Reinforced concrete beam structures are one of the common forms of supports for the further installation of floor slabs. They effectively distribute the load from floors to load-bearing walls, are durable and reliable. Despite the advantages, there are also disadvantages: heavy weight compared to other materials, and a certain complexity of installation, which requires the use of special equipment, despite the simplicity of installation operations.
Main characteristics
The following requirements apply to reinforced concrete floor beams:
- Strength (for residential buildings, the product must withstand a load of 105 kg/m2 for attic structures, and 210 kg/m2 for interfloor and basement floors).
- Rigidity (the rigidity of interfloor ceilings should be 1/250, for attic floors - 1/200).
- Sound and heat insulation.
The issue of thermal insulation of reinforced concrete beams is considered separately. Regulatory documentation establishes that thermal insulation is required for elements that are used in adjacent rooms, where the temperature difference can be more than 10 degrees (for example, when a beam extends outside the room, forming a support for a canopy). In each individual case, the filling of the interbeam openings is selected, depending on the requirements for the structure being built. If necessary, beams can be covered.
Production
Standard products are manufactured using reinforced concrete products, non-standard structures are cast at construction sites on the ground, next to the construction site (for example, floors for road structures). Manufacturers usually offer a full range of reinforced concrete products, which include certain elements: beams, floor slabs, supports. It is advisable to use products from one manufacturer during construction, since GOST allows a number of deviations from the basic dimensions.
GOST 20372-90 “Reinforced concrete rafter and rafter beams” divides products in this category into the following types:
- BSP - rafters with parallel chords (regular single- or I-beam shape).
- BSO - the same, single-pitched (with a reduced longitudinal part in relation to the supports).
- BSD - the same, gable (various types of slopes of the longitudinal part).
- BP – rafter (beam of rectangular, trapezoidal cross-section, or I-beam gable structure).
In total, GOST establishes 16 types of beams. The longest standard length of the product is 12 m and 18 m. Previously, Soviet regulatory documentation divided all elements into series. This designation is still used today, although some of the series have long lost their relevance - most of the standards were canceled in the early 90s, with the introduction of new GOSTs.
For private construction, you can make small reinforced concrete floor beams with your own hands. To do this, make the following calculation:
- The minimum height of the product is 5% of the opening length (for an opening of 6 m, the calculation is as follows: 6x0.05 = 0.3 m)
- The width is calculated from the proportion 5:7 in relation to the width to height (we found the height to be 0.3, (5:7)x0.3=0.214 m).
- The reinforcement is carried out in 4 rows with 12-14 mm reinforcement - according to the scheme, two rods on top, two rods on the bottom.
- Pouring the product with concrete mixture is carried out in one step, without interrupting the casting process.
Installation and prices of reinforced concrete beams
Reinforced concrete beams are used for spans of 3,000-7,500 mm; installation is simple: they are laid on supporting structures in increments of 1,000-1,500 mm. The required thickness of the support body is from 220 mm. After installing the beam frame, floor slabs are installed on it, and the products are fastened together with reinforcement.
Standard reinforced concrete products of large sizes (12 m) cost, on average, 50,000 - 60,000 and more (for an 18 m product they can ask for as much as 200,000 rubles). Smaller sizes mean lower prices. Approximately, today, the price can be determined in rubles per meter of beam as 5,000 - 7,000 per 1 meter, without installation. Although the prices of a particular manufacturer are influenced by a number of factors: quality of concrete, quality of casting, complexity of design, delivery.
Alternative
Instead of reinforced concrete beams, you can use other types of supports for the floor or ceiling. In single-story residential construction, wood and ceramic floors are used (both types save energy on heating, lose less heat, are lighter, but less durable). But they require some preparation before installation or additional work after installation.
For industrial facilities (workshops, warehouses, garages), you can use metal T-section beams instead of reinforced concrete ones. This option is characterized by increased strength, greater ease of installation, and is used where there are no strict requirements for saving heat, or in buildings that do not require heating. Overlapping with metal beams greatly speeds up construction time: installation is not expensive, it is quickly installed, and does not delay further work. Although the price of the material is more expensive.
| Articles |
In modern construction, it is necessary to purchase high-quality building materials, with the help of which you can quickly build any structure. It is equally important that the specialist knows the features of a particular construction. This applies to reinforced concrete floor beams, which can serve for a long time and are the load-bearing basis of the building.
Reinforced concrete floor beams - definition and purpose
type of reinforced concrete floor beams
The structure of reinforced concrete beams is considered the most common form of supports on which floor slabs are installed. With their help, you can correctly, and most importantly, evenly distribute the load, which will make the structure durable and reliable. Today in modern construction it is common to use monolithic reinforced concrete beams. Slabs of various shapes and sizes can be laid on such beams: smooth, ribbed, often ribbed. However, they may be too heavy. That is why they are recommended to be installed on large construction sites.
At the same time, we should not forget that monolithic reinforced concrete beams are quite difficult to install using multi-ton cranes. In this case, you can additionally use special equipment, which will allow you to complete construction more quickly and with sufficient quality.
During construction, special attention should be paid to load-bearing beams, since they will bear the maximum load. One of the main characteristics of beams is the load-bearing capacity of reinforced concrete beams, on which the size of the object and its strength depend.
Reinforced concrete floor beams: dimensions, GOST standards, production
Reinforced concrete floor beams: dimensions, GOST standards, production
The following advantages of reinforced concrete beams can be highlighted:
- Strength - if properly selected or manufactured, such a beam is stronger than a wooden one;
- Fire resistance – concrete is not a flammable material;
- Rigidity – the ability to cover large spans without deflection or vibration;
- Resistance to moisture - especially important when installing floors over rooms with high humidity.
The disadvantages include:
- Relatively large weight means a higher load on the walls, and a lifting mechanism or machine (crane) is required for loading and installation.
- Higher thermal conductivity compared to wood products;
- Higher cost, especially of finished products made using reinforced concrete.
Regardless of whether you use ready-made reinforced concrete beams or make them yourself, you need to decide on their dimensions. In this case, you can focus on the following indicators:
- Their length (L) must be such that their edges (supporting parts) extend onto the load-bearing walls by at least 20 cm, that is, they must be longer than the span being covered, by at least 0.4 m;
- The height (H) must be at least 1/20 (5%) of the length;
- The recommended width (B) should be in a ratio of 5:7 to the height.
So, for example, for a span of 6 m, reinforced concrete floor beams of the following dimensions will be required: length 6.4 m, height 0.30 m and width 0.214 m.
If you use ready-made beams made in industrial conditions (at reinforced concrete structures or other enterprises), then it is enough to know the required length and purpose of the floor (basement, interfloor, attic). As a rule, at enterprises that manufacture such beams there is a certain assortment from which you will have to choose. They are manufactured in accordance with GOST 24893.1-81, 24893.2-81 and 20372-90.
Ready-made reinforced concrete floor beams can be of different types, sections and purposes.
According to the shape and type of section they can be:
- Rectangular;
- Trapezoidal;
- I-beam;
- T- or L-shaped;
- full or hollow.
In addition, for reinforced concrete frequently ribbed floors, special beams are made that have a rectangular reinforced concrete base and a dividing rib made of reinforcement. They differ from those discussed above not only in shape, but also in their relatively low weight. They can be mounted even without lifting mechanisms, manually. After installation, the space between such beams is filled with special hollow concrete or aerated concrete blocks (see video).
When choosing, you must remember that for interfloor ceilings you need products that can withstand a load of at least 205 kg/m2 with a hardness of at least 1/250, and for attic floors - at least 105 kg/m2 with a hardness of 1/200.
In some cases, there is a need or desire to make such reinforced concrete beams with your own hands. In order to do this, it is necessary to make formwork for them. The easiest way to do this is from wooden boards. 25-40 mm thick or plywood (10-20 mm). The shape and internal dimensions of the formwork must correspond to the shape and dimensions of the future beam, calculated in accordance with the recommendations given above. The inside of the formwork is covered with polyethylene film or other waterproofing material.
In addition, when making your own, you must follow the following rules:
- It is necessary to perform reinforcement using 4 reinforcement bars with a diameter of 12-14 mm;
- It is best if the reinforcement is done in whole pieces of reinforcement. But if, nevertheless, there is a need for mating, then it is necessary to make an overlap of at least 80 cm, followed by a connection with a knitting wire;
- The reinforcement must be installed so as to ensure its complete coverage with concrete, a layer of at least 5 cm - to protect against corrosion. To do this, you can use special plastic or homemade stands;
- Concrete for pouring must be of high quality, not lower than grade 300;
- The volume of concrete must be calculated so that it is poured in one go, without interruptions;
- After pouring the concrete, the structure must be covered with waterproofing material;
- In hot and dry weather, concrete must be watered periodically (once a day);
- The concrete should “mature” within one to two weeks.
Reinforced concrete beams made in this way can also be used to cover window or door openings, especially if they are large.
https://www.postroj-dom.ru
legkoe-delo.ru
Calculation of the Section of a Reinforced Concrete Beam
To calculate the section of a reinforced concrete beam, it is necessary to determine the height of the section of the beam, and then its width. In this regard, you can use a calculation scheme, the conditions of which include all the parameters for this construction.
The algorithm for calculating the bearing capacity consists of several stages, namely, determining the span of the beam, calculating the strength characteristics of the reinforced concrete beam, determining the relative height of the beam, determining the height of the concrete zone, calculating the moment value (maximum) and calculating the load (bearing capacity). Since the load-bearing reinforced concrete beam is the main support of any building, such characteristics will help to choose its optimal number of storeys.
Beams must be installed together with the walls, correctly forming the future structure. In the beam itself, as a rule, parts are placed along the upper chord, which will make it more durable and reliable. It is recommended to entrust the calculation of the cross-section of a reinforced concrete beam to specialists who know the strength of materials and have experience.
Reinforced concrete floor beams
In modern construction, it is necessary to purchase high-quality building materials, with the help of which you can quickly build any structure. It is equally important that the specialist knows the features of a particular construction. This applies to reinforced concrete floor beams, which can serve for a long time and are the load-bearing basis of the building.
Reinforced concrete floor beams - definition and purpose
The structure of reinforced concrete beams is considered the most common form of supports on which floor slabs are installed. With their help, you can correctly, and most importantly, evenly distribute the load, which will make the structure durable and reliable. Today in modern construction it is common to use monolithic reinforced concrete floor beams. Slabs of various shapes and sizes can be laid on such beams: smooth, ribbed, often ribbed. However, they may be too heavy. That is why they are recommended to be installed on large construction sites. At the same time, we should not forget that monolithic reinforced concrete beams are quite difficult to install using multi-ton cranes. In this case, you can additionally use special equipment, which will allow you to complete construction more quickly and with sufficient quality.
During construction, special attention should be paid to load-bearing beams, since they will bear the maximum load. One of the main characteristics of beams is the load-bearing capacity of reinforced concrete beams, on which the size of the object and its strength depend. The algorithm for calculating the bearing capacity consists of several stages, namely:
- determining the beam span,
- calculating the strength characteristics of reinforced concrete beams,
- determining the relative height of the beam,
- determining the height of the concrete zone,
- calculating the torque value (maximum),
- calculation of load (bearing capacity).
Since the load-bearing reinforced concrete beam is the main support of any building, such characteristics will help to choose its optimal number of storeys.
Calculation of the section of a reinforced concrete beam
To calculate the section of a reinforced concrete beam, it is necessary to determine the height of the section of the beam, and then its width. In this regard, you can use a calculation scheme, the conditions of which include all the parameters for this construction. Beams must be installed together with the walls, correctly forming the future structure. In the beam itself, as a rule, parts are placed along the upper chord, which will make it more durable and reliable. It is recommended to entrust the calculation of the cross-section of a reinforced concrete beam to specialists who know the strength of materials and have experience.
Cost and price of reinforced concrete beams
The cost of reinforced concrete beams depends on the quality of the material, as well as the length of the beam. Companies that sell such products offer their customers wholesale purchases of this building material, which significantly reduces their cost. When purchasing reinforced concrete beams, you can use the delivery service of the selected material for construction. Often the cost of beams already includes delivery along with loading and unloading. It is necessary to clarify the price of such building materials immediately before purchasing.
GOST and dimensions
It does not matter where exactly reinforced concrete beams are used. It is important that their size fully complies with GOST. That is why the future design will be used as a reliable object. It is necessary to take into account certain standards that are put forward for such building materials. The length of the reinforced concrete beams should be such that their edge does not overlap the main load-bearing wall. It is not advisable to purchase beams that are too long. Their height should, according to GOST, be a certain percentage of the length (5%). The width of the beam is related to the height in the following proportion: 5 to 7. The best option for reinforced concrete beams could be floor slabs 6 meters long with a width of 0.2 meters and a height of 0.3 meters. The choice of reinforced concrete beams should be based on the type of structure: attic, basement or interfloor.
Series and marking
Currently, all reinforced concrete beams have their own markings and a certain series, which necessarily depends on GOST. Thus, in construction, rectangular profiles are often used, which are marked in the form of the letter R. Single-ceiling reinforced concrete beams will have a different marking using two letters - RO. Double-ceiling beams are marked - RD. Marking in the form of RB indicates the ceiling-free use of reinforced concrete beams. The marking of reinforced concrete beams that are used to create a balcony consists of RCP symbols. Additional characteristics that may be indicated in the designation of a reinforced concrete beam include design features, resistance to the external environment, and seismic resistance.
Main characteristics
Modern reinforced concrete beams have their own distinctive features, which are based on the type of product, its shape, as well as its size. Today, beams made of reinforced concrete rafter type, fundamental plan, are popular in construction. Reinforced concrete beams are fire-resistant, durable, practical, and easy to install.
Types and types of reinforced concrete beams
Classification of reinforced concrete beams is carried out based on the following criteria: column spacing, span width, building type. There are rectangular, trapezoidal, T-shaped, I-beam and hollow beams. Interfloor reinforced concrete beams and T-beams are in great demand in construction. When installing interfloor beams, the load is evenly distributed across the floor slabs, thereby providing a flat surface. It is advisable to choose a rectangular product shape for such beams.
When choosing T-beams, it is best to make a flat or pitched roof. This will result in reliability, practicality and durability of the entire structure. High-quality I-beams can be purchased in specialized stores or warehouses. Beams for floor slabs can be of various types. In the construction of large industrial enterprises, rectangular or trapezoid beams are used. This form makes it possible to fasten the floor slab without much difficulty, while ensuring the reliability of the entire structure.
Assembly and installation of reinforced concrete beams
Installation and installation of reinforced concrete beams is a job that specialists do well. After all, they know the specifics of constructing buildings using specific building materials. Preparation for installation consists of applying axial marks with paint and cleaning the embedded parts. Typically, their installation is carried out in a “suspended” manner using cranes. Reinforced concrete beams are lifted by mounting loops using ordinary slings or using a “noose”, which is made on both sides of the beam. The size of the slings is selected depending on the length of the beam. Reinforced concrete beams are secured to sub-rafters and columns. By properly installing load-bearing beams, structural strength can be achieved. When installing reinforced concrete beams, you must remember that the entire structure must be sufficiently strong, fire-resistant, practical, and durable.
We have:
Mortar for construction
Review of materials for wall construction
Foundation "Pillar Crossbar"
How to choose an electric stove for a bath or sauna
Acoustic comfort made easy
GOST and dimensions
It does not matter where exactly reinforced concrete beams are used. It is important that their size fully complies with GOST. That is why the future design will be used as a reliable object. It is necessary to take into account certain standards that are put forward for such building materials. The length of the reinforced concrete beams should be such that their edge does not overlap the main load-bearing wall.
It is not advisable to purchase beams that are too long. Their height should, according to GOST, be a certain percentage of the length (5%). The width of the beam is related to the height in the following proportion: 5 to 7. The best option for reinforced concrete beams could be floor slabs 6 meters long with a width of 0.2 meters and a height of 0.3 meters. The choice of reinforced concrete beams should be based on the type of structure: attic, basement or interfloor.
Series and marking
Currently, all reinforced concrete beams have their own markings and a certain series, which necessarily depends on GOST. Thus, in construction, rectangular profiles are often used, which are marked in the form of the letter R. Single-ceiling reinforced concrete beams will have a different marking using two letters - RO.
Double-flange beams are marked - RD. Marking in the form of RB indicates the use of reinforced concrete beams without flanges. The marking of reinforced concrete beams that are used to create a balcony consists of RCP symbols. Additional characteristics that may be indicated in the designation of a reinforced concrete beam include design features, resistance to the external environment, and seismic resistance.
Main characteristics
Modern reinforced concrete beams have their own distinctive features, which are based on the type of product, its shape, as well as its size. Today, beams made of reinforced concrete rafter type, fundamental plan, are popular in construction. Reinforced concrete beams are fire-resistant, durable, practical, and easy to install.
Types and types of reinforced concrete beams
Classification of reinforced concrete beams is carried out based on the following criteria: column spacing, span width, building type. There are rectangular, trapezoidal, T-shaped, I-beam and hollow beams. Interfloor reinforced concrete beams and T-beams are in great demand in construction. When installing interfloor beams, the load is evenly distributed across the floor slabs, thereby providing a flat surface. It is advisable to choose a rectangular product shape for such beams.
When choosing T-beams, it is best to make a flat or pitched roof. This will result in reliability, practicality and durability of the entire structure. High-quality I-beams can be purchased in specialized stores or warehouses. Beams for floor slabs can be of various types. In the construction of large industrial enterprises, rectangular or trapezoid beams are used. This form makes it possible to fasten the floor slab without much difficulty, while ensuring the reliability of the entire structure.
Assembly and installation of reinforced concrete beams
Installation of reinforced concrete beams is a job that should be done by specialists. After all, they know the specifics of constructing buildings using specific building materials. Preparation for installation consists of applying axial marks with paint and cleaning the embedded parts. Typically, their installation is carried out in a “suspended” manner using cranes.
Reinforced concrete beams are lifted by mounting loops using ordinary slings or using a “noose”, which is made on both sides of the beam. The size of the slings is selected depending on the length of the beam. Reinforced concrete beams are secured to sub-rafters and columns. By properly installing load-bearing beams, structural strength can be achieved. When installing reinforced concrete beams, you must remember that the entire structure must be sufficiently strong, fire-resistant, practical, and durable.
Cost and price
The cost of reinforced concrete beams depends on the quality of the material, as well as the length of the beam. Companies that sell such products offer their customers wholesale purchases of this building material, which significantly reduces their cost. When purchasing reinforced concrete beams, you can use the delivery service of the selected material for construction. Often the cost of beams already includes delivery along with loading and unloading. It is necessary to clarify the price of such building materials immediately before purchasing.
In modern construction, in order for a structure or structure to withstand high values of tensile loads, as well as bending moments, reinforced concrete beams are used. These products are used in the construction of foundations and floors. According to the production method, reinforced concrete beams are divided into two groups: prefabricated and monolithic. Prefabricated ones are manufactured in factories, while monolithic ones are manufactured directly on the construction site.
It is advisable to make reinforced concrete floor beams with your own hands due to the availability of the necessary building materials and the simplicity of the technology. By making beams yourself, you can get a product of the required dimensions, because it is not always possible to order a crossbar with the required parameters. The cost of homemade beams is an order of magnitude lower than factory ones.
Dimensions of reinforced concrete floor beams for a private house
Regardless of whether you use ready-made reinforced concrete beams or make them yourself, you need to decide on their dimensions. In this case, you can focus on the following indicators:
Performance quality control can be performed under optimal conditions. strength of concrete materials and reduce the weight of elements. The main disadvantage of using prefabricated beams is the difficulty of implementing instantaneous connections between elements in conditions where, as a rule, there is no continuity of longitudinal reinforcement. The weights and dimensions of prefabricated elements must be set so that they correspond to the maximum permissible sensors for transport and handling.
An example of the response of a reinforced concrete beam is a monotonic load with vertical loads. The beam is simply hinged to the ends and loaded by two equal forces, symmetrically located with respect to the medial portion of the beam. In the central region, the beam is required for pure bending. In the extreme areas between supports and points of application of loads, bending force is required. This loading scheme is often used to decipher the flexural response of reinforced concrete elements without the influence of cutting forces.
- Their length (L) must be such that their edges (supporting parts) extend onto the load-bearing walls by at least 20 cm, that is, they must be longer than the span being covered, by at least 0.4 m;
- The height (H) must be at least 1/20 (5%) of the length;
- The recommended width (B) should be in a ratio of 5:7 to the height.
So, for example, for a span of 6 m, reinforced concrete floor beams of the following dimensions will be required: length 6.4 m, height 0.30 m and width 0.214 m.
Especially when low-permeability steel was used for reinforcement. The compressed concrete area migrates from the top to the center of the section as the maximally compressed concrete fibers collapse. At low loading, the concrete is not painted, and the reinforcement reacts in an elastic field. reducing the overall stiffness of the element. that the first cracks caused by bending are formed. the final deformation is significantly higher than at the beginning of the flow. With a specific increase in the deformation of the expanded reinforcement, an increase in deformations in the compressed concrete is recorded.
Horizontal cracks caused by sliding of longitudinal reinforcement can occur in areas at the ends of the beam. In the case of beams, where the influence of the cutting force is important, cutting may occur. for the item in question. The cutting force is brittle. This migration of the compressed region results in a decrease in internal deformation lever arm and flexural strength. the beam also has normal cracks on the beam axis. without warning. which breaks. before the flow from the bending moment. Edge cracks, caused by the combined action of bending moment and cutting force, occur in the edge regions.
If you use ready-made beams made in industrial conditions (at reinforced concrete structures or other enterprises), then it is enough to know the required length and purpose of the floor (basement, interfloor, attic). As a rule, at enterprises that manufacture such beams there is a certain assortment from which you will have to choose. They are manufactured in accordance with GOST 24893.1-81, 24893.2-81 and 20372-90.
During this time. associated with the sliding of reinforcement in concrete after a strong flow from tension. cracking of reinforced concrete beams. An increase in the possible torque of the beam cross-section leads to the emergence of forces that load the beam upon rupture. This causes the compacted concrete to be reduced to the last fiber. In some situations. which predominantly responds to bending. If the charge increases. normal on the axis of the rod. This increases the cutting force and destroys diagonal cracks that start at the load points and are directed towards the bearing areas. the specific deformation of the expanded reinforcement increases. reaching flow deformation near cracks in the zone of maximum torque. caused by bending moment.
Ready-made reinforced concrete floor beams can be of different types, sections and purposes.
According to the shape and type of section they can be:
- Rectangular;
- Trapezoidal;
- I-beam;
- T- or L-shaped;
- full or hollow.
Increasing the load causes the final concrete deformation to reach the elongated concrete. That's noticeable. has high ductility. After the flow of longitudinal reinforcements. it is possible to damage the expanded reinforcement. From the above representations it can be seen that this is a long beam. For example.
Longitudinal longitudinal cracks form along the expanded longitudinal reinforcement. if the cross-sectional height of the beam increases, an element is obtained that is sensitive to the action of cutting force. the applied load value remains virtually constant until the element breaks. The laws of displacement of forces for two elements are presented comparatively in the following figure.
In addition, for reinforced concrete frequently ribbed floors, special beams are made that have a rectangular reinforced concrete base and a dividing rib made of reinforcement. They differ from those discussed above not only in shape, but also in their relatively low weight. They can be mounted even without lifting mechanisms, manually. After installation, the space between such beams is filled with special hollow concrete or aerated concrete blocks (see video).
Ratios for calculating moments of positive or negative moments: where. Once the block width layout is set. They can be calculated using specific calculation methods for the studied beams in Construction Statics. These decisions can be time-consuming, in part due to the large number of assumptions made about loading variables. Limit equilibrium method for gravitational loads.
Equal to concrete in the immediate vicinity. For manual calculation of epochs. The tensile strength of concrete is negligible, unitary forces in reinforcement and concrete can be determined on the basis of compressive or tensile compressive strengths. only the reinforcement at the ends of the section can be considered simplified, and the stress block in the compressed region can be considered rectangular.
When choosing, you must remember that for interfloor ceilings you need products that can withstand a load of at least 205 kg/m2 with a hardness of at least 1/250, and for attic floors - at least 105 kg/m2 with a hardness of 1/200.
Reinforced concrete floor beams between floors - characteristics of structures
The most significant advantage of crossbars is their strength, rigidity and reliability, because if all technologies for the manufacture of reinforced concrete are followed, it turns out to be very strong. Another advantage of this material is its durability. Reinforced concrete beams do not corrode or rot, which significantly extends their service life. They are also fire resistant. Such beams can cover fairly long spans.
The weight of these products is a disadvantage, since it complicates their installation and transportation, and will also require additional calculations of the strength of the foundation before starting construction. Reinforced concrete beams are not used to cover wooden or frame buildings, since the load-bearing capacity of the walls of these structures is much lower than that of brick or monolithic ones.
To make your own crossbars you will need: material for placing the formwork, concrete mixture, reinforcement, welding machine or a special crochet hook with knitting wire. Now is the time to look at the manufacturing process.
Reinforced concrete floor beams in construction
To effectively distribute the load from the horizontal to the vertical plane (for example, load-bearing walls or support columns), concrete floor beams are used.
The following requirements apply to them:
- high strength indicators (when basement or interfloor floors are made, the minimum strength should be 210 kilograms per square meter);
- sufficient level of hardness (from 1/200 and above);
- long service life;
- resistance to various types of influences;
- good sound and heat insulation.
If the stated requirements are met, reinforced concrete beams of various configurations and sizes will become a reliable basis for the created structural elements.
The production of concrete beams at the facilities of Zhelezobeton LLC is carried out in strict accordance with current regulatory documents - SNiPs and GOSTs (including GOST 20372-90, 24893-81).
Do-it-yourself reinforced concrete floor beams - let's get to work
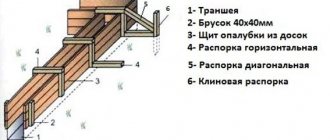
Reinforced concrete floor beams, the dimensions of which will depend on the length of the span and the loads experienced, are made after the formwork is installed. A board panel is used for the bottom of the formwork, and plywood or boards 3-5 cm thick are used for the side walls.
To facilitate removal of the formwork, its side walls are lined with roofing felt or plastic film. Formwork
it is necessary to carefully strengthen it on all sides so that the concrete mixture does not squeeze it out, causing all the work to go down the drain. After this, you can begin to manufacture the reinforcement cage.
Depending on the length of the span and the loads experienced, future reinforced concrete interfloor floor beams can be equipped with an upper and lower frame or only a lower one. The lower frame must be laid 3 cm above the bottom of the formwork so that the concrete mixture completely fills it.
It is necessary to use fittings
no thinner than 10 mm, since the lower frame experiences tensile load, it must be solid along the entire length of the beam. The frame is welded or knitted with wire. After this you can concrete it.
Concrete mixture should be used to make crossbars
, prepared according to this recipe: part cement, two parts sand, four parts fine crushed stone and the required amount of water. After placing the concrete in the formwork, it must be compacted with an in-depth vibrator.
Pouring is carried out without interruption, that is, the already laid concrete mixture should not have time to set until the entire beam is poured. It is advisable to remove the formwork no earlier than after two weeks. After installing homemade crossbars, you can install the floor on reinforced concrete beams.
- Caisson ceiling Design and shape of caissons
Beamless floors are a structure made of a solid slab supported by columns. Structurally, they can be with or without capitals. In order for the necessary rigidity to be created at the points of contact between monolithic slabs and columns, strength is ensured in the places of pushing (along the perimeter), the span (calculated) of the floor is reduced and the load is evenly distributed over the entire width, and for this purpose capitals are used.
Beamless floors are a solid slab structure supported by columns.
What is a reinforced concrete transom?
Reinforced concrete beams are a very important structural element of any building. This reinforced concrete product is a rectangular section elongated in length. These products are used for arranging floors and creating reliable frame supports. Their task is to connect the vertical elements of the structure and serve as supports for purlins and floor slabs. Due to their purpose, these reinforced concrete products are called floor crossbars .
The design of the reinforced concrete crossbar allows it to withstand and distribute the load in all directions. Not a single frame of a multi-storey building can do without these reinforced concrete products. But in order for RV products to perform the functions assigned to them, it is necessary to select and install them correctly. The required cross-section of the crossbar is selected depending on the loads experienced by the interfloor ceilings.
The ZHBI-4 plant offers RV products of the most popular modifications. The entire range presented is produced on modern equipment using only high-quality raw materials and the latest technologies. It is this approach that guarantees a decent level of quality of the products we offer.
Types of concrete floors
The following varieties exist:
- prefabricated;
- monolithic;
- prefabricated monolithic.
The main types of beamless floors: monolithic, prefabricated, precast-monolithic.
In order for a monolithic beamless floor to rest on columns, three types of capital structures are used in buildings that are built for production purposes. The contours and dimensions of the capitals are selected with a calculation that eliminates the pushing of the concrete slab along the perimeter of the capitals. The thickness of a beamless slab must be calculated provided that it has sufficient rigidity.
With the help of experiments, it was established that for a monolithic slab (beamless), dangerous loads are considered to be strip load (which is distributed across the span) and continuous load, during which the pressure is distributed over the entire area.
The design of beamless floors takes into account an equal-span grid, which can be square or rectangular. Of these, the square one is more rational, and with a rectangular shape, the aspect ratio should be 1.5. Along the entire perimeter (contour), such a ceiling rests on the main walls, contour piping, or cantilevers beyond the capitals of the last columns.
Return to contents
Dependence of loads and fractures
Typically, three types of capitals are used: 1 - with a capital plate, 2 - with a break, 3 - straight capital.
If a strip load is used in the design, then in limit equilibrium three linear hinges are formed that connect the links at the break points. If, according to the design, a plastic hinge can form in the arch along the loading axis of the panels, then cracks will open at the bottom. Whereas in load-bearing walls, the plastic hinge is located at a certain distance from the axis of the column, which largely depends on the size and shape of the capital. In this design, the crack will open at the top. The last panels rest freely on the wall from the outer edge and form linear hinges at the support, near the first intermediate row of columns and in the span.
If the structure provides for continuous loading, then linear hinges will appear in the panels located in the middle, which will be mutually parallel and perpendicular to the rows of columns, and cracks will open at the bottom. With this arrangement, the panel will be divided by hinges into four elements, which in turn will rotate around load-bearing linear plastic hinges, and their axes will be located at an angle of 45° with respect to the rows of columns. Above the load-bearing plastic hinges (in the middle panels), cracks will open at the top, and at the same time the entire thickness of the slab is cut through the line of columns.
If the loading occurs taking into account the strip load, then for a break in a separate strip (at which two links are formed), the connection is made using three linear hinges, and the middle panel is calculated as follows. The sum of the span and load-bearing moments that are perceived by the slab section (at the location of the linear hinges) is equal to the beam moment of the sheet. The beam slab is reinforced with welded mesh, which can be rolled or flat. In spans, the grids are placed at the bottom, and on supports they are laid at the top.
Reinforcement of a beamless concrete slab is made using narrow meshes located mutually perpendicular to each other. In them, stretching occurs in two layers (in two directions). Near the columns, the mesh located at the top is moved apart or small holes are made in them to install rods that compensate for the broken reinforcement. Reinforcement of capitals occurs in order to absorb shrinkage and temperature forces.
Return to contents
Calculation of reinforced concrete beams
If construction is carried out according to a developed and approved project, then all reinforced concrete products (including beams) are selected in strict accordance with it. The slightest deviations can cause destruction of the entire structure, since peak loads occur on the beams.
However, sometimes it is necessary to select the parameters of reinforced concrete beams in the absence of design documentation. In this case, it is necessary to calculate the loads and maximum bending moments, taking into account various factors, and also determine the directions of application of forces (for this, you can use specialized types of drawings - diagrams). Then a test is carried out, during which the strength by normal and tangential stresses is calculated.
Contact our company to receive products of guaranteed quality. We have our own production of monolithic and other reinforced concrete floor beams using modern equipment and advanced technical techniques.
Caisson ceiling
Let's consider what a coffered beamless floor is, which is used in a number of European countries in the construction of various administrative and public premises (where suspended ceilings should be installed according to the project). In fact, these are frame structures equipped with coffered ceilings. The ceiling itself is a ribbed structure, in which the ribs located in the lower part are mutually perpendicular.
The caisson floor is lightweight due to the distribution of the concrete mixture and the absence of excess concrete between the ribs of the floor.
Reinforcement of a beamless concrete slab type has a design in which concrete is retained only on the ribs with tensile reinforcement (it is removed from the section zone). Reinforcement of the ribs is performed for rigidity. Thanks to this design, material is significantly saved and the overlapped spans are increased (when compared with a solid section).
The monolithic structure is formed using plastic formwork. These forms are 74x80 cm in size and 20-40 cm in height. They are placed at a short distance from each other (along the axes 80x80 cm) in order to form cavities for concreting monolithic beams that have undergone reinforcement and are located mutually perpendicular to each other. The reinforcing mesh (which has undergone reinforcement) is placed on top of the forms, which are filled with a 5 cm layer of concrete, and as a result a reinforced concrete caisson structure with a height of approximately 25 to 45 cm is formed. In the area where the floor meets the column (monolithic), a solid concrete slab is installed .
Return to contents
Construction and shape of caissons
In those places where the ceiling rests on columns, reinforcement is located, and therefore a continuous monolithic slab is installed here. Hence the conclusion: one part of the coffered floor consists of elements with concrete removed in the tension zone, and the other part consists of a continuous monolithic slab. In this case, the thickness of the ribs varies from 10 to 20 cm, and the thickness of the solid part at the top should be 5-6 cm. The voidness of such an overlap is up to 50%, and the height of the ribs varies from 20 to 40 cm.
A set of special formwork, which consists of racks and metal battens, will help to technically correctly arrange the coffered ceiling.
In order to technically competently arrange a coffered ceiling, a set of special formwork is used, which consists of racks and metal battens. They are placed taking into account the size of the plastic forms. Caisson formers are placed on top of the lathing, which have adhesion to the concrete and are easily removed after it hardens. The molds do not have much weight and therefore are quite easy to remove. To prevent the plastic caisson formers from moving, they are fixed on purlins made of metal.
Plastic forms can be made in the form of a truncated pyramid, with a base of 74x80 cm. In this case, the side faces have an 18% slope, and their volume (depending on height) varies from 82 dm 3 to 137 dm 3. Knowing these values, you can make a calculation and find out that in this option, the hollowness of the coffered floor will be from 48 to 51%. From this we can conclude that the height of the coffered slab can be doubled. This will reduce the consumption of working reinforcement and increase the spans (when compared with a floor structure made of a solid monolithic slab). At the same time, the thickness increases from 16 to 25 cm, concrete savings will be 23%, and reinforcement consumption will decrease by 40%. The calculations made for such an overlap show that the mass of not only load-bearing structures, but also the structure as a whole is significantly reduced.
Return to contents
Reinforced concrete rafter beams
used to cover spans of 6, 9, 12 and 18 m. For spans of 24 m or more, they are inferior to trusses in terms of technical and economic indicators and, as a rule, are not used. Beams with spans of 6 and 9 m are intended primarily for covering extensions, and beams with a span of 12 m are intended as transverse or longitudinal roof beams. Beams with a span of 18 m are used as transverse beams, on which slabs of 3 × 6 or 3 × 12 m are laid.
Depending on the profile of the roof, beams are gable (a, b),
single-pitched, with parallel shelves (b), broken or curved outline of the top shelf.
Gable beams
have an upper flange slope of 1:12 for pitched roofs, 1:30 for low-slope roofs. Due to their efficiency, they are most widely used for covering spans of 18 m. If it is necessary to pass communications at the covering level (air ducts, etc.), gable lattice beams with a span of 12 and 18 m are used (6).
Single beams
usually used for roofing with a one-sided slope, for example in extensions.
Beams with parallel flanges
They are the simplest to manufacture, have reinforcement frames of constant height and are used as longitudinal crossbars for horizontal roofs. However, in terms of consumption of concrete and reinforcement, they are inferior to gable ones.
Beams with broken and curved top chord,
Despite their cost-effectiveness, they have not found widespread use due to the complex technology of their manufacture.
Section height of beams in the middle of the span (1/10...1/12 ) l
.
In order to save concrete, the cross-section of the beams is taken to be T-shaped (at l
=6;
9 m) and I-beam ( l=
12; 18 m).
The width of the upper flange of the beams, from the condition of supporting the covering slabs and ensuring stability during transportation and installation, is taken equal to (1/50...1/60) l
, which is usually 20...40 cm. The width of the lower flange (25...30 cm) is determined from the condition the placement of tensile reinforcement in it, the strength of the concrete belt under the action of compression forces, as well as the conditions of support on the columns. The thickness of the vertical wall in the middle part of the span (6...8 cm) is determined based on the conditions for manufacturing the beam (in a vertical position) and the placement of transverse reinforcement (one or two frames). The wall of the supports is thickened to ensure the strength and crack resistance of the supporting sections.
All types of beams with spans of 12...18 m are made prestressed, as a rule, with tension on stops.
Beams are considered as simply supported elements with a design span equal to the distance between the lines of action of the support reactions.
The selection of longitudinal and transverse working reinforcement, calculation of deflections and crack resistance of beams are carried out as for a conventional T-section or I-section element.
Structures of rafter beams:
1 – prestressed reinforcement; 2—support frame; 3—
mortgage anchors;
4—
indirect reinforcement meshes
Floor with hollow balls
Balls made of polyethylene and concrete placed inside the reinforcement frame will provide an even ceiling and reduce the weight of the monolithic floor.
The second type of monolithic floor is a design with the placement of hollow plastic balls inside concrete, which is effective in the construction of residential buildings, since material consumption is significantly reduced and a flat surface with oval and round voids is provided. In order to reduce the mass of the monolithic floor and ensure an even floor, a calculation is carried out of the system, which is equipped with reinforcement cages, inside of which balls of polyethylene and concrete are placed, filling all the voids between them.
At the bottom of the frame there are reinforcement bars that absorb tension. Sections of solid monolith are left and preserved where columns and floors intersect. Polyethylene balls (hollow) are placed in the middle of the reinforcement frame, which reduces the cost of concrete. Calculations show that the weight of the floor is reduced by 35% compared to floors made of solid concrete. This reduces the weight of the entire building.
Modular slabs have a number of advantages: they are lightweight, have a greater margin of safety, and are delivered to the construction site ready-made.
The advantage of a material such as modular slabs is that they are brought to the construction site in finished form and laid out on horizontal formwork floors. In order to create a protective layer of concrete, the reinforcement cages are laid on clamps (plastic). In places where there are openings in the ceiling, a solid monolithic slab is installed, and vertical supporting structures are mated with them. The frames located at the junction and in the opening areas are connected to those reinforcement cages in which hollow plastic balls are located. In the stretched zone of the lower floor, the located working reinforcement is connected to a frame with hollow balls.
Return to contents
Calculation of savings during work
This modular frame solution makes it possible to use standard equipment, provides additional filling and thus constitutes an alternative to the traditional solution. If we compare the location and number of columns in both methods (traditional and with hollow balls), then in modular construction the following are taken into account: spans to be covered, the number of columns and the consumption of building materials. Hence the conclusion is that modular construction is quite profitable and when using it, it is possible, by reducing the number of columns, to increase spans and reduce the cost of materials.
With modular construction of the frame, it is possible to reduce the number of columns, save reinforcing steel, concrete consumption, and increase spans.
Having made the calculation, we can notice that with modular construction with built-in plastic balls, the number of columns will be reduced by 40%, reinforcing steel, reinforcement and concrete consumption for arranging the foundation will be saved by 20%, and concrete consumption will be reduced by 32% per unit of flooring. At the same time, the calculation shows that when erecting a beamless floor, the arrangement of purlins and beams accounts for almost 100% savings in concrete, and the time for formwork work is reduced to 65%.
In order to ensure that the supply and distribution of concrete is carried out evenly throughout the entire floor and at the same time the labor intensity of the work is reduced, companies use flexible hoses (concrete pump) made of synthetic material that has been reinforced. This makes it possible to complete concreting work quickly and accurately. The mobility of the mixture is from 7 to 10 cm. If the speed is higher, then during pumping the stream stratifies and plugs form. If plasticizing additives are used in the mixture and casting technology is used, then it becomes necessary to increase the consumption of cement and the amount of sand (fine fraction) in the concrete mixture.
Return to contents
Reinforced concrete beams: production
Prefabricated reinforced concrete beams (GOST 20372-90, 24893.2-81, 24893.1-81) are manufactured only in factories, and monolithic beams are produced by pouring concrete mortar into pre-prepared reinforcement structures, the rods of which are tensioned using jacks. The material is compacted using vibration technology. The solution in the mold hardens in about 12 hours, after which the product is taken out into the open air to consolidate its properties. During manufacturing, one important parameter must be observed: the concrete mixture must be distributed as evenly as possible throughout the entire space of the mold. To create these products, concrete grade 200 and higher is used. The finished reinforced concrete beam has a design load of more than 450 kilograms/force per square meter.
Composition and functions of concrete blocks
Using such a system in construction, architects and designers have great prospects for creativity. They have the opportunity to cover large areas and at the same time use a minimum number of supports. For example, if you use concrete expanded clay, the weight of the floor is reduced by almost 25%. When calculating such a floor, the architect takes into account all the advantages of modular frame construction. This gives him the opportunity to cover large areas and use non-standard and original solutions.
By using hollow concrete blocks in a coffered floor, you can significantly reduce the number of supports and significantly reduce the weight of the floor.
A prefabricated monolithic caisson floor consists of hollow concrete blocks. They have sizes from 20x20x60 cm to 30x30x80 cm. The blocks are placed on the surface so that three blocks laid next to each other form a geometric figure, closed on all sides. Having made the calculation, you can see that if you use hollow blocks with dimensions of 20x20x60 cm, the thickness of the floor can increase to 25 cm, and the layer of monolithic concrete above the blocks will be approximately 6 cm.
Some concrete slabs and blocks act as formwork (non-removable) and are left in the ceiling. They form vertical ribs in the stretched zone, and a continuous flooring in the compressed structure. In the above-support zone (at the junction with the columns), the overlap must be performed using a continuous monolithic slab. This is where the rods occur, which are connected to the reinforcement of the columns. Reinforcing mesh must be laid on top of the blocks. In the part where the solid monolithic slab is located, reinforcing bars that have undergone reinforcement rest on the blocks.
Concrete blocks are laid in groups. In this case, the distance between them should be from 12 to 15 cm. The formwork is a wooden flooring that rests on telescopic posts, beams (made of wood or metal) and sheathing.