The mesh for cutting off concrete is a durable metal sheet made by weaving steel wires together with square-shaped cells. The wire can be of different sections, as well as the size of the cells. Most often, such a woven mesh is used when carrying out repair and construction work in order to strengthen the solution during the hardening process, if it is possible to allow excess water to pass through.
The cut-off mesh for concrete demonstrates excellent performance characteristics, is strong and reliable, flexible (which allows it to be used to create reinforced concrete of complex shapes), is sold at an affordable price, and has found application in a wide variety of types of work. This universal structural product is used when performing plastering work, for strengthening (reinforcement), sifting bulk building materials, effective filtration of dispersion mixtures, etc.
But the main purpose of the mesh is to be used in various types of concrete work. Due to the strength of the mesh, it is successfully used to strengthen vertical permanent formwork. Due to the presence of small cells, excess moisture from the solution is well removed through the mesh, and the concrete is held securely, which significantly increases its strength.
The use of cutoff is especially important when performing concrete work on large-scale areas. Once the boundaries of the grips have been determined, the mesh is mounted vertically and held in place by ribs made of reinforcement or boards. It is sometimes impossible to do without such a mesh when implementing different types of concrete work, but before use it is advisable to study all the types, features, and nuances of installation.
Kinds
Woven mesh for concrete screening is made from wire, which can be regular/galvanized, stainless, etc. All standards are defined in GOST 3826-82. For concrete work, it is recommended to use stainless mesh due to its ability to resist corrosion and maintain its original performance characteristics longer.
The main types of mesh for cutting off concrete:
- Woven metal mesh - it is produced low-carbon, with heat treatment, with or without coating. Cells can be rectangular or square.
- Ordinary wire - made in the format of interlacing wires located perpendicular to each other.
- Galvanized woven mesh is a high-quality product with a galvanized coating, suitable for laying tiles, cladding and other types of work. Sold in rolls weighing a maximum of 500 kilograms.
- Stainless steel mesh - used in construction, oil and gas industry, often in mechanical engineering and other industries.
Any cut-off mesh is a fabric made by interlacing transverse and longitudinal steel wires, without bends or breaks. The mesh is usually sold in rolls 1-1.5 meters wide with a maximum length of 80 meters. The size of the cells can be different - both 5x5 and 10x10, usually ranging from 0.03-20 millimeters. The wire cross-section can be 0.03-3 millimeters.
Types of meshes by purpose:
- Expanded – for filtering/screening building materials.
- Plastering – for performing plastering and facade work.
Types of mesh by weaving method:
- Linen - rectangular or square cells with one weft woven through one wire.
- Single-sided twill - the weave is dense, one weft intertwines two warps, the cells are square in shape. The texture is diagonal with a slope of 45 degrees.
- Double-sided twill - two wefts and one/two warps.
By type, the mesh can be partially corrugated (rigid, wavy in the longitudinal part), smooth without bulges or bends, filter (when the cells are not visible), and also conveyor, which is made from thin wires twisted into ropes.
The meshes also differ quite greatly in cell size. The larger the diameter of the wire and the smaller the mesh, the stronger the mesh is considered. The more carbon in the material, the harder the product is.
Description and types
A cut-off mesh is a fabric made by interlacing longitudinal and transverse steel wires, without breaks or bends. Sold in rolls 1-1.5 m wide with a maximum length of 80 m. Cell sizes range from 0.03 to 20 mm. They retain the concrete mass, but allow water to pass through, which speeds up the hardening of the mortar and the construction process. Wire diameter from 0.03 to 3 mm.
The following types of meshes are distinguished:
There are such products intended for plastering work.
- By application: Plastering - for facade and plastering works.
- Perforated - for sifting and filtering materials.
- Twill one-sided. Dense weave, 1 weft interweaves 2 warps, square-shaped cells. Diagonal texture with a 45 degree slope.
- Partially grooved. Wavy in the longitudinal part, hard.
- Stainless. Durable and elastic.
The smaller the mesh and the larger the wire diameter, the stronger the mesh. The more carbon, the tougher it is.
Advantages
Such products are not damaged under the influence of different temperatures.
- Durability.
- Withstand heavy loads.
- Resistant to temperature changes.
- Resistance to aggressive environmental influences.
- Elasticity. Allows you to create concrete products of complex shapes.
Application
The scope of use is quite wide:
- Plaster finishing works. Increases the service life of buildings. Improves adhesion between plaster and base. Prevents cracking of surfaces. A mesh is used when applying a thick layer of mortar or when finishing surfaces with poor adhesion.
- Floor screed. Increases strength and prevents cracks. Used when screeding foam-insulated floors.
- Laying concrete. Increases strength. Distributes weight evenly over a large area. It is used when laying asphalt, creating steps, ramps, etc.
- Construction of masonry houses from light and porous materials.
- Filling large areas with concrete. The mesh acts as permanent formwork.
- Filtration of dispersed mixtures and sifting of bulk materials.
When laying asphalt, such material is an irreplaceable thing.
Benefits of using a grid
Woven steel mesh is used in a number of repair and construction works and is considered an essential material for various tasks. The mesh is flexible, durable, and easily withstands changes in humidity/temperature. It makes it possible to qualitatively strengthen brickwork and is actively used in air filtration, plastering work, fencing areas, etc.
The scope of application of the mesh is quite wide, especially due to its low cost. Often the mesh is used to cut off concrete. Thanks to the many small cells and density, the mesh sifts various bulk materials well. The product is characterized by durability, can be easily transformed to any basic base, elastic, does not affect telephone communications or TV reception.
Key advantages of cut-off mesh:
- Long service life with preservation of properties.
- Ability to withstand heavy loads.
- Resistant to changes in humidity and temperature.
- Elasticity, which makes it possible to create products of unusual configurations and shapes.
- Resistance to aggressive environmental influences.
- Relatively low cost.
Application of shotcrete concrete
The shotcrete method is ideal for quickly creating monolithic structures with a thickness of no more than 150 mm - 200 mm, with reinforcement of no more than 100 kg per m3. This is due to the peculiarities of applying shotcrete concrete. With a thicker wall, cold seams may form inside the structure (layers); with stronger reinforcement, gunite may stick to the reinforcement, without filling the internal cavities.
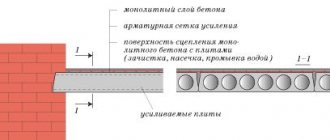
Concrete repair, restoration of the protective layer. During the operation of reinforced concrete structures, surface defects may occur. This can result from concrete destruction from erosion, fires, or mechanical damage. When repairing defects of this kind, shotcrete is an indispensable tool. It is shotcrete that allows you to create a monolithic layer with good adhesion to old concrete. If the damaged layer was removed using perforators, then it is necessary to reinforce the layers as shown in the figure. This is due to the fact that the layer of concrete that was hit by the hammer drill chisel is weakened. When drilling cores, this is clearly visible - the core always breaks not along the contact zone of the gunite and old concrete, but tears out several millimeters from the old concrete.
Strengthening “Clip” type structures When reconstructing old buildings, the problem of strengthening foundations or load-bearing walls very often arises. For example, it is necessary to add 2-3 additional floors, but the walls of the building are not designed for this load or have already begun to collapse (for example, the brickwork of which is more than 50 years old). This problem is solved using the “Clip” design. Screeds - reinforcement - are passed through through holes in the wall. On the outside, a mesh is knitted onto the curved ends of the ties. Next, the concrete is sprayed with gunite.
Strengthening walls for installing a ventilated facade. When installing ventilated facades, you are often faced with the fact that the anchors for attaching the brackets do not stay in the walls due to the destruction of the brickwork, erosion, etc. This problem is easily solved with the help of gunite. You can’t just spray concrete on the wall; it will tear off 1-2 mm of the surface layer of the old wall and fall off. Therefore, reinforced shotcrete is attached to the walls. You can do it according to the clip principle, but there is a cheaper option. The reinforcement is passed through the wall and a heel (metal plate) is welded to it from the inside. A mesh is knitted on the outside and concrete is sprayed with shotcrete.
Creating the walls of pits using gunite concrete. Usually our pits are made according to the classical scheme - sheet piling around the perimeter. Then it is fastened with anchors to the ground or with spacers inside the pit. Then the eternal struggle with water leaks through the piles into the pit begins. The quality of concreting of bored piles leaves much to be desired, etc.
nbsp;When the pit depth is less than 8 m, you can avoid the expensive operation of installing sheet piling. The pit is dug in a circle, to a depth of no more than 1-2 meters. Reinforced gunite concrete is immediately sprayed onto the walls of the pit. The concrete wall is secured with anchors. The top of the wall can be secured with rods. After securing the first tier, the second, third, and so on are dug out. The advantage of this method:
- The wall is obtained without defects, unlike bored piles.
- It is possible to immediately spray a waterproof membrane onto the concrete and make the structure waterproof from the start.
When working in cramped conditions and when constructing buildings using topdown technology, shotcrete is simply irreplaceable.
Concreting the side walls with shotcrete during the construction of structures using Top Down technology. After pouring the interfloor floors below the zero level, bored piles act as walls in the rooms.
They need to be leveled for gluing waterproofing and then pouring the wall. If you carry out work without using gunite, then you must: 1. Order expensive formwork 2. Stop the flow of water between the piles 3. Fill the first wall. 4. Glue the waterproofing 5. Install the reinforcement 6. Fill the second wall. This sequence of work entails additional costs for the purchase or rental of formwork and sealing of water flow through the piles. When using shotcrete, the number of operations is sharply reduced, and the quality of work becomes much better.
1. The surface of the piles is leveled with shotcrete (the concrete is reinforced with welded mesh) 2. A polymer membrane is sprayed (the elastic material, when set, forms a strong rubber-like membrane) 3. Wall reinforcement is installed. 4. Gunite is sprayed.
The speed of work increases by 2-3 days. Costs are reduced. The quality of work is incomparably higher than with classical concreting.
Creating Shotcrete Structures with Concrete Formwork limits the shapes that can be created from concrete to the plane of the formwork sheet. The extent to which you bend it and place it on a rigid frame, the extent to which your structure will bend.
Shotcrete allows you to create arbitrary shapes.
Main stages: The frame of the future structure is created from fine mesh and metal structures. When concrete is sprayed onto a fine mesh with reinforcement, a thin-walled reinforced frame is formed, which will subsequently serve as the basis for creating a full-fledged reinforced concrete structure. Return
Cell sizes and wire thickness used in meshes
According to GOST, the diameter of the wire for weaving a mesh should be a minimum of 0.03 and a maximum of 3 millimeters. The shape of the cells can be square or rectangular, which depends only on the method of weaving the wire. The network can be made with or without closures so that the outer wires do not fall out.
The cut-off network must be free of any deformations and cuts; bending at the beginning of the piece and loop is allowed, the optimal number of which is a maximum of two per square meter. Woven mesh is sold in the form of rolls, at different prices, which depend on the type of wire and the width of the cells.
You can buy mesh at any hardware store (in Moscow and the regions). Before purchasing, it is important to decide what work you plan to perform with its help - filtration of liquids/gases, cladding or plastering, creating a fence or ventilation grill, cage or enclosure.
Steel mesh perfectly strengthens concrete, preventing it from crumbling. Before installing the mesh, it must be cleaned of corrosion and contamination. The product efficiently seals and protects self-leveling concrete floors, brickwork, screed under heated floors, asphalt layers, ramps/steps, curb stones, etc. from cracks.
Scope of use of the cut-off mesh:
- Finishing plastering work - mesh significantly extends the service life of buildings, increases adhesion between the base and plaster, and prevents surfaces from becoming cracked. Typically, meshes are used when applying a thick layer of mortar, as well as for finishing surfaces with poor adhesion.
- Laying concrete - the mesh increases strength, distributes the weight evenly over a large area, is used for laying asphalt sheets, in the production of ramps and steps.
- Floor screed - eliminates the risk of cracks and increases strength. Often, meshes are used to create screeds with foam-insulated floors.
- Masonry of houses made of porous/light materials.
- Filling large areas with concrete - here the mesh becomes permanent formwork.
- Sifting of bulk materials, filtration of dispersed mixtures.
Mesh for concrete: the use of fiberglass, metal products
Concrete is a fairly strong material, but at the same time fragile, prone to cracking. To eliminate this drawback, a reinforcing mesh is used when pouring it. Next, we will take a closer look at the cases in which this material is used and what types it comes in.
Sectional metal reinforcing mesh for concrete
When to use a mesh
Reinforcing mesh is used exclusively in two cases:
- If it is necessary to achieve high strength concrete;
- If there is a need to connect materials between which there is poor adhesion.
Now let's look at the most common cases in which it is necessary to use reinforcing mesh:
- Floor screed - in this case, reinforcement is never superfluous, as it helps prevent cracking of the material and also increases the strength characteristics of the floor. Metal mesh for concrete reinforcement is especially needed in cases where the screed is installed on top of a foam-insulated floor. If it is not used, the concrete will crack in the first months of operation, no matter how high-quality and durable the solution is.
- Plastering surfaces - when performing this operation, reinforcement improves the adhesion between the cement plaster and the base. As a rule, it is used in two cases - when a thick layer of mortar is applied, or a surface with poor adhesion is finished.
- When laying concrete - in this case, the geogrid for asphalt concrete performs two functions at once : it increases the tensile strength of asphalt;
- absorbs the bulk of the horizontal tensile loads and allows them to be evenly distributed over a larger area of the asphalt road surface.
Plaster mesh
Most often, plastic mesh for concrete reinforcement or metal mesh is used for these purposes. In particular, it is necessary when plastering foam plastic, painted walls, wooden surfaces or metal. It must be said that in the case of plastering foam plastic, a mesh is also needed to prevent cracking of the surface.
Note! Reinforced concrete is called reinforced concrete. This material is very durable, as a result of which it is difficult to process; for example, even cutting reinforced concrete with diamond wheels will require some time. Therefore, when pouring, it is immediately necessary to think through all the nuances so that later you do not have to perform any additional work on the finished surface.
Metal masonry mesh for aerated concrete
It must be said that there is another construction operation in which reinforcing mesh is used - the construction of masonry. The armored belt allows you to evenly distribute the load on the base, as well as tighten the walls and thereby prevent the occurrence of cracks (
Stainless steel TsPVS
| Article according to the formula A*B-D-C | Edge cell size | Sheet thickness, mm, G | Jumper, mm, V | Width | Length | Roll/card area, m2 |
| PVS R10*4-0.5-0.8 AISI409 /1000-2000/ | 4×4 | 0,5 | 0,8 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R10*4-0.5-0.8 AISI409 /1000-5000/ | 4×4 | 0,5 | 0,8 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| PVS R16*6-0.5-1.47 AISI409 /1000-2000/ | 6×6 | 0,5 | 1,47 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R16*6-0.5-1.47 AISI409 /1000-5000/ | 6×6 | 0,5 | 1,47 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| PVS R16*6-0.5-1.47 AISI304 /1000-2000/ | 6×6 | 0,5 | 1,47 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R16*6-0.5-1.47 AISI304 /1000-5000/ | 6×6 | 0,5 | 1,47 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| PVS R16*6-0.7-1.47 AISI304 /1000-2000/ | 6×6 | 0,7 | 1,47 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R16*6-0.7-1.47 AISI304 /1000-5000/ | 6×6 | 0,7 | 1,47 | 1 | 5 | 5 |
TsPVS made of aluminum A5M
| Article according to the formula A*B-D-C | Edge cell size | Sheet thickness, mm, G | Jumper, mm, V | Width | Length | Roll/card area, m2 |
| PVS Q6*4-0.8-0.8 A5M /1000-2000/ | 2×2 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS Q8*5-0.8-0.8 A5M /1000-2000/ | 3×3 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R10*4-0.8-0.8 A5M /1200-2000/ | 4×4 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1,2 | 2 | 2,4 |
| PVS R10*4-0.8-0.8 A5M /1000-2000/ | 4×4 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R10*4-0.8-0.8 A5M /1000-500/ | 4×4 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| PVS R16*7-0.8-0.8 A5M /1000-500/ | 6×6 | 0,8 | 0,8 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| PVS R16*7-0.8-1.47 A5M /1000-500/ | 6×6 | 0,8 | 1,47 | 1 | 0,5 | 0,5 |
| PVS R16*7-0.8-1.47 A5M /1000-2000/ | 6×6 | 0,8 | 1,47 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R16*7-0.8-1.5 A5M /1200-2000/ | 6×6 | 0,8 | 1,47 | 1,2 | 2 | 2,4 |
| PVS R20*8-0.8-2.0 A5M /1000-2000/ | 8×8 | 0,8 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| PVS R20*8-0.8-2.0 A5M /1200-2000/ | 8×8 | 0,8 | 2 | 1,2 | 2 | 2,4 |
| PVS Q6*7-0.1-1.25 FOIL /500-25000/ | 2×2 | 0,1 | 1,25 | 0,5 | 25 | 12,5 |
| PVS R16*7-0.1-1.47 FOIL /500-50000/ | 6×6 | 0,1 | 1,47 | 0,5 | 50 | 25 |
Plaster TsPVS
| Article according to the formula A*B-D-C | Edge cell size | Sheet thickness, mm, G | Jumper, mm, V | Width | Length | Roll/card area, m2 |
| PVS R16*7-0.35-0.5 OTs /1000-6000/ | 6×6 | 0,35 | 0,5 | 1 | 6 | 6 |
| PVS R25*10-0.3-0.5 OTs /1250-25000/ | 10×10 | 0,35 | 1 | 1,25 | 25 | 31,25 |
| PVS R50*20-0.3-0.5 OTs /1250-35000/ | 20×20 | 0,35 | 1 | 1,25 | 35 | 43,75 |
Square woven wire mesh GOST 3826-82
Woven mesh is produced at the AVALDA plant in accordance with GOST 3826-82, TU 14-4-1563-89, TU 14-178-215-2001 from heat-treated low-carbon wire GOST 3282-74: uncoated, galvanized, brass, copper, bronze, nichrome, fechral, stainless.
The main cell accuracy group is No. 2 - woven mesh is used for fencing, plastering, sifting bulk materials, and air purification. The manufacturing process is quite simple, the weaving machine interweaves steel threads at right angles - warp wires (which run along the fabric) and weft wires (these are threads that run across the fabric of the product).
Woven wire mesh has found wide application as reinforcement in the production of heat-insulating mats and slabs; as a replacement we can offer Manier mesh.
These technical conditions significantly expand the range (standard sizes) of produced woven mesh provided by GOST 3826-82. They are manufactured in widths of 1000, 1300, 1500, 1800, 2000 mm and are supplied to customers in rolls weighing no more than 80 kg. All mesh with a mesh size of up to 1.0 mm is subject to packaging. Rolls are wrapped in paper, then with polymer film or packaging fabric.
Precision of manufacturing woven mesh:
Group 1 is used for sifting bulk solids, where it is necessary to ensure a highly accurate granulometric composition of the sifted materials, filters in mechanical engineering, space technology, pharmaceuticals, gold mining: purification of air, gases, filtration of liquid solutions and medications, sorting of crushed abrasive and other materials by size , dehydration, drying, filtration under vacuum or pressure, enrichment of metal ores, washing of clay solution during oil and gold mining, for sifting various powders.
Group 2 is used in everyday life, as a strengthening and protective effect: plastering walls, laying under road surfaces, cutting off concrete when working on a monolith, reinforcing reinforced concrete structures, foundations, house walls, fences, enclosures for rabbits, pigeons and other animals.
| Tolerances | Group 1, % | Group 2, % |
| Permissible deviation from the nominal size for the arithmetic mean size of the cell side in the clear | ± 5-6 | ± 9 |
| Maximum permissible deviation from the nominal for the size of an individual enlarged cell in the clear | ± 15-25 | ± 40 |
| Allowable number of cells with maximally increased clear side dimensions | ± 6-8 | no rules |
Examples of designations when purchasing at the factory:
Request: Mesh 2-10-2.0 GOST 3826-82
Explanation: Woven mesh with a nominal clear mesh side size of 10 mm, made of wire with a diameter of 2.0 mm, low-carbon steel without coating, group 2.