08/25/2018 Category: Foundation
Thanks to the constant development of concrete technologies, modern architects have learned to create not only technologically complex, but beautiful building projects from.
The architectural expressiveness of modern concrete structures is ensured by the high quality and uniformity of their front surface, or, conversely, by giving it a certain decorative texture.
These energy losses can be reduced by increasing the thermal resistance of the partitions, which significantly affects the heat loss in the premises. Principles of installing the base and floor on the ground. The foundation is the lowest and most importantly supports the entire structure of the building. This part of the building is difficult to change and update once the building is built, so it is important to properly design and insulate the foundations from the beginning. In multi-apartment residential buildings, polar foundations are usually created, combined with grillages or basement walls.
What classes of concrete surfaces are there?
Straightness measurement
To assess the surface quality and appearance of monolithic reinforced concrete and concrete structures, the set of rules SP 70.13330.2012 (Appendix C) provides 4 classes (not to be confused with):
- class A3;
- class A4;
- class A6;
- class A7.
The class of the concrete surface is determined by the maximum tolerances for straightness and local unevenness (see table below). Straightness tolerance refers to the largest permissible deviation from straightness (see figure).
The main thing to consider when designing is the cold of the foundations. Water sucked into concrete vapors lays the foundation and damages the entire structure of the building. Good insulation can protect against colds and other problems. The entire structure of the house must be very well insulated. Bases, edges, corners, seams must be very clearly defined to avoid thermal bridges. In order to avoid thermal bridges between the raft and the external insulating wall materials, the thermal insulation materials of the raft should be used on the wall, and the wall insulation at the cutting angle gives on the insulated base.
| Class | Straightness tolerances for measured distances, mm | |||
| Local unevenness -0.1m It is also very important to properly install the floor of energy efficient buildings on the ground. The main prerequisite in order to avoid thermal bridges for energy efficient buildings is that the integrity of the thermal insulation materials must be ensured, as well as the installation of the building foundations and on the ground floor, it is important to ensure that the thermal insulation material contacts the foundation and floor. Structures of main walls. For a long time, the thermal insulation of bricks or blocks was sufficient to build a house. Current thermal insulation standards corresponding to wall insulation are only possible using very thick blocks or additional façade insulation with expanded polystyrene foam, mineral wool or stone. This increases the thermal insulation of the bricks or blocks and reduces the width and volume of the wall itself. | 1m | 2 m | 3m Lithuania construction of new residential buildings is the most commonly used and most popular two-wall insulation system: it is ventilated and plastered facades, otherwise known as “wet” facades. Ventilated facade walls can be installed on a metal or wooden frame, installing three-layer masonry trusses. The most widely used ventilated walls in Lithuania are metal frames. The most important phase of installing ventilated facades is the installation of the metal console. The consoles must be installed on thermocouples, which eliminates the cold bridge between the metal console and the supporting wall structure. Installation of facade thermal insulation begins only after the console is completely installed. The main aspects of installing thermal insulation panels are: | |
| A4 | 10,5 Thermal insulation panels must adhere to the internal insulated surface; The panels should be stacked on top of each other so that they do not match the seams of two layers of insulation or create a four-corner swirl; There should be no cracks between the insulating boards. The inevitable cracks are filled with equivalent insulating material; Windshield wipers used for wind protection must be covered with all the seams of the universal board and must be strictly adhered to. The insulation materials under the wall structure are fixed with pins selected according to the thickness of the insulation. | |||
| A6 | ||||
| A7 Studs are installed in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations. After installing the thermal insulation layer, metal cables are installed on the console on which the selected façade panels are fixed. The main disadvantages of ventilated facades on the Lithuanian market are such that the experienced labor shortage and cost-saving considerations resulted in a number of technological and installation errors. The ventilated façade walls are not sealed properly because there is not enough insulation to ensure a good seal. | ||||
Exposure of reinforcement is not allowed
The specified maximum tolerances are applied provided that they correspond to the thickness and cross-sectional dimensions of the elements.
The concrete surface class is determined for:
In addition, anti-roll film must be installed, and all connections interspersed with the console must be sealed with special insulating tape. The main positive aspects when installing ventilated facade wall structures are the seasonal characteristics of the work.
These wall structures can be installed at any time of the year, regardless of weather conditions, but proper preparation of work sites is required. Painted facades in Lithuania are usually installed using thermal insulation boards made of stone wool, mineral wool or expanded polystyrene. Regardless of the type of insulating material, the technology of these walls is very similar to the basic principles of insulation. However, various elements, adhesive compounds, reinforcing nails, studs, corner profiles can be used, which are selected in accordance with the manufacturer's choice and recommended guidelines and techniques.
- foundations;
- walls;
- floors;
- columns;
- other structures with straight surfaces.
The class and quality of the concrete surface must be indicated in the design documentation. In cases where the class is not specified, it is taken equal to A6 or A7 depending on the purpose (the purpose of concrete surfaces of different classes is written below).
Basic principles of “wet” facade installation. The surface must be cleaned of dust, dried if necessary, and primed. Panels can only be glued on a properly prepared surface. . The main advantages of plastered facade walls are that the installation of these walls provides better integrity of the structure than the installation of a ventilated facade. The greatest disadvantages appear in the nodes where capillary profiles are needed, and they are mainly used to save metal, thus creating a direct thermal bridge between the base and the wall.
The design documentation also specifies additional requirements for concrete surfaces operated under conditions of constant exposure to moving or other aggressive influences.
Concrete (reinforced concrete) products (structures)
Reinforced concrete products (RCP) are widely used in all areas of construction, from housing to engineering. For the construction of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures, prefabricated reinforced concrete products are used, the production of which is carried out by injection molding in a factory.
Concrete products
This article discusses concrete and reinforced concrete products, their scope of application, classification, varieties and labeling. We will also tell you how to install reinforced concrete structures using crane equipment.
General information about concrete products
Reinforced concrete products are prefabricated building elements of increased strength, which is achieved through the joint work of metal and concrete. Concrete, as a material, is characterized by increased resistance to compressive loads, but it is highly vulnerable to bending and tensile loads, the resistance to which is almost 15 times less than to compressive deformation.
These loads are absorbed and compensated by steel reinforcement, through which reinforced concrete structures are strengthened. The metal has a high tensile strength, as a result of which reinforced concrete products reinforced with non-rebar are equally resistant to loads of different types.
The joint work of steel and concrete is achieved due to the strong adhesion of the two materials to each other, while they have almost the same coefficient of thermal expansion, which guarantees the monolithic nature of reinforced concrete. An additional advantage is that concrete protects the reinforcement embedded in it from corrosion.
What is possible and what is not?
It is important to know what can and cannot be allowed on a concrete surface.
The object chosen for the survey is an apartment building on the street. Uzhtvankosh. 36, Marijampole. The apartment is four floors. Parking is planned on the ground floor of the building. There are 24 apartments on the second, third and fourth floors. The frame consists of monolithic reinforced concrete foundations, columns, beams, linings and horizontal load-bearing rigid vertical reinforced concrete diaphragms.
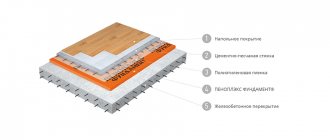
The external walls are covered with masonry, which does not include: 300 mm interlocked concrete blocks, extruded polystyrene foam, 150 mm thermal insulation, external finishing - a regular wall. Between rooms - 120 mm, porous concrete blocks. Garage floors on compacted soil by installing a 100 mm layer of crushed stone or gravel, waterproofing, reinforced concrete layer - 130 mm. The top layer of the garage floor is installed with a slope in the drainage channels.
Irregularities beyond the straightness tolerances are not allowed
NOT ALLOWED on concrete surfaces:
- areas of uncompacted concrete;
- rust stains and grease stains (except class A7);
- exposure of reinforcement (except for working outlets of reinforcement, mounting fasteners of formwork);
- exposure of steel embedded products (without anti-corrosion treatment);
- cracks, opening width specified in the project (recommended value: 0.1 mm - for structures not protected from precipitation; 0.2 mm - indoors);
- sinks (chips of concrete ribs) for:
- class A3 – with a diameter of more than 4 mm / depth of more than 2 mm (depth of 5 mm / total length of more than 50 mm per 1 m of ribs);
- class A4 – from 10 mm / from 2 mm (5 mm / from 50 mm per 1 m of ribs);
- class A6 – from 15 mm / from 5 mm (10 mm / from 100 mm per 1 m of ribs);
- class A7 - from 20 mm (from 20 mm/length - not regulated);
- local irregularities (, bulges or depressions) exceeding the tolerances for the corresponding classes at a measured distance of 0.1 m. For surfaces of class A3, protrusions and bulges are not allowed.
The flooring is installed on a monolithic frame: polystyrene foam - 50 mm, polyethylene film, reinforced smoothing layer - 60 mm, floor covering. Designed for the construction of autonomous heating and hot water supply systems, boilers with suspended gas in apartments.
Alternative Exterior Wall Assemblies
For each project, four different alternatives are selected. When analyzing alternatives to the building and walls, the following indicators are accepted. The relative importance of the parameters of the selected structural units is determined by the method of expert assessments - a specific type of survey in which industry specialists, experts, based on their professional experience and knowledge, break down a number of alternative indicators in accordance with their significance. Scores are awarded on a scale of points: the highest score is the highest value, the lowest score is the lowest.
Imprints of formwork panels on the concrete surface are allowed
ALLOWED on concrete surfaces:
- for wall structures - holes for tie rods (with plastic protective tubes for the tie rods left in them); holes for anchors;
- imprints of panels/formwork elements;
- exposure of reinforcement fasteners;
- for the lower surface of the floors - imprints of panels/formwork elements, electrical wiring elements, fastening of plastic structures, etc.
To ensure compliance with the requirements for concrete surfaces of classes A3 and A4, local projections are ground and local depressions are rubbed.
A total of 31 experts were interviewed. It can be used when it comes to choosing among the best target discrete alternatives. This method is used by both builders, mathematicians and economists. The calculation results are presented in tables.
Decision-making matrix for border units
Decision matrix for base nodes. The best capillary unit. Calculations are the best alternative for walls. Best wall detail. The selection of the Energy Efficient building design unit was carried out sequentially, so that the work can collectively produce a model that reflects the main energy efficient steps of the residential selection of building blocks in the construction of the energy efficiency class to achieve.
Why we have high-quality concrete and reinforced concrete
The constant rise in prices for raw materials (metal, sand, crushed stone), electricity and fuels and lubricants is a good incentive for the enterprise to invest in its own capacities. In order to withstand serious competition, in the interests of our customers, the plant team constantly modernizes production and carefully controls the quality of reinforced concrete products and building mixtures.
Control of compliance with the requirements of Russian and international GOSTs, TUs and SNiPs is carried out in a specially equipped laboratory at the plant. The laboratory staff monitors the quality of materials supplied to the plant and tests finished reinforced concrete products and concrete.
In addition to high quality standards, the company’s team is ready to provide high standards of service and support to our clients.
Purpose of concrete surface depending on class
The table below shows the main purpose of concrete surfaces of different qualities:
| Class It is not enough to note the stages whose implementation is currently unsatisfactory. Summarizing all the research and calculations carried out at work, we can draw the following general conclusions and recommendations. When designing energy efficient buildings, it is necessary to select high-quality thermal insulation materials, pay attention to the building orientation, volume, floor plans, window layout of the world, as it has a significant impact on the energy efficiency of buildings, there is not enough building insulation with the thickness of the thermal insulation material layer in order to be energy efficient. In addition, energy efficient buildings should be equipped with recuperative ventilation, cooling systems, and renewable energy sources; The selection of the main structural units of an energy efficient building can be carried out in accordance with the recommended thermal conductivity coefficients using an alternative method. The energy efficiency of buildings is also of great importance for the quality of work performed and the qualifications of employees and technology for installing the selected structure; It is recommended that the density of an energy efficient building should not exceed 0.6 h -1. A professional level of design and mastery of current construction work are prerequisites for the energy efficiency of buildings. | Purpose of structures |
| floors that have increased requirements for appearance. Surface for improved painting without putty. | |
| A4 | The front surface of columns, walls and the bottom surface of floors prepared for finishing (, wallpapering). |
| A6 | The front surface of columns, walls, the bottom surface of floors, for which there are no special requirements for surface quality. Surface for simple painting or without finishing. |
| A7 | Concealed and plastered surfaces. |
General technical requirements
It is worth noting that in accordance with GOST 23009-78, reinforced concrete prefabricated structures must be assigned grades. The stamps contain alphabetic and numeric symbols that reflect information about the size, type, load-bearing capacity of the structure, the materials used (reinforcement, concrete), and additional characteristics (resistance to aggressive environments, seismic resistance, and others).
Information on general technical requirements for prefabricated reinforced concrete structures is contained in GOST 13015.0-83. Full guidance on this will be found in this document. It is worth knowing that the requirements will be for the following:
Reinforced concrete structures are assigned grades that contain information about the size, type, load-bearing capacity of the structure, the materials used (reinforcement, concrete), and additional characteristics.
- To the accuracy of manufacturing structures (limit values for the deviation of geometric parameters, actual mass, and thickness of protective layers must be established).
- For embedded parts and fittings (it will be necessary to comply with the types, grades and classes of steel with the standards for structures of certain types; the level of pre-stressing of the fittings is established and controlled; the technical characteristics and type of anti-corrosion coating are assigned).
- For concrete (the tempering strength of concrete must be standardized; grades for waterproofness and frost resistance of concrete will need to comply with standards depending on the climatic conditions of the construction area and the operating mode; if necessary, the average density, thermal conductivity, humidity, and abrasion of concrete must be standardized).
- To the appearance and quality of surfaces of structures. That is, the conformity of the quality of finishing of smooth surfaces with finishing standards of a certain category: A0 – front surface of factory complete readiness; A1, A2 – front surface for painting for interiors or complete factory readiness; A3 – front surface for finishing with paints, glazes or paste-like compositions for facades and interiors; A4 – front surface for finishing with thin polymer tiles or wallpaper; A5 – front surface for finishing with ceramic or other mortar tiles; A6 – front surface, which is not finished; A7 – non-facial surface.
How to ensure the quality requirements of a concrete surface
About lubrication
Ironing of concrete blind area
To ensure the quality of the surfaces of concrete structures without the use of special finishing methods, it is necessary:
- prevent concrete from sticking to the formwork deck;
- fulfill the requirement for the size of pores and cavities and their number on the surface of a concrete monolithic structure.
Special ones for formwork help to cope with this task. High-quality lubricant provides good adhesion to the formwork deck and at the same time poor adhesion to the concrete surface. The choice of lubricant depends on:
- formwork material;
- location of the formwork – horizontal or vertical;
- method of applying lubricant to;
- on the type of plasticizers in the concrete mixture.
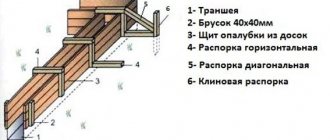
The main purpose of the lubricant is to reduce the effort required to tear the formwork away from the concrete when stripping the structure. Previously, clay, lime-clay, chalk, and talc compositions were used for these purposes. However, their use did not exclude corrosion of metal formwork, the formation of greasy or rusty stains on the concrete surface, and did not reduce the number and size of air pores. In addition, the formwork forms were overgrown with cement.
Later they began to use lubricants based on petroleum products, incl. based on diesel fuel and lubricating oils. These lubricants were already better, but at the same time, a large number of pores formed on the concrete from the pinched air, dark oil stains appeared, and during the operation of the building, the finishing layer peeled off and peeled off in this place. Therefore, they began to use lubricants based on machine, brake, and spindle oils in combination with solid oil, paraffin, and petrolatum.
In addition to the use of formwork release agent, good quality of the concrete surface is ensured by displacing air from the formwork during the process of feeding and compacting the concrete mixture. When concreting, it is necessary to avoid air entrapment on the surface of the formwork as much as possible. To do this, it is important to follow the compaction regime and use plasticizing agents correctly.
About compaction of mobile concrete mixtures
Movable and highly mobile concrete mixtures contain a large amount of cement glue and, therefore, they quickly liquefy and compact. Compaction of mixtures of grades P, P2, P3 is carried out. Mixtures of grade P4 and higher are self-leveling, since they spread and compact under their own weight, so they are only leveled and smoothed.
Areas of uncompacted concrete are not allowed.
In general, the more fluid the concrete mixture, the greater the likelihood of it separating. As the mobility of the mixture increases, the viscosity of the solution included in its composition decreases and the mixture is less able to hold the coarse aggregate in suspension.
When concreting monolithic structures with highly fluid and cast mixtures, the formwork is filled either from one end or from the middle. With this filling, maximum displacement of air from the formwork occurs. With other formwork filling schemes, air may remain (pinched) both inside the mixture and on the formwork.
The duration of vibration of moving concrete mixtures is:
- for P1 brand mixture – 25-35 s;
- brand P2 – 18-25 s;
- brand P3 – 10-20 s;
- grade P4 – 7 s;
- brand P5 – no more than 5 s.