Preparation of mortar for bricklaying
To do this, sand is first sifted through a fine mesh to remove large fragments of aggregate, stones, and debris. Then an astringent component is added to it, and the mixture is thoroughly mixed. After this, the required amount of water is added to the mixture.
But the solution quickly separates into its constituent components, so it must be constantly stirred. Based on this, the solution is prepared in an amount that is guaranteed to be used within a certain time. To speed up the process of creating a solution and improve its quality, mechanical or electromechanical devices called mortar mixers are used.
In addition, mechanical mixers are used. An electric drill with a special attachment can be used as an electric mixer.
Types of mortars for bricklaying
Depending on the binder component, mortars are divided into lime, cement-lime, and cement. In lime mortars, quicklime is used as a binder. Lime and sand are taken in proportions from 1:2 to 1:5.
But, since lime mortar masonry is not durable, it is therefore practically not used in construction. Cement-lime mortars are prepared from cement and lime milk. The lime dough is diluted with water to the consistency of milk and filtered.
Then a mixture is prepared from sand and cement, into which lime milk is poured and mixed thoroughly. Cement-lime mortars have good plasticity and are preferable for use in bricklaying. The most common cement mortars consist of cement, sand and water.
The ratio of cement and sand is from 1:3 to 1:6. This proportion depends on the brand of cement and the requirements for the solution. Water consumption – 0.8:1 (water:cement).
The table shows the proportions of cement-lime mortars. In the right column is the brand of cement, horizontally, the resulting brand of mortar.
Sand with a grain size of no more than 2.5 mm is used. You can find out more detailed information about cement from the article “Cement - deciphering brands, additives.”
Component ratio
To properly make brick mortars, you need to determine the ratio of the main ingredients. It is recommended to take sand of medium coarseness, that is, with a fraction of two and a half and above; the brand of solution may be different, but it is this that affects the proportions. Here are examples of how you can make brick mortars based on this:
- when using grade 500 cement, the proportions are: one part cement, 2/10 lime, three parts sand;
- when using grade 400, the proportions will be as follows: one part cement, 1-3/10 parts lime, 2.5-4 parts sand;
- for grade 300 the proportions will be as follows: one part cement, 2/10 lime and 3.5 sand.
All components must be thoroughly mixed until a homogeneous mass is obtained. This example was presented for cement-limestone masses; for a cement-sand mortar the proportions will be slightly different:
- with a cement grade of 500, the proportions will be: 1 part cement to 3 parts sand;
- for grade 400: 1 part cement and 2.5 parts sand.
Brickwork is based on the implementation of basic rules, otherwise the necessary strength and solidity of the entire building structure will not be achieved.
The water taken is cold and clean, its temperature should be from 15 degrees to 20. During production, all dosages must be observed exactly.
The optimal water consumption is:
- when using concrete grade 100, take from 1/2 to 7/10 water for 1 part of cement;
- for cement-sand, for each part of cement you need to take 8/10 water.
Attention: when carrying out work in the winter months, you cannot use Portland slag cement, as the quality of the solution will be extremely low!
Cement consumption for laying can be as follows:
- for brand M100 – 300-250 kg per cubic m;
- for M150: 400-330 kg per cubic m;
- for M200: 490-410 kg;
- for M300: 600-510 kg.
Dry mixtures for mortar for bricklaying
Currently, the process of preparing the solution has been much simplified. A large number of ready-made dry mixtures of various brands have appeared on the building materials market, into which you just need to add water and mix thoroughly. The amount of water added is indicated on the packaging.
- Date: 05/11/2015 Comments: Rating: 41
Brickwork is the basis of many buildings. Bricks are used to build structures of various purposes and strength. Proper preparation of mortar for bricklaying largely determines the quality and reliability of the entire construction.
In order to build a high-quality and reliable brick structure, it is necessary to properly prepare the mortar.
By changing the composition of the solutions, you can influence the parameters of brick walls.
Various additives can change the capabilities of such a binder. Preparing a mixture for laying bricks is a fairly simple, but very important task. Compliance with manufacturing technology and composition is the key to the strength of the house.
What is required to prepare mortar
Brick mortar is in demand at every construction site. To mix the composition in large volumes, you will need a concrete mixer. If the binder is needed for cosmetic repairs, a small amount will suffice. In this case, the kneading is done with your own hands.
The mixture for laying bricks consists of several components:
Cement production scheme.
- binder;
- water;
- sand;
- filler.
The first is cement, clay or lime. Clay-based compositions are suitable for use much longer than cement-based mixtures. Lime mortar has lower strength than cement and clay mortar.
The sand for the solution should be medium-grained and obtained from a quarry. River sand is not suitable, since the grains of sand in it are too small, so they will cause the fragility of the masonry. Various materials are used as filler:
Table of application of cement mortars.
- crushed stone;
- gravel;
- sawdust;
- pine needles;
- expanded clay;
- slag (waste from metallurgical production);
- straw.
Depending on the type of filler, different types of concrete are obtained: sawdust concrete, slag concrete, expanded clay concrete. An important criterion for the quality of mortar for bricklaying is plasticity. To achieve this, special additives are added: plasticizers. You can use those offered by the retail chain. But you can use less expensive, but no less effective means.
These include washing powder and liquid glass. The latter will make the composition not only elastic, but also water-repellent. But the most economical way is to use inexpensive washing powder. In the recent past, builders ensured the flexibility of masonry mortar by adding PVA glue to it. But at present this method is considered obsolete.
Table of proportions of cement consumption for bricklaying.
To mix it yourself, without using a concrete mixer, you will need the following:
- kneading container;
- shovel;
- bucket;
- metal mesh for sifting sand.
The cement-sand mixture can be prepared with or without filler. Compounds without filler are suitable for laying walls. The brand of solution depends on the type of binder used. Traditionally, M400 grade cement is used for masonry. His other brands are also suitable: M300, M500.
Features of mortar for bricklaying
In general, a brick mortar is an aqueous mixture of a binder and filler, into which additives can be added to impart additional properties. It should be remembered that masonry mortar differs markedly from mixtures intended for other purposes (for example, plaster).
Table of compositions of mortars for brickwork.
Cement and lime are used as a binder (base), each individually or in combination. The main filler is sand. Clay can be used in combination with it.
In addition, plasticizers and other additives can be added to the mixture to increase heat resistance, resistance to moisture, steam, etc. The use of detergents to increase elasticity is quite common.
There are a number of requirements for mortars for laying brick walls. They must have good adhesion to the brick, which ensures reliable adhesion to it. It must be elastic enough to spread evenly over the surface without effort and fill in any unevenness in the brick.
It is important that the mixture, after hardening, has high compressive strength. The drying time of the solution should allow it to be used. In addition, additional conditions include thermal resistance and moisture resistance.
An analysis of the use of different binders shows the following. Lime mortar has high elasticity and good thermal insulation properties, but has low mechanical strength.
It can only be used in minor buildings - fences, light outbuildings. Cement mortar has increased mechanical strength and excellent adhesion to brick, but is considered a cold and insufficiently plastic material. Many disadvantages are eliminated by using cement-lime mortar, which is quite strong and elastic. It is widely used in the preparation of mortars for bricklaying.
Return to contents
Components of masonry mortar.
Solutions have their own brands, which can be assigned even to those options that are prepared by hand. It is customary to fix the brand in the following form: for example, M50 is a solution with a compressive strength of 50 kg/cm³.
The most widely used options for bricklaying are M10, M25, M50 and M75. Solutions M100 and higher are used in particularly durable structures. You can carry out a strength test yourself - a cube of mortar with a side of 7 cm is subjected to compressive load after 28 days of drying.
An important standardized parameter is mobility. To determine mobility, a cone with an angle of 30º and a height of 15 cm, having a mass of 300 g, is immersed in a fresh solution.
It is customary to consider mobility according to the depth of immersion of the cone (in cm) for 1 hour. For laying red brick, the mobility should be no more than 13, and for hollow bricks - no more than 8. When building in warm weather, mixtures with high mobility are recommended.
Return to contents
When preparing a solution, special attention is paid to the quality of the components. The water for the solution should not contain impurities, oils, or dirt. Well and spring water shows the best results.
If the mixture is prepared in the summer, then the water should be cold, that is, not heated by direct sunlight; and in winter, on the contrary, it needs to be heated a little.
The sand used is well cleaned and sifted. It should not contain clay or impurities. Cement determines the basic properties, so it should be checked especially carefully.
When purchasing, you should ensure that the packaging has not been damaged. Cement that has been stored in a humid atmosphere is unusable. Lime should be used in slaked form.
You can use almost any cleaning products - shampoo, washing powder, etc. You should not use only cleaning products.
Return to contents
Determining the readiness of mortar for brickwork.
The simplest mortar for bricklaying is an aqueous mixture of two components (cement or lime with sand).
In the construction of houses, a simple cement-sand mortar is used. It is prepared in the following proportion: one part cement to 3 parts sand. This dry mixture is loaded into a tray-type container (with an increased area) and mixed thoroughly.
When the mixture acquires a uniform gray color, add water little by little with constant stirring. The mixture should acquire a viscous consistency that allows it to be applied to the surface; without being too liquid. The last condition can be easily checked by tilting the container 40º - nothing should spill out.
If the question arises about how to prepare a mortar for laying bricks of different strengths, i.e.
That is, different brands, then you should change the ratio of components. It has been determined in practice that the M50 solution is obtained by diluting a mixture of cement (Portland 300 brand) and sand in a ratio of 1:5; M75 - at a ratio of 1:3; M100 - 1:2; M150 - 1:1.5.
Return to contents
When you need to decide how to prepare a solution with increased elasticity, it is worth adding slaked lime. This solution will retain its plasticity for up to 5 hours.
It is undesirable to use this solution in the basement of an external wall with high soil moisture. The recommended mixture is the following ratio of cement, lime and sand: 1:1:4 (based on the use of Portland 400 cement), which corresponds to grade M75. For brand M50 this proportion will be 1:0.5:4.5.
The solution is prepared as follows. First, lime dough is prepared - a mixture of lime and sand is diluted in water with stirring to the consistency of thick sour cream. Then the cement is mixed with lime paste with the addition of water with constant stirring.
Return to contents
The preparation of mortar for bricklaying is sometimes done with the addition of detergents, which significantly improves the plasticity of the mass.
Liquid soap or other detergent is added in a proportion of 50-100 g per 10 liters. The detergent is first mixed in water until foam forms, i.e.
within 3-5 minutes. This solution is then mixed with a cement-sand or cement-lime-sand mixture. The mixture is thoroughly mixed to a uniform gray mass with the consistency of very thick sour cream.
Clay is sometimes used as a plasticizer. It is pre-mixed in water - alone or together with lime. In addition, a pigment of the desired color can be added to obtain a colored solution.
If the wall is laid from refractory bricks, then it is advisable to increase the fire resistance of the mortar.
To do this, special fireclay or fireclay powder is added to the cement-sand mortar. This mixture is recommended when laying stoves or fireplaces.
Return to contents
Tools for preparing cement mortar.
In order for the solution to meet the requirements for strength and reliability, it is recommended to use certain types of cement for different conditions. Thus, for external walls in areas with an average humidity of no more than 60%, binders such as Portland cement, plasticized Portland cement, and lime-slag binders should be used. For wetter climates, pozzolanic and hydrophobic Portland cement is recommended.
Preparing mortar for bricklaying will require the use of the following tool:
- bayonet and scoop shovel; trowel; spatula; grater; scales; measuring bucket; ruler.
Currently, there is a large selection of dry building mixtures for bricklaying on sale. They may well satisfy all requirements. However, during large construction projects, it is more convenient and cheaper to prepare the mortar for laying bricks with your own hands.
This will allow you to choose the optimal composition and consistency.
Brick is a traditional material for the construction of various buildings.
It is used for the construction of walls of a residential building, fences, interior partitions, stoves, etc. Due to the fact that brick does not lose its attractiveness over time, buildings look beautiful.
In addition, everyone knows the positive qualities of brick: strength, reliability, environmental friendliness, low thermal conductivity, fire resistance, high frost resistance, etc. But in order for the finished brick structure to be durable and reliable, it is important to pay attention to the binding material - the mortar.
It is very important to do it correctly, since the bonding of individual bricks and rows of masonry depends on its quality.
The question arises? How to prepare a mortar for brickwork so that it meets all the requirements. In this article you will learn what mortars are available, their correct ratio and the rules for mixing high-quality mortar for bricklaying.
Proportionality of the components of the masonry mortar
Depending on the purpose or place of use, the proportions in the mixture for bricklaying mortar will vary. For laying load-bearing walls and partitions, a cement-sand mixture is most often used. The main criterion for its quality is the proportions of sand and cement. It is easy to prepare and can be used without additional additives. The cement-sand mixture can be called a universal mortar for masonry. Brickwork laid on such a mortar can withstand both horizontal and vertical loads. The seams are resistant to temperature changes, damp environments and precipitation. On the Internet you can find many tables that indicate the ratio of sand and cement.
Let's look at examples of how to prepare a solution
Common options:
- Brand 75. This mortar is used for bricklaying solid brick or wild stone. This is a solution for laying cinder blocks and foam concrete blocks. It is used for screeding floors with a small layer. It is used both for external and internal masonry. It is used in rooms with high humidity (bathroom, shower, etc.). Used in industrial premises in which equipment that produces strong vibrations is constantly operating. Most often, the proportions of cement and sand are 1 part M400, 4 parts sand.
- Brand 100. Found its application in filling joints in panel houses. Used for screeding floors and installing lintels up to 2 meters. The hundredth grade is used for plastering walls. Suitable for laying solid bricks or heavy natural stone. It can be used to build a brick foundation. Good strength characteristics allow it to be used in monolithic frame construction. When used in damp conditions, it is recommended to use additional moisture-repellent substances in the mixture. To prepare grade 100, use M400 cement to four parts sand.
- Brand 150-200. This brand is more durable. When producing grade 150, it does not allow the presence of impurities in the form of clay or lime. Such components reduce strength characteristics. It is almost never used for brickwork, as it is relatively expensive. It has found application in the construction of foundations, as well as in plastering work in wet structures and buildings (swimming pools, aquariums, etc.). Mortars 200 grade are used to fill joints in prefabricated buildings or as waterproofing. To produce grade 200, a ratio of two parts sand to one part Portland cement M400 is used.
What should be the correct solution?
Making a ready-made mixture is a simple matter.
Any master can do this. However, it is important that the mass meets the necessary requirements. What are they?
The finished mixture should be quite plastic to fill all the irregularities, seams and voids in the bricks. It is important to know the correct consistency: if the mass is too liquid, everything will spread out, but if it is too thick, all the voids will not be filled. The finished solution should resemble sour cream in consistency. After hardening, the mixture should be strong enough and not crumble.
Otherwise, this is fraught with deformation of the masonry walls and, ultimately, the entire structure. After mixing, the mortar should not set immediately. You should be able to use it before it hardens. Therefore it is important to ensure a good setting time.
When you follow these simple rules, you will get the right masonry mortar. But that's not all. To obtain it, it is important to know the composition and the required proportions.
Types of solutions
Let's look at the types of solutions and their characteristics in the table:
| Type of solution | Characteristic | Proportions |
| Lime based mixture | It is made by thoroughly mixing sand and quicklime. The components are mixed dry, then water is added. The solution is stirred until a mass of homogeneous consistency is formed. They have high plasticity, are easy to install and do not allow cold to pass through them. If lumps have formed, sift the lime mixture through a sieve. | 1 part lime, 3 parts sand |
| Cement mortar | Made from sand-cement mixture. The mixture adheres well to the surface. But it is too rigid, so during operation it begins to crumble under mechanical and natural influences. | 1 part cement, 3 parts sand |
| Lime-cement mixture | We prepare the lime mixture to the consistency of homemade milk. Strain the solution through a sieve. Add the remaining lime in the sieve to the cement mortar. This composition has the best qualities: it adheres firmly to the brick and has sufficient ductility. | 1 part lime, 1 part cement, 5 parts sand |
| Clay mixture | Made from clay and sand. To increase strength, you can add 100 - 250 g to a bucket of mortar. salt or 750 gr. cement. | 2 parts clay, 1 part sand |
The mortar for brickwork is selected depending on the weight of the building and its operating conditions. The durability of the building depends on the quality of the brickwork mortar used.
Limestone: composition and properties
The limestone mixture is ideal for constructing fences and partitions between rooms. Why?
This composition is the most flexible and easy to work with. It turns out warm due to its composition, which is quite simple: quicklime, ground lime, sand and water. Sand and lime are thoroughly mixed until smooth, after which plain water is added.
The composition is mixed again until it is ready. It should not contain foreign impurities or lumps. As for the proportion, it is as follows: 1 part lime to 4 parts sand.
Why is it not recommended to use the solution for laying external walls?
The answer is quite simple: since there is no cement in the composition, over time the rain will simply wash everything away. They are not strong enough. That is why this mixture is used only for interior work.
Note! There are other types of limestone mortars: cement-limestone, limestone-gypsum, limestone-clayey.
Cement-limestone composition can be used for external masonry walls.
Cement-lime composition
Determining the readiness of the solution.
A simple solution has high mechanical strength, but has low processability due to reduced ductility and mobility. To eliminate these shortcomings, mixtures are used in which the binder is composed of cement and lime. The second component is introduced into the composition in the form of a lime paste: quicklime with water in a ratio of 3:1 (when this composition is kept for several hours, the lime is quenched upon contact with water).
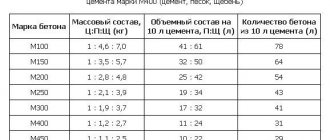
Cement-lime mortar is the most common masonry composition. It has a fairly high compressive strength, while being plastic and manufacturable. The setting time of the solution allows you to easily work with it for several hours. In addition, its thermal insulation properties, resistance to cracking and frost resistance fully satisfy the requirements. Below are the recommended proportions of cement, lime and sand when preparing mortars corresponding to different brands.
| Brand of solution | Proportion of cement, lime and sand (in parts) by cement grade | ||||
| 500 | 400 | 300 | 200 | 150 | |
| 300 | 1:0,15:2,1 | 1:0,7:1,8 | — | — | — |
| 200 | 1:0,2:2,3 | 1:0,1:2,5 | — | — | — |
| 150 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,2:3 | 1:0,1:2,5 | — | — |
| 100 | 1:0,5:5,5 | 1:0,4:4,5 | 1:0,2:3,5 | — | — |
| 75 | 1:0,8:7 | 1:0,5:5,5 | 1:0,3:4 | 1:0,1:2,5 | — |
| 50 | — | 1:0,9:8 | 1:0,6:6 | 1:0,3:4 | — |
| 25 | — | — | 1:1,4:10,5 | 1:0,8:7 | 1:0,3:4 |
| 10 | — | — | — | — | 1:1,2:9,5 |
Cement mortar
This is the most common type of mixture used to build walls. It is quite durable and suitable for work both inside and outside.
Its composition is as follows: cement, sand and water. The proportions of the components depend on the brand of the solution. The finished mass is cold, inactive and has excessive rigidity.
To give it plasticity, various plasticizers are added. And if you need to increase the hardening time, then add lime to the composition. This way you can prepare more solution at one time.
The advantages of the cement mixture are as follows:
- high strength; good thermal insulation properties; frost resistance; possibility of use in rooms with high humidity (bathrooms, basements, baths, etc.); durability and environmental friendliness.
Solutions with added clay
The plasticizing effect in masonry mortar can be achieved by using clay instead of lime (taking into account the chemical activity of lime). In this case, you should use clay of normal fat content after grinding and thoroughly removing impurities. Its introduction into the composition is carried out in the form of a creamy aqueous solution. The proportions of clay in the mixture are similar to the corresponding proportions of lime (by brand of solution).
Masonry mortars are especially in demand when using refractory bricks (stoves, fireplaces), where clay can significantly increase the adhesion of the mixture.
Preparatory work
Since this type is most often used, we will analyze its preparation. The components are known: cement mortar, sand and water. What materials will you need?
- Portland cement M400 or M500. Sand without impurities, sifted, 2 mm fraction. Plain running water.
Also prepare the following tools:
- a large mixing container or a concrete mixer (if you need a lot of solution); a shovel; a drill with a mixer; a sieve; several buckets (not necessarily new); a trowel.
Accent! The greater the amount of sand in the solution, the less its strength will be. Conversely, the less sand, the stronger the cement.
As for the correct ratio, there are no uniform standards; it all depends on the desired brand. Below is a table with the name of the brand of the mixture and the required proportion of components.
You may notice that only the amount of sand changes.
If you need to make particularly critical areas of masonry (the basement of a bathhouse, a columnar brick foundation in wet soil), mix grades M50 and M75. In other cases, you can make an M25 solution. To mix 1 m3 of mixture, you will need approximately 268 kg of cement, 2064 kg of sand and 350 liters of water.
How to prepare cement mortar
Decide once how much you need. If you work on your own, you can knead everything by hand and make do with a large container, in the form of a trough or bucket. When a whole team is involved, it is advisable to use a concrete mixer.
Note! The cement mortar dries in approximately 1.5–2 hours. During this time you must use it completely.
Now, let’s look step by step at how to properly make a mortar that would be suitable for brickwork.
First, sift the sand. It must be clean, free of impurities and other debris.
It is better if the sand used is river sand. Adding quarry sand is not prohibited. Keep in mind that its fraction should be no more than 2.5 mm. Pour the required amount of components into the prepared container.
You must choose a brand in advance and know the exact ratio. Use a shovel and buckets. Don't make the mistake of counting materials by weight! Mix sand and cement until smooth, then add water.
Keep stirring the solution so that the sand does not settle at the bottom. For 1 kg of cement there is approximately 0.8 liters of water. The correct composition should resemble sour cream.
All is ready. Now you can use the mixture for your purposes.