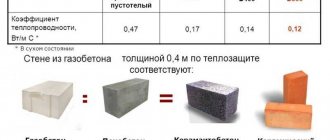
Impact of moisture on concrete
Water is considered an essential component of a concrete mixture; the plasticity of the material depends on it. It also has a destructive effect on buildings made of brick, metal, and concrete. The degree of water contamination, as well as the density of cement, does not matter; even a pure liquid without chemical components in its composition has the property of a solvent and washes out the binding elements from the building material.
Soil waters are also often contaminated with harmful impurities that enter the environment with automobile exhausts and industrial waste. In many cottage villages, groundwater upon contact with brick surfaces dissolves salts, and when they evaporate, all components dissolved in the liquid are released into the atmosphere. This phenomenon is evidenced by the formation of efflorescence on the walls of buildings that cannot be removed.
In winter, water transforms into ice, which leads to the expansion of building materials from the inside. Freezing and thawing cycles are repeated annually, resulting in a constant decrease in the strength of concrete walls.
The level of humidity is an important parameter; strength, drying speed, resistance to loads, etc. depend on it. Excess moisture in the concrete mixture will make it unsuitable for use; a solution that is too thin will not ensure the binding of all components. The lack of water in the concrete mixture, as in deep penetration acrylic primer, leads to rapid hardening of the material. It will be fragile and prone to destruction. This concrete mixture is not suitable for building houses. Strict adherence to the instructions for preparing different grades of concrete will help you avoid negative consequences. Read about the technical characteristics of ShB-5 brick here.
Water also has a negative effect on reinforcement in reinforced concrete structures; upon contact with moisture, the material undergoes corrosion, and if the floor is screeded dry, it can lead to premature failure.
Density, humidity, water absorption and porosity of concrete
These properties characterize the physical characteristics and structural features of concrete. They are determined according to GOST 12730-78.
Average concrete density
characterizes its mass per unit volume, taking into account pores and voids. When determining density, the mass of concrete is measured with an error of no more than 0.1%, the volume - no more than 1%.
The density of concrete is determined both on samples (GOST 12730.1 - 78) and directly in structures. The most common methods for determining the average density of concrete on samples that can be in a state of natural moisture or in a dry, air-dry, normal-humidity and water-saturated state. Samples are prepared and tested in batches. The series includes three samples.
When determining the density of concrete in a state of natural moisture, samples are tested immediately after their manufacture, or stored in vapor-tight packaging or sealed containers, the volume of which is no more than twice the volume of the samples.
To determine the average dry density of concrete, samples are dried to constant weight in an electrical cabinet at a temperature of (105 ± 10) °C. Drying is considered complete if the difference between two successive weighings during the drying process does not exceed 1 g.
To determine the average density of concrete in an air-dry state, before testing, the samples are kept for at least 28 days in a room at a temperature of (25±10) °C and relative air humidity (60±10)%.
When determining the average density of concrete under normal humidity conditions, samples are stored for 28 days in a normal curing chamber, desiccator or other hermetic container at a relative air humidity of at least 95% and a temperature of (20±2) °C.
When determining the average density of concrete in a water-saturated state, the samples are saturated with water. For this purpose, they are placed in a vessel filled with water, so that the water level in it is approximately 50 mm higher than the upper level of the samples. After every 24 hours in water, samples are weighed on a laboratory scale or hydrostatic weighing scale until the results of two subsequent weighings differ by no more than 0.1%.
Test specimens can have both regular and irregular geometric shapes. They are made from a concrete mixture of the working composition or cut out (drilled out, broken out) from products and structures.
The average density of concrete on porous aggregates and cellular concrete during production control is determined by testing samples of the correct geometric shape, intended to determine the strength of concrete. The nominal dimensions of samples of the correct geometric shape, the methods of their manufacture must comply with the requirements of GOST 10180-90. The volume of samples of regular shape is calculated from their geometric dimensions.
The smallest volume of irregularly shaped samples depends on the size of the coarse aggregate fraction, mm: more than 5 to 20 - 1, from 20 to 40 - 3, from 40 to 80 - 8 dm 3. The volume of irregularly shaped samples is determined using a volume meter (Fig. 2.6) or hydrostatic weighing (Fig. 2.7). Before testing, concrete samples are dried to a constant weight, heated in a drying cabinet to a temperature of 60°C and coated with paraffin heated to 100°C. Paraffin forms a thin film, filling open cavities, cavities and pores on the surface of the samples. When using a volume meter (Fig. 2.6), it is filled with water and the volume Ve
water according to the formula:
where gp/
— mass of an empty vessel, g;
m2 is
the mass of the vessel with water displaced by the sample, g;
рв
is the density of water,
рв =
1 g/cm3.
Sample volume (Vo)
on a hydrostatic balance, it is determined by weighing it in air and water and calculated using the formula
where are we -
mass of a sample saturated with water, determined by conventional weighing, g;
t'us
is the mass of a sample saturated with water, determined by weighing in water, g;
ts
is the mass of the dried sample, g;
tp
is the mass of the waxed sample, g;
рв
is the density of water, (pe = 1 g/cm 3 );
p p
- density of paraffin,
(p p =
0.93 g/cm 3 ).
Valid values
The humidity and thermal conductivity of sand is measured in accordance with existing standards that set quality standards for the construction of buildings for various purposes. There are certain standards for water content that must be taken into account during the construction process.
Optimal
The humidity level reaches 15%, such concrete is used for the construction of residential and industrial buildings; the presence of ash/perlite sand in the concrete mixture is considered a prerequisite.
Minimum
The humidity level is 13%, the concrete mixture is recommended for use in the construction of public, industrial buildings, residential buildings, and household buildings. Read about M150 building brick here.
Increased
A solution with a water content of 18% is used exclusively in the construction of industrial buildings.
How to determine and check the moisture content of a concrete mixture
When measuring the moisture level of concrete, special instruments are used. The measurement technique is different in each case. This material will tell you about the marking of bricks according to GOST 530 2012.
Determination with a moisture meter according to GOST - conductometric
A digital moisture meter is a special meter with two probes. The measurement method involves inserting probes into a concrete surface, after which all data is reflected on the device monitor. The humidity indicator is measured in accordance with the scale programmed in the moisture meter's memory. The main advantages of the method are the speed and simplicity of measurements. The device is not suitable for measuring relative humidity of material less than 5-8%.
Sensors for concrete mixer
Universal moisture meters for concrete mixers are distinguished by wide functionality. They are suitable for checking the moisture level of liquid and solid materials and exhibit excellent properties when working in difficult conditions. The body is made of hard alloy, the top of the device is covered with a special protective coating. The sensors operate in microwave and radio wave ranges. Find out which brick is best for making a stove in your home using this link.
The operating principle is based on a change in the absorbed wave energy, which differs depending on the humidity level. Sensors are installed on the mixer or on each dispenser.
Dilkometric
The technique is based on the relationship between the dielectric constant of concrete and relative humidity. The device is equipped with 2 remote sensor platforms, a high-frequency current generator, a monitor and an electronic unit. To measure humidity, the device must be brought close to the object with its sensors. The program converts dielectric constant into relative humidity in accordance with the established algorithm.
The indicator is shown on the display. The main advantages are the accuracy and speed of readings, the absence of mechanical damage to the surface of the object being measured. What kind of adhesive is needed for ceiling tiles can be found in this article.
Why are moisture meters needed?
Very often on the Mastergrad forum, and on other resources, topics and questions arise related to the appearance of humidity and mold in houses. It would seem that the long-awaited construction is completed, the keys have been received, and repairs have been made. But the joy is suddenly overshadowed by the appearance of an unexpected neighborhood. Literally a couple of months pass after the renovation is completed, and dark spots of mold appear on the light wallpaper, and the corners in the bathroom become an unpleasant dark color. The appearance of mold not only spoils the appearance of your home, but also leads to health problems. Often, its appearance is associated with the occurrence of allergic reactions in children, as well as exacerbations of respiratory tract diseases. Alas, the fungus is extremely difficult to remove until the cause of its appearance is eliminated. Any means and methods of treating the premises will only be a temporary measure.
Most often, the problem of mold is not directly related to the humidity in the room - the air in our homes is usually quite dry, but to the moisture remaining or returning to the walls. This situation may arise if house construction technologies or repair work are violated.
The use of moisture meters during repairs allows you to prevent problems associated with materials that have not dried during repairs. Currently, to control the moisture content in floor screed, plaster or brickwork during the repair process, professionals prefer to rely not on their own feelings or the instructions on the package of dry mix, but on instrument readings. Drying times for materials can vary greatly depending on room conditions.
Moisture meters and climate meters will be useful primarily for those who actively work in the field of construction and repairs and are responsible for the results and high quality of their work. And also to apartment owners who want to control the quality of repairs.
A moisture meter and climate station are necessary for:
- determining the readiness of the base for coverings, such as floor screed or plaster;
- determining the moisture level of wood;
- superficial and deep measurement of wall or floor moisture to identify sources of internal damage;
- measuring the wall surface temperature before applying the coating;
- determining air temperature and humidity during coating work;
- determining the dew point. To prevent finishing defects.
The main methods on which the work of moisture meters is based:
- measuring the electrical resistance between the needle sensors and recalculating the result into percentage moisture content. The method is based on the fact that, depending on the moisture content of the material, its electrical resistance changes. The advantages of this method are the speed of measurement and the simplicity of the device design. The disadvantages include the dependence of the accuracy of measuring moisture content on the quality of contact of the sensors with the material and the need to pierce the material being tested with needles;
- measurement of the dielectric constant of a material. In the design of this version of the moisture meter, instead of needles, an external sensor is used, which must be pressed to the surface of the material and a measurement is taken. High-frequency currents penetrate the material to a depth of 20-50 mm. The moisture meter evaluates the amount of current attenuation, which depends on the properties of the material and its humidity, and converts the value of dielectric constant into absolute humidity. This measurement option is characterized by high accuracy, speed of obtaining results and the absence of damage to the coating.
At the moment, there are many options on the market for instruments that allow you to measure humidity, but not all can meet the basic requirements for modern models of moisture meters - portability, ease of use, measurement accuracy, ease of use and the absence of the need for special knowledge to evaluate the results.
Concrete moisture indicator
The best way to monitor the condition is to use a moisture meter.
To obtain the mixture, ingredients such as cement of the selected brand, crushed stone or gravel, sand and water are used. In this case, the properties of the resulting concrete largely depend not only on what brand of cement is used, but also on the temperature and the amount of water added to the solution. It is water that makes the mass plastic, turning it into a monolithic solution that has all the required properties.
Therefore, humidity is one of the most important indicators that you need to pay attention to. The strength, stability of the material, its ability to withstand a wide variety of loads, drying speed and much more will depend on it.
Standards for indicators
Conditions for the occurrence and components of acid-base reaction in concrete.
Humidity is determined in accordance with accepted standards that define the quality of material for industrial, residential and other buildings, works, and fences. Today the following moisture content standards have been adopted:
- 13% – for public and residential buildings, domestic buildings, industrial buildings;
- 15% – for residential buildings, industrial buildings, if the composition includes perlite sand or ash;
- 18% – only for industrial buildings.
When dispensing ready-made products, the humidity should not exceed 25% if the solution was mixed on the basis of sand, and no more than 35% if the solution was mixed on the basis of ash, a waste product for cellular concrete.
Solution moisture balance
Moisture balance is one of the most important indicators, which has a special impact on the characteristics of the mass.
The strength of the material and its ability to bind the components of the mixture into a single, monolithic whole depend on the moisture content.
But in any case, it is important to maintain a balance. If you add a lot of moisture to concrete, the cement will no longer be able to bind all the components of the solution into one whole, that is, the mixture will turn out to be too liquid and of poor quality.
If you add less water than required, then such concrete will harden quickly, but will become brittle, the ingredients will crumble, and they simply will have nothing to hold each other together. That is, it will no longer be possible to use the mass, and this entails additional costs. That is why it is recommended to add water to the mixture in a strictly prescribed amount, like all other components.
So how much water should you add to concrete when preparing it? It is impossible to answer this question unambiguously, since the other components of the mass also contain a certain level of moisture. For each composition, this percentage must be calculated individually; it depends on many circumstances.
Will the substrate help?
Special substrates are produced with a polyethylene base, which protects the laminate from the effects of residual moisture in the concrete.
When using conventional substrates, a polyethylene film is sometimes placed on the screed to serve as a vapor barrier. However, all this is done for preventive purposes a month after laying the leveling screed.
The key to high-quality and durable installation of flooring is a properly executed subfloor, the physical characteristics of which must meet certain requirements. One of the most important characteristics of the subfloor is the residual moisture content of the subfloor. An erroneous assessment of this criterion over time leads to peeling of part or even the entire coating, regardless of the material of manufacture. If carpet is laid on the floor, then exposure to moisture threatens the appearance of wrinkles and an unpleasant odor. Natural linoleum absorbs moisture, which leads to the destruction of its internal structure. Parquet boards or laminates installed in a floating manner rise at the joints and form “waves,” while cork floors bulge and can separate at the seams. If the base is too wet, block parquet becomes deformed, swelling at the edges, and can tear away from its base. Natural stone floors may partially darken; ceramic granite and tiles may have less adhesion to the base. Even with rolled PVC flooring materials, when exposed to dampness, swellings in the form of bubbles appear on the surface. Water vapor has a negative effect on the properties of adhesives and putties used during installation. Dispersion glue breaks down and loses its characteristics, gypsum and magnesium putties, cement-based materials lose their strength. Such serious consequences indicate significant violations in the design of the base itself (lack of a vapor barrier layer), or an erroneous assessment of the humidity level.
Standard moisture content of concrete mixture
Determination of moisture content of a concrete mixture according to GOST 12730.2-78 was approved in 1980. The following concrete moisture standards have been established:
- for the construction of residential buildings and other structures its level is 13%;
- when perlite sand is included in the concrete composition, the moisture content reaches 15%;
- for industrial facilities it is 18%.
When mixing concrete, you need to remember the water balance, which affects the durability of the concrete coating.
- when adding a large amount of water to a dry mixture, the solution will turn out to be very liquid and of poor quality;
- If you add little water, the concrete will harden quickly and will be very brittle.
The water must be clean and free of foreign impurities. For high-quality preparation of a concrete mixture, it is necessary that water exceeds the total mass of cement by 40-70%. If there is more water, it may escape through evaporation or remain in the concrete as tiny water holes.
GOST 12730.2-78 “Concrete. Method for determining humidity"
STATE STANDARD OF THE USSR UNION
| CONCRETE Humidity Determination Method Concrete. Method of determination of moisture content | GOST 12730.2-78 |
Date of introduction 01/01/80
This standard applies to all types of concrete and establishes a method for determining moisture content by testing samples.
GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
1.1. General requirements for the method for determining the moisture content of concrete are in accordance with GOST 12730.0.
EQUIPMENT AND REAGENTS
2.1. To carry out the test use:
— laboratory scales according to GOST 24104;
— drying cabinet according to GOST 13474;
— desiccator according to GOST 25336;
- baking trays;
— calcium chloride according to GOST 450.
PREPARATION FOR THE TEST
3.1. The moisture content of concrete is determined by testing samples or samples obtained by crushing samples after their strength testing or extracted from finished products or structures.
3.2. The largest size of crushed pieces of concrete should be:
- for heavy concrete and concrete with porous aggregates - no more than the maximum size of aggregate grains;
- for fine-grained concrete (including cellular and silicate) - no more than 5 mm.
3.3. An average sample weighing at least:
1000 g - for heavy concrete and concrete with porous aggregates;
100 g - for cellular, silicate and fine-grained concrete.
During production control of concrete moisture in concrete and reinforced concrete products, it is allowed to test concrete samples of smaller mass in accordance with the requirements of the standards for these products.
3.4. Samples or specimens are crushed and weighed immediately after sampling or stored in a vapor-tight package or airtight container, the volume of which is no more than twice the volume of the samples placed in it.
CONDUCTING THE TEST
4.1. The prepared samples or specimens are weighed, placed in a drying cabinet and dried to constant weight at a temperature of (105 ± 5) °C.
The mass of a sample (sample) is considered constant if the results of two consecutive weighings differ by no more than 0.1%. In this case, the time between weighings should be at least 4 hours.
4.2. Before re-weighing, the sample(s) are cooled in a desiccator with anhydrous calcium chloride or together with a drying oven to room temperature.
4.3. Weighing is carried out with an error of up to 0.01 g.
4.4. The collected moisture content of heavy concrete, concrete with porous aggregates and silicate concrete is determined according to the GOST 12852.6 method.
In this case, the sample weight of heavy concrete and concrete on porous aggregates, depending on the largest size of the aggregate grains, is taken according to the table.
| Largest grain size filler, mm | Sample weight, g |
| 20 or less | 100 |
| 40 | 200 |
| More than 40 | 500 |
PROCESSING RESULTS
5.1. The moisture content of concrete sample (sample) by mass Wm in percent is calculated with an error of up to 0.1% using the formula
(1)
where is the mass of the concrete sample (sample) before drying, g;
— mass of concrete sample (sample) after drying, g.
5.2. The moisture content of concrete sample (sample) by volume Wo in percent is calculated with an error of up to 0.1% using the formula
(2)
where is the density of dry concrete, determined according to GOST 12730.1, g/cm3;
— density of water, taken equal to 1 g/cm3.
5.3. The moisture content of concrete of a series of samples (samples) is determined as the arithmetic mean of the results of determining the moisture content of individual samples (samples) of concrete.
5.4. The journal in which test results are recorded must contain the following columns:
— marking of samples;
— place and time of sampling;
— moisture state of concrete;
— age of concrete and test date;
— moisture content of concrete samples (samples) and series by weight;
— moisture content of concrete samples (samples) and series by volume.
INFORMATION DATA
1. DEVELOPED
USSR State Committee for Construction Affairs
Ministry of Construction Materials Industry of the USSR
Ministry of Energy and Electrification of the USSR
DEVELOPERS
M. I. Brusser, Ph.D. tech. Sciences (topic leader); L. A. Malinina, Dr. tech. sciences; A. T. Baranov, Ph.D. tech. sciences; G. A. Buzhevich, Ph.D. tech. sciences; L. I. Karpikova, Ph.D. tech. sciences; T. A. Ukhova, Ph.D. tech. sciences; Yu. A. Savvina, Ph.D. tech. sciences; Yu. A. Belov; V. L. Rubetskoy; N. V. Myakoshin; V. G. Dovzhik, Ph.D. tech. sciences; V. A. Piskarev, Ph.D. tech. sciences; G. Ya. Amkhanitsky, Ph.D. tech. sciences; S. N. Levin, Ph.D. tech. sciences; E. N. Leontiev, Ph.D. tech. sciences; V. N. Tarasova, Ph.D. tech. sciences; L. I. Levin; V. A. Dorf, Ph.D. tech. sciences; Yu. G. Khayutin, Ph.D., Tech. sciences; V. B. Sudakov, Ph.D. tech. sciences; Ts. G. Ginzburg, Ph.D. tech. sciences; R. E. Litvinova, Ph.D. chem. sciences; A. G. Malinovsky
INTRODUCED by the USSR State Committee for Construction Affairs
2. APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Construction Affairs dated December 22, 1978 No. 242
3. INSTEAD GOST 12852.2-77, GOST 11050-64 regarding determination of humidity
4. REFERENCE REGULATIVE AND TECHNICAL DOCUMENTS
5. REPUBLICATION. June 1994
content
files.stroyinf.ru
Methods for calculating residual moisture
The residual moisture content of concrete foundations must meet approved standards. If it is incorrectly assessed, then subsequently the floor coverings will be subject to peeling.
Weight humidity
One way to measure the moisture content of a concrete base is the gravimetric method.
To accurately determine this indicator, a concrete sample is taken. This sample is crushed, weighed, and then heated to a temperature of 100 degrees. The sample should stand for 30-60 minutes, then it is weighed again. This procedure is repeated several times until the weight of the sample stops changing. If we subtract the final weight of the sample from the initial one and convert the value into a percentage, then this indicator will be the weight moisture content of the base.
Calcium carbide measurement method
In the European Union countries, residual concrete moisture is measured using the calcium carbide method. During construction, a concrete sample weighing 50 grams is taken from various depths, mixed with calcium carbide, which reacts to the sample by releasing gas, and the pressure is determined with a pressure gauge. Next, a table is used to calculate the percentage of moisture.
Using modern devices
Moisture meters determine the dielectric constant of materials. It depends on the amount of moisture that is in them. Then, using tables, the percentage of humidity is calculated. The electronic devices RTO 600 and Hydromette Compact determine humidity by measuring the resistance between electrodes: they are immersed in a concrete base at a distance from each other. Such devices allow you to take measurements at any depth and provide accurate data. This method of determining humidity is called conductometric. The use of modern electronic devices makes it possible to quickly and easily measure the percentage of humidity.
Alternative way to measure humidity
It helps to determine the moisture content of the screed and a piece of ordinary plastic film. To use this “old-fashioned” method, you must:
- cut a square piece from a roll of plastic film, the side of which should be 1 m;
- place the film on the surface of the concrete floor in one of the corners of the room;
- glue all sides of the film to the screed using tape, ensuring tightness;
- leave the film for a day;
- After 24 hours, see if there is condensation on the inside of the polyethylene.
The presence of water droplets on the film indicates that the screed has not yet dried. It is necessary to extend the time allotted for drying the concrete layer.
Important! This method does not allow you to obtain a specific humidity indicator, so its results cannot be completely trusted. Meanwhile, laminate manufacturers indicate a specific moisture level of the base on which the finishing coating can be installed.
Summarizing
When carrying out cement screed, the temperature regime must be maintained within 20-25 degrees, and the humidity in the building must be at least 70%. If these indicators are not met, this will lead to rapid evaporation of water and the formation of cracks over the entire surface. Now a new moisture meter is used for cement mortar - Franz-Ludwig, which is represented by microwave probes. This is a high-precision device that measures the moisture content of a material in certain doses.
Ease of use and high performance of a moisture meter (and other electronic devices) allows you to quickly determine the moisture content of concrete, brick and cement. This indicator is important for the quality use of all types of materials.