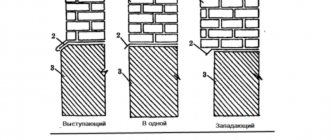
Pits are depressions in the ground adjacent to the wall of a building. As a rule, they have a rectangular (less often semicircular or trapezoidal) shape. On one side they have an opening (entrance or window)
The purpose of the pit is to limit the space in front of the window. Its dimensions depend on the area of the window (that part of it that is below ground level). If the window is almost completely recessed, then you need to follow the rule: the area of the bottom of the pit should be approximately equal to the area of the window. Naturally, its shape also matters. Most often, rectangular pits are arranged: the long side is parallel to the wall of the building and one and a half times wider than the window. The short sides have a length of no more than 1 m. The bottom of the pit is, as a rule, 20 cm deeper than the bottom edge of the window and it should always have a drain for rain and melt water.
- At this stage, it is necessary to create wooden formwork that would allow the walls to be filled with a thickness of at least 15 cm.
- It is worth noting that the pit can be made flush with the ground and then it will receive all the wastewater, or it can be made with a threshold of 15 - 20 cm.
The work includes the following main processes: preparation of the concrete mixture, delivery of it to the construction site, supply, distribution and compaction of the mixture in the form (formwork), “care” of hardening concrete, quality control of concrete work.
In the construction and repair of individual residential buildings and in the improvement of personal plots, artificial stone material - concrete - is widely used. Ordinary concrete is produced from a mixture of cement with water and various aggregates (sand, gravel, crushed stone, pebbles, etc.) after it has been molded and hardened. Before molding, this mixture is called concrete mix. Ordinary concrete can withstand heavy loads in compression well, but poorly in tension; it is used in structures such as foundations, thick walls. To give concrete greater bending strength in structures that perceive tensile forces (lintels, slabs, floors, etc.), the concrete mixture is reinforced, that is, steel or iron reinforcement is included in it. Concrete reinforced with steel or iron is called reinforced concrete.
To manufacture a concrete and reinforced concrete structure of a certain size and configuration, it is necessary to place the concrete mixture and reinforcement in a pre-prepared form, which is called formwork.
In reinforced concrete, reinforcement refers to steel rods of various sections and shapes, steel ropes and strands that absorb tensile and shear stresses arising in reinforced concrete elements from external loads and the structure’s own weight. Reinforcement can be of constant cross-section (smooth rods) or periodic profile.
Laying concrete mixture
Lowering the concrete mixture from a height, in order to avoid delamination, is carried out in compliance with the following rules:
The height of free dumping of concrete mixture into reinforced structures should not exceed 2 m;
The concrete mixture should be lowered from a height of more than 2 m through vibrating chutes, which ensure slow sliding of the mixture without delamination.
The solidity of the concrete foundation structure is ensured by continuous concreting. If this cannot be done, then working seams are made, which is understood as the joint plane between the hardened old and freshly laid concrete. Working seams can be horizontal and vertical, but they are never inclined. It is possible to resume interrupted concreting if the concrete mixture has acquired a strength of at least 1 MPa, and also if the previously laid concrete mixture liquefies during vibration, that is, the process of its crystallization is still in the initial stage. Before laying concrete, the surface of the working joint is washed and the cement film is cleaned with a steel brush.
The increase in concrete strength over a certain period of time is controlled by the laboratory by testing a series of samples. Taking into account the strength of concrete, the time limits for stripping concrete and reinforced concrete structures are assigned.
Before stripping begins, exposed concrete surfaces are inspected and tapped. When stripping, it is necessary to protect the formwork from damage in order to reduce the cost of its repair.
The stripping process always begins with the removal of the side elements of the formwork that do not bear the load from the structure’s own weight. In summer, when the outside air temperature is 15-20°, the side surfaces are stripped after 2-3 days.
The load-bearing formwork of reinforced concrete structures of small spans is removed after approximately 10-12 days, depending on the type of structure, outside temperature, grade and type of cement, magnitude and nature of loads, etc. These periods are determined in relation to the type of structure, based on the required strength of concrete by the time of demoulding.
Slab foundations: features of constructing maintainable communications
When is this type of foundation used?
A slab foundation is great for residential and non-residential spaces, especially if you are not planning on building a basement. Another small plus is that you don’t have to put logs under the floor, since the monolithic slab will be a ready-made floor for the future structure. The monolithic slab foundation is characterized by great strength and seismic resistance; it is practically impossible to wash it away with water, since the foundation area is quite large. This foundation is perfect if your site has problematic soil.
DIY foundation slab: step-by-step instructions
The entire range of work on arranging the slab foundation of a house or outbuilding can be done on your own.
Preparatory stage
The area for the foundation is cleared of debris, trees and shrubs, after which the future pit is marked. It is important to ensure that the stretched cords form right angles. For accuracy of geometry, the coincidence of the lengths of the diagonals of the marked rectangular section is checked.
In the marked area, it is necessary to dig a pit, taking into account the thickness of the sand-crushed stone cushion, concrete base, waterproofing and the design depth of the slab.
It is necessary to remove a layer of fertile soil with vegetation from the building site; the depth of the pit is calculated relative to the prepared surface.
The bottom of the pit should be flat and horizontal, the soil should be thoroughly compacted. The technology for constructing a slab foundation may involve the use of geotextiles to create a barrier between the soil and the sand cushion - in this case, the sand does not silt and is not washed away when flood groundwater rises. Geotextile sheets are laid with an overlap of 30 cm and overlap the walls of the pit.
Technology
There are two ways to create a foundation slab - monolithic and prefabricated. If the slab is monolithic, the formwork is first installed, then the reinforcement frame is assembled, and after that concrete is poured once for the entire structure. In the case of a prefabricated foundation, it is mounted from ready-made reinforced concrete slabs, the seams between them are filled with concrete. This design does not require formwork or installation of reinforcement cage, but it has its drawbacks. It is impossible to achieve the required thickness of the foundation since the slabs manufactured at the factory have a certain thickness. In fact, the foundation will not be monolithic, which makes it less durable. A crane is required to lay the slabs. Due to the unevenness of the soil, the slabs cannot be laid flat; they will have to be leveled, which is almost impossible to do manually.
Insulated plate USHP
The foundation with a heat-insulating layer under the sole and integrated underfloor heating contours is called the “Swedish” slab. The main advantage of the USHP design is the reduction in the finishing budget. The owner receives simultaneously with the foundation:
- finished floor on the ground
- bottom heating
- comfort of stay
- reduction of energy consumption in the main heating circuit
The disadvantage is the complex design and construction technology. For a Swedish slab, you will have to make a concrete base, waterproof it, purchase and lay expensive XPS polystyrene foam.
Advantages common to all stoves
Any foundation of this type is much stronger and more reliable than tape, pillars, or grillage. Loads on the ground are distributed evenly, there are no problems with the construction of partitions or moving them during redevelopment. In addition, a monolithic slab has advantages:
- variability - when designing, you can choose a smooth, reinforced with ribs, bowl-shaped structure, inverted bowl, option with a caisson, deep laying
- high resource - the slabs do not require periodic repairs, they can winter without reducing their strength for resuming construction the next season
- simple design - eliminates the need for earth-moving equipment
The slab has no restrictions on the number of floors, so even a three-story cottage may have an attic. The strength reserve of the foundation of the house many times exceeds the prefabricated loads in any case. Blind areas do not cause difficulties when choosing any modification of the MLP; if necessary, they can be insulated with polystyrene foam to reduce lateral freezing.
Advantages
The main advantage of a monolithic slab is its ability to withstand heavy loads even with a small width. The advantages include the ease of installation of the slab and its durability, as well as the fact that you will not have to install the floor in the future building. The monolithic slab perfectly insulates from groundwater and the cold of the earth. The slab cannot float in individual elements; if it moves, it can only move completely. The house seems to float entirely in the ground, which makes it resistant to earthquakes. Such a foundation usually does not crack. A monolithic slab is erected quickly enough and does not require heavy equipment on site. Based on a not very thick monolithic slab, you can build a two-story house.
Reliability and modernization of house engineering systems on the German Bauplatte plate
A very common question among customers of insulated slabs is: what to do if the sewer pipes fail? The consumer believes that builders are bound to screw things up somewhere, and he must have the opportunity to fix it.
High-quality materials - 70% success!
It so happens that builders in our country strive to use cheaper materials, despite the fact that in building materials price is an indicator of quality.
For sewerage, we use a German Ostendorf pipe with an estimated service life of 100 years and nothing can happen to it. There are domestic analogues, but they are lighter, with a thinner wall, and therefore less durable. When you hold Ostendorf in your hands, you feel solidity and quality. Yes, it is more expensive, but is it wise to save on yourself?
If the sewer line is more than 10 m long, then a place for inspection is provided through which the pipe can be cleaned at any time. But we have not yet encountered such a need. Well, what if the unthinkable happens... for example, someone has “concreted” your sewer pipe and it is impossible to clean it. What to do? You can lead the new pipe through the wall. As the Jews say, this is not a problem, but an expense. We are sure that such a scenario is from the realm of fantasy, but there is a way out.
There is a huge range of pipes for heated floors on the market today. Many builders have switched to domestically produced cross-linked polyethylene at 25-30 rubles per meter. It is possible that such a pipe will last a long time, but we are not sure. The warm floor is monolithic into the slab forever, which means it must be “eternal”. We do not experiment with our clients' engineering systems and install the best pipes from German leaders: Rehau and Prineto . Yes, such a pipe costs 3 times more than a domestic one, but you won’t remember us with a bad word even in 50 years.
The same approach applies to any materials in our homes: quality comes first!
Sometimes clients ask us for a certificate for concrete. They fear that we have saved on the brand of concrete). We ourselves are concerned about the quality of concrete on the market, so we always buy concrete of a higher grade than in the project, that is, with a safety margin.
We are installing water supply from HDPE food pipe, produced by Politek. This pipe has no odor or emissions, because it is made from primary raw materials.
In addition, if the client is able to provide a diagram of the ground floor outlets before the start of construction, we will lay out channels from HDPE pipes for future laying of electrical cables. This will save the electrician's time, and therefore your money. There is no need to make grooves in the walls, attach cables, and then plaster.
How to make a slab
In general, the construction itself is done as follows: a pit of the required size and depth is dug. Then a layer of sand or crushed stone is poured, communications are laid (sewage and water pipes. A concrete screed is made on top. All this is insulated, then the formwork is built, the reinforcement frame and the slab can be filled with concrete.
Monolithic slab foundation diagram
How to determine the thickness of the slab?
The thickness of the monolithic slab depends on what kind of house you will build. The heavier it is, the thicker the slab should be. If the foundation is planned to be shallow, then the thickness of the slab can be no more than 30 cm; a deep foundation can be made. This can reach a thickness of 1.5 meters. Most often, for private buildings, a foundation is used whose thickness does not exceed 40 cm.
Concrete grade m 200 is used for the foundation slab. Concrete mobility should be p-3, cold resistance F200, but no less. Pay attention to the waterproof markings. It must be no less than W8.
Monolithic slab foundation, inside view
Preparation for laying
When installing a sewer system under a floor slab, more than just pipes will be required. You will need various fittings, such as a pipe clamp (this type). You will also need:
- special tees for sewerage;
- docking adapters, plugs, couplings, etc.
The connections are sealed using a silicone gun. Laying sewerage under the foundation slab must satisfy a number of conditions:
- In order to prevent damage to communications, the depth of laying pipes must be at a depth of at least 0.5 m from the blind area;
- The sewerage system under the foundation slab should have a distance to the septic tank of 5-10 m;
- The required pipe slope per 1 m length should be 2-4 cm;
- If possible, place all water intake points in the house as compactly as possible.
To protect underground pipes from mechanical damage, you can use the so-called. sleeves. They are pipes of larger diameter in which working communications are already located. Another advantage of using sleeves when installing sewerage under floor slabs is the ability to quickly remove a damaged pipe without the need to dig it up and refill the trench.
Stages of foundation construction
First you need to mark the site on which the future structure will be located. Please note that the formwork will take up some space; to make it more convenient to work with it, add about a meter to the sides of the pit.
In order for the pressure on the slab to be uniform in the future, the platform is leveled. There should be no bumps or drops at the bottom of the pit. the drainage system must be done immediately. To do this, you can dig transverse trenches to drain water. Geotextiles are placed on their bottom. Then you need to lay plastic pipes with pre-drilled holes. All this is covered with fine crushed stone and again covered with geotextile.
Substrate for the foundation
The procedure for pouring the foundation and niches for communications
Communication diagram in the foundation.
First, all the necessary holes are made in the foundation, then the foundation itself is poured. If holes are made after pouring, they may crack in the base, and they will not turn out even. At the time of pouring, it is worth placing plugs on all proposed holes. Then the plugs are removed, pipes are installed in their place, which will act as a cover, and communication wiring is installed in them. It is also important to think about where the drainage well will be and where the waste will go. This is where the drain pipe should go. Everything needs to be carefully planned and thought through and only then can construction begin.
It is important to remember that the height of the foundation should be quite large, since the protective casings of communications laid in the foundation may freeze if the temperature is low in winter. This should not be allowed, so it is better to protect yourself in advance.
In order to protect the pipeline from merging with the concrete with which the trench is poured, it is necessary to make a kind of sarcophagus that will keep it from the pressure of the house.
If you are planning to build a house with a basement or basement, then the task is simplified. Communication pipes will be installed on the basement ceiling, which will avoid going deep into the foundation. But if, nevertheless, a basement is not planned, then the project will be developed with the condition that it is in the foundation that the communication “world” will be laid.
Formwork
The most convenient way is to make a schematic formwork. It is knocked together around the perimeter of the pit from boards. The outer side is strengthened with the help of struts.
After the formwork is ready, you need to make a foundation cushion. It is made from a layer of sand and gravel. The pillow is used to remove moisture from the foundation and cushion the soil. The cushion can be from 15 to 30 cm thick. If the soil is too wet, you can add small crushed stone.
The pillow should be well compacted. Ideally, there should be no traces of shoes left on the sand after high-quality compaction.
then waterproofing is done. First, a solution of sand and cement is made. The pillow is filled with it. The thickness of such a solution should be about five. Afterwards you can lay waterproofing using rolled material for this purpose. For example, roofing felt. It’s good if some of the material gets on the formwork
Foundation formwork
When the waterproofing is ready, you can begin reinforcement; for this you will need reinforcement. Use twisted fittings and do not use welding. The rods tied with wire will be more mobile and will save the slab in case of uneven load. Whereas welded rods will increase the load and it may burst. The frame is knitted in the pit itself.
After the reinforcement is completed, you can begin pouring the slab. It is best to invite a machine with ready-made mortar and pour the entire foundation at once. This way it will definitely be homogeneous and will not crack.
Design Features
The construction of a slab foundation may have different features and sequence of actions. Thus, builders often make do with a monolithic concrete slab, but in particularly difficult situations, when the quality and density of the soil leaves much to be desired, a reinforced concrete structure is created.
Before starting construction, you need to consider how feasible it is to build such a foundation for the building, since you will need not only a large amount of concrete, but also sand and crushed stone to make the cushion.
A house on a slab foundation may require a recessed version of the structure, which will significantly increase the amount of materials used. Additionally, you will have to use the services of professionals and special equipment to dig a pit of sufficient depth. It is possible to independently carry out work of such large volumes over a very long period of time.
If construction is planned on difficult terrain, in particular on a slope, then in such cases there is a high risk of displacement of the upper layers of soil. In this case, a pile or columnar foundation for construction is often installed, however, the best option is a slab foundation on a slope. As noted above, this is due to the ability of such a structure to withstand vertical and horizontal soil movement.
Very often, this type of foundation for construction is used in cases of large-scale construction, and the foundation site turns out to be quite impressive in size. Of course, the concrete slab itself is a very strong structure, however, over time there is a high risk of it sagging under its own weight. Therefore, for large object sizes, a slab foundation is equipped with stiffening ribs, which are concrete elements shaped like a trapezoid and located along the perimeter of the structure.
Calculation of a monolithic base for construction
The dimensions of the structure are taken to be equal to the dimensions of the future building, taking into account the project. The calculation of a slab foundation is carried out taking into account its tidal height (most often this figure is 0.3 m, but the quality of the soil and the presence/absence of groundwater play a role here). However, part of the structure, which is defined as the depth, also takes part in the calculations.
The calculation of concrete for a slab foundation is carried out by multiplying the volume of the structure (it is necessary to multiply the length, width and depth) by the density, which is about 2,500 kg / cubic meter. m. The result will be the total weight of the future slabs.
But concrete for a slab foundation is a ready-made mixture, which is created by mixing cement, sand and water. It is necessary to obtain the final amount of cement.
Considering that for this purpose one share of cement is used, one share of water, three shares of sand, you can get a number equal to the amount of cement by dividing the previously obtained volume of concrete mixture by 5 (the total number of shares of sand, water, cement).