to use ready-mixed concrete with reinforced concrete concrete. The solution prepared directly at the construction site may not have the appropriate proportions. In addition, there is a problem associated with quickly preparing large quantities of the mixture.
The concrete is compacted using a vibrator or crowbar/rebar. The choice of compaction method depends only on the capabilities of the investor.
Strip foundations require time to dry completely, slowly. The solution should not lose moisture too quickly, so after 24 hours from the moment of pouring it is worth covering it with film. If there is a high temperature outside, it is worth additionally watering the foundation with water.
A professional architect can determine which foundation is suitable in a doubtful situation, slab or strip, taking into account the results of studies of groundwater and soil.
Pillar foundation
There are two main types of columnar foundations:
- Solid-monolithic buried - a hole with a diameter of 30-50 cm and a depth of 1-2 meters is dug (the depth clearly depends on the depth of soil freezing), a sand cushion is poured onto the bottom, made of clean sand without gravel, and the whole thing is filled with concrete with OPGS. This type of pillars is the most attractive compared to pillars made from ready-made blocks.
- A folded shallow foundation made of sand blocks - a hole is dug to a depth of 50-70 cm, a sand cushion is filled in and the blocks are laid.
In both cases, the distance between the posts should not exceed 3 meters (we recommend 1.5 meters). This foundation has its pros and cons:
| Pros: | Minuses: |
| Not expensive | Requires strict soil requirements |
| Easy to do it yourself | Not durable |
| Saves time | Uneven load on the ground |
| The base of the bathhouse is well ventilated | Requires exterior finishing |
| The supports are not connected to each other and can “float” |
When choosing this type of foundation for your bathhouse, think about this decision seven times and make sure that the soil is sufficiently dense
Difficult choice
The completion of the foundation should be understood as the performance of any excavation work, structural and insulating - associated with building elements immersed in the soil. When analyzing costs, it should always be taken into account that at this stage the building materials must meet different criteria than those used in the above-ground parts of buildings.
The building material must, first of all, be stable, durable, frost-resistant and resistant to the destructive effects of rain and groundwater. As already mentioned, the building can be erected using a strip foundation or a monolithic slab. Each case requires a different amount of work.
Works that make up the construction of a traditional foundation:
- excavation;
- reinforcement works;
- production of strip foundations;
- production of foundation walls;
- laying thermal insulation and waterproofing of foundation walls;
- backfilling trenches;
- execution of floor structure layers on the ground;
- waterproofing and thermal insulation of floors on the ground.
Work involved in the production of a foundation in the form of a slab:
- removing the humus layer;
- laying and compacting the lining/drainage layer under the slab;
- execution of the foundation slab (possibly also the heating system);
- laying hydro- and thermal insulation of the foundation slab.
Pouring a monolithic slab
Monolithic and prefabricated foundations: comparative characteristics
To make a comparison and draw a conclusion - which foundation is cheaper: monolithic or prefabricated from FSB blocks, you need to understand their structure and installation.
Monolithic concrete and prefabricated load-bearing structures can have two types of designs: strip and column. There are many differences in the construction of these types of foundation structures:
| Monolithic made of concrete | Prefabricated from FBS blocks | |
| Preparatory stage: excavation work | Required to be completed in full | Required to be completed in full |
| Financial costs for purchasing or renting removable formwork | Required in full | Not needed |
| Labor costs for installation and dismantling of formwork | Required, but can be reduced when using permanent formwork structures | Not needed |
| Time and season of work | Significant, including the period of strengthening of the concrete mixture and the warm season | Minimum |
Block structures are recommended for use in deep foundations.
Ready-made FBS significantly speeds up the laying of the underground part of the house, and therefore prefabricated foundations are cheaper than other types.
Monolithic slab or strip foundation?
Each idea is good in its own way. There is no need to talk too much about the advantages and disadvantages of strip foundations, because many buildings have been built this way, and the method is well known and widely used. At the same time, an increasing number of developers are using monolithic slabs for their houses.
The most tangible advantage of a foundation slab is the fact that its use shortens the construction process. In addition, in the case of a slab foundation, a floor immediately appears on the ground, and the weight of the building is distributed more evenly and over a larger area than in the case of a traditional foundation.
The slab works on any type of soil and can be used safely also on soils with poor bearing capacity and heterogeneous foundations.
The production of a monolithic slab as a foundation is shown in sufficient detail in the video:
However, a slab foundation has its drawbacks. It is essential that already at the design stage it is necessary to provide for the location of communication connectors. To make a slab, it is not advisable to use home-made concrete; industrially produced concrete is better. And the last thing you need to remember when deciding on this method is the fact that in the future it will not be possible to complete the construction of even a small cellar.
What to choose?
As already mentioned at the beginning, it is possible to determine which of these types of foundations is better only for each case individually . Based on the soil that is characteristic of the site, a monolithic variety is selected in the case of unstable problem soils. If the soil is sufficiently stable and stable, then you should definitely choose a strip type of foundation .
Many owners of private houses cannot imagine their home without a basement or cellar. They can be made only by constructing a strip foundation, if there is no desire to spend large sums on construction. Construction of a basement with a slab buried one and a half to two meters will cost significantly more.
Both types of foundations have the ability to withstand a fairly large level of load from the structure . Therefore, under other identical conditions, it is better to opt for a shallow monolithic slab.
Both varieties have many advantages and other features. Regarding the simplicity of the installation process, a monolithic slab takes much less time and effort than a strip foundation when using modern technology, but in the end it all depends on the individual characteristics of the future building, the type of soil and the financial capabilities of the owner of the future building.