The thickness of the walls of a panel house. Internal and external walls
Very often in an apartment we want to hang a TV, a shelf, or maybe just a picture on the wall, but we are afraid to drill holes in the wall of a panel house.
What if the drill goes right through? And in order not to be afraid, you need to know the thickness and types of walls in panel houses, which I will talk about in this article. As a rule, panel manufacturers do not deviate from standard sizes, so the thickness of such walls is, in principle, predictable, unlike the thickness of a brick wall of an individual house.
Walls, as we know, are usually divided into three types:
- external
- internal load-bearing
- internal partitions
External walls of a panel house
These walls are the thickest and come in two types:
- single-layer external walls consisting of lightweight concrete
- multilayer walls consisting of reinforced concrete and, as a rule, polystyrene foam slabs
Single-layer panels
Most often, single-layer panels are made of expanded clay concrete with a thickness of 300-350 mm, depending on the climate zone. Expanded clay concrete is suitable for these purposes, both in strength and thermal conductivity.
There are single-layer slabs consisting of cellular concrete. The thickness of such panels also ranges from 300 to 350mm.
Multilayer panels
Most often, such panels consist of two layers of reinforced concrete (external and internal) and polystyrene foam (foam) slabs between them. The standard thickness of such a wall is 380mm.
The internal reinforced concrete layer is 80-100 mm (previously the layer was thinner). The outer reinforced concrete layer is at least 60 mm.
Expanded polystyrene is usually used as insulation, since mineral wool is too “soft” a material, and if it is used for the production of panels, it is very rarely.
Slab for balconies and loggias
The balcony slab is the actual basis of the entire balcony structure. The classification by design, as well as the requirements for materials for their production, is explained in the document GOST 25697-83 “Reinforced concrete slabs for balconies and loggias”.
Width and length may vary depending on architectural solutions. As a rule, slabs are manufactured according to the following parameters; this also applies to loggia slabs:
- Length - from 1.2 m to 7.2 m
- Width - from 1.2 m to 1.8 m
- Thickness - from 15 cm to 22 cm
Thickness of the internal walls of a panel house
Internal walls are also of two types: firstly, these are load-bearing walls, on which the entire structure of the house rests, and secondly, these are internal partitions, which serve exclusively to divide the area of the house or apartment into rooms.
Thickness of load-bearing walls of a panel house
Load-bearing panels of reinforced concrete structures are usually from 140 to 200 mm thick. To be more precise, the most common panels have thicknesses of 140mm, 180mm and 200mm.
It is very rare to find a load-bearing wall 120mm thick.
Thickness of internal partitions
In most panel houses, internal partitions consist of gypsum concrete panels, the thickness of which does not exceed 80mm.
Sometimes the thickness of the internal partitions of a panel house varies from 80mm to 100mm.
How to distinguish a load-bearing wall of a panel house from a partition
When remodeling an apartment, you need to know exactly where the load-bearing walls are located, which cannot be touched, and where there are simply internal partitions that can be demolished, moved, etc.
Remember! When moving or demolishing walls in an apartment, you must first order a redevelopment project from a licensed organization. If this is not done and the layout is changed without approval, then in the future problems may arise with the design and re-decoration of your apartment.
And so, let's continue.
The easiest way, without drawings and projects, to determine where the load-bearing wall is and where it is not, is to measure the thickness of the wall with a tape measure or ruler.
I have already talked about the thickness of load-bearing walls, it starts from 120mm. Therefore, we take a ruler and measure the wall, if it is greater than or equal to 120mm, then this wall is load-bearing, if less, then it is a partition.
Using this method, you can quite accurately determine the type of wall, since in most cases the panels of a panel house have standard sizes, but it must be remembered that the thickness of the wall is measured without finishing layers, i.e. without plaster, wallpaper, additional internal insulation, and so on.
Related article: Installing a Mauerlat on a brick wall
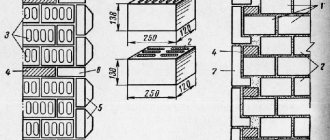
Thickness of internal brick walls
Mostly solid bricks are used for laying internal walls. The sufficient thickness of internal walls made of such material is no more than 25 cm. In cases where there is an increased load on the walls, the use of reinforcing structures is allowed.
If we talk about internal partitions with a minimum length of up to one and a half meters, half-brick masonry is sufficient. In this case, the thickness of the partition will be 12 cm. An alternative option is to lay a quarter of a brick - 6.5 cm.
In cases where the partitions have a length of more than 1.5 m, it is advisable to use reinforcement to improve the load-bearing qualities. For this, steel reinforcement with a diameter of 2 to 5 mm is used. Reinforcing material is laid approximately every 3 rows of bricks.
The thickness of the walls of a panel house. Internal and external walls
External walls of a panel house
These walls are the thickest and come in two types:
- single-layer external walls consisting of lightweight concrete
- multilayer walls consisting of reinforced concrete and, as a rule, polystyrene foam slabs
Single-layer panels
Most often, single-layer panels are made of expanded clay concrete with a thickness of 300-350 mm, depending on the climate zone. Expanded clay concrete is suitable for these purposes, both in strength and thermal conductivity.
There are single-layer slabs consisting of cellular concrete. The thickness of such panels also ranges from 300 to 350mm.
Multilayer panels
Most often, such panels consist of two layers of reinforced concrete (external and internal) and polystyrene foam (foam) slabs between them. The standard thickness of such a wall is 380 mm.
The internal reinforced concrete layer is 80-100 mm (previously the layer was thinner). The outer reinforced concrete layer is at least 60 mm.
Expanded polystyrene is usually used as insulation, since mineral wool is too “soft” a material, and if it is used for the production of panels, it is very rarely.
Thickness of the internal walls of a panel house
Internal walls are also of two types: firstly, these are load-bearing walls, on which the entire structure of the house rests, and secondly, these are internal partitions, which serve exclusively to divide the area of the house or apartment into rooms.
Thickness of load-bearing walls of a panel house
Load-bearing panels of reinforced concrete structures are usually from 140 to 200 mm thick. To be more precise, the most common panels have thicknesses of 140mm, 180mm and 200mm.
It is very rare to find a load-bearing wall 120mm thick.
Thickness of internal partitions
In most panel houses, internal partitions consist of gypsum concrete panels, the thickness of which does not exceed 80mm.
Sometimes the thickness of the internal partitions of a panel house varies from 80mm to 100mm.
Load-bearing brick walls
With proper implementation of calculations that lead to an even distribution of loads, walls one brick thick have the highest load-bearing capacity. Thickening of walls due to increased thermal insulation properties leads to the need to lay a stronger foundation, which affects the increase in planned costs.
The aesthetically attractive thickness of a brick wall can be maintained through the use of felt insulators. When installed, heat retention rates increase by approximately 30%. When using foam plastic as insulation, it is possible to achieve an increase in thermal insulation efficiency by 2-3 times.
The use of other least expensive insulators allows you to increase the thermal insulation properties of load-bearing walls by about 10-15%:
- sawdust;
- tuff;
- perplite;
- mortar based on slag or fine aggregate.
When creating a continuous masonry, it is advisable to install insulation from the inside or outside. In this case, the minimum thickness of the brick wall is maintained.
As for the thickness of load-bearing walls made from the most modern, innovative types of bricks, it can be almost anything. Moreover, in this case, maintaining the heat balance practically does not depend on the presence of insulation.
Wall thickness in a panel house
There is a task - to attach a TV mount to the wall. The mounting kit includes 10 cm dowels. The wall is panel, inter-apartment, and does not border the street. One thing confuses me: when making such deep holes, I’m afraid to see my neighbor through them) Or are the fears unnecessary?
If the house is built according to the project, it is unnecessary.
Vladimir_Vas wrote: If the house is built according to the project, it is unnecessary.
Who will tell me this? Probably only the Lord God knows.
karinin wrote: Who will tell me this? Probably only the Lord God knows.
Do you think - Is he looking at the site here?
No, he saw whether the house was built according to the project or not
karinin wrote: One thing confuses me: when making such deep holes, I’m afraid to see my neighbor through them) Or are the fears unnecessary?
The fears are not unfounded. You didn't say which walls. There are also paired plaster ones in a frame-panel house. Concrete internal wall 14-16-22cm, depending on the series of the house. If the wall is 14-16cm, then you need to drill carefully. Maybe a neighbor's clothes will fly out.
The panel walls have through holes for socket boxes. You can try to estimate the thickness of the wall by looking into this very hole.
karinin wrote: I have a task - to attach a TV mount to the wall. The mounting kit includes 10 cm dowels. The wall is panel, inter-apartment, and does not border the street. One thing confuses me: when making such deep holes, I’m afraid to see my neighbor through them) Or are the fears unnecessary?
5 cm anchor is enough
Or 7 cm. No more. The probability of getting to a neighbor is 10, it does happen. In a new house, in the wall with a neighbor, I changed the socket and discovered a wire. The neighbor was stealing electricity. There was a through hole. But the fact is that both his and our sub-soldiers’ depths corresponded in total to the thickness of the wall. And this is only 10 cm
Related article: Protecting bathhouse walls from stove heat
Labor without art is barbarism!
The panel usually has a thickness of 14-16cm
However "yes"
Koroviev wrote: On the panel walls there are through holes for socket boxes. You can try to estimate the thickness of the wall by looking into this very hole.
You are speaking the truth! But you still need to unscrew the socket on the same wall.
The deeper, the more reliable. Compensate for cutting with quantity - the frame is designed for at least half a dozen holes. So mark approximately evenly along the wall
Types of siding
The material has many varieties.
First of all, one must distinguish:
- Basement siding. Initially, it was created for cladding the lower (basement) part of the building, but practice very quickly gave it equal rights with the main type - facade. The reasons for this were the high decorative qualities of the material, mainly specializing in imitation of various types of stone or brickwork, as well as the strength and ease of installation work.
- Facade (wall) siding . The main cladding used to finish all external parts of the building - walls, gables, attics, soffits, etc.
In addition, for wall panels there is a division into:
- Vertical. The panels are arranged in a vertical orientation and installed from left to right (or vice versa). Stonework is often imitated.
- Horizontal. The main type, the panels are horizontal and fastened from bottom to top. The main imitation is wood.
NOTE!
Notable is the fact that facade types of siding, as a rule, imitate walls made of wood - timber, logs, ship planks, while basement types predominantly imitate stone (or brick) masonry.
The most important division of material is the type of material.
Today there are samples from the following materials:
- Wood.
- Metal.
- Plastic.
- Fiber cement.
At the same time, all materials have their own subtypes - for example, wooden siding can be made from pressed or stabilized wood, plastic siding has acrylic , etc. All properties of panels of the same type are usually the same, which gives reason to talk about them as a single group.
How to determine a load-bearing wall in a panel house
Have questions? Consult a lawyer (free of charge, 24 hours a day, seven days a week):
8 Moscow and Moscow region.
8 St. Petersburg and Len. region
Many owners of apartments in panel houses dream of redevelopment to expand the space and more rational use of the living area. But not everyone knows what actions can or cannot be performed during such a procedure. For example, it is prohibited to demolish load-bearing walls in panel houses (and not only in them). The main issues relating to the redevelopment of an apartment in such a building will be discussed further.
What is the standard ceiling height in panel houses?
Home / Features of various premises / Panel house - what is the standard ceiling height?
The most noticeable and significant difference between panel houses is the method of their construction. They consist of separate blocks, which are commonly called panels. Such panels are manufactured in factories, and the height of the ceilings in the panel house depends on the dimensions of the panels.
Different series of houses
The sizes of apartments and blocks from which houses were built or are being built depend on the series of the project. There are quite a lot of such series and they all have different vertical dimensions of the premises. It is customary to divide standard houses into several main types, which differ in the arrangement of the area inside and height characteristics:
- "Khrushchevka". One of the most common houses until recently. Now, such buildings are gradually being demolished due to the end of their service life. The distance from floor to ceiling in such houses is one of the smallest and is equal to 248 centimeters.
- "Improvements." A slightly larger area of the rooms and their different location on the landing - that’s all their differences from the previous ones. The walls in the apartments are also small - 255 cm.
- Standard "nine-story buildings". Apartments are the most common type. The area is different, and the distance to the ceiling is 2 meters 64 centimeters.
- Houses 606, as well as the P-44K series. The more comfortable and vertical dimensions of the walls here are also larger - 2 meters 70 centimeters. Very popular houses precisely because of the high rooms.
- Modern 137 series. The most spacious among the rooms with a typical layout. The standard ceiling height in such a panel house reaches 2.8 meters, or 270 in houses built quite a long time ago.
Now, when buying or choosing an option for exchange, people tend to choose something more comfortable and ignore old houses. However, on the secondary housing market you can find examples of all modifications and years of construction. So, when choosing your future home, you can also choose how spacious the rooms will be.
Defining Changes
Redevelopment is a change in the configuration of a room. The Housing Code of the Russian Federation stipulates that any changes to the apartment must be reflected in the technical passport and approved by government agencies. Redevelopment is considered to be: moving window and door openings, changing walls (supporting and partitions), dividing space, moving the kitchen and bathroom.
Typically, apartment owners limit themselves to removing interior partitions to expand the living area.
Important: This procedure must be clearly planned in order to maintain the supporting structures in an unchanged condition. If you make a mistake and remove the load-bearing plane, the apartments located below may suffer: without support, the ceilings may collapse.
The concept of a “load-bearing wall”
From an architectural point of view, the planes in the building are divided into 2 types:
- Load-bearing walls (NS). These vertical structures are made in such a way that they can withstand significant weight. The reliability of the entire building depends on the quality of such a wall.
- Partitions. They serve to divide the room into zones. They are not subject to significant loads, but they must withstand some weight.
The homeowner has the right to change or demolish only partitions; any impact on the supporting structure is prohibited. If the owner decides to make changes to the Tax Code, he must obtain permission from the relevant institutions. Such paper is provided only after detailed calculations have been made and with reservations. After an unplanned opening has been made in the plane, it must be strengthened so that these supports are replaced and are not inferior in strength to the removed element.
Advice: If the owner arbitrarily made changes to the load-bearing block, considering contacting the housing inspection unnecessary and unimportant, he may encounter a number of problems when selling, privatizing, donating or exchanging housing.
Housing inspection specialists will apply penalties to such a citizen and require him to return the original structure at his own expense. In rare situations, such redevelopment can be legalized, but payment of a fine is required in any case.
Technology for dismantling a load-bearing wall in a Khrushchev building
Options for dismantling load-bearing fencing in Khrushchev and other panel houses are carried out in two ways. For more information on how walls are dismantled in Khrushchev-era buildings, watch this video:
Inserting a load-bearing beam
After receiving permits, the following work begins:
- If load-bearing fences are adjacent to the walls on the sides, then in their upper parts under the floor slabs, recesses are made (the masonry or concrete is cut out with a jackhammer).
- The lower plane of the cutout must correspond to the calculated supporting area of the crossbar. The beam design must meet the project requirements.
- The crossbar is inserted into the side openings. The crossbar can be reinforced concrete or made of a metal I-beam with stiffening ribs.
- Metal wedges are driven into the support areas of the beam in order to obtain maximum expansion. This achieves a smooth transition of the upper load from the wall to the beam.
- They begin to dismantle the masonry or remove the concrete with a jackhammer.
- The reinforcement is cut with an abrasive wheel.
- After dismantling the walls, the trash is taken out and finishing work begins.
Installation of vertical supports
Instead of a load-bearing fence, support columns are installed in the corners of the room. To ensure that the process of transferring the load from the wall smoothly moves to the supporting platforms of the columns, jacks in the form of hydraulic racks are used. Such jacks can be rented from a construction company. For more information on how to make an opening in a load-bearing wall, watch this video:
The order of work is as follows:
- jacks in an amount corresponding to the upper floor slabs are placed on both sides of the wall;
- The hydraulic racks rest their upper platforms against the floor slabs. The load smoothly flows onto the shoulders of the jacks;
- dismantle the fence;
- install supports in the form of columns; support platforms are located in the middle of the joining seams of the slabs;
- in case of a large span of flooring, a beam is laid on the columns.
In order to ensure safety measures, professionals who have documents confirming their qualification level are allowed to perform this type of work.
Before construction begins, the required wall thickness must be determined and the type of masonry and material selected. Solving these issues can baffle any novice builder, given the huge selection of materials and the availability of all kinds of masonry methods.
The most important point when choosing wall thickness is the economic rationale. In order to accurately calculate sufficient wall thickness parameters, you should determine the parameters of the future structure, heated area, estimated service life, mode of residence, type and efficiency of the heating system.
The main method for determining NS
The main and unmistakable way to determine which walls are load-bearing in a panel house is to study the technical passport or building design. To do this, you need to contact the executive committee, where the Capital Construction Department is located. As a rule, you do not even need to write an application - the interested person will be provided with a constructive plan, from which they can make a copy for more detailed study. The registration certificate for the apartment also indicates the location of load-bearing walls and partitions.
Related article: How to drill a hole in a concrete wall with a drill
But in this case, you will need the ability to read construction documentation. If problems arise with the technical method, you can use indirect methods to determine the load-bearing wall in a panel house.
Determination by location of vertical structure
NS are usually located at right angles to the floor beams. If the floor is made of concrete slabs, then their ends should lie on the supporting structure. Basically, these are external, inter-apartment and inter-block walls.
The base of the room (its box) is surrounded by supporting planes. These include:
- External walls facing the street (yard). Some people mistakenly believe that the walls in the yard are not supporting - this is a big misconception.
- Structures that enclose the apartment from the staircase and elevator space.
- Walls between neighboring apartments. But we cannot confidently assume that the interior planes are partitions. In some panel houses with 5 floors, load-bearing walls are even located between rooms.
Partitions cannot serve as an accurate guide. A person who is not a specialist in this field will not be able to accurately determine the NS without dismantling the coating.
Orientation to the thickness of the vertical plane
This method is the most reliable besides studying technical documentation. But, after taking measurements, you need to determine their value. In a brick house, if the thickness of the structure is 38 cm, this means that it is supporting. In this case, you don’t even need a tape measure: 3 bricks (add seams) serve as a guide. The partitions are made 1-2 bricks thick.
In panel houses, the approach is more complex. As a rule, the PS can be built with a thickness of 14 cm. But you can also find options of 16, 18, 20 cm. The partitions are made at 8-10 cm. This applies to load-bearing walls in panel houses with 9 floors. But this method should be used very carefully. For example, in some old Khrushchev-era buildings, the NS are built only 12 cm deep. In this case, only the use of a structural plan is the correct solution to the problem. Sometimes the plane can be a reinforced partition for sound insulation purposes.
In block houses, NS are usually made in 20-centimeter or greater thickness. But even here there are some nuances: some buildings do not have such planes at all, and sometimes such thickness is found in partitions.
Important to know: When taking measurements of the structure, you should take into account only the thickness of the main building material.
Finishing layers (plasterboard, tiles, plaster) should not be taken into account. The most accurate measurement is considered to be measuring the plane after dismantling all surface coatings to the very base.
Vinyl siding sizes
Vinyl panels are most in demand among users. The reasons for this were the relative cheapness, ease and simplicity of installation work . The disadvantages of this type are the fragility of the material when frozen and a high coefficient of thermal expansion.
At the same time, the specifics of use make it possible to put up with such disadvantages, and the high level of wood imitation - there are panels for timber, logs, bricks, herringbone or shiplap - creates an excellent appearance for the finished house.
The sizes of siding panels may have some differences from each other depending on the manufacturer, the average values are as follows:
- Thickness - 0.7-1.2 mm.
- Length - 2.5-3.8 m.
- Width - 0.2-0.3 m.
- Weight - 1.5-2 kg/panel.
- Profile thickness - 12-40 mm.
Single, double or triple panels are available, marked S, D or T respectively . The numbers next to them indicate the width in inches.
Metal
Metal cladding is unanimously recognized by experts as the most durable and stable, but high prices (on average, twice as high as vinyl) significantly reduce demand.
In general, metal and vinyl samples have very similar parameters both in terms of profile and panel sizes, since vinyl initially simply duplicated metal panels.
Dimensions:
- Length up to 8 m.
- Width - 22-36 cm.
- Thickness -0.5-1.1 mm.
- Weight - 4-5 kg/sq.m.
Tsokolny
Basement panels (sometimes called façade panels, which introduces confusion and discrepancies) were originally intended for contrasting cladding of the lower part of the house, but quite soon they turned into a specific finishing product for both external and internal work.
Aesthetically, this type of material can compete with any wall samples, and the shape of the panels makes installation somewhat easier . Both metal and vinyl types of basement siding are available, although initially it was all metal.
Main Dimensions:
- Length - 0.79-1.25 m.
- Width - 0.45-0.59 m.
- Thickness - 1-3 mm.
- Profile height - 26 mm.
- Weight - 1.8-2.5 kg/panel.
Ceramic
Ceramic siding came to Russia quite recently from Japan, where it has been successfully used for about 50 years. The material has a porous structure, based on a cement composite that has been hardened in a furnace.
The service life declared by the manufacturers is about 30 years. The panels are of high quality, but the prices for this type of cladding are 4-8 times higher than for other types, so in practice the use of ceramic samples is greatly limited .
There are various imitation options - all types of stone, brick, wood. The installation of such material has its own specifics and is considered quite complex and is not recommended for independent implementation. Particular problems are expected during installation work on upper floors, mainly due to the high weight of the panels.
Panel options:
- Length - 3 m.
- Width - 45-91 cm.
- Thickness - 14 mm.
- Weight - 18-20 kg/sq.m.
Ceramic siding is a new product, so there are no broad reviews about it yet, and statistics on its use in Russian climatic conditions have not been collected.
Cement
Cement (fiber cement) panels are a type of ceramic, but with some difference in manufacturing technology. The composition of fiber cement panels is sand, cement, water and cellulose fibers as a reinforcing additive .
The material is very similar to ceramic samples and has almost identical properties. At the same time, there is a somewhat more meager choice of form - fiber cement panels are presented mainly in the form of narrow oblong panels for horizontal installation, designed in the form of wooden boards (surface relief).
Dimensions:
- Length - 3.6 m.
- Width - 19 cm.
- Thickness - 10 mm.
- Weight - 10 kg/panel.
The demand for fiber cement siding is relatively low, the reason for this, most likely, is the lack of awareness of users about this type of cladding . However, we can predict low demand due to the too high price of the material, forcing us to look for more acceptable options.
Wooden
Wooden (Canadian) siding is the progenitor of all currently existing types . Siding was originally invented in Canada and was made from wood (hence the surviving name wood siding) .
Today, wood siding is panels made of pressed (stabilized) wood that has undergone a special treatment that stops the processes of shrinkage or build-up of stress in the material. Wood siding has several profile options and connection methods - from traditional lining to overlapping.
The material is quite capricious, prone to mold, various insects grow in it, etc. Requires a protective layer of paint, which must be renewed periodically . The material's requirement for constant maintenance and the significant difference in prices depending on the type of wood are the weaknesses of wooden panels.
In addition, wood siding is flammable, which reduces its competitiveness in the finishing materials market.
Dimensions:
- Length - 3.5-5.5 m.
- Width - 14 cm.
- Thickness - 15-40 mm.
IMPORTANT!
The dimensions of wooden siding can vary greatly depending on the manufacturer's conditions. Experts recommend using wooden panels with a thickness of no more than 20 mm and a maximum width of 14 cm. This restriction is aimed at reducing the risk of warping of the material, which, despite all measures taken, is a common disease of wood cladding.
Steel (aluminum)
Steel (galvanized) siding has high strength and corrosion resistance . Its performance qualities give reason to classify it as one of the most stable and durable types of cladding, but the picture is somewhat spoiled by its higher cost .
Nevertheless, there is a certain demand for this material, and the recommendations of professionals also find their audience, so the demand for this type of panels is quite stable.
Aluminum panels are much more expensive, which greatly reduces their practical use . For a private owner, such prices are too high; it is mainly used for public or commercial buildings.
Dimensions:
- Length - 0.5-6 m (galvanized), up to 6 m (aluminum).
- Width - 20.25 and 30 cm.
- Thickness - 1 mm (steel), 0.5-0.6 mm (aluminum).
- Weight - 2.4-3.5 kg/sq.m. (aluminum), up to 10 kg/sq.m. (steel).
NOTE!
Metal siding deserves more attention among consumers, but the need to save money sharply reduces demand, negating the positive qualities of the material.
What is needed to change a wall
Before changing (demolition, moving, etc.) any structure in the apartment, you must consult with a qualified specialist. It is also necessary to perform a full calculation that takes into account the distribution of loads after changes are made. In some cases it is necessary to change the electrical circuit. The redevelopment project must be approved by the government agency responsible for the architecture of the building. For approval you must:
- The plan developed by the BTI service is precisely for this type of redevelopment.
- A technical report was drawn up for changing the wall.
- Availability of a positive decision from the housing inspection at the place of residence.
When planning a major renovation of an apartment, the owner, first of all, should know whether he has the right to make changes to the premises without permission from the relevant housing authorities. In exceptional cases, the housing inspectorate may grant permission for such work. But in any case, it is better to order a professional engineering survey to make a decision whether it is worth changing the design or not.