Cement is an artificial powdery substance that acts as a binder when mixing concrete mixtures. In combination with water, it forms a plastic mass, which subsequently hardens and becomes stone-like. What cement is made of primarily depends on the production method. In general, the base is clinker in combination with mineral additives and gypsum.
History of cement
The word “cement” comes from the Latin caementum, which translates as “crushed, broken stone.” This substance was the result of a search for ways to cope with the low water resistance of gypsum and limestone rocks. For this purpose, water-resistant mineral substances were introduced into their composition. At the very beginning, they were the remains of baked clay bricks and volcanic rocks. The ancient Romans used ash deposits from the famous volcano Vesuvius - pozzolans.
The optimal cement production technology was developed many years later, when the need for large quantities of inexpensive and durable binder did not become most acute. The greatest contribution to the research was made by:
- Mason John Aspind, who received a patent for Portland cement in 1824.
- Russian builder Egor Cheliev, who wrote a book about cement for underwater work in 1825.
The name Portland cement comes from the English island of Portland, which consists of limestone rocks. In England, stones from this island were considered the most prestigious building material. Aspind managed to obtain an artificial stone, which in strength and color was very similar to the specified material.
But it was made without firing the raw materials. Greater compliance of the technology with what is Portland cement today is noted precisely in the Cheliev production process.
Related equipment for cement production
We offer design, manufacture and installation of technological complexes for the production of cement on a turnkey basis. Our technological systems are distinguished by simple and clear design, ease of operation, good performance and reliability.
The cement production process may include additional components and assemblies produced in Samara. From us you can purchase sorting and mixing equipment, filtering units and cyclones, as well as transport equipment - conveyors, transporters at a favorable price.
What is cement made from: composition and main raw materials
The composition of cement includes the following components:
- Lime (calcium oxide, CaO) – 60%.
- Silicon dioxide (SiO2) – 20%.
- Aluminum (alumina, Al2O3) – 4%.
- Gypsum and iron oxides (Fe2O3) – 2%.
- Magnesium oxide (MgO) – 1%.
The indicated percentage of the listed components is typical for the most popular type of cement - Portland cement. It may vary somewhat. It all depends on the production technology and class of cement products.
Important! The existence of different types and brands explains the lack of an exact chemical formula for cement. All important information is provided by indicators of mineralogical composition.
The main thing cement is made from is clinker. This is the name given to the product of firing the raw materials – limestone and clay, which are taken in a 3:1 ratio. Clinker is a semi-finished product for producing cement. After firing at temperatures up to 1500 °C, the clinker is crushed, as a result of which it is presented in the form of granules with a diameter of up to 60 mm.
During grinding, additives are added to the clinker composition:
- Gypsum (CaSO42H2O), which regulates setting times.
- Corrective additives (up to 15-20%), improving certain properties of cement: plasticizers, additives, etc.).
Different rocks are used as the main raw material for cement production:
- Carbonate type fossils. They can have an amorphous or crystalline structure, which determines how effectively the material will interact with other components in the composition when fired.
- Sedimentary origin. This is a clay raw material with a mineral base, which, when excessively moistened, becomes plastic and swells, i.e. increases in volume. The main feature of the material is its viscosity, which determines its use in the dry production process.
Carbonate rocks
Among the carbonate rocks used for cement production are:
- Marly limestone, or marl. Contains clay impurities, therefore it is considered a transitional material between carbonate and clayey rocks.
- Chalk is a type of smearing limestone, which is characterized by ease of grinding.
- Shell rock. It is characterized by a porous structure, which is not very resistant to compressive loads.
- Dolomite rocks. Of all types of carbonate rocks, they have the most valuable physical properties.
Clay rocks
Clay rocks used in cement production include:
- Clay. The main type of clayey rock with mineral inclusions in its composition.
- Loam. It differs from clay in the increased concentration of dust particles and sand fraction.
- Loess. Less plastic rock. It is more characterized by porosity, friability and fine grain. Loess may contain inclusions of quartz or silicate.
- Shale. Of all types of similar rocks, it has the highest strength. When crushed, shale is converted into plate-like particles. The material contains little moisture and is characterized by a stable granulometric composition.
Corrective additives
For the purpose of adjustment, special mineral additives are introduced into the cement composition. First of all, these are modifiers based on fossils containing:
- iron,
- flint-belite
- fluorspar,
- apatite,
- alumina.
Also, corrective additives can be provided by industrial waste from other industries. They are used:
- pyrite cinders;
- dust from blast furnaces;
- belite sludge;
- mineralizers.
The use of additives makes it possible to improve the characteristics of cement and concrete mortar, which is prepared on its basis. Each of the modifiers gives the mixture special properties, for example:
- CemFrio – has anti-frost, plasticizing and accelerating effects.
- CemPlast - allows you to obtain a highly mobile concrete mixture with increased workability, as well as increase the activity of the binder, i.e. cement, and ensure complete hydration.
- CemAqua and CemAquaStop are waterproofing, water-reducing, water-repellent surface treatment products.
- CemBase – increases the strength, frost resistance, water resistance and durability of concrete products.
- Plastix is a multifunctional water-reducing and plasticizing additive that increases the grade strength of concrete products.
- CemFix is an accelerator additive used for concrete mixtures that require high early strength.
Main Product Features
The starting materials for production are solid minerals, near which cement factories are located. Carbonate stones and clays are used in the production of clinker - a product of joint firing of rocks. The first category of mineral formations is consumed in larger quantities and is represented by limestone varieties of amorphous or crystalline structure, these are:
- chalk is a soft, white rock consisting of calcium carbonate with an admixture of magnesium, metal oxides and quartz grains;
- marl is a natural mixture of 50-75% calcite derivatives with 25-50% silicate clay formations, well suited for the production of cement clinker;
- shell rock is limestone from the shells of marine animals, its variety metamorphosed by pressure at high temperatures is called marble;
- dolomite - in addition to calcium carbonate CaCO3, it contains a magnesium component: MgCO3.
Cement density indicators: bulk - 900-1100 kg/m³, with compaction - 1400-1700. The true specific gravity values reach 3 t/m³. There are several technical characteristics by which the quality of binder powder is judged:
- The fineness of grinding determines the activity of the cement: the smaller the particles, the larger the surface they cover in one layer. Control measurements are performed by scattering on a sieve with a mesh size of 80 microns.
- Water requirement is the amount of moisture required to hydrate the cement and make the dough plastic. Excess water in the solution leads to the formation of pores and cracks, reducing strength.
- Frost resistance is the ability of products based on cement powder to withstand repeated freezing and thawing without destruction. The required indicator is achieved with special additives when mixing the solution.
- Setting time - depending on the thickness of the batch, is in the range of 0.7-10 hours. The indicator also depends on the amount of gypsum added to the clinker during grinding.
- Strength is determined by the destruction of a sample made of cement from each batch of released mortar. The age of the cubes is set by the standard - 28 days.
Main characteristics.
For all volumes shipped by the cement plant, quality certificates are filled out, which include the listed characteristics. Consumers independently carry out incoming inspection to confirm the integrity of the supplier.
The basis for cement production is a calcined mass called “clinker”. The composition of clinker can be varied, so we will talk about it later.
The entire technological process of cement production can be divided into two main stages:
- obtaining clinker is the most expensive and labor-intensive process;
- crushing clinker to obtain a powdery mass.
The production of clinker itself is divided into four stages:
- the raw materials from which clinker will be prepared are mined and delivered to the processing site;
- raw materials are crushed;
- the raw material mixture is prepared in the required proportions;
- the finished mixture is fired under high temperatures.
- wet;
- dry;
- combined.
The choice of one of them depends on the thermal power of the enterprise and the quality of the raw materials.
Wet method
The main advantage of this method is that, no matter what the clinker is made from, no matter how heterogeneous the raw material is initially taken, the wet method allows you to accurately select the desired composition of the sludge.
Scheme of cement production using dry and wet methods
Sludge, in this case, is a liquid, jelly-like mass containing up to 40% water. Its composition is adjusted in special pools and then fired in rotary kilns at temperatures above 1000ºC.
The wet method requires more thermal energy consumption, but allows the production of cement of the highest quality, due to the absence of the influence of sludge heterogeneity on the final product.
The use of cement is related to its properties. The current standard regulates the following characteristics:
- strength properties. They vary for cement compositions of different brands. Strength is determined by a laboratory method by compressing a reference sample of the frozen mixture. Strength control in accordance with the requirements of the regulatory document is carried out in three stages: after two days, as well as one and four weeks after pouring. The parameter value is measured in megapascals. The digital strength value corresponds to the brand of cement composition;
- duration of setting. The parameter characterizes the time period during which the plastic characteristics of the cement mixture change. A properly prepared solution begins to harden a couple of hours after pouring in the hot season. In autumn, the hydration process can take 8–10 hours. The setting time increases sharply at zero temperature and can be 15–20 hours. The introduction of additives allows you to regulate the setting speed;
- resistance to negative temperatures. This characteristic is called frost resistance. It characterizes the ability of a hardened cement mass to withstand deep freezing with further thawing over many cycles. At the same time, the integrity of the array and strength characteristics must be maintained. The cause of destruction is an increase in the volume of water saturating the pores. The introduction of additives increases the frost resistance threshold;
- density. The parameter characterizes the mass of a powdery substance in one cubic meter of material. Freshly prepared cement composition has the lowest specific gravity. During long-term storage, the material cakes, and during transportation it becomes compacted. At the same time, the density increases. The characteristics depend on the size of the crushed clinker. The average value is 1.3 t/m3.
After the cement hardens, a strong connection is formed, which is not inferior in density to stone.
Among other characteristics, the following can be noted:
- hygroscopicity. The degree of water absorption differs between brands;
- grind size. Determined by sifting through a sieve;
- corrosion resistance. Increased by introducing special additives;
- best before date. It depends on storage conditions and permissible humidity levels.
Construction materials, including cement, are most often tested for compliance with the following characteristics:
- Strength. To check this characteristic, you will need to make a concrete cylinder, which is subsequently subjected to compression tests. Duration of exposure to sample {amp}amp;mdsah; at least 28 days. This is the period required for the material to fully gain strength. After checking and comparing the indicators in MPa, you can determine the grade of this cement, which is designated: M200, M300, M400, M500, M600;
- Resistance of the material to corrosion. Being in a humid environment, concrete structures that are not treated with special compounds are subject to corrosion. To eliminate this process, it is recommended to use special additives when forming a solution for concreting. The same applies to protection from the effects of active substances and various household chemicals. For work in aggressive environments and high humidity, a special brand has been developed - pozzolanic cement;
- Frost resistance. This characteristic is determined in cycles of freezing and thawing of the material, during which it is able to retain its original properties. When moisture freezes, expansion occurs in the pores and microcracks of the concrete base, which affects the quality of the concrete and leads to its destruction. To strengthen the structure of concrete, it is necessary to use special additives that allow the concrete to withstand sudden temperature changes. Additives are also used to organize work in winter;
- Water demand. Expressed as a percentage relative to the total volume of the solution of the required plasticity. The maximum water requirement in Portland cement is 28%. It should be understood that a mixture that requires a minimum amount of water produces stronger and more reliable concrete, while a solution saturated with water produces a porous concrete structure, which is characterized by lower strength;
- Setting time. This indicator is important for the organization of work. It should not be too long or short so as not to disrupt the process of pouring the base or masonry. This characteristic is regulated by the amount of gypsum in the dry mixture. If the volume of gypsum is higher, setting occurs faster, if lower, it sets more slowly. Optimally, the cement setting process occurs within 10 hours, and the beginning of setting is within 40-50 minutes.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Features of treating soil in a greenhouse with bleach
How cement is made: 3 main ways
Cement production in modern conditions is carried out in one of three ways:
- Wet. Its main feature is the replacement of lime with chalk, as well as the production process with the addition of water. The raw material for production here is a mixture (a mixture of starting materials) with a humidity of up to 50%.
- Dry. This technology has minimal energy consumption and cost, since several technological operations are combined into one process. Entering the ball mill, all components are simultaneously ground and dried.
- Combined. This production method combines the features of dry and wet technology processes. Here, based on the results of firing, a semi-dry composition with a moisture content of 18% is obtained.
Dry production method
How cement is made using dry technology:
- The feedstock is crushed.
- Dry it to a certain humidity level.
- The dried mixture is ground to flour.
- It is fired inside a rotating kiln, after which it is cooled and sent to storage.
Wet production technology
Unlike the dry manufacturing method, here after grinding the components, additional water is added to them. The result is not flour, but raw material sludge, which goes into the oven for firing, and then into the refrigerator for cooling. Already cooled clinker is crushed and supplemented with additives.
Combined manufacturing technology
The combined method of cement production combines the stages of dry and wet:
- First, raw sludge is obtained using wet technology.
- The sludge is subjected to dewatering and granulation.
- The granules are fired in a kiln, which is used for dry technology.
Combined production method
This method is based on the preparation of raw material components using the wet method, but their firing is carried out according to the semi-dry method. The sludge obtained in the raw mill has a moisture content in the range of 30-45%, it is sent to a filter: here it is dehydrated to a moisture level of 15-20%, then the raw materials are mixed with dust, the humidity is adjusted to 12-14%.
At the next stage, the mixture is sent for firing, which is carried out in kilns of the semi-dry method of cement production. All other operations are no different from similar stages of the wet production method.
A suitable cement production method is selected in accordance with technological and technical-economic factors - quality and type of raw materials, moisture content and homogeneity of the mixture, availability of appropriate equipment, capabilities, etc. In Moscow, factories operate according to all three schemes and supply high quality cement to the market.
Clinker-free production method
In clinker-free production technology, hydraulic or blast furnace slag is used as the raw material for cement production. It is also supplemented with various additives and activators. The resulting slag-alkali mixture is crushed and ground to a powder state. This production technology has several advantages:
- Improving the cleanliness of the environment by recycling waste from the metallurgical industry.
- Obtaining a product with high resistance to negative environmental influences.
- The ability to produce cement with different properties and in a wide range of shades.
- Lower costs for electricity and heat.
Cement production in factories
The production of cement using the wet method is traditionally carried out by domestic cement factories. Dry technology is more often used abroad. It is used by cement factories in China, Turkey and Egypt. White cement is produced by only one Russian enterprise - Holsim (Rus) SM LLC. Much of this type of binder is often supplied by foreign companies, such as:
- AalborgWhite (Denmark).
- Cimsa/Adana (Türkiye).
- "Holcim" (Slovakia).
In general, cement production technology includes several stages:
- Mixing all components to make clinker (75% limestone and 25% clay).
- Roasting of raw materials at high temperature. At this stage, clinker is obtained, which is the basis for cement.
- Grinding clinker in ball mills. The result should be a substance with a powdery consistency. A ball mill is a horizontal drum with steel balls inside.
Please note: the smaller the clinker grinding fraction, the higher the performance characteristics and grade of the cement composition.
Differences between wet and dry production technology
Both cement production technologies have their own nuances, pros and cons. But there are key features that must be taken into account first of all when planning a business and calculating expenses and profits. The main disadvantage of the wet method of cement production is the significant energy intensity of the entire process, which is reflected accordingly in the upward price of the final product.
Dry technology is less environmentally friendly and hazardous to the environment, and therefore requires significant costs to eliminate this factor. At the same time, the production process itself is cheaper in all respects and allows the price of the final product to be reduced.
How to make cement at home
You can get cement at home, but only if you have all the starting materials and necessary equipment:
- blast furnace for firing at a temperature of 1500 °C;
- crusher for grinding clinker into flour.
One method of making cement at home uses resin and sulfur. The resulting cement can be used for laying tiles and bricks and creating a cement screed. The manufacturing technology is as follows:
- Melt 1 kg of resin in a metal container and 1 kg of sulfur in a fireproof container.
- Combine the liquid ingredients and mix until smooth.
- Add 2 kg of sifted homogeneous sand and 3 kg of lead oxide (lead litharge).
- Constantly heating the mixture, stir it until a homogeneous mass is obtained.
- Fire in a blast furnace and let the product settle.
In reality, there are certain difficulties in making cement at home, since production requires a kiln and a mill for grinding. In this regard, at home it is necessary to slightly change the cement recipe, using water, aqueous lime and stone ash for its production. The resulting solution is suitable for sealing small cracks, and it must be used immediately after production.
Video: how to make fireproof cement from ash
How cement is produced - manufacturing technology
The manufacturing process involves performing the following operations:
- Development of deposits of limestone, gypsum and clay.
- Grinding of extracted materials.
- Drying of the crushed raw material mass.
- Obtaining limestone-clay sludge.
- Roasting of raw materials to produce clinker granules.
- Crushing clinker to a powdery consistency.
- Dosing and mixing of components.
Cement is a widely used material that is used for any type of work related to repair, restoration, construction.
Various technologies are used, differing in the method of sludge preparation:
- dry. Drying and crushing are carried out in a grinder into which heated air is pumped. The finished fraction has the required moisture content;
- wet. Involves the use of chalk. It is crushed in a wet state, then the charge is fired and crushed;
- combined. Combines the features of previous methods depending on the equipment used in the technological cycle.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the staghorn sumac with photos and descriptions
Currently, manufacturers prefer the dry production method.
Depending on the characteristics of the raw materials used, the cement composition is produced using proven technologies, which provide various methods for preparing the initial components.
The slurry used can be obtained as follows:
- Using a dry method, which significantly reduces the cost of cement production. A feature of the dry method is a shortened production cycle, combining a number of technological stages. The process of grinding and drying the ingredients is carried out simultaneously in a special mill, into which gases heated to a high temperature are supplied. The resulting charge fraction represents a powdery composition with the required moisture content.
- Using wet technology, according to which chalk is used instead of lime. The chalk is mixed with the components specified in the recipe and crushed in a humid environment. The result is a batch with a moisture content of up to 50%. The charge mass is fired, followed by grinding of the resulting clinker.
- Using a combined technology that combines elements of dry and wet methods. The process involves both moistening the dry composition, subsequent granulation, annealing, and drying the semi-dry charge composition produced by the wet method.
In some cases, when you need to make a concrete screed, but have to travel far for cement, craftsmen undertake to make cement at home. Let us note right away that the process of making cement at home is a very labor-intensive process and requires serious equipment and skills.
Kiln for producing cement at home
Don't expect that you will get a quality product the first time. Before you get real cement, you will have to ruin dozens of kilograms of material.
The raw materials used to make cement at home can vary, as can the technology for its production. As an example, consider the production of building materials based on resin and sulfur.
The final product, if properly manufactured, can withstand changes in temperature, humidity and other atmospheric conditions.
Do-it-yourself cement production
It can be used for laying bricks and tiles, as well as for cement screed.
- Take a kilogram of resin and melt it in a metal container.
- In another fireproof container, melt a kilogram of sulfur.
- After both of the above components are brought to a liquid state, they must be combined and thoroughly stirred until smooth. To prevent this composition from freezing, it is better to constantly heat it.
- Add two kilograms of sand (the sand must be sifted and homogeneous) and three kilograms of lead litharge (lead oxide) to the liquid mixture of resin and sulfur.
- The clinker blank must be stirred for a long time at high temperature until the mass becomes completely homogeneous. To do this, you need to make a high-temperature rotary kiln.
- After firing, the clinker must be allowed to settle well.
This cement, prepared at home, has fairly high quality and strength characteristics.
This product should never be used on wet surfaces. Also, the surface, before applying such homemade cement, needs to be coated with drying oil.
How is white cement made?
The difference between white cement also lies in its composition. It contains less iron than gray, and also contains additives:
The starting raw materials for the production of white cement are clayey or carbonate rocks. The main advantage of the binder is its snow-white color, which increases the decorative properties of the cement mixture. Because of this, white cement is often called decorative. At the same time, due to more complex production technology, the material has a higher cost.
Video: white concrete table in Loft style
Video: how to prepare a mortar on white cement
Video: how and from what cement is made
How to properly prepare cement mortar
To mix cement mortar, it is necessary to maintain the proportions of its components. For 1 part cement there are 3 parts sand. Water is added depending on how plastic or viscous the solution needs to be. Also, the proportions are selected taking into account the type of work and brand of cement. For example, to prepare a solution for a floor screed, use the proportions from the table:
First, dry fractions, i.e. cement and sand, are mixed together. Only then do they begin to add water in small portions, gradually bringing the composition to the desired consistency. As a filler, you can use not only sand, but also gravel or crushed stone.
Please note: it is better to use sediment water for mixing the solution rather than tap water.
Mortar classes for different types of work:
- M50 or M100 – for plastering work;
- M50 or M100 - for the construction of brickwork;
- M100 or M200 – for floor screed;
- M200 or M300 - for foundations and foundations.
Product compliance with code (2020)
| Product name in the declaration | HS Code |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: a system for transporting cement from silos of industrial buildings to bulk shipment points into cement trucks and railway cars | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for the production of building materials: a new technological line for the production of cement with a production capacity of 10,000 (ten thousand) tons of clinker per day at JSC Mikhailovcement, brand SINOMA, in co | 8474200009 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: system for pneumatic bulk loading of cement into railway cars | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: system for transporting and unloading cement from silos of industrial buildings | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for preparing construction mixtures: terminal-type mortar-concrete plant with built-in silo for storing cement | 8474310000 |
| Equipment for the automatic production of products from cement, sand and other industrial waste. BY MOLDING AND AGGLOMERATION model: QT4-15D: QT12-15; QT10-15; QT8-15; QT6-15C; QT6-15B; QT4-15C QT4-20C; QT4-25; QT4-2 | 8474809080 |
| Gas cleaning equipment: cement filter | 8421392009 |
| Construction equipment and machines: Equipment for storing and transporting cement and other bulk materials | 8479820000 |
| Gas cleaning and dust collection equipment for cement production lines, Scheuch brand | 8421398007 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: Cement unloading equipment type BBE-100/25 | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: Cement grinding plant with the following components (see Appendix) | 8474200009 |
| Chemical, oil and gas processing equipment: tanks RVS, RGS, RChV, RGSN, RGSP, double-walled RGSD with a volume from 5 to 5000 m3, underground tanks, above-ground EP, EPP, tanks for fuels and lubricants, silos for cement and bulk materials | 7309005100 |
| Equipment for the building materials and cement industry: ventilation system module | 8474 |
| Equipment for the production of building materials: silos for loading, storing, dosing sand, cement and building mixtures | 7309009000 |
| Equipment for preparing construction (cement) mixtures: line for mixing and packaging cement | 8474390009 |
| Gas cleaning and dust collection equipment: air filters for cement silos, | 8421392009 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: unloading plant with pneumatic cement supply | 8428909000 |
| Equipment for preparing construction mixtures: cement production line with a capacity of 8,500 tons of clinker per day | 2710124110 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: cement production line with a capacity of 1500 tons/day | 8474809080 |
| Chemical equipment: tanks RVS, RGS, RFV, RGSN, RGSP, double-walled RGSD with a volume from 25 to 3000 m3, underground tanks, tanks for fuels and lubricants, silos for cement and bulk materials, storage tanks for hot water. | 7309005100 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: line for palletizing and packaging bags of bulk products (cement) | 8422400008 |
| Oilfield equipment: Constant flow cement bunker | 7309005900 |
| Construction equipment: cement grinding equipment (line), | 8474200009 |
| Laboratory equipment: consistometer model Model 15-400 RP, cement analyzer model M2000 | 9027801700 |
| Laboratory equipment: cement cement strength analyzer | 9024801900 |
| Technological equipment for the elevator industry (cement storage silos), | 7309009000 |
| Chemical equipment: tanks types RVS, RGS, RChV, RGSN, RGSP double-walled type RGSD with a volume from 25 to 3000 m3 (for petroleum products), underground tanks, silos for cement and bulk materials, accumulator tanks for hot | 730900 |
| Technological equipment for the building materials industry: pneumatic cement transportation system | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: A set of equipment for converting a cement mill to operating mode in a closed cycle of cement grinding | 2710124110 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: Air chute for transporting cement | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: pneumatic screw lifts for cement and other dusty materials | 8428202000 |
| Equipment for preparing construction mixtures: Shaking device for briquetting and compacting cement, concrete, | 8479820000 |
| Construction equipment and machines: cement and sand machine with bucket, | 8704101080 |
| Equipment for the building materials industry: complete technological installation, model “Rozmysel”, for unloading, storing, moving, lifting and loading construction bulk mixtures (cement, sand, lime | 8428909000 |
| Units of equipment for the preparation of building materials - a bunker for storing and supplying dry mixture of “cement” (silo) marked “PREFABET-KURZETNIK SP.ZOO”, | 7309009000 |
| Equipment for preparing construction mixtures: vibrators for sand and cement dosing bunkers | 8474809080 |
Cement composition
Cement is obtained by long-term crushing of clinker and gypsum. Clinker is a product of uniform firing before sintering a homogeneous raw material mixture consisting of limestone and clay of a certain composition, ensuring the predominance of calcium silicates.
When grinding clinker, additives are introduced: gypsum CaSO4 2H2O to regulate the setting time, up to 15% active mineral additives (pyrite cinders, flue dust, bauxite, sand) to improve some properties and reduce the cost of cement.
Cement production in factories
At this point in time, cement manufacturers use three binder production technologies:
- Wet method.
- Dry method.
- Combined method.
It is worth noting that “dry” technology is used by foreign cement manufacturers: Egypt, Turkey and China. “Wet” technology is traditionally used by domestic cement plants.
cement production cycles
Dry method
There is no need to use water here. The source material (clay and limestone) is crushed using special equipment. They are dried and ground into fine flour, mixed pneumatically and served for firing.
The cement clinker formed as a result of firing is crushed to the appropriate fraction, packaged and sent to the finished product warehouse. This method allows you to reduce production costs, but is characterized by “capriciousness” regarding the homogeneity of the starting materials and is an environmentally hazardous option.
Wet method
The undeniable advantages of this method lie in the possibility of accurately selecting the composition of the starting material with high heterogeneity of the starting components: rock, type of rock, etc. The starting material (sludge) is a liquid substance containing up to forty percent moisture.
Before making cement, the composition of the sludge is adjusted in special technological pools. After aging the raw materials in a pool, they are annealed in special rotary kilns and then crushed.
The wet method requires a greater consumption of thermal energy spent on drying the feedstock. This significantly increases the cost of cement production, but the quality of the final product does not suffer from possible heterogeneity of the clinker, as with the wet version.
Combined methods
This technology is based on the wet type of binder production. The intermediate substance is dehydrated using a special technology. The clinker is granulated with the addition of water, after which it is annealed and subsequently crushed into one or another grade of cement.
Among the advantages of the combined method of cement production: high yield of “usable” cement, the possibility of using waste from the metallurgical industry.
Structure
Cement production is carried out on the basis of the following components:
- clinker, the basis of which is clay and limestone. Clinker determines the strength of the material and is produced by firing clay-containing and limestone raw materials. When heated, it melts, forming a granular composition with a high concentration of silica, crushed, and re-firing;
Cement is produced in factories on an industrial scale
- gypsum, which affects the duration of the hardening process of the cement composition. It is administered, according to the recipe, as stones or ready-made powder, the concentration of which does not exceed 5%;
- modifying additives that expand the range of use of the material by acquiring special performance properties.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Small greenhouses, characteristics of types and features of making them yourself
How is white cement made?
The technology for the production of white cement differs slightly from the technology for the production of conventional “gray” material. Like regular “gray” material, white cement is produced using dry and wet methods. The main difference between the technology is the firing of raw materials at high temperatures and rapid cooling in water.
White cement clinker is characterized as “low iron” and contains in its composition: mineral additives, limestone, gypsum, salts and other components. Carbonate and clay rocks (limestone, kaolin clay, enrichment waste, quartz sand) are used as feedstock for clinker.
In the Russian Federation, white cement is produced only at one enterprise - Holsim (Rus) SM LLC (until 2012, Shchurovsky Cement OJSC). Most white cement is supplied to the Russian market from abroad as follows (Slovakia), Cimsa and Adana (Turkey), AalborgWhite (Denmark) and AalborgWhite (Egypt).
The main advantage of white cement is its unique characteristic - snow-whiteness, and the main disadvantage is its many times higher cost compared to ordinary “gray” material.
Cement production technology + video on how to do it
Modern technologies and materials make it possible to produce various types of cement. Some have practically ceased to be produced, others are only becoming famous. There are also mixtures designed to perform highly specialized tasks.
Kinds
- Portland cement
. Represents one of the most famous brands. It consists of clinker with gypsum, various additives, and the mixture is finely ground. Actively exhibits its properties upon contact with water. The name was given in honor of a rock in England called Portland, due to its similar color after hardening. - White cement
is a mixture of finely ground clinker, maximally purified from iron oxides, which increases the reaction rate. Used mainly for decorative purposes. - Slag
. It consists of crushed blast furnace slag with activators and additives - hence the name. It is characterized by increased strength indicators, which determines the main scope of its application - underground and underwater load-bearing structures. - Expanding
– the mortar mixture expands during the curing process. Thanks to its later acquired waterproof properties, it is used in underwater structures when there is constant water pressure. - Non-shrinkable
. It has the property of retaining its volume during the curing process. Used when carrying out waterproofing work when maintaining the volume of the cement mass is required. - Fast-hardening
. It is characterized by the shortest time for hardening compared to other brands of cement. - Hydrophobic
. It is a modification of Portland cement with special additives that make the cement resistant to freezing and thawing processes. - Backfilling
. Used to strengthen wells in the oil and gas industry. - Aluminous
. It has a number of properties that allow it to be used instead of several brands of cement in construction work during the cold season and in the construction of heat-resistant structures. - Pozzolanic
is a type produced from Portland cement by adding compounds of volcanic origin, which allows it to be used in the construction of water tanks.
Stamps
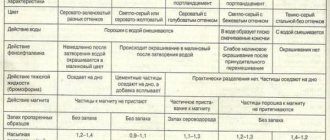
Based on strength, cement is divided into grades, determined by the compressive strength of halves of prism samples measuring 40×40×160 mm, which are made from a solution containing 1:3 quartz sand. The grades have a range of M200-M600 (in increments of 50 or 100), indicating compressive strength (respectively 200-600 kg/cm² (20-60 MPa)). Because of its strength, M600 cement is called “military” or “fortification” and stands noticeably higher than the rest. It is mainly used in the construction of military facilities and structures.
There are also strength classes. Their main difference from brands is that strength is not derived as an average indicator, but requires at least 95% security (that is, 95 samples out of 100 must correspond to the declared class). The strength class is expressed in numbers from 30 to 60, expressed in MPa.