Today, in the construction of garages, cottages, and private houses, building blocks made of expanded clay are often used. Often such blocks are used for external cladding as load-bearing structures. Laying a foundation for a building made from such blocks is very effective and expedient. The main point to pay attention to is the use of the appropriate type of blocks. For the foundation, solid blocks are needed, but for laying walls made of expanded clay concrete, hollow blocks are needed.
Installation of a foundation made of blocks.
For a block house you will need to use the following tools:
- construction level;
- plumb line;
- measuring tape (roulette);
- shovel;
- mooring cord;
- construction square;
- ordering (distance between marks is about 200 mm);
- rubber hammer (weight up to 1000 g);
- angle grinder (cutting wheel diameter 220 m);
- jointing
Construction using expanded clay concrete blocks is carried out using different methods, each of them is used based on the type and purpose of the building, soil characteristics, climatic conditions and other characteristics.
Advantages of expanded clay concrete
Expanded clay is obtained by heat treatment of low-melting grades of clay. It is as porous as gas silicate. This material has the following positive properties:
- Quite strong, but not suitable as a foundation for tall buildings.
- It has excellent soundproofing and thermal insulation characteristics.
- Resistant to changes in weather temperature and humidity levels.
- Non-flammable.
Expanded clay blocks are produced using the following methods:
- Monolithic production of walls by pouring.
- Preparation of blocks of various shapes.
For expanded clay mortar, make the following mixture: cement (1 part), sand (2 parts), expanded clay (3 parts). For the construction of a building, cement of grade M400, no less, is taken. Water is added to the solution while constantly stirring the mixture until the consistency of sour cream is obtained.
We build individual elements of the house structure
The calculation of interior partitions, the insulating layer of expanded clay concrete, as well as non-residential premises (porch, veranda, summer kitchen) is carried out similarly to load-bearing walls. The differences lie in the material used - partition blocks, which have a smaller thickness and a larger number of voids.
Costs at this stage of construction will be more modest, but you should initially think about the exterior decoration. It may be necessary to select some other, more elegant material for some decorative designs.
Types of foundations for expanded clay house construction
For houses that are built from expanded clay concrete blocks, various foundations can be installed. The weight of such buildings is small, so the load on the foundation will be low. Among the most popular types, there are several types of foundation foundations: strip, slab, screw and even expanded clay.
Strip foundation base
This type of base is very common due to its technical simplicity. It requires a minimum amount of materials. It is erected at low groundwater levels. On a different type of soil, a house with such a foundation may fail.
Stages of creating this foundation:
- Prepare a trench along the future walls of the house. The depth of the trench should be below the freezing level of the soil.
- They make formwork.
- Sand is poured into the bottom of the trench and compacted.
- Reinforcement is placed in the trench in order to strengthen the rigidity of the foundation.
- Then concrete is poured inside.
Strip foundation is one of the simplest and most common. But for areas where the soil is unstable, a pile-screw foundation is more suitable.
Screw foundation
The support of this foundation is screw pile structures. Pile-type foundations are distinguished by grillages. To construct it, wells of a given diameter are drilled. The resulting wells are reinforced and filled with concrete.
The base has a low installation cost and is suitable for light buildings, for example, for country houses. Therefore, it may be ideal for houses made of expanded clay block buildings on swampy soils. But there cannot be a basement in such a house.
Such foundations are used in the construction of light country houses.
Slab foundation
This support for the building is quite reliable. It is used in climates where low temperatures prevail most of the year. Since the slab base can withstand extreme cold, a house made of expanded clay blocks will protect the foundation from hypothermia. Such a foundation is also used on unstable soils, since it:
- resistant to unstable soils;
- tolerates low temperatures;
- durable;
- durable
Its construction requires precise preparation procedures. Among them: the need to compact the soil, making a cushion of sand, deepening the blocks and the operation of compacting concrete using vibration.
Columnar foundation
It is used for lightweight houses made of expanded clay concrete blocks on constantly freezing soils. Columns for the foundation of a house are made of concrete, brick, expanded clay concrete blocks or foam blocks.
This support is sometimes combined with a reinforced concrete slab, which is installed on posts. The result is a columnar-slab base that can support the heaviest houses made of expanded clay concrete blocks, even on swampy soils.
Expanded clay block foundation
A foundation made of expanded clay concrete blocks has many advantages. It is used not only for house construction. It can also be used to build foundations. But such a foundation is suitable only for light buildings, for example, for garages, bathhouses and others. Advantages of expanded clay foundation:
- strength not inferior to concrete;
- can serve for a long time without changing under the influence of climate;
- quickly and easily erected;
- it is waterproof.
Types of suitable foundations
The use of lightweight blocks in the construction of an expanded clay concrete house allows the use of different types of foundations:
- tape-monolithic;
- prefabricated strip made from masonry building materials;
- pile with grillage;
- slab;
- columnar.
- Strip monolithic foundation. The most popular type, laid on dense rock soils and relatively flat areas. If a basement is planned for the house, this is the best choice. When laid professionally with mandatory hydro- and thermal insulation, the foundation is durable and reliable.
- Prefabricated strip foundation. The choice of soil and the arrangement of the cushion are similar to the laying of a monolithic foundation. The construction itself is carried out by analogy with laying walls from blocks. The permissible height does not exceed 5 rows. The blocks are laid on cement. The result: high laying speed, low cost, reliability, excellent thermal insulation properties.
- Pile base with grillage. The use of bored piles with a recessed grillage allows you to build houses on any soil or water-logged areas. The foundation is reliable, extremely economical, and durable. Restrictions on the light weight of installed structures do not apply to lightweight structures made from blocks.
- Slab foundation. It is distinguished by absolute reliability, no restrictions on the weight of buildings and the type of soil. The disadvantages include the impossibility of laying in areas with complex terrain, the lack of a basement floor and high cost.
- Columnar base. When columns made of concrete, stone or brick are combined with a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, a reliable basis for lightweight structures is obtained. It is laid on heaving soils. Regardless of the choice of the type of foundation for the future home, the fundamental factors are its quality and feasibility.
Source: kamedom.ru
Selection of foundation
When choosing the type of foundation for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks, you need to take into account the depth of soil freezing and the topography of the site. You also need to know the level of groundwater, the level of street noise and much more.
This selection must be done especially carefully in areas with constantly frozen soils or on slopes. On this type of soil, it is dangerous to build houses from expanded clay concrete blocks, unless it is a slab house.
Due to the large area, the load on the soil in this case is distributed evenly in all directions. The soil experiences almost no pressure. This makes it possible to erect any buildings on a slab foundation. But due to the size of the slab, this is not very convenient to do, especially when building from blocks.
And, in general, there is no point in chasing imaginary savings. It is better to entrust the construction of a house from expanded clay concrete blocks and the foundation for it to qualified specialists. They will select the type of foundation appropriate to the area.
Selecting a base type
In order to find out which foundation is best for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks, you need to take into account the following indicators:
- weight load;
- peculiarity of soil heaving at a construction site;
- tendency to frost heaving;
- level of the underground aquifer.
Load
The property is determined not only by the material of the building, but also by the number of floors. When doing the work yourself, you should consider the given data, where the calculation was made for a one- and two-story house:
- For a one-story building with a density of 700 or 1000 kg/m3, a pile, slab, or shallow strip foundation (depending on the characteristics of the soil) is suitable. To save money, the piles are made of screws; the strip foundation can be T-shaped or rectangular. The slab base can be easily and without any particular fears set up with your own hands, especially on fairly light soils. Shallow or deep immersion columnar supports are very suitable.
- For a two-story building, elements with a density of 1000 kg/m3 require the construction of a slab foundation in various layers: strip, T-shaped shallow, recessed. It is not recommended to use columnar types of foundations due to their low load-bearing capacity; you will also have to abandon pile structures, or make fairly frequent pile spacing and strengthen the entire system with a grillage.
- For a two-story building made of expanded clay blocks with a density of 700 kg/m3, a pile foundation is suitable, but with a preliminary calculation of the mass of the entire structure. A standard guideline value can be the load per pile (up to 6 tons). You can consider strip and slab bases.
Important! The equipment of the ground floor or basement requires the choice of a slab strip foundation for a house with a thorough penetration into the ground.
Calculation of bearing capacity requires the following steps:
- determination of soil type;
- collection of load indicators of the mass of the entire structure;
- calculation of base parameters (thickness, width), reinforcement and the need for pile depth.
Soil characteristics
This indicator is influenced by: moisture saturation, heaving of the soil. To minimize the risk of collapse, consider the following tips:
- When arranging a building on conditionally non-heaving and medium-bearing coarse-grained, sandy soils, it is necessary to ensure that the soil is properly dry. Otherwise, you should stick to pile foundations;
- clays and loams, as well as sandy loams and fine-grained sands are defined as heaving soils with reduced bearing capacity. Therefore, it is necessary to immerse the supports well below the freezing point, reaching dense layers of soil deposits. If this deepening is not possible (at least 0.5 meters), drainage work is carried out.
Monolithic strip foundation
It is chosen by the vast majority of developers. Why him? Because the foam block (or other porous stone) has low bending resistance, and during seasonal soil movements there is a high risk that cracks will appear along the walls of a building that does not have a solid solid base. There are two types of such foundations: buried and shallow.
How to choose the right tape depth?
Textbooks and construction instructions offer formulas for calculating the correct laying of foundations, but all this information is rarely used in practice. It is more important for a private developer to understand the main reasons that have a decisive influence on the choice of the depth of a pit or trench for pouring concrete. - this is an indicator of how far the base of the base is located from the surface of the soil.
Types of foundations.
There is a widespread belief that the stability of the foundation directly depends on whether it is located above the freezing point of the soil or below it.
In fact, in most cases this factor is not so important. The opinion of experienced foremen is this: in most cases, for frame and block houses, a shallow monolithic tape (no more than 50 cm, optimally 40 cm) is quite sufficient, regardless of what the TPG is in the area
The classic calculation is as follows: a shallow one is one whose sole is located at a distance from the surface of the soil that is 1/3 of the freezing point.
There are rules, following which, you can independently determine how many centimeters will be enough at this particular construction site.
- if the soil is heaving (clay and loam) and groundwater comes close, then the developer is out of luck: he is faced with the most difficult option. The choice here is as follows: either a “floating” slab or a monolithic tape below the TPG;
- if the soil is heaving, but not waterlogged, the base can be installed at a depth of 1.7 m, even if the TPG is significantly lower. But the height of the tape or supports must be at least 80 cm;
- if the groundwater level and the TPG coincide, the base should be located 20 cm below the freezing point;
- if the soil is marshy or mobile (sandy), then screw piles are optimal.
Construction technologies
So, depending on the type of construction of a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks, the foundation is selected.
Tape
It can be either prefabricated or monolithic. Monolithic has many advantages, since it minimizes the need to use special equipment. In this case, the width of the tape must be no less than the thickness of the wall panels to create a strong support and prevent displacement of the axis of the blocks and the base.
The material requirements are as follows:
- concrete grade B20-25;
- reinforcing bars A400;
- backfill made of medium sand;
- for tape with shallow or deep immersion, provide insulation materials.
Columnar base
It can be made of concrete blocks or be monolithic. A mandatory grillage is provided to ensure uniform distribution of the load on all elements.
Important! Columnar foundations are not suitable for heavy buildings!
Slab base
It is equipped with reinforced concrete monolithic slabs. For private buildings, slabs with a cross-section of up to 300 mm, class B20-25 concrete, and A400 reinforcement are used. Reinforcement frames are required, as is pouring in one go, which will increase the reliability of the entire structure.
They can be screw or bored. To build a house from blocks with your own hands, it is better to choose bored piles, which increase the strength of the entire structure, but screw pile elements will reduce excavation work and deepen them much faster and easier. It is necessary to arrange a grillage, which is best made of reinforced concrete, but an ordinary metal one can also be used.
Important! It is not recommended to use wood frames under a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks.
When choosing a foundation for a building made of blocks, it is necessary to clearly understand the characteristics and capabilities of the soil. Only with correct calculations will it be possible to avoid mistakes and make the foundation truly strong. Do not forget about insulating the underside of a house made of blocks if the choice fell on pile or slab foundations. Experts recommend choosing the latter option, but you can use strip types of foundations, provided the soil quality at the construction site is acceptable.
Types of expanded clay blocks for foundations
To construct a foundation made of expanded clay blocks, two types of products are usually used: wall and cushion. The wall sections should form a quadrangle. They are usually equipped with cutouts on the sides to fit tightly together. Their role is to form the underground and above-ground parts of the foundation.
As for the cushion blocks, they are trapezoidal in shape, and this significantly increases the supporting area. Their purpose is to lay a balancing first row of “sole”, which ensures excellent stability of the entire structure.
To build a foundation, you need special foundation blocks; they have special technological slots for wiring communications.
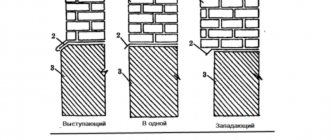
Scheme of a wall made of expanded clay concrete.
Making holes in a solid finished product with your own hands is problematic. Therefore, factories produce 3 types of blocks. FBS blocks are reinforced concrete blocks, solid, without holes. FBV blocks are blocks with cutouts; they facilitate the installation of various communications. U-shaped FBP - hollow blocks, reinforced concrete.
Massive products weigh up to 1.4 tons, which requires the use of lifting equipment for their installation. This causes additional costs.
However, for self-building there is an optimal solution - you can build a foundation of 20x20x40 cm from blocks. Such blocks are specially designed for “sole”, made by hand, for light, small-sized buildings. These “cubes” are made from heavy classic concrete or lightweight expanded clay concrete. For example, a foundation made of expanded clay concrete blocks, with its technically useful characteristics, solves two problems: arrangement of a reliable foundation and its insulation.
Remember that for a foundation made of expanded clay concrete blocks, they usually use building materials only from proven ones and must be at least 1800 kg/cub.m.
Which foundation is suitable?
For a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks, you can use 3 types of base. Each of them has its own characteristics and construction conditions.
Slab
This type of foundation is worth using for those who want to build a small house. It is easy to manufacture and requires minimal cash outlay. But such a foundation for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks should only be built on stable soil.
A tiled base is perfect for a one-story house that does not have a basement. But you can see what a slab foundation with stiffening ribs down looks like in the photo in the article.
Tape
A strip structure for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks is considered the most reliable and practical. It is not influenced by factors such as temperature fluctuations and ground movement. In addition, the strip base allows you to build a house with a basement. But when choosing it, you need to understand that it takes longer to build, and the financial costs are high.
Creating a strip foundation can be done using special blocks or concrete. The choice of this or that material is determined taking into account the personal wishes of the person. But if you want to build a house with a warm basement, then it is more rational to use blocks. But what is the technology for constructing a strip foundation, this article will help you understand.
Construction of a slab foundation
Different types of foundations have their own design and construction features. Construction using screw piles is quite simple and does not have any nuances. The same applies to the strip type, which is just a strip of concrete around the perimeter of the house. The slab foundation, the most reliable type, requires special preparations and procedures during construction, so it is worth describing it.
Slab structures are installed on heaving and watery soils, which is why they are called floating, because when the soil changes, they move entirely, which does not harm the building. Construction takes place in several stages:
- Preparing the area. Includes removal of the top layer of soil.
- Installation of the pillow. The area for the structure is filled with a cushion of sand and gravel, which prevents soil deformation and drains groundwater.
- Formwork installation. Using planed boards, a formwork is created that marks the boundaries of the foundation and its segments and prevents the movement of concrete.
- Installation of communications and insulation. Communications are created for the future home and insulation is installed to prevent the movement of moisture and heat loss.
- Installation of fittings. The reinforcement frame is tied and placed in the formwork. This will ensure the strength and solidity of the structure.
- Pouring concrete. Concrete is poured along the edge of the formwork, completely covering the reinforcing mesh.
- Drying concrete. The drying process takes 5 weeks. The foundation should not dry out or be exposed to rain; temperature changes are also undesirable. During drying, it gains the necessary strength, after which it is ready for construction.
How to calculate
When choosing the dimensions of the foundation, it is worth calculating the thickness of the base. A special formula is used for this. According to it, it is necessary to divide the weight of the house by the area of the building. The resulting value should not exceed the parameters that the soil can withstand.
To avoid mistakes, builders make a foundation with a thickness that is proportional to the thickness of the walls of the house, adding 40-50 cm as a margin.
The choice of base height is carried out taking into account the condition of the soil and the level of groundwater. The standard value of the foundation height is 50 cm. When building the foundation for a house from expanded clay concrete blocks, lintels are used. For 1 m3 of concrete solution, 200 kg of reinforcement is used. But what types of foundations exist for a private house, and how to choose the right one, this article will help you understand.
The video shows how to calculate the foundation for a house:
Step-by-step calculation algorithm
Block calculation table.
- Step It is necessary to determine the length of the external walls (L). If the house is rectangular, their length is equal to the sum of the length and width, multiplied by 2; if the shape is different, the lengths of all the walls are summed up.
- Step Let's determine the height of the building (h). This value entirely depends on the wishes of the owner, and ranges from 2.5-3.5 m.
- Step It is necessary to determine the thickness of the walls (t). In addition to the standards, it depends on the size of the block used for construction. For example, if the block is 0.2*0.3*0.6 m, then the value 0.35 m will not work.
- Step We calculate (according to the plan) how many windows and doorways there will be, their area (P).
- Step Calculate the volume of blocks (number of cubes) for construction. We multiply the length of the walls by the height, subtract the area of the openings and multiply by the thickness (L*h – P)*t.
- Step Similarly, we determine the volume of load-bearing walls and piers.
We sum the two quantities and get the number of cubes.
- Step If the blocks are sold individually, you need to find out how many pieces to purchase. We measure the block in centimeters (with an ordinary ruler), then multiply the length by the width and by the height, and divide 1,000,000 by the resulting value. The remainder is the number of blocks per cubic meter. The seller can provide this value. We multiply it by the result of step 6 and get the required number of pieces.
Formula for calculating the number of blocks.
For example, consider a 9 x 9 house, 3 m high with one internal load-bearing wall. The perimeter of the house is 36 m, the area of the walls is 36 * 3 = 108 m 2, windows (6 pieces of 1.8 m 2 = 10.8 m 2) and 2 doors. (4.8 m 2) volume (108 m 2 -10.8 m 2 -4.80 m 2) * 0.35 m = 32.34 m 3 (0.35 m - thickness in meters). Load-bearing wall: 9*3*0.35 = 9.45 m3. Walls 4 pcs. 4.5 m long (from load-bearing to external): 4 pcs * 4.5 * 3 * 0.1 = 5.4 m 3.
Total: to build a 9 x 9 house, with one load-bearing wall and four piers, you need 47.19 cubic meters. m of building materials.
But the actual size of the block can make changes to our calculations: 0.2 m * 0.3 m * 0.6 m taken as an example will determine the wall thickness of 30 cm, and for the piers you will have to find something else.
Example: let's calculate how many blocks described above are needed to build a 6x6 house.
- Length of external walls: (6+6)*2=24 m.
- Let us take the height of the building to be 2.8 m.
- The thickness according to the block size will be 30 cm = 0.3 m.
- Windows 4 pcs. 1.8 m2 each and a door 2.52 m2, together = 4.32 m2.
- Volume of building materials for external walls (24*2.8-4.32 m2)*0.3=18.864 cubic meters. m.
- Load-bearing wall with one door (6 * 2.8-2.52) * 0.3 = 4.284 m 3, together with external walls: 18.864 m 3 +4.284 m 3 = 23.148 m 3. We will take a different material for the construction of the walls.
- Block volume 20*30*60=36000 cm3. 1000000:36000=27.8 pcs. per square meter, and for a 6x6 house you need to buy 23.148*27.8=644 pieces.
Of course, on a real construction site there will definitely be construction waste - block fighting. When carrying out loading and unloading operations, moving materials, and even construction itself, “losses” are possible, so some reserve still needs to be made. Take into account one more trick - the wholesale price is always lower, and if you are lucky, the wholesaler has 1000 pcs. blocks can cost as much as 644 retail. It would also be a good idea to determine in advance the budget that will be spent on transport.
When choosing blocks, you need to pay attention to how different the sizes of individual copies are, that is, how different blocks from the same batch are from each other. The smaller the difference, the thinner the seams in the masonry can be made, the better it will be for construction. After all, for masonry they use sand-cement mortar, which does not retain heat well, and the less mortar is used (the thinner the seams), the warmer the house.
Using an online building block calculator, you can determine the quantity and volume of building materials needed for the construction of walls of houses, garages, boxes, bathhouses, country houses and other premises. The calculations may take into account the dimensions of the building's gables, door and window openings, additional openings (for example, gates), as well as related materials, such as mortar and masonry mesh.
When working, pay special attention to the units of measurement of the entered data!
Print Send by email
If you found the calculator useful, please click on one or more social buttons. This will greatly help the further development of our site. Thanks a lot!!!
How to pour a slab base
To pour a slab foundation, you must use the following action plan:
- Prepare the soil. Clean and deepen the selected area.
- Compact the soil so that the foundation for the house has a firm foundation.
- Make a pillow from crushed stone and sand. Make sure that it does not extend beyond the edges of the trench.
- Install the formwork and pour concrete over the entire area. The height of the formwork should be 10-15 cm.
- When the solution hardens, reinforce the surface, which involves the use of metal structures.
- Finally, the screed is finished poured. Subsequent work can be carried out only after a month. But the information from the article will help you understand what the foundation for an extension to a house looks like, and how to make it yourself.
The video shows how to properly fill a slab base:
Expanded clay concrete extension is an important aspect
It is often necessary to expand the area of a residential building or add a new room to it - a summer kitchen, veranda, barn. In this case, they make do with an extension using one of the finished walls.
Calculations and technology for building extensions are not fundamentally different from building a house. The only condition is the implementation of a free-standing foundation.
The reason lies in the properties of the soil - the foundation of the house, which in most cases is heterogeneous and sensitive to changes in load. If the foundations of the extension and the house are rigidly tied together, the entire structure may become distorted.
To avoid this, the new foundation is designed at a short distance from the old one (up to 10 cm). The remaining space is called an expansion joint and is filled with insulation.
How to fill a strip base
To make a strip foundation, you first have to dig a trench around the perimeter of the future building. Its depth should be at least 80 cm. But it is better to adjust this size with the architect. The filling process is carried out according to the following plan:
- After the trench has been dug, compact the soil and fill the bottom with crushed stone and sand. The layer thickness is 30 cm.
- To protect the base from moisture, it is necessary to lay plastic film or roofing felt along the walls of the recess.
- Strengthening the foundation can be achieved through reinforcement. Place the metal elements in the trench and tie them together using wire. Of course, you can use welding, but then the structure will lose its elasticity.
- Now you can proceed to the installation of formwork. At the same time, make sure that it rises 10 cm above the ground. To do this, use sheets of plywood or boards.
- The foundation should be poured using concrete. The most commonly used class is B-15 or B-20.
- After pouring, wait 20 days for the foundation to harden.
The video shows everything about the strip foundation:
How to start building a garage
Before building a garage from cinder blocks, it is necessary to carry out preparatory operations:
- Perform a geodetic assessment of the territory.
- Determine the distance to communications: power supply, water supply.
- Develop a building project (see), taking into account all the details - this is the basis of all work.
- Decide what type of masonry.
- Calculate the blocks for the garage and their cost.
Advice: Before starting construction, you should consider what the purpose of the garage will be: only for storing a car in it or for also carrying out vehicle repairs, which may require an inspection hole, whether a cellar is needed, what the dimensions of the room will be.
The construction of a garage is divided into several stages, which helps to properly plan all the work:
- Build a foundation
. Cinder blocks are fairly light in weight, which allows... - Prepare the base from protective materials for vapor barrier and thermal insulation.
- Build garage frames from cinder blocks.
- Screed the floors.
- Create a ceiling and carry out roofing work.
- Install gates.
- Perform finishing work
:
- connect electricity;
- make interior and exterior decoration of the building.
How to count the number of blocks
Before starting work, calculate how much material will be needed.
For this you will need:
- A piece of paper.
- Roulette.
- To count blocks - a calculator.
- Pencil.
- Decide on the size of the cinder blocks. Their standard sizes:
- cross section with dimensions 188x190 millimeters, length 390 millimeters;
- There are blocks with a cross-section of 120x188 and a length of 390 millimeters.
Tip: If you have doubts about the size of the purchased cinder blocks, you should measure it yourself. In this case, the plane of the block, which will be located on the outside of the building, is of great importance.
For example, when building walls into the floor of a block, you first need to calculate the area of the face.
- To calculate the material per 1 square meter, you need to: divide one square meter by the area of the end surface of the block, which is equal to 0.19 x 0.39 = 0.074. As a result, 1/0.074 = 13.51, the resulting value needs to be rounded, you get 14 pieces.
Tip: The result should only be rounded up.
Calculations are carried out as follows:
- The perimeter of the garage is calculated using the formula: (7+5)x2= 24 meters.
- The total area of the walls is calculated: 24x2.5 = 60 square meters.
- The area of the gate is calculated and subtracted from the total area of the building. So, with gate dimensions: 2.5x3.2 = 8.75 square meters, the total area for cinder blocks will be: 60 - 8.75 = 51.25 square meters.
- The total number of cinder blocks is calculated. To do this, the total area is multiplied by the number of blocks that are needed for one square meter: 51.25x14 = 717 blocks.
Advice: It is necessary to purchase material for building a garage with some reserve, taking into account possible defects or damage to the blocks during laying.
How to build a foundation
When laying a foundation, its depth (see) depends on:
- Ground freezing depths.
- Availability of groundwater.
- The type of soil, its density.
The foundation for a garage is built in several ways.
The first one:
- The top layer on a piece of land is removed.
- A trench is dug and filled with several layers of sand, cobblestones or broken bricks with sand.
- The layers are impregnated with cement mortar, which will protect the structure from destruction and the action of melt water.
The second way is:
- Dig a trench 40 centimeters wide to a depth of 50 centimeters.
- Cover the bottom with a layer of sand.
- Water is pouring in.
- The layer is carefully compacted, which will make the base strong and durable.
- Reinforcement is placed on the bottom in different directions.
- The structure is concreted.
- Stands for at least 28 days.
According to the third method, the simplest or rubble concrete:
- Rubble stone is laid in layers in the trench.
- Filled with cement, which must be at least grade 150.
- Portland cement is mixed with sand in a ratio of 1:2.5.
- Water is added until the mixture becomes fluid.
After the foundation has been poured and hardened, it is waterproofed with roofing felt, which extends a few centimeters beyond the construction area. The gates are mounted using spacers.
How walls are built
When laying cinder block, the same principles are used as when working with brick.
Laying is done in one of the following ways:
- Lozhkov, half block.
- Tychkov, in one block, in 1.5 or 2 blocks.
The thickness of the masonry affects the garage's ability to withstand temperature fluctuations and wind gusts.
Typically, cinder block walls are laid out like bricks: the next element overlaps the seams from the previous row. First, the corners are built, cords are stretched between them and cinder blocks are placed.
Laying the pile foundation
To pour a pile-type foundation, you must use the following instructions:
- When the area has been prepared and leveled, make holes in the soil. This must be done in the places indicated in the pile field. The depth will be determined taking into account the design features of the supports.
- Install the piles using a special tool. Screw them in to a specific depth. It will correspond to the parameters of a particular product.
- Now you can proceed to tying the piles. To do this, it is advisable to use a metal channel. Weld it around the perimeter of the structure and where the partitions are concentrated.
- Now you need to create an armored belt. To do this, make formwork and fill it with concrete. This is where the blocks will be installed.
- Next, you can proceed to sewing the base around the entire perimeter. You will need to use flat slate or metal profiles. If desired, the entire structure can be insulated.
The video shows everything about the pile foundation:
A house made of expanded clay concrete blocks is beginning to gain popularity today. This material can be used for the construction of both one-story and two-story houses. With a properly selected foundation and its calculation, you are guaranteed to get a strong and durable structure. And although building a foundation is not so difficult, it is better to entrust this task to specialists who will perform not only construction, but also calculation work.
We recommend choosing a foundation for a house made of expanded clay concrete blocks
115,000 rub. Pile foundation TISE
Modification 1
1 TISE piles: diameter 250 mm, bottom extension 600 mm; 2 Depth of piles: 1500 mm; 3 Height of piles exiting the ground: 200 mm; 4 Fittings: diameter 12 mm; 5 Concrete: M300 (B22.5).
1
122,000 rub.
Pile foundation
Modification 2
1 TISE piles: diameter 250 mm, bottom extension 600 mm; 2 Depth of piles: 1500 mm; 3 Height of piles exiting the ground: 500 mm; 4 Fittings: diameter 12 mm; 5 Concrete: M300 (B22.5).
2
139,000 rub.
Pile foundation
Modification 3
1 TISE piles: diameter 250 mm, bottom extension 600 mm; 2 Depth of piles: 1500 mm; 3 Height of piles exiting the ground: 500 mm; 4 Fittings: diameter 12 mm; 5 Mortgages: stud 24 mm, exit height from the pile 200 mm; 6 Concrete: M300 (B22.5).
3
*provided there are no problematic soils