The correct calculation of the volume of concrete required for the foundation is important to determine for several reasons. The developer needs to know the exact amount of the required mixture in order to plan its delivery in the minimum number of trips of automixers. The lack of material to fill the entire volume of the foundation results in additional costs for delivery of the missing volume. Delivering concrete in quantities greater than required is also unprofitable: in this case, the “extra” paid concrete often simply has nowhere to be received. In addition, the technology of laying monolithic concrete requires a minimum number of cold joints. The base, if possible, should be poured as quickly as possible, without joints between the fresh mixture and already set concrete. In this article we will tell you how to calculate the cubic capacity of concrete for constructing different types of foundations, which will allow you to avoid unjustified costs and build the correct technological cycle.
Methods for calculating concrete volumes
There are two calculation methods - simple “manual” or automated. The second is a specialized computer program into which the initial data (type of foundation, dimensions, depth, etc.) is entered and the results of calculations of concrete volume with the necessary corrections are instantly read. The program additionally provides reference and other information on individual characteristics. The “manual” method involves using formulas from a school geometry course to calculate the volumes of figures with different shapes of the foundation area. The calculated volume can be obtained from design data, as well as from installed formwork.
[ads-pc-1] [ads-mob-2]
The second method is more accurate, because takes into account the actual volumes in which concrete should be taken. The volumes of complex types of foundations for buildings are determined as the sum of the volumes of several components. The correction for the reinforcing mesh in the formwork is, as a rule, not taken into account due to its insignificant effect on the final result. We give examples of calculating the volume of concrete for different types of foundations.
Calculation for a columnar foundation
The columnar type is a collection of reinforced concrete elements that are installed in the ground in certain places. They are usually concentrated where walls intersect, but can also be found in bays. The height is not only what is visible from the outside, but also the part of the pile that is in the ground.
The advantage of such a foundation is the low consumption of concrete for its arrangement. If pillars with a round cross-section are used, then you need to know their height, number and cross-section radius.
In order to calculate the amount of concrete for all piles, you need to calculate how much it will be needed for one. To do this, the height is multiplied by the cross-sectional area. To obtain the cross-sectional area, you need to multiply the square of the cross-sectional radius by a number equal to 3.14.
If the piles have a square cross-section, then the calculation is much simpler. You just need to multiply the length of the side of the pile squared by the height and multiply by the number of parts.
If the quantity is calculated for rectangular piles, then the length is multiplied by the width.
Therefore, before calculating the volume of concrete for the foundation, you need to find out the exact parameters of the piles that should be obtained.
Strip foundation
In plan, this type of base structure is a strip contour of a rectangular or more complex shape with internal sections for partitions. To calculate the volume of concrete for a rectangular foundation, you need to subtract the volume of the parallelepiped along the inner contour from the volume of the parallelepiped with dimensions along the outer contour. The result will be the volume of the foundation tape itself. The internal partition parts can be divided into sections of the same cross-section to calculate each section separately. To determine the total volume, the volumes of all such sections are summed up.
Example 1.
Plan of a strip foundation for an example of calculating concrete cubic capacity.
- The volume along the external contour will be equal to 10 x 8 x 2.4 = 192 m³
- The volume along the internal contour is 143.63 m³.
- The volume of the external part along the perimeter will be 192 – 143.63 = 48.4 m³
- The volume of the internal part (8.8 + 6.2) x 0.6 x 2.4 = 17.72 m³ is the product of the cross-sectional area and the total length in m.
- In total, 66.13 m³ of concrete will be needed for pouring
Calculations in this case were made according to the drawings. When determining the volume of concrete in the installed formwork, you should take actual measurements of the formwork and similarly make the necessary calculations.
[ads-pc-1] [ads-mob-2]
How to calculate how much concrete is needed for a strip foundation
Strip foundations are widely used by private developers in the construction of low-rise residential buildings, bathhouses, garages, sheds, temporary buildings and other similar buildings. The popularity of strip foundations lies in the simplicity of the design and the possibility of independent calculation and construction.
To calculate the amount of concrete needed to pour the foundation, you will need to calculate the volume of the foundation in cubic meters. In this regard, two options are possible. The first option is that the length, width and height of the structure are the same along the entire perimeter of the “ribbon”. The second option is that the height and width of the foundation are variable.
For example, by measuring the length of the foundation “ribbon” (perimeter), width and height, you received the following initial data:
- Foundation perimeter (L): 40 meters. Important! The perimeter is measured not along the external or internal border, but strictly along the center of the foundation trench;
- Height(H) 1.5 meters;
- Width(S) 0.7 meters.
We substitute the initial data into the formula for the volume of the parallelepiped V=LxHxS: V=40x1.5x0.7=42 m3. To pour a strip foundation you will need 42 cubic meters of concrete.
An example of calculating concrete for a strip foundation
Let's say your foundation with a total length of 40 meters consists of two parts that differ in width: 10 meters of tape 0.7 meters wide and 30 meters of tape 0.5 meters wide. In this case, we use the same formula for the volume of a parallelepiped, only we make two calculations: for a “piece” of 10 meters (V1) and a “piece” of 30 meters (v2). Then we sum up the resulting volumes and get the volume of concrete to be poured (V)
- V1=10x1.5x0.7=10.5 m3;
- V2=30x1.5x0.5=22.5 m3;
- V=10.5+22.5=33 cubic meters of concrete.
Pile foundation
The simplest design for calculating the required volume of concrete. To calculate the volume of concrete, you should determine the volume of each individual pile and multiply it by the number of piles in the base. Piles are most often pipes buried in the ground, which are then filled with concrete.
Example 2.
Initial data:
- Number of piles – 30 pieces;
- Pile diameter – 0.2 m;
- Depth of burial (filling) 2.0 m.
Calculation:
We determine the cross-sectional area of one pile, and multiplying it by the depth, we obtain the volume of concrete required to construct one pile. In the calculations, 3.14 is the constant “Pi”, 0.1 is the radius of the pile, 2.0 is the pouring depth in m.
3.14 x 0.1 x 0.1 x 2.0 = 0.0628 m²
In total, 30 piles will be poured:
0.0628 x 30 = 1.88 m³ of concrete mixture.
If the cross-section of the piles is rectangular, then the volume of the pile is determined by the product of the lengths of the sides and the pouring depth.
[ads-pc-1] [ads-mob-2]
Slab foundation
In plan, this type of foundation is usually a rectangle, the dimensions of which can be determined from drawings or measured from the actually installed formwork. The volume of concrete to be poured is determined simply by the product of the area and the height. The area is determined by the product of the length of the base and the width.
Example 3.
Initial data:
- Foundation length – 10 m;
- Width – 8 m;
- Depth – 0.4 m.
The volume of concrete for the foundation will be equal to the product of these characteristics:
10 x 8 x 0.4 = 32 m³
A slab foundation can have a complex plan shape. In this case, the general plan is divided into several simple components, the area of each of them is determined, and then the total area is calculated by addition.
[ads-pc-1] [ads-mob-3]
Bored foundation with monolithic grillage
Calculating the volume of this type of base is very simple. To do this, you need to divide it into two parts - the support pillar, the grillage, and calculate the volume of each of them. The grillage is a concrete monolithic slab, the calculation of the volume of which was shown in examples earlier. The calculation of the volumes of the pile part is similar to the calculation of the pillar supporting part of a bored foundation. The total volume of pouring in cubic meters is determined by adding the volumes of concrete for pouring each of the specified parts.
[ads-pc-1] [ads-mob-3]
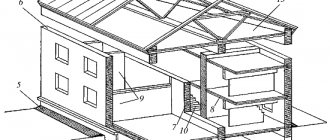
Construction volume of the building
The main reason why calculations of the construction volume of a building are carried out is the need to correctly draw up an estimate for construction or repair and restoration work. Thus, the amount of money that the customer of the work will give to the construction organization will depend on whether this indicator was calculated correctly. Of course, the best course of action if the need arises to determine the construction volume of a designed or finished building would be to contact a specialist. However, if you have the desire and some free time, you can make the necessary calculations yourself. There are no particular difficulties here. The only thing you need to remember is the existence of rules that should be followed when carrying out measurements and calculations. Otherwise, the obtained figures will be unreliable, and this, in turn, may lead to the design and estimate documentation being invalidated. What should you keep in mind when determining the building volume of a building?
Rules indicating how to calculate the construction volume of a building can be easily found on the pages of various sites dedicated to construction topics. In short, this is what they say:
- the construction volume of a building is the sum of the volumes of its above-ground part and basement;
- The above-ground part of the building is considered to be the part of the building from the floor of the first floor to the top of the attic floor or roof. Everything below refers to the underground part;
- depending on whether the building has an attic floor or whether it is absent, the volume of the above-ground part is calculated either by multiplying its area in the horizontal section by the height, or by multiplying its area in the vertical section by the length of the building;
- if the floors of a building have unequal areas, it is necessary to calculate the volumes of each floor, and the results obtained must be summed up;
- The volume of the building includes the volumes of attics, skylights, verandas and vestibules. Not included are the volumes of balconies, porticoes and passages;
- technical floors must also be taken into account;
- the volume of the building's basement is calculated similarly to the volume of its above-ground part;
- The length of the walls is measured taking into account the thickness of the plaster and cladding.
How to order concrete correctly
Correctly calculating the volume of concrete cubes for pouring is important, but not enough to avoid unexpected costs. If concrete is planned to be imported from the manufacturer for the construction of the foundation, the organization of work on the preparation and acceptance of concrete must be impeccable. What to pay attention to:
- The formwork must be installed and ready to receive concrete. The installation of formwork should be entrusted to professionals. The rigid and durable structure holds the concrete after pouring without changing its shape.
- Provide access for the mixer to the unloading site. If the base is large in area, it is advisable to prepare several unloading points to reduce labor costs for pouring. The downtime of the mixer during unloading is paid additionally by the client, so the concrete must be received as quickly as possible.
Pouring formwork from a mixer
[ads-pc-1] [ads-mob-3]
- To avoid conflicts with the supplier regarding delivery volumes, we advise you to warn the seller that the amount of concrete required has been calculated and ask to ensure that the mixers are loaded according to the shipping documents.
- Additional equipment for unloading concrete (hoses, conveyors, concrete pumps, etc.) should be identified and ordered from the supplier in advance.
- When unloading concrete, losses may occur due to accidental spills, mixture residues on equipment and pumps, etc. When ordering concrete, you should provide for such losses by increasing the declared volume by 5 - 7%.
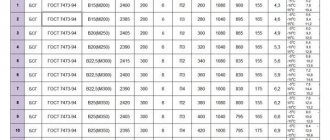
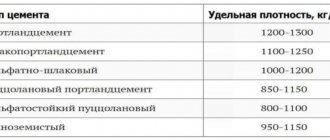
If the developer plans to prepare concrete at the construction site, then the correct calculation of the cubic capacity of concrete is needed to purchase the amount of materials. In this case, the correct preparation of the concrete mixture of the required grade comes to the fore in importance.