Caring for concrete in the summer is a mandatory activity, on which the quality of concrete depends. It begins as soon as the concrete is laid and compacted, and continues for a certain period of time. The time for laying and vibrating at temperatures above 20 degrees is reduced.
The purpose of these rules is to create favorable conditions for hydration of cement stone. As a result, concrete gains strength characteristics when liquid and plastic glue transforms into a stone state.
CONCRETE PROTECTION
The main element of construction is the use of concrete structures and concrete surfaces. But having strength characteristics, concrete can lose its load-bearing capacity and other physical characteristics due to non-compliance with the rules of concrete care. These simple rules will help protect concrete from excess moisture (rain), high temperature, weathering and, as a result, from destruction (peeling). surface layer, cracks, lack of strength, loss of performance characteristics)
As soon as the concrete is laid, it is necessary to protect it from the high ambient temperature. In sunny or windy weather, the concrete structure should be covered with available material and moistened (without washing out the top layer from hoses)
METHODS OF CARE OF CONCRETE MIXTURE
Therefore, caring for concrete after pouring consists of creating conditions that can stop excessive evaporation. The active phase, during which stone is formed from a mixture of cement and sand, lasts about a month. Within 7 days, the concrete must gain at least 60% of the specified strength, subject to the rules of concrete care. If water is lost before this time, microcracks will appear on the surface and the strength of the top layer will decrease.
Evaporation can lead to dehydration of concrete. Which will lead to a slowdown or termination of the hardening process. The strength properties will decrease and cause cracking and shrinkage. Therefore, the main task is to provide the surface with normal temperature and moisture. The type, type of cement and local climatic conditions determine the method of maintenance. When hardening occurs, the volume changes. During rapid drying, shrinkage appears, then microcracks appear. In huge monolithic structures, large cracks appear during uneven heating in different parts.
When everything is moistened abundantly, the possibility of cracks is reduced. Maintenance work for slow-hardening cement lasts at least two weeks. And with Portland cement, at least a week. Humidification is done using a spray bottle. It is forbidden to water with a strong stream to avoid blurring the surface. The moist state is maintained by constant frequency of watering. After pouring, moisten after 10 hours, and in windy and hot weather after 2-2.5 hours.
Ways to keep the surface moist:
- Applying a protective composition to the surface of freshly laid concrete;
- Sprinkling with water using protective coatings;
- Aged with salts that absorb water.
When watering, the surfaces should be protected from drying out and in the interval between waterings it should be taken into account that:
- slow-hardening cement must be kept for more than two weeks;
- quick-hardening cement is subjected to initial 8 hours of saturation with water, and then 16 hours to a completely moistened state.
During humidification, the temperature decreases.
CARE AT HIGH TEMPERATURES
In warm weather, summer concrete care has certain features. Especially at temperatures above 28-30 ° C. All that is needed is to maintain moisture on the surface and a temperature of about 24-25 degrees.
It is important to cover the entire top surface to prevent cracking due to evaporation. You can use film, burlap, sheet metal and other materials.
But there are often cases when maintaining a wet state is difficult and sometimes impossible. Sometimes it happens that the water can evaporate and leave behind the salts that were in it. They are deposited on the surface and begin to interact. As a result, the surface layer weakens. Therefore, it is recommended to cover the surface. Protective materials are placed 2 cm above the surface and watered with water. The material delays the passage of salt. The surface itself is moistened with steam. Therefore, caring for concrete in the summer should be based on certain principles.
Tips for high temperatures:
- Carry out concrete work in the morning or evening, when the temperature is lower than during the day.
- Provide protection from rays (film, slate sheets, roofing felt and other materials).
- Delivery of the mixture to the site in the shortest possible time and prompt installation.
- Watering during the first days. Watering begins after 8-10 hours.
- Please note that the water jet should be in the form of splashes.
- And care in forty-degree heat involves watering and covering with protective materials. We hope that our recommendations for caring for concrete during the hardening period during the summer season will help you, and we wish you success in construction! Choose only reputable concrete producers. When ordering concrete, find out not only the price, but also the composition (what kind of cement, granite or crushed gravel, whether additives are used) There is a misconception that concrete is the same everywhere. Quality and characteristics: strength, frost resistance, water resistance, abrasion depend from the materials used (concrete aggregates) Crushed stone with low strength and a large number of weak grains will not ultimately produce strong concrete. At our factory you can look and see what inert materials your concrete mixture will be made from.
When starting the construction of monolithic concrete structures, you should familiarize yourself with all the rules for caring for them in advance. They are necessary for the concrete to gain its original strength and serve for many years. Otherwise, cracks will begin to appear on its surface, which will lead to shrinkage of the building and loss of its functionality. SNIP provides for concrete maintenance at any time of the year, but if you can choose a construction season, it is better to choose the summer option.
At this time of year, it is necessary to provide the concrete with optimal hydration conditions in order to achieve maximum structural strength. All protective measures take place in two stages.
Complete hardening of concrete takes about a month, of which the first two weeks the concrete gains almost eighty percent, so the maintenance process takes a long time. If the moment is missed, cracks will appear on the surface of the concrete, which will lead to a significant loss of strength and functionality. Maintenance of concrete in the summer SNIP provides for all this. Their main requirement is to maintain the level of humidity on the surface of the structure. It is achieved by preventing evaporation or regularly maintaining the level of humidity by replenishing it. The required amount of water is added to the mixture that is still being prepared, which should be kept until it hardens completely, that is, for a month.
The speed of drying is also affected by the ambient temperature. When large monolithic structures are heated unevenly, large cracks appear on them, and when foundations or floor coverings dry out, microcracks form. All this leads to a large loss of strength and shrinkage of the building. Drying slows down, and sometimes even stops, the hardening process. At this time, the volume occupied by concrete also changes. All this should be taken into account when choosing cement for preparing the mixture.
In different temperature conditions, the hardening period also varies. For example, at temperatures above ten degrees Celsius and air humidity of more than eighty percent, the full hardening time increases. This is because under these conditions, water will penetrate into the concrete slowly. Surface maintenance will take about two weeks, as with other slowly hardening cement mixtures. Portland cement will require a moistening period that is half as long.
All methods of maintaining the required moisture content of concrete can be divided into three:
- watering;
- coating with a protective composition (allows you to retain moisture and avoid negative environmental influences);
- aging with salts (used in winter).
All work to moisten the surface with water must be carried out from a sprayer, otherwise a strong jet can wash away the concrete. The first watering is carried out after a couple of hours in very hot weather and after ten hours in average temperatures. Subsequent wetting depends on environmental conditions and the composition of the cement itself. For example, low-heat grades will require care for a couple of weeks, aluminous (quickly hardening) grades should be moistened for only a day, of which the first eight hours should be heavily saturated with moisture, and the remaining time should be completely moistened. In any case, the regularity of this process significantly reduces the risk of cracks. But do not forget that during watering the concrete cools.
Care rules during the warm season
During this period, the air temperature rises significantly, which means that caring for concrete in the summer will have its own characteristics. It all comes down to maintaining a temperature on its surface no higher than twenty-five degrees Celsius and an optimal level of humidity throughout the entire hardening period. To do this, concrete must be covered immediately after pouring to reduce moisture evaporation, which will lead to cracking. Straw, sheets of tin, burlap and any other materials will do. Sometimes, when moisture evaporates, traces of salts remain on the concrete surface, which destroy the surface layer. To prevent their interaction, it is recommended to cover the concrete so that the materials do not come into contact with its surface. To do this, it will be enough to maintain a distance of a couple of centimeters. All subsequent moistening occurs directly through the shelter, which retains salts and allows moisture to pass through. The entire process of laying and maintaining concrete in hot weather is based on certain rules:
- regularly maintaining the level of humidity on the surface;
- at elevated temperatures, moisten the formwork;
- protection of the surface from the sun and wind;
- avoid contact with rain and melt water;
- exclude the possibility of mechanical impact on the surface.
In addition to the rules for protecting the surface, you should also adhere to the rules when pouring concrete. To do this, it is necessary to carry out the main work in the morning or evening, when the air temperature is not too high. It takes no more than an hour to deliver the material to the site or prepare it on site. Immediately after laying, protect the concrete surface from the sun and moisten it regularly throughout the curing period. The frequency of watering, as well as its intensity, depends on the air temperature. In forty-degree heat, not only the concrete, but also its formwork and shelter should be moistened. Particular attention must be paid to the nodes and edges, and it is advisable to water the plant from a sprayer.
If these standards are ignored, the strength of the concrete coating is reduced by half due to rapid drying. And the full period for gaining brand strength of concrete depends on temperature, which has been proven by scientific research, so you need to take weather conditions into account when drawing up a schedule.
To increase the strength of the concrete coating, various protective mixtures are sprayed onto its surface. They are white, black and colorless.
Black protects well from wind and direct sun, but its surface, on the contrary, increases heat absorption and overheats the concrete. Black bituminous mastic acts even worse; it evaporates a large amount of moisture during the wind. White additives, due to their color, reduce heat absorption, while colorless additives do not affect the appearance of concrete. Modern technologies have made it possible to obtain a product that creates a transparent film on the surface. This type of coating can be found on the floors of large hypermarkets. It involves improving the durability of concrete at average temperatures and humidity. But even when using such additives, one should not forget about the need to regularly moisten the coating.
Concrete structures
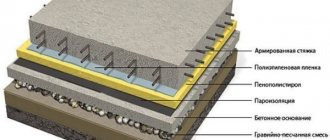
Modern formworks sufficiently protect concrete from drying out, with the exception of exposed concrete surfaces, which in dry weather must be covered immediately after laying.
To prevent wooden formwork from absorbing moisture, it must be coated inside with a special oil before use. It is also useful to periodically spray it with water outside, especially in dry weather.
In dry weather, after removing the formwork, concrete should be regularly watered throughout the specified curing period, i.e., either 7 or 14 days. In England, it is usually not necessary to dampen concrete in winter, since in a cold atmosphere the rate of water evaporation is low. In order to reduce water consumption and prevent it from dripping and interfering with other work under the structure, it is sometimes necessary to cover the structure with burlap or straw mats.
Covering the structure with a tarp or waterproof paper can also reduce water evaporation.
Small concrete elements require greater protection from moisture evaporation than concrete masses, since they have a more developed surface compared to their volume. Corners and edges are especially susceptible to drying out in small elements.
Rules for caring for monolithic structures
Large surfaces lose moisture much faster, so they should be moistened more often. To ensure sufficient watering, you can build a continuous irrigation system, it is important to use galvanized pipes for this. The fact is that tap water contains a lot of iron, which will settle on the surface of the concrete, and galvanized pipes will prevent this. If the structure is being erected using concrete blocks, then each of them must be watered from all sides and must be covered with film or a protective compound.
If it rains while pouring the concrete solution, its surface must be covered from excess moisture with polyethylene or a mobile canopy.
As soon as the weather settles, the shelter is removed and water-damaged surfaces are replaced with new ones.
The process of concrete hydration is a physical and chemical process extended over time. During this period, all concrete structures without exception need proper care. Practical studies show that improper maintenance in summer can reduce the strength of concrete by up to 50%.
Large surfaces
Concrete, which has a large open surface not protected by formwork, requires careful maintenance from the moment it is laid, which can be carried out in several ways.
To moisten the concrete surface, a regular hose with a spray nozzle connected to a water supply can be used. Sometimes it is advisable to install a continuous irrigation system. However, in this case, the incoming water can often contain dissolved iron, causing the concrete to bloom. Therefore, it is recommended to use galvanized pipes or pipes made of special alloys.
During watering, precautions should be taken so as not to interfere with work being carried out below.
When concreting dams, each concrete block has a large open surface, so in these cases, maintenance should consist of watering and covering.
Road and airfield pavements also have a large open surface area.
Concrete floors, due to their small thickness, lose moisture very quickly. This often leads to floors that are dusty and have little wear resistance. Therefore, appropriate measures must be taken against moisture loss. Immediately after final smoothing, the floor surface should be watered and then covered with waterproof paper or clean sand. Coverings are suitable when this can be done without damaging the floor surface. The sand should be moistened regularly. Other methods of keeping concrete floors wet are also used, but they are less satisfactory than these.
Rules for caring for freshly poured concrete in summer
The strength gain of concrete directly depends on the temperature and humidity of the environment at which the hydration process occurs. The optimal hardening temperature is 19-22 degrees Celsius and 80-90% air humidity.
Empirical studies of some enthusiastic builders have shown that concrete structures that gain strength at a temperature of 30-40 degrees Celsius without appropriate maintenance, at the “age” of 28 days (the time to reach 80% of brand strength) had a real irreplaceable compressive strength of no more than 56%, cracks and greater shrinkage.
Caring for concrete in summer
- Preparing formwork for pouring. The pouring base and formwork parts are thoroughly watered. In this case, they will not “pull” moisture from the concrete. If it is necessary to dismantle the formwork before the end of the maintenance line, not only horizontal, but also vertical surfaces of the structure are watered. In very hot summer conditions, a special drip irrigation system is installed to ensure guaranteed moisture on inclined and vertical surfaces;
- All open surfaces are securely protected from wind and direct sunlight. At home, they use: plastic film, tarpaulin, burlap, and any rags. In capital construction conditions, characterized by large volumes of concrete work, several hours after pouring, the surfaces are covered with wood shavings (sawdust) and regularly watered. The regularity of moistening is determined by specific climatic conditions. In general, the surface should be kept wet at all times. 3-4 waterings per day for two weeks will be enough;
- Structures made of lightweight porous concrete and particularly large-scale objects are protected with special chemicals: polymer films, paint coatings, tar or bitumen emulsions.
Features of filling in winter
When it’s frosty outside, it’s important to prevent the water in the prepared solution from freezing. For this purpose, special additives are used. They retain the thermal energy released during the hydration process in hardening concrete.
Scientists have found that when hardening, one cube of concrete releases heat, the volume of which is equal to 36,000 kcal. Half of this heat is lost in the first three days, the rest over the next seven days. If this process happens faster, the finished product loses its strength. Supplements help prevent unwanted effects from occurring. Their use allows pouring at temperatures below -15 °C.
But still, subsequent care is not canceled. Experienced builders use the following technologies to prevent freezing:
- A “warmhouse” or warm tent is built on top of the foundation or site, and a heat gun is placed inside. But practice shows that it is very difficult to control its operation (overdrying may occur). It is easier to prevent this by giving preference to infrared heaters. It is important to strictly maintain the distance between the heating lamp and the top layer of the structure. It must be at least 120 cm.
Warmhouse for concreting Source searchbiznes.ru
See also: Catalog of companies that specialize in the design, installation and repair of foundations.
- You can insulate the formwork itself by covering it with foam plastic or mineral wool. In this case, the concrete will heat itself. The method is justified when pouring is carried out in a zone of border temperatures.
- When it's below -20°C outside, construction work doesn't stop. The foundations are poured using a structure consisting of metal plates. Heating elements are installed in them, then formwork is assembled from them. The outer layer is additionally insulated. While the solution is setting, it is forcibly heated. After three or four days, the formwork is removed, and the foundation is covered from above with a tarpaulin or special thermomats. Under such a cocoon, the concrete finally cools down. This process is under the constant control of the foreman.
Concrete covered with thermomats Source prom.st
- Some builders heat up the newly mixed solution using electrical heating using powerful transformers. The measures are expensive, but completely justified: after all, if the foundation becomes covered with cracks, it will need to be redone. And this is an even bigger expense.
- If the solution is prepared without adding special additives, you need to use water that has been highly heated beforehand.
- It is important to carry out the laying continuously; if the top layer manages to freeze at low temperatures, the builders remove the ice with steam and immediately continue concreting.
Steam treatment of concrete Source monolitpro.info
There are cases when the use of combined methods is required. Often builders combine electrical heating and insulation of formwork. In such a situation, forced heating is carried out for two days, and then for another five, only external measures cope with the task. In this situation, concrete gains 80% of its strength within a week after pouring.
Concrete care products after summer pouring
- Antisol®E 20 (POLYMERTECHNOLOGIES LLC, Russia). It is a non-flammable, white liquid inert to concrete. Meets the requirements of regulatory documents for concrete care products. Allows you to avoid covering and moistening concrete surfaces. It is used when it is necessary to immediately protect large surfaces of freshly poured concrete on: highways, runways, bridge crossings, overpasses, load-bearing walls, concrete channels, etc. Applying a thin layer of Antisol®E 20 prevents premature drying, cracking and loss of strength;
- Novapor EXTRA (Stachema CZ SRO, Czech Republic). Environmentally friendly white liquid. Used to care for freshly poured concrete surfaces. Forms a thin waterproof film that prevents premature loss of moisture in conditions of low air humidity, exposure to direct sunlight and strong wind. Eliminates the appearance of shrinkage cracks, dust formation, shedding of the surface layer and a decrease in the strength of concrete;
- Etida (JSC Poliplast Group of Companies, Russia). Paraffin based composition. Forms a stable waterproof film. Used to prevent moisture evaporation and the formation of cracks on the surface of all types of concrete;
- Polipast Barrier (JSC Poliplast Group of Companies, Russia). A composition based on inorganic salts designed to effectively protect freshly poured concrete from the harmful effects of wind, sunlight and significant temperature changes.
- If watering concrete with fresh water is undesirable due to the presence of a large amount of salts in it. Covering materials in one way or another are placed at a certain distance from the surface (3-4 cm) and water is poured only over burlap, rags or tarpaulins;
- Excess of water above recommended standards is not allowed. In this case, a sharp loss of strength and cracking of concrete occurs;
When the air temperature increases to 30 degrees Celsius and above, it is not allowed to moisten the surface without subsequent protection with covering materials. In such heat, water from the surface instantly evaporates, and not only does not bring any benefit, but even harms the surface layers of the structure. Subsequently, they delaminate and crumble.
Maintenance of freshly laid concrete begins immediately after the completion of laying the concrete mixture and continues until 70% of the brand strength is reached [clause 2.66 of SNiP 3.03.01-87] or another reasonable time for stripping.
Upon completion of concreting, it is necessary to inspect the formwork for preservation of the specified geometric dimensions, leaks and breakages. All identified defects should be eliminated before the concrete begins to set (1-2 hours from laying the concrete mixture). Hardening concrete must be protected from impacts, shocks and any other mechanical influences. During the initial period of caring for concrete, immediately after finishing its laying, in order to avoid erosion and damage to its surface, the concrete should be covered with plastic film, tarpaulin or burlap.
Particular care should be taken to maintain the temperature and humidity conditions of concrete hardening. Normal humidity for hardening is 90-100% in excess water. Strength gain by concrete under humid conditions significantly increases the final strength of the cement stone. With premature dehydration (which can also occur when laitance leaks from non-waterproofed formwork), concrete gains insufficient surface strength, a tendency for sand to peel off from the concrete, increased water absorption, and reduced resistance to atmospheric and chemical influences. Also, with premature dehydration, early shrinkage cracks occur, and there is a danger of subsequent formation of late shrinkage cracks.
Premature shrinkage cracks are formed primarily due to the rapid decrease in the volume of freshly laid concrete in exposed surface areas due to evaporation and weathering of water. As concrete dries, it decreases in volume and shrinks. As a result of this deformation, structural and internal stresses arise, which can lead to cracks. Shrinkage cracks appear first on the surface of concrete, and then can penetrate deeper. Therefore, it is necessary to take care of delayed drying of the concrete. It should only begin when the concrete has gained sufficient strength to withstand shrinkage stress without cracking. When early cracks form. When the concrete is still plastic, the resulting shrinkage cracks can be closed by vibrating. We will soon talk in more detail about the types of cracks and how to eliminate them in a separate chapter.
Drying of concrete is accelerated in the wind, at low humidity and at air temperatures lower than the temperature of the hardening concrete. Therefore, the concrete surface must be protected from drying out during the concrete maintenance period. After the concrete gains a strength of 1.5 MPa (approximately 8 hours of hardening), you need to regularly moisten the surface of the concrete with water by scattered watering (not a stream!). You can cover the surface with burlap, tarpaulin or sawdust and moisten them with water, covering them with plastic film on top, creating conditions similar to a wet-drying compress. Concrete is not moistened at average daily temperatures below +5°C. If there is a threat of freezing, concrete can be covered with additional heat-insulating materials (foam plastic, mineral wool, rags, hay, sawdust, etc.).
Even if constant moistening of concrete with water is not possible, the concrete should be covered with a polymer film with a thickness of at least 0.2 mm (200 microns). Film panels should be laid in as many single pieces as possible with a minimum of seams. The film panels are overlapped with an overlap of 30 cm and sealed with adhesive tape. The edges of the film should fit tightly to the concrete to minimize the evaporation of water from under the film.
To avoid damage to freshly laid concrete by moving groundwater, it is necessary to protect it from erosion until a strength of at least 25% is achieved (1-5 days, depending on conditions at positive temperatures).
The deadline for finishing concrete care coincides with the period for its safe removal of formwork.
Table. Relative compressive strength of concrete at different curing temperatures
Proper construction of the foundation of a house is a priority for dacha owners. The reliability of the building depends on the quality of the work performed. The rules for constructing the foundation provide not only for laying, but also for further care of the foundation after pouring - periodically moistening it. How often, how much and why should the foundation be watered after pouring? Few people think about this question. The technology differs for different types of cement buildings, which are not familiar to everyone.
Protective compounds
There are many different protective compounds sprayed onto the surface of concrete. They can be divided into three types: colorless, white-dyed and black. The former cause the least staining of concrete. White substances should reduce the heating of concrete from sunlight, as well as cover its surface and reduce moisture evaporation. Tests have shown that a white concrete surface has approximately the same effect as protecting concrete from sunlight in reducing its surface temperature.
Solutions and emulsions of asphalt and resins have been used to coat airfield surfaces to protect the concrete immediately after it is placed until it is strong enough for normal maintenance. The effectiveness of these protective coatings is significantly reduced due to their black color, which increases heat absorption. Observations show that surfaces coated with bitumen solutions are subject to daily temperature fluctuations within the range of 28°C. For uncoated surfaces the temperature fluctuation is 14°C. The increase in temperature provided by bituminous coatings causes intense evaporation if the coating is not continuous, increases thermal stress and consequently leads to the formation of cracks. Bitumen coatings help reduce cracking on days with little sun, but do not prevent moisture evaporation during dry winds. Heat absorption can be reduced by additional application of a white coating. However, the white coating does not completely eliminate the shortcomings of black protective compounds, since it disappears under the influence of atmospheric conditions. Therefore, in any case, it is recommended to cover the concrete with straw, burlap or other material and begin moistening as soon as possible in the usual way.
Bitumen or tar coatings are useful in tunnels and pipes, and for surfaces that will subsequently be backfilled. Before the concrete is poured, the coating should be whitewashed to reduce heat absorption.
Recently, protective compounds have been introduced into practice that form a dense transparent plastic film on the surface of concrete. The value of such substances is still a matter of debate, but evidence suggests that if used correctly they may be of some value in weather that is not very hot and not very dry. In dry areas they lose their effectiveness.
Examination of concrete coated with transparent substances shows that there is usually not a protective film over the entire surface, resulting in the concrete being exposed to abnormal conditions in uncoated areas. Under practical conditions, it is impossible to obtain a continuous waterproof film at one time. Therefore, the coating is carried out twice, one after the other, as quickly as possible, but in such a way as not to cause shifting or wrinkling of the previously applied film. Typically 5 liters of the substance is enough to cover 27.8 m2 of concrete surface. According to some claims, this method of caring for concrete is approximately equivalent to wetting it for 14 days.
Components of standard concrete
Concrete dough is relevant for the construction of strip, monolithic or columnar foundations.
Components of cement mortar
A typical concrete mass consists of the following raw materials:
- cement - has astringent properties that ensure the combination of ingredients into a single solution. To prepare a high-quality mass, you will need material marked M500;
- sand is one of the fillers of the mixture. Only bulk raw materials with uniform fractions from 1.5 to 5 mm are used. Foreign impurities are sifted through a fine sieve. To make the composition durable, use river sand;
- crushed stone is the main filler. In home construction conditions, crushed stone or gravel materials with fractions of 8 – 35 mm are purchased. To ensure a tight fit of the particles, small and large raw materials are mixed.
To prevent debris from getting into the mixture, the components are poured out on a clean tarpaulin. The binding element of the solution is water. The liquid is filtered before adding to the remaining ingredients.
Do I need to add plasticizers?
- ready-made slaked lime, which ensures the strength of the composition;
- plasticizers that impart fluidity or viscosity to the solution;
- reinforcing components - needed to strengthen the foundation in conditions of soil instability.
Before purchasing, it is important to study the technical characteristics and technology of using auxiliary components.
Solution calculation technology
At home, it is advisable to prepare the concrete composition manually. You will need 1 part cement mixture, 2 parts sand, 3 parts gravel, additives and water. Take into account the difference in the volumetric mass of the material and carry out the calculation in buckets: a bucket of sand will weigh 19 kg, cement - 15 kg, and crushed stone - 17.5 kg. Water is added to the ingredients and the solution is mixed until smooth. After pouring the foundation, what follows is a technologically complex physical and chemical reaction - the release of heat and evaporation of water, as a result of which an artificial stone is formed.
Why water concrete?
During the hardening process of concrete, special attention should be paid to moistening the composition. Why do you need to water concrete? There are a number of factors that prove this need.
- Water is the main element of cement mortar. It participates in physical and chemical processes, as a result of which it is quickly neutralized. For optimal hardening of the concrete mixture, a certain amount of moisture is required, which must be compensated.
- The hardening of cement occurs heterogeneously. The upper layers are characterized by weak exchange processes and, as a result, the unstable hardened surface quickly deforms when the concrete layer inside is still liquid. In order for the structure to gain strength, it is necessary to ensure optimally identical conditions.
- During hardening, the base decreases in volume. You can make up for losses using a dosed amount of liquid.
- Climatic conditions are a factor that has a direct impact on the formation of a durable structure. Hot air promotes rapid evaporation of water, so the foundation needs constant watering. Windy weather leads to the removal of moisture particles from the cement, which provokes the appearance of numerous cracks in the surface.
Microcracks are one of the risks when forming a foundation. Through them, rainwater, dirt and dust enter the product. As a result, the surface remains intact, but the internal part of the structure is deformed. The formation of cracks and cracks in the foundation occurs in winter with strong temperature changes. When moisture gets inside, it turns into ice, which has the properties to expand and increase the size of the crack. Swelling of the base occurs, and after the foundation, destruction proceeds to the main structure. Water is involved in hydration processes. The optimal level of moisture contributes to the development of strength characteristics.
Features of proper concrete care
Proper care of a concrete structure involves ensuring optimal conditions for hardening. They depend on climatic conditions, type of cement, type of product, etc. How many days does concrete need watering? This indicator is determined by the rate of hardening of the mixture for the following types:
- the structure, made of slowly hardening cement, needs to be wetted for about 4 weeks;
- Portland cement products - 2-3 weeks;
- systems made from aluminous quick-hardening concrete require about 8 days.
In the first day after pouring, it is better to cover the foundation with burlap or wet sawdust to protect it from overheating and slow down the evaporation of water.
Methods for caring for concrete mixture
The setting of cement is manifested by a chemical reaction that depends on the water in the cement-sand mixture. To ensure complete hydration of the cement, a certain volume of water is added to the mixture. The supply must either be maintained or replenished over the course of several days and weeks.
Therefore, caring for concrete after pouring consists of creating conditions that can stop evaporation. The active phase, during which stone is formed from a mixture of cement and sand, lasts about a month. During the first 15 days, concrete gains about 70-80% strength. If lost before this time, microcracks will appear on the surface and a significant reduction in strength will occur.
Concrete hardening
Evaporation can lead to dehydration of concrete. Which will lead to a slowdown or termination of the hardening process. The strength properties will decrease and cause cracking and shrinkage. Therefore, the main task is to provide the surface with normal temperature and moisture. The type, type of cement and local climatic conditions determine the method of maintenance. When hardening occurs, the volume changes. During rapid drying, shrinkage appears, then microcracks appear. In huge monolithic structures, large cracks appear during uneven heating in different parts.
If the air has a positive temperature of +15 ° C and humidity is more than 80% (water begins to penetrate slowly under such conditions), the hardening time becomes long.
When everything is moistened abundantly, the possibility of cracks is reduced. Maintenance work for slow-hardening cement lasts at least two weeks. And with Portland cement, at least a week. Humidification is done using a spray bottle. It is forbidden to water with a strong stream to avoid blurring the surface. The moist state is maintained by constant frequency of watering. After pouring, moisten after 10 hours, and in windy and hot weather after 2-2.5 hours.
Ways to keep the surface moist:
- Applying a protective composition to the surface of freshly laid concrete;
- Sprinkling with water using protective coatings;
- Aged with salts that absorb water.
When watering, the surfaces should be protected from drying out and in the interval between waterings it should be taken into account that:
Moisturizing concrete
- slow-hardening (low-heat) cement must be kept for more than two weeks;
- fast-hardening (alumina) is subjected to strong water saturation for the initial 8 hours, and then to a completely moistened state for 16 hours.
During humidification, its temperature decreases.
How the surface is wetted in the summer
Concreting a foundation is a complex and labor-intensive process that involves wetting the surface. How to care for concrete on hot days? Experts recommend taking into account the following nuances:
- The cement mortar should be poured early in the morning or after sunset. In the summer, it is necessary to take care of protecting the freshly laid mixture - cover the surface with slate, corrugated sheets, roofing felt or other material.
- The next point is that not only hot weather, but also the heat generated during the hardening processes contribute to the rapid evaporation of moisture. Therefore, on the first day and the next 2, the base should be constantly moistened with water. This should be done every 2-3 hours, especially in windy, sunny weather.
- Watering of the product is carried out 3 times a day for 28 days.
Wetting of concrete is carried out in a diffuse manner, in the form of raindrops. In case of water interruptions, another wetting should be done - treat the freshly poured mass with a film-forming agent with good adhesion.