Why add something to the solution?
Concrete really has extraordinary strength and a lot of advantages, but the solution also has disadvantages. For example, during frost it hardens for too long, as a result of which the water contained in the solution freezes and deteriorates the quality of the structure, making it brittle.
In the professional field, various plasticizers are used when preparing concrete. These are additives that improve the consumer qualities of concrete. Some substances can make the solution immune to frost or increase its strength many times over.
The disadvantage of plasticizers is their high cost, which is why they are only available to professionals. But similar properties of concrete can be achieved by adding other materials, which will be discussed below.
Additives to mortar for bricklaying in winter - review of manufacturers
Today it is easy to purchase antifreeze additives. They are offered in a wide range. However, without consulting a specialist, it is difficult to understand the variety of products.
Please note that special additives contain toxic substances that are dangerous to people
Builders respond positively to additives from the following companies:
- . It is known on the Russian market as a manufacturer of high-quality additives. Modern technological solutions are used in the production cycle, allowing products to confidently compete with foreign models. A wide range contains components that reduce the crystallization threshold, maintain the integrity of the reinforcement and are insensitive to temperature fluctuations in the environment;
- . This is a powerful domestic holding, a leader in the production of chemicals for the construction industry. It produces various types of additives for concrete mixtures, which allow construction activities to continue without a significant drop in temperature. Among the many drugs, it is necessary to use o, which belongs to the new generation of antifreeze compounds. Thanks to it, when the temperature drops to minus 25 degrees Celsius, it is possible to build brick walls;
- enterprise "Optimist". This is a well-known company that produces materials for the construction industry. Thanks to the latest developments and the use of innovative solutions, it has been possible to develop modern anti-frost compounds that can significantly reduce the consumption of Portland cement. When the proportion of cement is reduced to 10%, strength increases by 15%, and elasticity and resistance to negative temperatures also improves;
- from SIKA. It occupies one of the leading positions in the global market of chemicals for the construction industry. Along with the high performance characteristics of special additives for performing work in winter, manufacturers pay attention to their environmental friendliness. The proposed preparations are highly effective and ensure the preservation of concrete properties at low temperatures, and also have a positive effect on increasing its anti-corrosion properties and ductility.
The construction chemicals market offers products of domestic and foreign production, which differ in price range and efficiency of use.
Chicken eggs
It seems incredible, but ordinary chicken eggs significantly improve the quality of concrete, making it suitable even for the construction of all kinds of structures. The recipe for mixing the mixture with the addition of chicken eggs comes from ancient times.
Nowadays, high-quality cement with a high degree of viscosity is used to prepare concrete, but many still add chicken eggs, which help:
- improve strength;
- increase adhesion properties;
- increase density indicators;
- enhance water resistance.
The question arises: how many eggs are needed to make super-quality concrete? The answer is simple - a lot. In modern realities, this is impractical; besides, there are many other ways to improve the quality of concrete, and it is better to leave chicken eggs for cooking.
Clay
It is used mainly to reduce the cost of mortar, since clay is a substitute for cement. No, it does not have similar properties and is significantly inferior to dry mortar in terms of quality. But with properly selected proportions, clay dilutes cement, while maintaining key indicators - strength, viscosity, tenacity.
Under no circumstances should you overdo it with adding clay. Please note that the solution obtained in this way is not suitable for creating monolithic structures that bear heavy loads. In other words, such concrete is not suitable for construction purposes, creating a foundation, etc. It can be used to fill paths in the backyard and create small architectural forms.
Winter laying conditions
The first condition when building walls in the cold period is that before laying, the brick or block must be cleared of snow, ice or frost. The second important rule is that cement and the finished mixture must be stored in insulated containers. Moreover, it is impossible to warm up a slightly set solution. Therefore, it is very important to ensure high laying speed and rapid compaction of the underlying rows with the upper ones. And during breaks, it is advisable to cover the finished part of the wall with plywood, roofing felt or film. Or thoroughly clean the surface of snow and frost when resuming work.
The solution is prepared at subzero temperatures in heated rooms, using cement grade M50 or more. Large lumps (more than 1 cm) and pieces of ice are not allowed in the sand.
Masonry using winter mortars must be carried out with thin joints of the order of 1-3 mm (that is, the same as in the summer). This requirement is due to the fact that large seams increase the heat loss of the structure and can lead to significant settlement in the spring. Also, during work, you should carefully check the verticality of the walls: any deviations are also fraught with problems during a thaw. The laying is carried out evenly along the entire perimeter of the building or the length of the wall so that there are no large differences in height. The pillars and partitions between the window openings are reinforced with steel mesh.
Finally, in the spring, during the thawing period, it is necessary to monitor the strength and stability of the wall made in winter. Indeed, as the temperature rises, the masonry also thaws, and small sedimentary phenomena and microcracks may occur. Therefore, as during masonry, you should check the verticality of the structures every 2-3 days, and if a minimal deviation is detected, you should immediately install struts and supports made of wooden logs or metal pipes, which will prevent further displacement. This is usually required for walls located on the south side. You can cover them during the thaw (for example, with glassine). After positive temperatures have been maintained around the clock for 7-10 days, the supporting elements are removed.
Another way to combat uneven settlement is the preliminary installation of supporting elements and forced thawing of the wall during early spring using air heaters, electric heaters or heat guns located inside the building. To do this, it is necessary to raise the room temperature to 30°C and maintain it for several days. However, this method is more labor-intensive and requires considerable energy consumption, a reliable connection to the power grid near the house, or the use of autonomous generators.
When laying in winter, it is especially important to maintain the thickness of the mortar and maintain the level
Failure to follow the rules for preparing mortars and masonry will, at a minimum, lead to the formation of efflorescence, and at a maximum, to the appearance of cracks
During breaks between work, you need to cover fresh masonry
Technical salt
A very interesting option that is recommended to be considered in detail. Technical salt increases the frost resistance of the solution, being a kind of plasticizer. Its addition in a reasonable amount does not impair the consumer qualities of concrete. According to professionals, 2% of the total mass will be enough to make the concrete resistant to frost and quickly harden at sub-zero temperatures.
People also actively use ordinary salt. It increases the heat resistance of the solution, so it is added when laying stoves, hearths, etc. Please note that an excessive amount of salt in the concrete solution can lead to an acceleration of corrosion processes, which is unacceptable in the case of the manufacture of reinforced structures.
Operating principle and types of frost-resistant compounds
Loading into a concrete mixer.
What to add to concrete at sub-zero temperatures is far from an idle question. There is no completely, 100% universal composition.
The choice depends on many factors, primarily on the temperature itself.
- The size of the monolith also has a big influence. Plus, you should take into account the purpose of the product, the fact is that different additives can change some of the physical properties of concrete and what is suitable for a strip foundation in a private house may not be suitable for the construction of a bridge or a large self-leveling plinth.
Warming up using the Thermos method.
How it works
As you know, the main task of water in a solution is to create conditions for the crystallization of the components of the solution, silicates, aluminates, and so on. In the language of professionals, this is called cement hydration.
Most comfortably, without additives, the solution hardens at a temperature of 15 - 20 ºС; everything higher and especially lower requires the creation of special conditions.
- The main task of this type of additive is to reduce the setting period of the solution and reduce the maturation time of concrete at low temperatures. That is, to reduce the level of freezing of water and at the same time not harm other processes occurring in the solution.
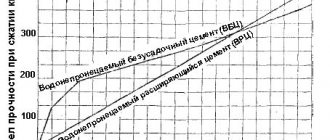
Dependence of strength gain on temperature.
Common compositions and methods of operation
- The most common materials for the manufacture of frost-resistant additives can safely be considered salts of monocarboxylic acids; among professionals this composition is known as “Potash”. The price for these compounds on the domestic market is quite reasonable.
- When pouring concrete at sub-zero temperatures, monocarboxylic acid additives must be strictly dosed. For each temperature, the number of additives is different. With such additives, you can prepare the solution for temperatures down to minus 30ºС. The lower the temperature, the more composition will be required.
Monocarboxylic acid salt.
Important: as mentioned earlier, the additive, if used incorrectly, can reduce other characteristics of the solution. Therefore, the principle, the more the better, can do harm here.
- The next leader in our market is sodium nitrite. The price for it is also not very high, but this substance has a strong, pungent, unpleasant odor. In addition, this composition can easily ignite. Upon contact with some types of modern plasticizers, poisonous and toxic gases may be released.
- The maximum temperature that sodium nitrate can hold is not lower than -15ºС. Experts recommend its use when preparing solutions using Portland cement or Portland slag cement. Adding this additive to aluminous cements is strictly prohibited.
- Sodium formate and calcium nitrate have a wide range of uses. In addition to the production of reinforced concrete products, these additives can be used in plaster mortars and mortars intended for bricklaying. But these compositions are used only in combination with a plasticizer, since due to the accumulation of salts, voids and efflorescence can form in the monolith.
Important: solutions with added additives must be prepared with your own hands at a temperature not lower than 5 - 10 ºС. In addition, they cannot be stored for a long time; the solution must be used within an hour after mixing.
- Do not forget about domestic manufacturers, additives from the line of frost-plast, frost-styrene, etc. They are complex-action compounds; after pouring, thanks to the processes occurring inside the monolith, the temperature is maintained naturally and even in light frosts, you just need to cover the concrete well.
Dependence on the concrete grade
Designs for electric heating of a monolith.
- According to SNiP 111-1-76, frost is dangerous for concrete only at the stage of strength building. It is necessary to maintain a certain temperature in the monolith up to a certain % strength. This percentage is individual for each brand of concrete.
- After the monolith has set, freezing is no longer so scary for it, but it is not yet recommended to use reinforced concrete products. The fact is that after thawing, the product will naturally ripen. The active phase of solidification of the monolith lasts for 27 days. After this, the strengthening will continue for several more years, but much more slowly.
- If frost-resistant additives were not introduced into the composition, then for solutions with the M150 grade, 50% strength is sufficient. Grades M200 – M300 can be frozen at 40% strength. For M400 and more, 30% is enough. But when using an additive, the permissible strength before freezing drops by an average of 10%.
Advice: the time for mixing the composition in winter conditions should be increased by at least 2 times.
Liquid soap or dishwashing detergent
Do you want to increase the plasticity of the mixture by making the solution mobile and pliable? Ordinary liquid soap copes with this task perfectly, improving the quality of concrete and simplifying work with it. This recipe is useful if you need to get a high-quality mixture for plastering walls and carrying out interior work.
Working with cement really takes a lot of effort. The increased viscosity of the solution affects this, and adding water does not save the situation, but only aggravates it, making the solution excessively liquid and ineffective. A small amount of liquid soap helps correct the situation. The concrete turns out to be more “obedient”, easier to mix and apply.
This effect occurs due to the enveloping of particles that make up the concrete. A slimy film forms between them, but at the same time they do not lose adhesion, providing excellent strength. As for the proportions of liquid soap, it is recommended to add no more than 5% of the total mass of the prepared solution.
Antifreeze additives for concrete mortar
Concrete additives are used very often today, and anti-frost additives occupy a special place, as they allow work to be carried out almost all year round. The concrete mixture contains about 10% water and when the temperature drops, it begins to freeze. If, when the temperature drops, all processes in concrete simply slow down, then at minus temperatures, hardening stops altogether.
And then, when the process may continue during thawing, it already occurs with a violation of the technology, strength and resistance to mechanical loads, and other characteristics may decrease. To preserve the ability of the solution to gain strength, it is necessary to leave the water liquid even at minus temperatures, which is achieved using additives.
Plasticizer additives improve the dispersion of all solid components of the cement mortar. The friability of sand, gravel, and binder increases, the mixture becomes a suspension, and resistance to freezing increases to -15 degrees, and the hardening process usually accelerates.
The disadvantage of introducing such additives into concrete is the presence of chlorides in their composition, which can cause reinforcement to corrode. But some manufacturers offer additives without chlorides; they are better suited for pouring concrete with a reinforcing frame.
Difficulties of winter concreting
Any concrete solution is a mixture of a certain brand of cement, fine filler (quartz quarry or river sand), coarse filler (granite or limestone crushed stone, gravel) and water. All components are taken in a certain proportion, mixed thoroughly, and placed in a mold.
Next, the cement begins to interact with water (a hydration reaction occurs), begins to set and harden gradually (the process is completely completed after 28 days). Normally, this process takes place only at positive temperatures, but minus temperatures negatively affect the monolith.
What changes can occur in concrete under the influence of minus:
- The hydration process takes noticeably longer – when the temperature drops below +5.
- At temperatures below 0, an ice crystal lattice forms in a liquid solution. During the freezing process, ice crystals increase in volume and cause the appearance of local stress zones in the still weak solution, as a result of which the structure is destroyed and breaks in the bonds of cement particles appear.
- When the concrete has already frozen, an ice crust appears around the metal parts, pushing the cement mass away from the steel reinforcement and thus compromising the integrity of the reinforced concrete products.
- When free water turns into ice, the volume of water decreases and then, when it thaws, it becomes insufficient for hydration.
All these phenomena are more dangerous the earlier the concrete freezes. If it has not reached at least 50% of its design strength, freezing can have a detrimental effect on quality and strength, significantly reducing performance.
Ways to combat solution freezing
The main task of winter concreting is to protect concrete solutions from freezing for as long as possible by keeping water in liquid form rather than ice. Several different methods are used for this.
Basic methods of combating freezing of concrete solutions:
- The thermos effect - the formwork for pouring is created from heat-insulating materials, and the components themselves for preparing the solution are heated (liquid, sand and crushed stone, but not cement), then the mixture is poured and covered with heat-insulating materials. This way it is possible to prevent the concrete from freezing until the moment when the frost is no longer afraid of it.
- Heating the solution in the formwork using different methods - steam, by passing current through it, using special devices. But this is a rather labor-intensive process and requires the use of special equipment.
- Creating a closed hut or canopy over the pouring site, heated by diesel or electric heat guns.
- Antifreeze is the introduction of antifreeze additives into the solution, which accelerate hydration and protect water from freezing.
The main advantages of antifreeze
Antifreeze additives can be dry or liquid. Liquids include ammonia water obtained by dissolving ammonia gas in water. The additive makes concrete frost-resistant, prevents reinforcement from corroding, and accelerates the hardening process of the monolith. Also on the market are a variety of solutions and universal mixtures made on the basis of dry substances. You can make an anti-frost additive to concrete with your own hands, but to do this you first need to understand the substances.
Types of dry additives in concrete mixture against frost:
- Potash (aka potassium carbonate) – activates the hardening of concrete and lowers the freezing temperature. It is usually added to the composition with borax (sodium tetraborate), because in its pure form it reduces the strength indicator. The potash mixture sets quickly and is difficult to work with, so a superplasticizer is usually added.
- Sodium tetraborate - used alone or with potash, preserves the structure of concrete after thawing, reduces the water permeability of the monolith, increases strength and prevents cracks from appearing.
- Sodium/calcium formate - significantly accelerates the hardening of concrete, working in a similar way to a plasticizer. Usually used with naphthalene lignosulfonate. The composition is introduced in a concentration of a maximum of 6% of the total mass of the solution.
- Sodium nitrite – lowers the freezing point of water in concrete, allowing the use of a non-freezing solution at temperatures from zero to -25 degrees.
What additives are added to complex formulations and how they are labeled:
- NC – calcium nitrite;
- M – urea;
- CC – calcium chloride (prohibited for use in reinforced concrete);
- MNC – urea, calcium nitrate;
- P – potassium carbonate (potash).
High-quality industrial additives often perform several functions simultaneously: regulating the rate of strength gain, lowering the freezing temperature of the solution, accelerating reactions, changing the properties of the mixture.
What additional properties do the additives provide:
- Increasing the mobility of the mixture, improving its distribution, reducing the volume of cement in the solution, increasing moisture resistance. Plasticizers based on organic polyacrylates, melamine resin sulfates or naphthalene have this effect.
- Significant increase in strength - strengthening additives based on iron and aluminum sulfates, calcium chloride and calcium nitrite.
- Protecting fittings from corrosion, extending the service life of products - corrosion-resistant additives.
- Mobility regulators significantly extend the time of working with the solution and prevent it from setting quickly.
- Complex action additives work in several directions at once.
The most effective is the use of ready-made liquid additives of complex action, which perform all the functions assigned to them and provide a lot of advantages. In Moscow and the regions it is not difficult to find mixtures; there are quite a lot of them on the market.
The main advantages of introducing antifreeze additives into the solution:
- The freezing point of water in the mixture decreases.
- Plasticizers reduce density and increase mobility without the need to add excess liquid, which allows for better and more comfortable pouring of the solution.
- Corrosion inhibitors are often added to anti-freeze products to protect steel reinforcing elements from oxidation and destruction.
- The strength gain of concrete accelerates to a point after which various impacts are no longer dangerous.
- Increasing water resistance, as well as the design strength of the finished monolith.
- Allows you to save money compared to the use of other methods that provide the possibility of pouring concrete at a disadvantage.
Features of working with antifreeze additives
A do-it-yourself anti-freeze agent for concrete, provided the correct choice of substances and their volumes is used, can provide the same properties as an industrial mixture. But it is much easier to purchase a ready-made solution with the correct proportions and desired properties. It’s easy to work with additives, the main thing is to follow the technology.
How to work with anti-freeze for concrete:
- Pour the required volume of water into the concrete mixer, pour anti-freeze liquid into it in the volume specified in the instructions.
- Allow the mixture to stir for 5-10 minutes.
- Without stopping stirring, load half the volume of sand into the container, then the entire volume of cement, then the rest of the sand.
- Load the entire volume of coarse filler into the concrete mixer and allow it to mix completely until the mixture is homogeneous.
- Develop the solution within the time specified in the instructions (the period may vary due to the properties of the additive).
PVA glue
A popular recipe used by many folk craftsmen. Surprisingly, this method has proven itself so well that it is actively used even in the professional sphere (when permissible according to GOST).
The main effects of adding PVA glue:
- increased strength;
- improved water resistance;
- providing excellent mobility.
Based on the last point, it is clear that the effect of using PVA glue is similar to the previous recipe when adding soap. However, keep in mind that PVA is an excellent adhesive material, actively used in repair work, and therefore its addition makes the concrete solution more reliable, efficient, and of high quality.
How much does it cost to add PVA when mixing concrete? Experts recommend using 200 grams of glue per standard 20-liter bucket. This is quite enough to obtain a truly high-quality solution.
The resulting mixture can be used for various purposes:
- filling of architectural forms;
- carrying out renovations in the apartment;
- construction of various objects in the country.
If the quality of the solution is a priority requirement, then you can replace PVA glue with pure polyvinyl acetate, since it does not contain any starch. This will help make the solution even more waterproof.
Features of national concrete pouring. How to pour concrete at low temperatures
First of all, let's remember what masonry mortar consists of. It usually includes: cement, sand, water. In order for the bricks to be properly bonded to each other, thereby giving the masonry strength, the mortar must dry well. When it's warm outside, there are no problems with this.
But what happens to the components of the newly laid masonry mortar when the ambient temperature drops below zero? Cement and sand are fine, but water turns into ice.
Of course, as long as it’s freezing outside, everything will be fine. But as soon as the thaw begins, the water will begin to thaw. And then we will have two unpleasant consequences at once:
- shrinkage. Frozen water, as we know, is more voluminous than liquid water. Therefore, as it thaws, the thickness of the masonry mortar will decrease. Therefore, the rows are lowered. Moreover, this happens rather unevenly. As a result, the structure will not only be lower than planned, but will also bend, become unstable and unreliable;
- deterioration in the quality of the solution. Even after the thawed composition dries, it will no longer be as strong as it should be.
As you can see, in conditions of negative temperatures it is not advisable to put a regular solution. I was convinced of this from personal experience. In ancient times, when there was no talk about a construction career, I decided
It was December, and I decided not to bother with the theory of construction. In general, in order not to bore you with details, I’ll go straight to the result: my lovingly folded fence in the spring took on the very intricate shape of a dragon’s back.
Frost protection is not only required when pouring in winter. Concrete hardening occurs within at least 1 month, and the first frosts in central Russia are possible as early as October. Therefore, when pouring in autumn, precautions are also necessary.
According to SNiP 3.03.01-87 “Load-bearing and enclosing structures”, the following rules for pouring concrete in the cold season must be observed:
- Mix the solution in heated devices or in a warm room.
- Use heated water and mixture components (except cement). Water should be heated to a temperature of no more than 70° C.
- Do not use frozen materials.
- Preheat the fittings.
- Increase the duration of the vibration formation process by 25%.
- Make sure that before freezing the concrete gains a strength of at least 5 MPa.
During winter mixing, the order of laying the components of the mixture changes: water is poured in first, then the PGS is laid in and several turns are made, and the cement is laid in last. Mixing time increases by 20-50%.
When mixing concrete from heated ingredients, the mixture turns out warm. In addition, reactions occurring in solution release heat. Therefore, if you cover the poured structure with heat-insulating materials, a “thermos effect” is created that prevents freezing, and at this time the concrete will have time to gain critical strength, after which freezing will no longer have a negative effect on its properties.
Winter concreting is carried out continuously. Each layer is poured before a film has formed on the surface of the previous one, while it is wet. The filled parts are immediately covered with heat-insulating materials.
Labor-intensive and expensive work on heating concrete during the hardening period can be replaced by using antifreeze additives.
In winter, the main enemy of high-quality concreting is low temperatures, which have a negative impact on the processes occurring both during concreting and during concrete hardening.
The formation of a solid substance - concrete - occurs as a result of the hydration reaction of the minerals that make up Portland cement. For this reaction to take place, a temperature above 0°C is necessary, since at negative temperatures water freezes and the hydration reaction stops.
We suggest you read: How to glue penoplex to iron
Already at temperatures below 5°C, the reaction rate sharply slows down, and the strength gain of concrete slows down.
Low temperatures cause the following problems:
- cessation of the hydration reaction;
- increase in internal pressure due to freezing and associated expansion of the material;
- the formation of ice crystals around the reinforcement, which leads to poor adhesion to concrete;
- obtaining low-strength concrete.
The main task in winter is to ensure that the concrete reaches critical strength (30–50% of the design strength), after which negative temperatures no longer have a negative impact on concrete. Typically, under optimal conditions, critical strength is achieved 4–6 days after installation.
Therefore, in winter, temperature becomes of primary importance.
The temperature of the concrete mixture is measured before, during and after placement.
Fluffy (lime)
Ordinary slaked lime is also excellent for increasing the consumer properties of concrete mortar. This recipe comes from the Soviet era, and at that time, as you know, they built to last. It has a beneficial effect on the quality of concrete, making the solution more elastic and sticky. When using lime, working with concrete becomes easier and more enjoyable.
Here it is important to draw the readers’ attention to another useful feature of slaked lime - its bactericidal properties. By adding it to concrete, you will get a mixture that is resistant to fungi and mold. This recipe is recommended for use in cases where it is necessary to carry out work in rooms with high dampness.
Is it possible to concrete in winter at sub-zero temperatures?
With the arrival of winter, many builders wonder whether freezing temperatures could interfere with planned construction work. Concreting in winter is possible, but involves the need to fulfill a number of additional requirements.
The recommendations are that you should not concrete outdoors when the temperature drops below -15°C. However, this does not mean that at higher temperatures (even negative) it is possible to concrete without obstacles. Failure to comply with the appropriate conditions can indeed lead to a construction disaster.
Concrete temperature
The concrete mixture poured into the formwork must have a temperature of at least 5°C - this is what the norm indicates. When concreting in winter, it is necessary to ensure such conditions that the temperature of the concrete does not fall below this 5°C. This requirement must be met at every stage of the work, both during the production and transportation process and on the construction site. The lower the ambient temperature, the more difficult it is to ensure the desired temperature of the mixture. When ordering ready-made concrete, the contractor has no influence on the conditions of its production, so you should pay special attention to the distance between the object and the concrete production base, since transportation time is of great importance.
It is worth remembering that the use of plasticizing additives does not lead to hardening and strength gain of concrete at low temperatures. Equally important is proper care and protection of concrete.
Freezing of fresh concrete
Freezing of concrete is a particularly dangerous phenomenon. The concrete is saturated with water, which has not yet had time to react with the cement and evaporate. Water located in the pores of concrete, freezing, increases its volume, which leads to rupture of the pores in which it is located. The standards state that until the compressive strength of concrete reaches 5 MPa, it should not freeze. Freezing of concrete is most dangerous after it has begun to set. If the concrete freezes before the setting process has begun, it will weaken the mixture, which will also affect the final properties of the concrete, including its compressive strength.
Curing
After pouring the mixture, you need to create such conditions so that the concrete can gain strength. It is especially important to prevent it from freezing before it has reached sufficient strength to guarantee freeze resistance.
Winter formwork
Construction works
During concreting in winter, certain conditions must be observed:
- preparation of formwork: the base on which the formwork is installed (soil, concrete, foundation) should not be frozen; it is necessary to insulate the formwork. During the concreting process, the mixture that passes through the gutter may freeze to it, so it must be constantly cleaned;
- the composition of the concrete mixture must be adapted to weather conditions: the type and amount of cement, the ratio of water and cement, the use of antifreeze, which helps reduce the setting time from 5 to 120 minutes, are important;
- When caring for concrete, it is necessary to use appropriate materials - insulated formwork (films, non-woven materials, insulating materials - polystyrene foam, mineral wool) or heating the concrete using appropriate equipment (fans, heaters, infrared emitters, heating mats).
The most dangerous thing is freezing of concrete after it begins to set, before obtaining the required strength. Premature freezing of the mixture will affect the final properties of concrete, its compressive strength.
Compliance with these conditions will minimize the negative impact of low temperatures on the quality of concrete, and will allow you to carry out work even in winter. It is worth remembering that the use of antifreeze additives cannot be the only procedure protecting setting concrete at low temperatures. Equally important is proper care and protection of concrete. The point is to ensure that the mixture is at sufficient temperature during concreting and that it does not freeze before it has reached sufficient strength.
Ash
The last folk supplement that deserves attention. At first glance, ash does not inspire confidence, but keep in mind that it is an environmentally friendly product. A small amount of ash helps make concrete strong and flexible. This mixture is perfect for renovation work in an apartment or private house.
As you can see, there are many folk additives that help you obtain professional concrete at home. Which recipe to resort to is up to you. The main thing is to remember something else: in the pursuit of cheapness, it is important not to forget about quality and further operating conditions. This will help you find a middle ground.